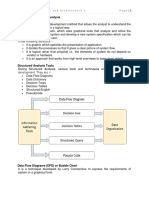
Structured Analysis
Main tools used
Data flow diagram (DFD) Data Dictionary Structured English Decision Trees Decision Tables
�Data Flow Diagram
Graphical representation of the logical flow of data. Square : represents source/destination
Employee
Arrow : identifies data flow
�Data Flow Diagram
Circle/bubble : a process
Open rectangle: a data store
�Data Flow Diagram
Illustration
Employee
Accounts Dept
Emp Data
Payroll Processing
Salary Statement
Updated Data
Employee File
�Data Dictionary
Provides definitions for all elements in the system which include:
Meaning of data flows and stores in DFDs Composition of the data flows e.g. customer address breaks down to street number, street name, city and postcode Composition of the data in stores e.g. in Customer store include name, date of birth, address, credit rating etc. Details of the relationships between entities
�Data Dictionary Notations
= + () {} [] ** @ | name = courtesy-title = first-name = middle-name = last-name = legal-character = is composed of and optional ( may be present or absent) iteration select one of several alternatives comment identifier (key field) for store separates alternative choices in the [ ] construct courtesy-title + first-name + (middle-name) + last-name [Mr. | Miss | Mrs. | Ms. | Dr. | Professor] {legal-character} {legal-character} {legal-character} [A-Z|a-z|0-9||-| |]
�Data Dictionary Examples
Current-height = ** *units: metres; range: 1.00-2.50* ** *values: [M|F]*
sex =
As both are elementary data, no composition need be shown, though an explanation of the relevant units/symbols is needed order = customer-name + shipping-address + 1{item}10
means that an order always has a customer name and a shipping address and has between 1 and 10 items
�Structured English
Used to represent logic
Common Statements Action Statement Example Profits = Revenues - Expenses Generate Inventory - Report Add Product record to Product Data Store IF Customer Not in Customer Data Store THEN Add Customer record to Customer Data Store ELSE Add Current-Sale to Customers Total-Sales Update Customer record in Customer Data Store FOR all Customers in Customer Data Store Generate a new line in the Customer-Report Add Customers Total-Sales to Report-Total CASE If Income < 10,000: Marginal-tax-rate = 10% If Income < 20,000: Marginal-tax-rate = 20% If Income < 30,000: Marginal-tax-rate = 31% If Income < 40,000: Marginal-tax-rate = 35% ELSE Marginal-tax-rate = 38% ENDCASE
If Statement
For Statement
Case Statement
�Decision Tree
Processing logic represented in a tree structure.
Types of Customer ---------------Size of Order ---------------Discount ----------------
Dealer
6 or more
Less than 6
35%
Nil
Discount Policy Educational Institution 50 or more 20-49 6-19 <6 30% 20% 15% Nil
�Decision Table
A matrix of rows and columns that shows conditions and actions. A decision table consists of 4 sections
Condition Entry: Condition stub: Questions or Rules to be followed conditions to be met. Action stub: Actions to be followed Action entry: Actions to be taken
�Decision Table
Illustration - The cash a cheque table
Cheque Cashing Policy Type of Cheque Rule 1 Rule 2 Rule 3 Rule 4 Rule 5
Personal Payroll
Personal Payroll
Other
Check amt yes <= $750 Employer preapproved? Cash the Cheque Reject the Cheque doesnt matter X
doesnt No matter yes doesnt matter
doesnt doesnt matter matter no doesnt matter
X X X
X
�Structured Tools Prons & Cons
Pros DFD Represent data flows. Used at high or low level analysis. Good system documentation Cons Weakly shows i/p & o/p. confuses users initially
Data Dictionary
Simplify the structure for meeting No functional details data requirement Detailed data flow not possible
Structured Best describes sequence of English action with decision
Decision tree
Decision table
Problems with complex decisions -do resulting in limited actions
Complex branching routines -do-