0% found this document useful (0 votes)
112 views30 pagesLEADING Powerpoint
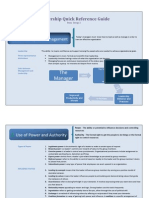
Engineer managers are expected to lead effectively by influencing others. Leaders influence others through various bases of power, including legitimate power from their position, reward power to give incentives, coercive power through punishments, referent power from admiration, and expert power from their skills. Effective leadership requires traits like drive and integrity, as well as skills in technical areas, managing people, and conceptual thinking. Leaders can adopt different styles like being directive, supportive, or participative. A boss manages employees through authority, while a leader inspires and develops people to accomplish goals.
Uploaded by
Luffy yagamiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
112 views30 pagesLEADING Powerpoint
Engineer managers are expected to lead effectively by influencing others. Leaders influence others through various bases of power, including legitimate power from their position, reward power to give incentives, coercive power through punishments, referent power from admiration, and expert power from their skills. Effective leadership requires traits like drive and integrity, as well as skills in technical areas, managing people, and conceptual thinking. Leaders can adopt different styles like being directive, supportive, or participative. A boss manages employees through authority, while a leader inspires and develops people to accomplish goals.
Uploaded by
Luffy yagamiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 30