0% found this document useful (0 votes)
799 views4 pagesLow PS CSSR
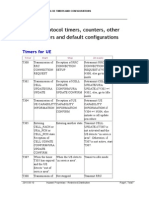
The document discusses reasons for low Circuit Switched Speech Call Setup Success Rate (CSSR) and Packet Switched Call Setup Success Rate (PS CSR) in a mobile network. It provides counters and formulas to analyze which part of the CSSR KPI is causing low values - RRC setup, RAB setup, or both. It then lists counters to help identify specific issues like radio resource congestion, transmission problems on the Iub interface, or RF problems that could be leading to high RRC or RAB setup failure rates. Solutions include checking for hardware faults, increasing capacity by adjusting admission control thresholds, and improving coverage in failure areas.
Uploaded by
Jamal StevensCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
799 views4 pagesLow PS CSSR
The document discusses reasons for low Circuit Switched Speech Call Setup Success Rate (CSSR) and Packet Switched Call Setup Success Rate (PS CSR) in a mobile network. It provides counters and formulas to analyze which part of the CSSR KPI is causing low values - RRC setup, RAB setup, or both. It then lists counters to help identify specific issues like radio resource congestion, transmission problems on the Iub interface, or RF problems that could be leading to high RRC or RAB setup failure rates. Solutions include checking for hardware faults, increasing capacity by adjusting admission control thresholds, and improving coverage in failure areas.
Uploaded by
Jamal StevensCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4