0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views30 pagesQ2 Module 1 Notes Final
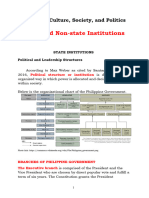
The document outlines the forms and functions of state and non-state institutions, focusing on the political structure of the Philippine government, which includes the executive, legislative, and judicial branches. It also discusses economic institutions and various types of organizations such as banks, corporations, cooperatives, trade unions, and development agencies. Additionally, it highlights the role of non-state institutions in influencing international politics and societal change.
Uploaded by
beamapepito824Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views30 pagesQ2 Module 1 Notes Final
The document outlines the forms and functions of state and non-state institutions, focusing on the political structure of the Philippine government, which includes the executive, legislative, and judicial branches. It also discusses economic institutions and various types of organizations such as banks, corporations, cooperatives, trade unions, and development agencies. Additionally, it highlights the role of non-state institutions in influencing international politics and societal change.
Uploaded by
beamapepito824Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 30