0% found this document useful (0 votes)
62 views8 pagesMFM42Support - Answers of End Module MSK1
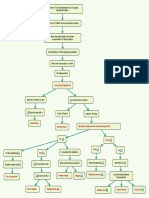
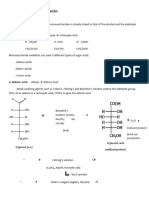
This document contains questions from modules on biochemistry, physiology, anatomy, and histology. It includes 20 multiple choice questions testing knowledge of topics like collagen composition, vitamin deficiencies, nerve signaling, muscle anatomy, and connective tissue histology. The questions have a single best answer format with choices A-E.
Uploaded by
Mohammed HashemCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
62 views8 pagesMFM42Support - Answers of End Module MSK1
This document contains questions from modules on biochemistry, physiology, anatomy, and histology. It includes 20 multiple choice questions testing knowledge of topics like collagen composition, vitamin deficiencies, nerve signaling, muscle anatomy, and connective tissue histology. The questions have a single best answer format with choices A-E.
Uploaded by
Mohammed HashemCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 8