100% found this document useful (2 votes)
233 views55 pagesSimple Process Control Loop (With Negative Feedback)
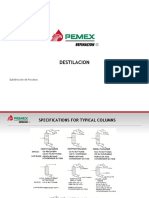
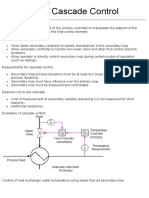
This document describes the basic components and functioning of a simple process control loop using negative feedback. The key components are the set point, controller, final control element, process, and measuring element. The controller compares the measured output to the set point and sends an actuating signal to the final control element to adjust the manipulated variable to drive the process output to match the set point. The goal is to achieve servo and regulatory control in the presence of disturbances.
Uploaded by
Ankan BhuniaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (2 votes)
233 views55 pagesSimple Process Control Loop (With Negative Feedback)
This document describes the basic components and functioning of a simple process control loop using negative feedback. The key components are the set point, controller, final control element, process, and measuring element. The controller compares the measured output to the set point and sends an actuating signal to the final control element to adjust the manipulated variable to drive the process output to match the set point. The goal is to achieve servo and regulatory control in the presence of disturbances.
Uploaded by
Ankan BhuniaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 55