0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views12 pagesAzure
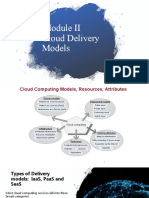
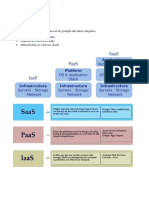
Azure is a public cloud computing platform offering IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS solutions for various services like analytics, storage, and networking. IaaS provides scalable infrastructure managed over the internet, allowing businesses to avoid the costs of physical servers, while PaaS supports the entire application lifecycle without server maintenance. Azure's flexibility, reliability, and global reach make it an economical choice for businesses looking to innovate and respond to changing demands.
Uploaded by
devendra.sharmaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views12 pagesAzure
Azure is a public cloud computing platform offering IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS solutions for various services like analytics, storage, and networking. IaaS provides scalable infrastructure managed over the internet, allowing businesses to avoid the costs of physical servers, while PaaS supports the entire application lifecycle without server maintenance. Azure's flexibility, reliability, and global reach make it an economical choice for businesses looking to innovate and respond to changing demands.
Uploaded by
devendra.sharmaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 12