0% found this document useful (0 votes)
199 views29 pagesLecture 4 - Introduction To UML
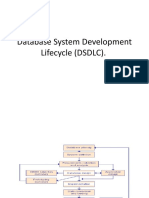
This document discusses the Unified Modeling Language (UML). UML is a graphical language used to visualize, specify, construct and document software systems. It provides standard modeling diagrams and allows developers to model systems before writing code. The document outlines the basic UML diagrams including use case diagrams, class diagrams, sequence diagrams, and state diagrams. It also categorizes UML diagrams into structure, behavioral, and interaction diagrams and provides examples of each type.
Uploaded by
Mariya IqbalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
199 views29 pagesLecture 4 - Introduction To UML
This document discusses the Unified Modeling Language (UML). UML is a graphical language used to visualize, specify, construct and document software systems. It provides standard modeling diagrams and allows developers to model systems before writing code. The document outlines the basic UML diagrams including use case diagrams, class diagrams, sequence diagrams, and state diagrams. It also categorizes UML diagrams into structure, behavioral, and interaction diagrams and provides examples of each type.
Uploaded by
Mariya IqbalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 29