0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views27 pagesModule 2 - Text Structure
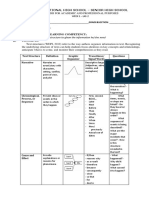
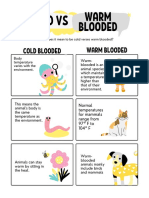
The document explains text structure, which refers to how information is organized within a passage. It outlines six common patterns of organization: chronological, cause and effect, compare and contrast, problem and solution, sequence, and spatial/descriptive writing, along with signal words for each type. Additionally, it provides tips for identifying text structure and includes exercises for practice.
Uploaded by
Haidric Mae Chan-CordovaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views27 pagesModule 2 - Text Structure
The document explains text structure, which refers to how information is organized within a passage. It outlines six common patterns of organization: chronological, cause and effect, compare and contrast, problem and solution, sequence, and spatial/descriptive writing, along with signal words for each type. Additionally, it provides tips for identifying text structure and includes exercises for practice.
Uploaded by
Haidric Mae Chan-CordovaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 27