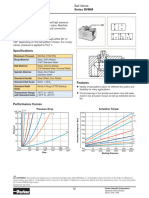
About the Presentations
The presentations cover the objectives found in the
opening of each chapter.
All chapter objectives are listed in the beginning of
each presentation.
You may customize the presentations to fit your
class needs.
Some figures from the chapters are included. A
complete set of images from the book can be found
on the Instructor Resources disc.
�Oracle 11g: SQL
Chapter 1
Overview of Database Concepts
�Objectives
Define database terms
Identify the purpose of a database
management system (DBMS)
Explain database design using entityrelationship models and normalization
Explain the purpose of a Structured Query
Language (SQL)
Understand how this textbooks topics are
sequenced and how the two sample databases
are used
Oracle 11g: SQL
�Database Terminology
Database logical structure to store data
Database management system (DBMS)
software used to create and interact with
the database
Oracle 11g: SQL
�Database Components
Character
Field
Record
File
Oracle 11g: SQL
�Database Components - Character
Basic unit of data
Can be a letter, number, or special symbol
Oracle 11g: SQL
�Database Components - Field
A group of related characters
Represents an attribute or characteristic of an
entity
Corresponds to a column in the physical database
Oracle 11g: SQL
�Database Components - Record
A collection of fields for one specific entity
Corresponds to a row in the physical database
Oracle 11g: SQL
�Database Components - File
A group of records about the same type of entity
Oracle 11g: SQL
�Components Example
Oracle 11g: SQL
10
�Database Example
Oracle 11g: SQL
11
�Database Management System
Data storage: manage the physical structure of the
database
Security: control user access and privileges
Multiuser access: manage concurrent data access
Backup: enable recovery options for database
failures
Data access language: provide a language that
allows database access
Data integrity: enable constraints or checks on data
Data dictionary: maintain information about database
structure
Oracle 11g: SQL
12
�Database Design
Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
Entity-relationship model (E-R model)
Normalization
Oracle 11g: SQL
13
�Systems Development Life Cycle
(SDLC)
Systems investigation understanding the problem
Systems analysis understanding the solution
Systems design creating the logical and physical
components
Systems implementation placing completed
system into operation
Systems maintenance and review evaluating the
implemented system
Oracle 11g: SQL
14
�Entity-Relationship Model
(E-R Model)
Used to depict the relationship that exists
among entities
The following relationships can be included
in an E-R model:
One-to-one
One-to-many
Many-to-many
Oracle 11g: SQL
15
�E-R Model Notation Examples
Oracle 11g: SQL
16
�One-to-One Relationship
Each occurrence of data in one entity is
represented by only one occurrence of data in the
other entity
Example: Each individual has just one Social
Security number (SSN) and each SSN is assigned
to just one person
Oracle 11g: SQL
17
�One-to-Many Relationship
Each occurrence of data in one entity can be
represented by many occurrences of the data in
the other entity
Example: A class has only one instructor, but each
instructor can teach many classes
Oracle 11g: SQL
18
�Many-to-Many Relationship
Data can have multiple occurrences in both entities
Example: A student can take many classes, and
each class is composed of many students
Can not be included in the physical database
Oracle 11g: SQL
19
�JustLee Example E-R Model
Oracle 11g: SQL
20
�Database Normalization
Determines required tables and columns for each
table
Multistep process
Used to reduce or control data redundancy
Oracle 11g: SQL
21
�Database Normalization (continued)
Data redundancy refers to having the same data in different
places within a database
Data anomalies refers to data inconsistencies
Oracle 11g: SQL
22
�Unnormalized Data
Contains repeating groups in the Author
column in the BOOKS table
Oracle 11g: SQL
23
�First-Normal Form (1NF)
Primary key is identified
Repeating groups are eliminated
Oracle 11g: SQL
24
�First-Normal Form (1NF) (continued)
ISBN and Author columns together create a
composite primary key
Oracle 11g: SQL
25
�Composite Primary Key
More than one column is required to uniquely
identify a row
Can lead to partial dependency a column is only
dependent on a portion of the primary key
Oracle 11g: SQL
26
�Second-Normal Form (2NF)
Partial dependency must be eliminated
Break the composite primary key into two parts,
each part representing a separate table
Oracle 11g: SQL
27
�Second-Normal Form (2NF)
(continued)
BOOKS table in 2NF
Oracle 11g: SQL
28
�Third-Normal Form (3NF)
Publisher contact name has been removed
Oracle 11g: SQL
29
�Summary of Normalization Steps
1NF: eliminate repeating groups, identify the
primary key
2NF: table is in 1NF, and partial dependencies are
eliminated
3NF: table is in 2NF, and transitive dependencies
are eliminated
Oracle 11g: SQL
30
�Relating Tables within the Database
Once tables are normalized, make certain tables
are linked
Tables are linked through a common field
A common field is usually a primary key in one
table and a foreign key in the other table
Oracle 11g: SQL
31
�Oracle 11g: SQL
32
�Lookup Table
Common reference for descriptive data tables
referenced in a foreign key
Oracle 11g: SQL
33
�Structured Query Language (SQL)
Data sublanguage
Used to:
Create or modify tables
Add data to tables
Edit data in tables
Retrieve data from tables
ANSI and ISO standards
Oracle 11g: SQL
34
�Databases Used in this Textbook
JustLee Books Database
Assumptions
No back orders or partial shipments
Only U.S. addresses
Completed orders are transferred to the annual
SALES table at the end of each month to enable
faster processing on the ORDERS table
Oracle 11g: SQL
35
�Topic Sequence
The first half of the text will focus on creating a
database
The second half of the text will focus on querying or
retrieving data from a database
Oracle 11g: SQL
36
�Summary
A DBMS is used to create and maintain a
database
A database is composed of a group of
interrelated tables
A file is a group of related records; a file is also
called a table in the physical database
A record is a group of related fields regarding one
specific entity; a record is also called a row
A record is considered unnormalized if it contains
repeating groups
Oracle 11g: SQL
37
�Summary (continued)
A record is in first-normal form (1NF) if no
repeating groups exist and it has a primary key
Second-normal form (2NF) is achieved if the
record is in 1NF and has no partial
dependencies
After a record is in 2NF and all transitive
dependencies have been removed, then it is in
third-normal form (3NF), which is generally
sufficient for most databases
A primary key is used to uniquely identify each record
Oracle 11g: SQL
38
�Summary (continued)
A common field is used to join data contained in
different tables
A foreign key is a common field that exists
between two tables but is also a primary key in
one of the tables
A lookup table is a common term for a table
referenced in a foreign key
A Structured Query Language (SQL) is a data
sublanguage that navigates the data stored
within a databases tables
Oracle 11g: SQL
39