0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views29 pagesFault Tree Analysis
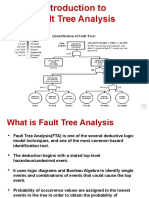
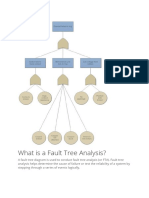
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) is a method used to identify and rank combinations of events that lead to system failure, estimating the system's failure probability. It involves the use of tie sets, which are sets of components whose success is necessary for system success, and employs various gates to model the relationships between events. The analysis is conducted in a top-down manner, focusing on the top event and utilizing Boolean logic to represent basic events as binary outcomes.
Uploaded by
S BharatCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views29 pagesFault Tree Analysis
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) is a method used to identify and rank combinations of events that lead to system failure, estimating the system's failure probability. It involves the use of tie sets, which are sets of components whose success is necessary for system success, and employs various gates to model the relationships between events. The analysis is conducted in a top-down manner, focusing on the top event and utilizing Boolean logic to represent basic events as binary outcomes.
Uploaded by
S BharatCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 29