0% found this document useful (0 votes)
95 views29 pagesLinux Filesystem Hierarchy: The Linux Documentation Project
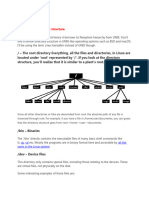
Usually contains shells like bash, csh, etc. And commonly used commands like cp, mv, rm, cat, ls. Also contains programs which boot scripts may depend on. Contains everything required for the boot process except for configuration files not included.
Uploaded by
karant1Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
95 views29 pagesLinux Filesystem Hierarchy: The Linux Documentation Project
Usually contains shells like bash, csh, etc. And commonly used commands like cp, mv, rm, cat, ls. Also contains programs which boot scripts may depend on. Contains everything required for the boot process except for configuration files not included.
Uploaded by
karant1Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 29