0% found this document useful (0 votes)
59 views53 pagesHardware Intro
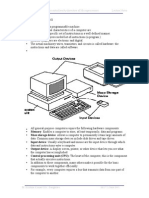
This document discusses the components of a basic computer system including the processor, memory, input and output devices. It describes different types of processors and memory. It also outlines various classes of computers like desktops, laptops, servers and how they differ in size, portability and usage. Server types discussed include mainframes, clusters and rack servers.
Uploaded by
Parthasarathy SowrirajanCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
59 views53 pagesHardware Intro
This document discusses the components of a basic computer system including the processor, memory, input and output devices. It describes different types of processors and memory. It also outlines various classes of computers like desktops, laptops, servers and how they differ in size, portability and usage. Server types discussed include mainframes, clusters and rack servers.
Uploaded by
Parthasarathy SowrirajanCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 53