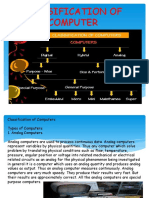
Classification of
computer
�Classification of Computers:
Computers can be classified in several ways
• depending on purpose,
• data handling,
• size,
• Performance.
�Based on Purpose Computers:
are divided into two major categories:
1.General Purpose Computers:
• Designed to perform a variety of operations.
• Can store different programs and switch between tasks easily.
• Examples: Personal Computers, Laptops, Workstations.
• Used in offices, homes, and educational institutions.
�2. Special Purpose Computers:
• Designed and built for a specific application.
• Cannot be used for multiple tasks.
• More efficient for the task they are designed
• Examples:ATM machines (banking only)Embedded
systems in cars (engine control)Traffic light controllers
�Based on Data Handling:
The way computers process and handle data
1.Analog Computers:
• Process continuous data such as temperature, speed, and voltage.
• Represent data in physical quantities.
• Not very accurate, but useful for scientific applications.
• Example: Thermometers, Speedometers, Flight simulators.
�2.Digital Computers:
• Process discrete data in the form of binary (0s and 1s).
• Most commonly used computers in everyday life.
• Provide high accuracy, reliability, and speed.
• Examples: Desktops, Smartphones, Servers.
�3.Hybrid Computers:
• Combine features of both analog and digital computers.
• Analog part measures physical quantities, digital part processes the data.
• Used in specialized applications like hospitals.
• Example: Medical devices (ECG machines, CT Scanners).
�Based on Size and Performance Computers:
1.Microcomputers:
• Smallest in size, designed for individual use.
• Examples: Desktop PCs, Laptops, Tablets, Smartphones.
2. Minicomputers:
• Medium-sized computers, more powerful than microcomputers.
• Support multiple users at the same time.
• Examples: Used in small businesses, departmental servers.
�3.Mainframe Computers:
• Very large in size and powerful.
• Handle large volumes of data and thousands of users simultaneously.
• Used in banks, insurance companies, railways.
4. Supercomputers:
• Most powerful computers in terms of speed and
performance.
• Used for complex scientific calculations, space
research, climate modeling, defense simulations.
• Examples: PARAM (India), IBM Summit, Fugaku (Japan).