0% found this document useful (0 votes)
335 views19 pagesDistributed & Parallel System
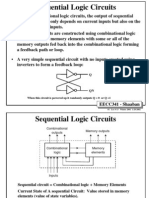
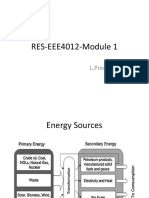
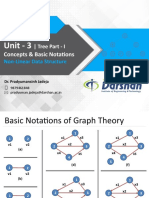
This document defines and compares distributed and parallel systems. Distributed systems are collections of independent computers that communicate over a network to collaborate on tasks, with no shared clock and increased reliability. Examples include computer networks and ATMs. Parallel systems have multiple processors that directly access shared memory, forming a common address space. Examples are supercomputers. Distributed systems have advantages like resource sharing but challenges like security, while parallel systems provide concurrency but programming is more difficult due to synchronization.
Uploaded by
Mcheaven NojramCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
335 views19 pagesDistributed & Parallel System
This document defines and compares distributed and parallel systems. Distributed systems are collections of independent computers that communicate over a network to collaborate on tasks, with no shared clock and increased reliability. Examples include computer networks and ATMs. Parallel systems have multiple processors that directly access shared memory, forming a common address space. Examples are supercomputers. Distributed systems have advantages like resource sharing but challenges like security, while parallel systems provide concurrency but programming is more difficult due to synchronization.
Uploaded by
Mcheaven NojramCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 19