0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views11 pagesIf Statement in Java
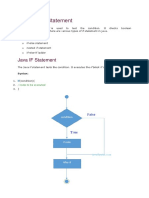
The document explains the use of conditional statements in Java, focusing on the if statement, if-else statement, else-if ladder, and nested if statements. It provides syntax and examples for each type of conditional statement to illustrate how they control program flow based on conditions. The summary highlights that these statements enable decision-making in Java programming.
Uploaded by
lebriasjade418Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views11 pagesIf Statement in Java
The document explains the use of conditional statements in Java, focusing on the if statement, if-else statement, else-if ladder, and nested if statements. It provides syntax and examples for each type of conditional statement to illustrate how they control program flow based on conditions. The summary highlights that these statements enable decision-making in Java programming.
Uploaded by
lebriasjade418Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 11