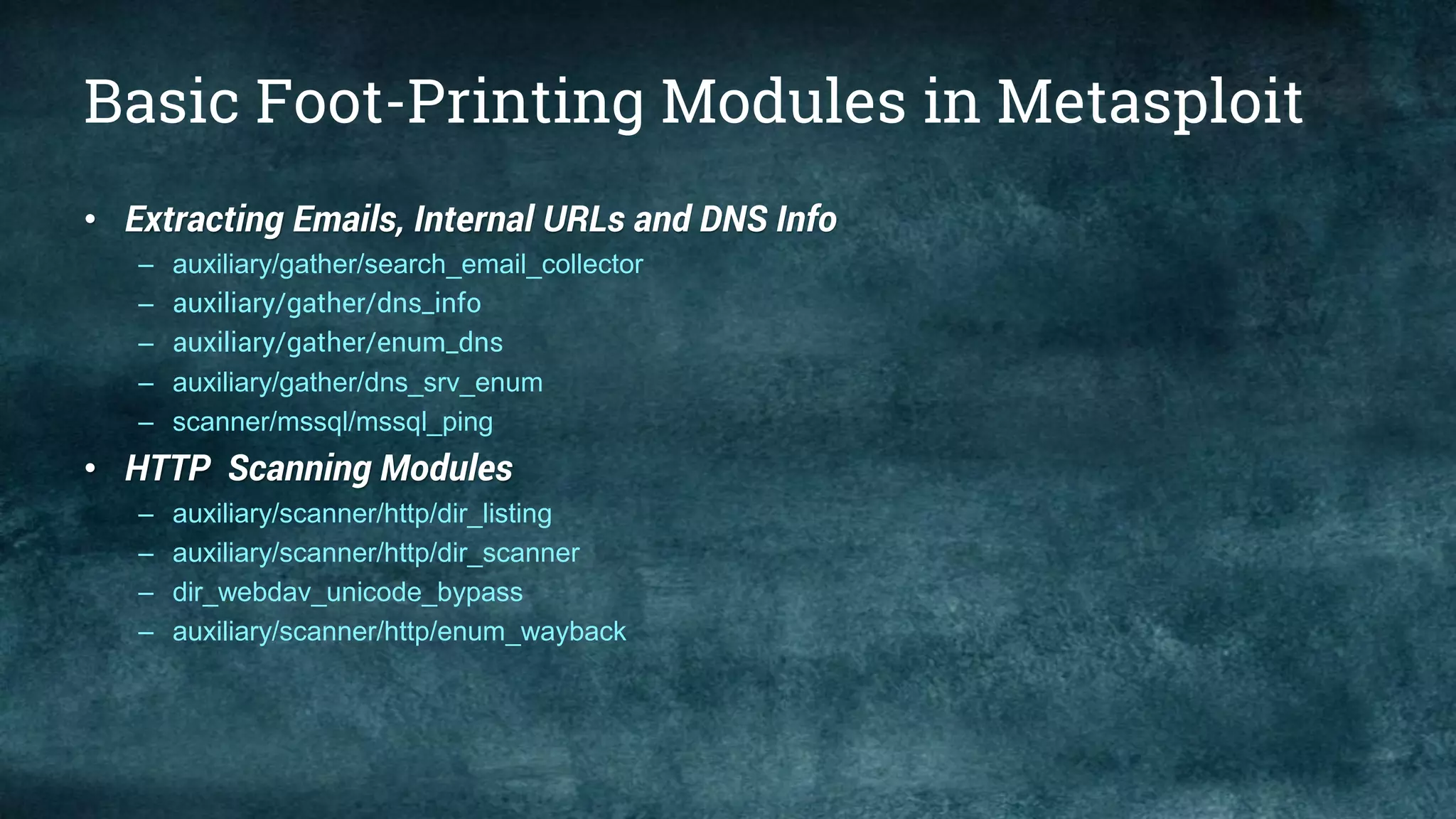
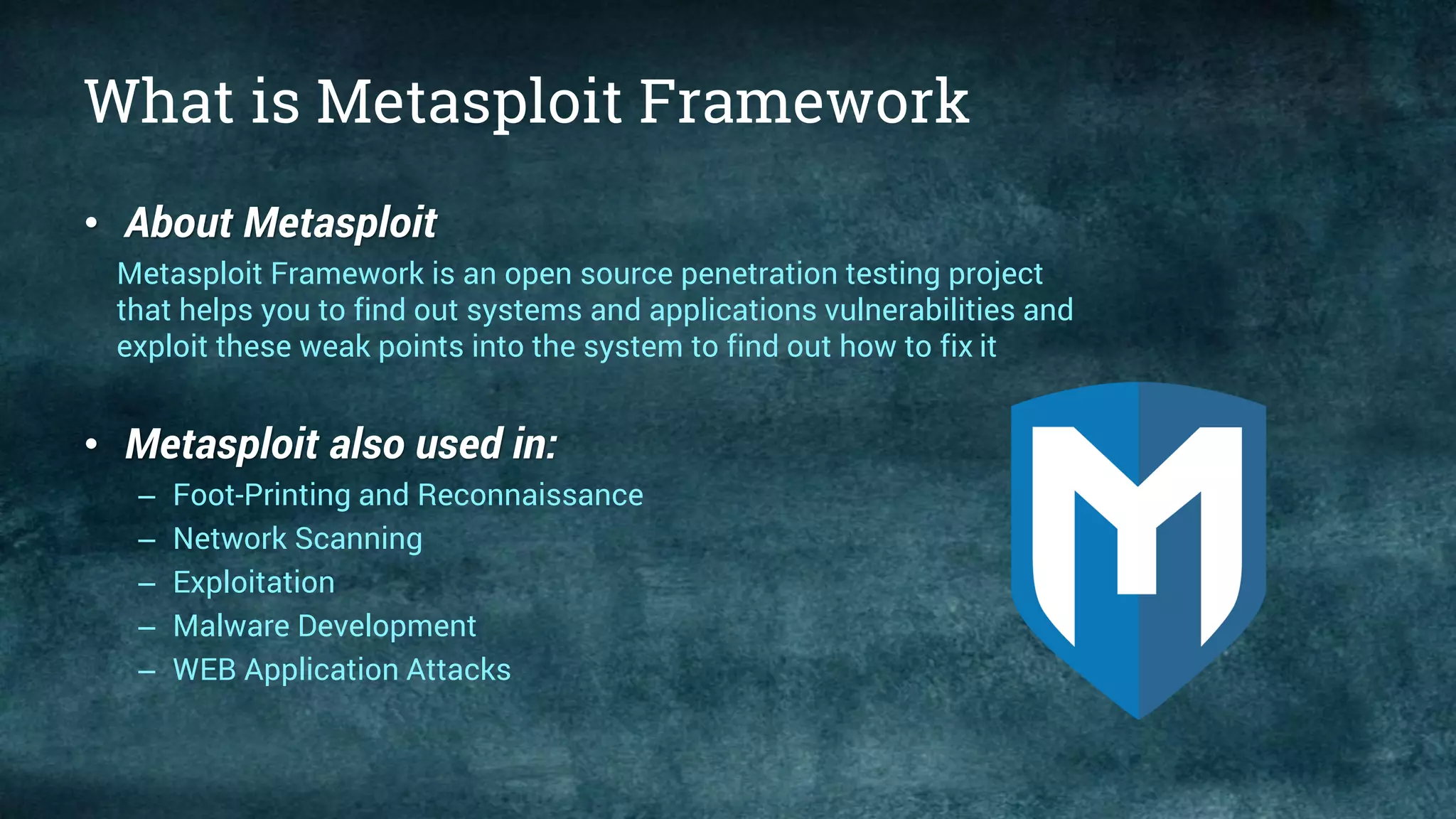
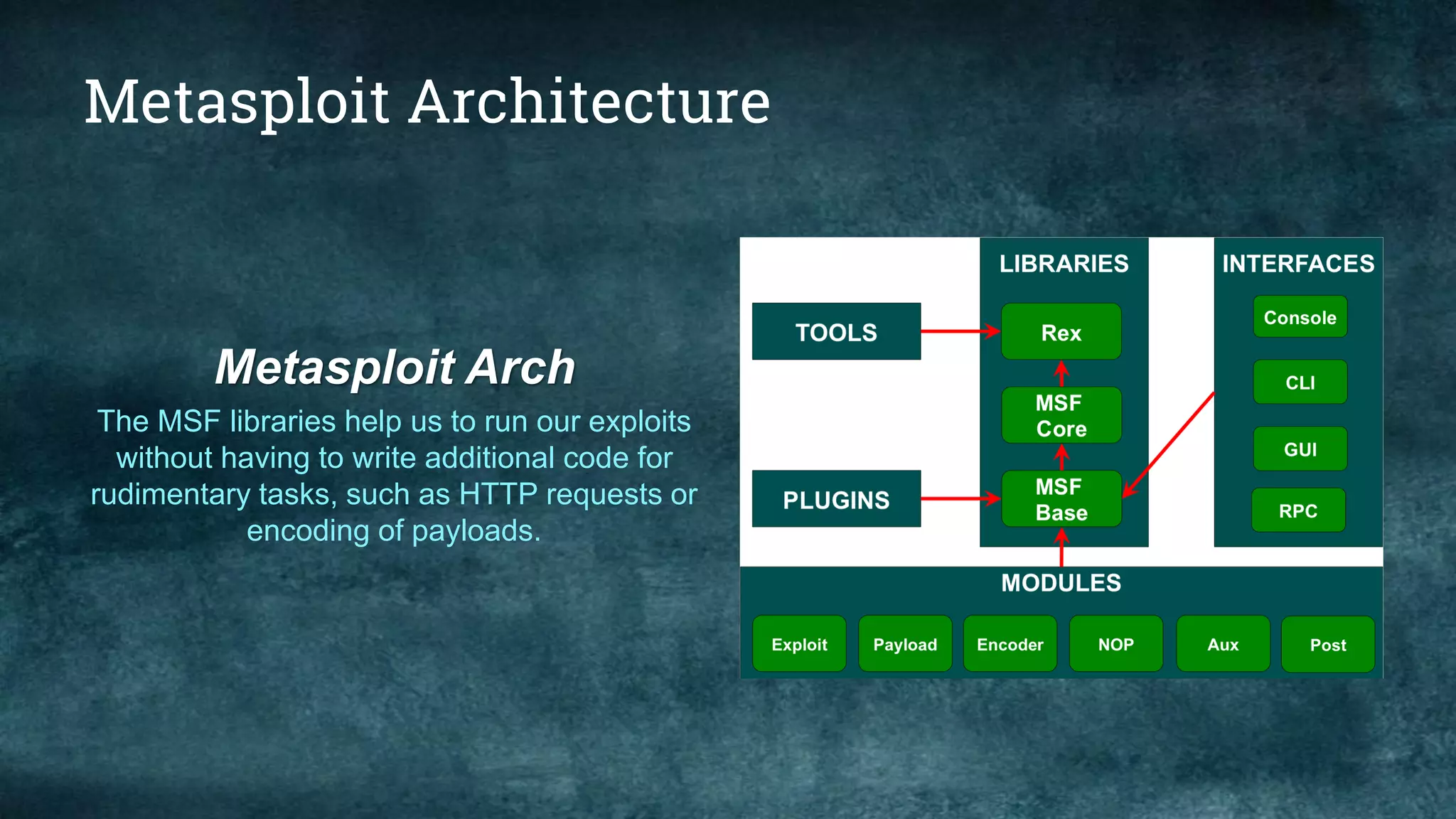
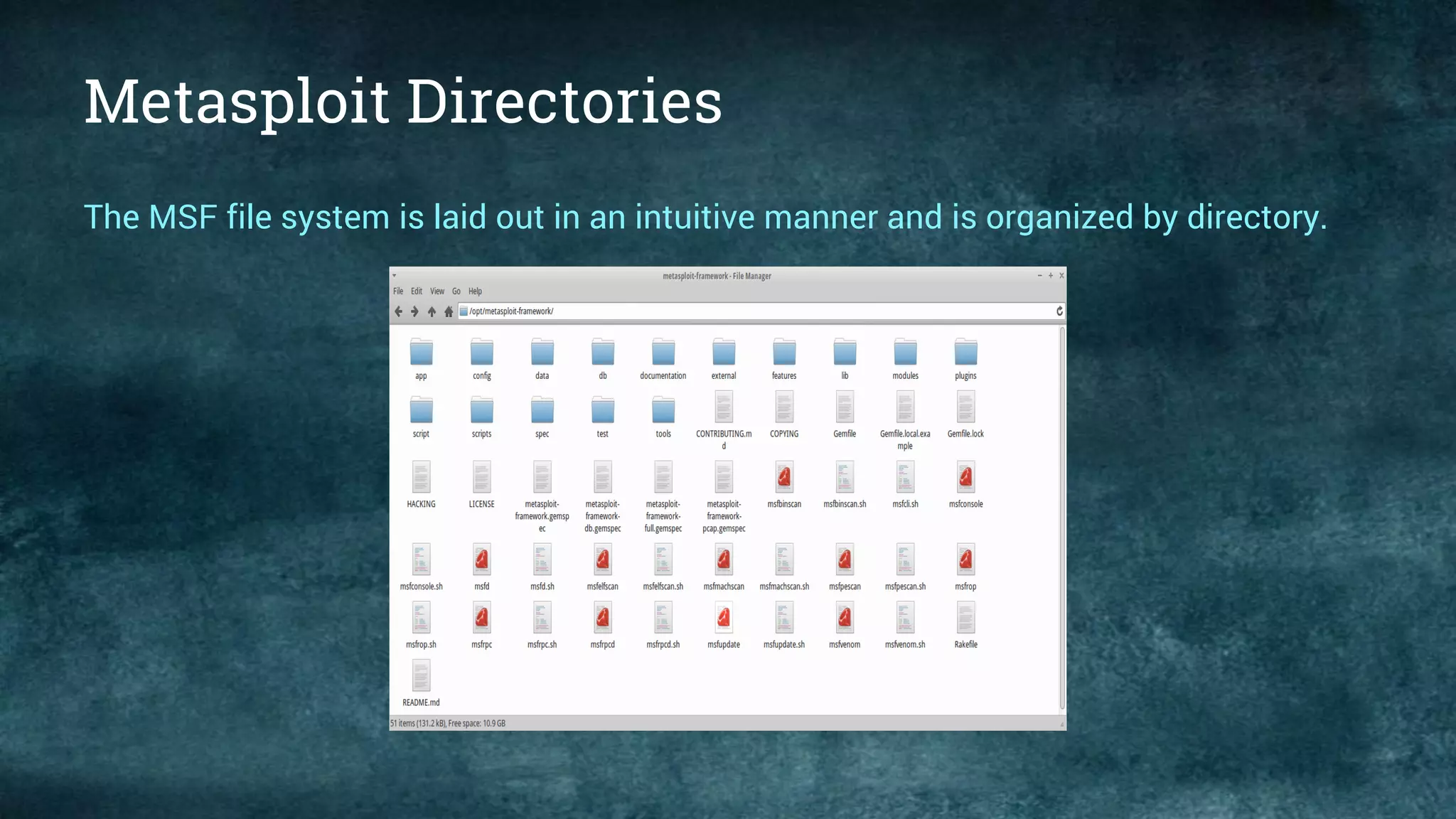
This document provides an overview of the Metasploit Framework, including its history, architecture, and various editions such as Community and Pro. It outlines the functionalities and uses of Metasploit in penetration testing, along with essential commands and information gathering techniques. Additionally, it highlights system requirements for running Metasploit and explains the purpose of various modules and interfaces within the framework.









![Metasploit Interfaces [msfconsole]
