0% found this document useful (0 votes)
100 views29 pagesTopic 1 Learning Design Principles
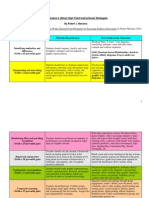
This document discusses learning design principles for an online course. It begins by defining learning design as the process of planning, structuring, and sequencing learning activities, as well as the product of this design process. It then outlines the 7Cs framework for learning design: conceptualize, create, communicate, collaborate, consider, combine, and consolidate. Each of the 7Cs is then defined in 1-2 sentences. The document also discusses the importance of incorporating 21st century skills like critical thinking, creativity, collaboration, and communication into the learning design.
Uploaded by
SEA ServerCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
100 views29 pagesTopic 1 Learning Design Principles
This document discusses learning design principles for an online course. It begins by defining learning design as the process of planning, structuring, and sequencing learning activities, as well as the product of this design process. It then outlines the 7Cs framework for learning design: conceptualize, create, communicate, collaborate, consider, combine, and consolidate. Each of the 7Cs is then defined in 1-2 sentences. The document also discusses the importance of incorporating 21st century skills like critical thinking, creativity, collaboration, and communication into the learning design.
Uploaded by
SEA ServerCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 29