0% found this document useful (0 votes)
379 views36 pagesRF Cellular Optimization
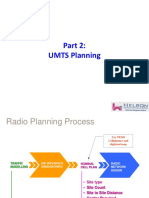
The document discusses network optimization. It explains that network optimization is important to delight customers with good quality service and fully utilize the network and its subsystems. It also discusses challenges like changing usage patterns and managing scarce spectrum. The document then covers types of optimization like soft and physical optimization. It provides details on why optimization is needed even after planning, and discusses concepts like network quality, key performance indicators, and the optimization process for both young and mature networks.
Uploaded by
Elio Jose Aguilar RomeroCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
379 views36 pagesRF Cellular Optimization
The document discusses network optimization. It explains that network optimization is important to delight customers with good quality service and fully utilize the network and its subsystems. It also discusses challenges like changing usage patterns and managing scarce spectrum. The document then covers types of optimization like soft and physical optimization. It provides details on why optimization is needed even after planning, and discusses concepts like network quality, key performance indicators, and the optimization process for both young and mature networks.
Uploaded by
Elio Jose Aguilar RomeroCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 36