0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views25 pagesCompetencies in The Affective Domain
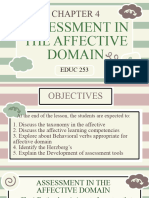
The document outlines the affective domain of learning, which focuses on emotions, attitudes, and values in educational settings. It details the levels of the affective domain as defined by David Krathwohl, including receiving, responding, valuing, organization, and characterization by value. Additionally, it discusses the importance of affective learning competencies and the role of motivation and self-efficacy in student engagement and performance.
Uploaded by
adelverpatag062323Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views25 pagesCompetencies in The Affective Domain
The document outlines the affective domain of learning, which focuses on emotions, attitudes, and values in educational settings. It details the levels of the affective domain as defined by David Krathwohl, including receiving, responding, valuing, organization, and characterization by value. Additionally, it discusses the importance of affective learning competencies and the role of motivation and self-efficacy in student engagement and performance.
Uploaded by
adelverpatag062323Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 25