0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views37 pagesCloud Computing
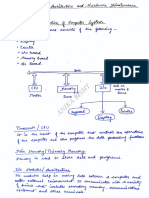
The document provides an overview of cloud computing, including its definition, services, deployment models, and examples of cloud providers. It details the evolution of computing from first-generation hardware to the development of the Internet and cloud technologies. Additionally, it includes instructions for registering with Google Cloud and links to related video resources.
Uploaded by
Boomija ITCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views37 pagesCloud Computing
The document provides an overview of cloud computing, including its definition, services, deployment models, and examples of cloud providers. It details the evolution of computing from first-generation hardware to the development of the Internet and cloud technologies. Additionally, it includes instructions for registering with Google Cloud and links to related video resources.
Uploaded by
Boomija ITCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 37