• What is the msfconsole?
– The msfconsole is probably the most popular interface to the Metasploit Framework
(MSF). It provides an “all-in-one” centralized console and allows you efficient access to
virtually all of the options available in the MSF. Msfconsole may seem intimidating at
first, but once you learn the syntax of the commands you will learn to appreciate the
power of utilizing this interface.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metasploitkung-fu1introduction-170814140040/75/01-Metasploit-kung-fu-introduction-13-2048.jpg)
![Metasploit GUI [msfgui]
• What is MSFWEB ?
– Metasploit Web interface are very easy to use but it’s note faster than other interfaces
but it will help you when you need to explain something to your job manager or
administrator](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metasploitkung-fu1introduction-170814140040/75/01-Metasploit-kung-fu-introduction-14-2048.jpg)
![Metasploit GUI [msfgui]
• What is MSFGUI ?
– msfgui is the Metasploit Framework Graphical User Interface.
It provides the easiest way to use Metasploit, whether running locally or connecting
remotely, build payloads, launch exploits, control sessions, and keep track of activity as
you penetration test or just learn about security. It will never have ads, nag you to buy
products, abuse your personal information, or even ask for your personal information.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metasploitkung-fu1introduction-170814140040/75/01-Metasploit-kung-fu-introduction-15-2048.jpg)
![Metasploit Armitage [Armitage]
• What is Armitage ?
– Armitage is a scriptable red team collaboration tool for Metasploit that visualizes
targets, recommends exploits, and exposes the advanced post-exploitation features in
the framework.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metasploitkung-fu1introduction-170814140040/75/01-Metasploit-kung-fu-introduction-16-2048.jpg)