100% found this document useful (2 votes)
644 views10 pagesDDA Line Drawing Algorithm
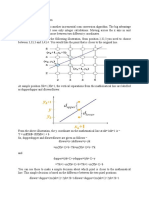
The document discusses algorithms for drawing lines on a raster display. It describes determining the pixels that should be turned on to represent a line between two points. Methods include calculating the slope of the line and using that slope to determine the change in y-values over increments of x. The digital differential analyzer algorithm samples the line at integer x-values and rounds the corresponding y-values to the nearest pixels. Considerations for lines with negative slope or slope greater than one are also discussed.
Uploaded by
thirumalaikumaranCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (2 votes)
644 views10 pagesDDA Line Drawing Algorithm
The document discusses algorithms for drawing lines on a raster display. It describes determining the pixels that should be turned on to represent a line between two points. Methods include calculating the slope of the line and using that slope to determine the change in y-values over increments of x. The digital differential analyzer algorithm samples the line at integer x-values and rounds the corresponding y-values to the nearest pixels. Considerations for lines with negative slope or slope greater than one are also discussed.
Uploaded by
thirumalaikumaranCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10