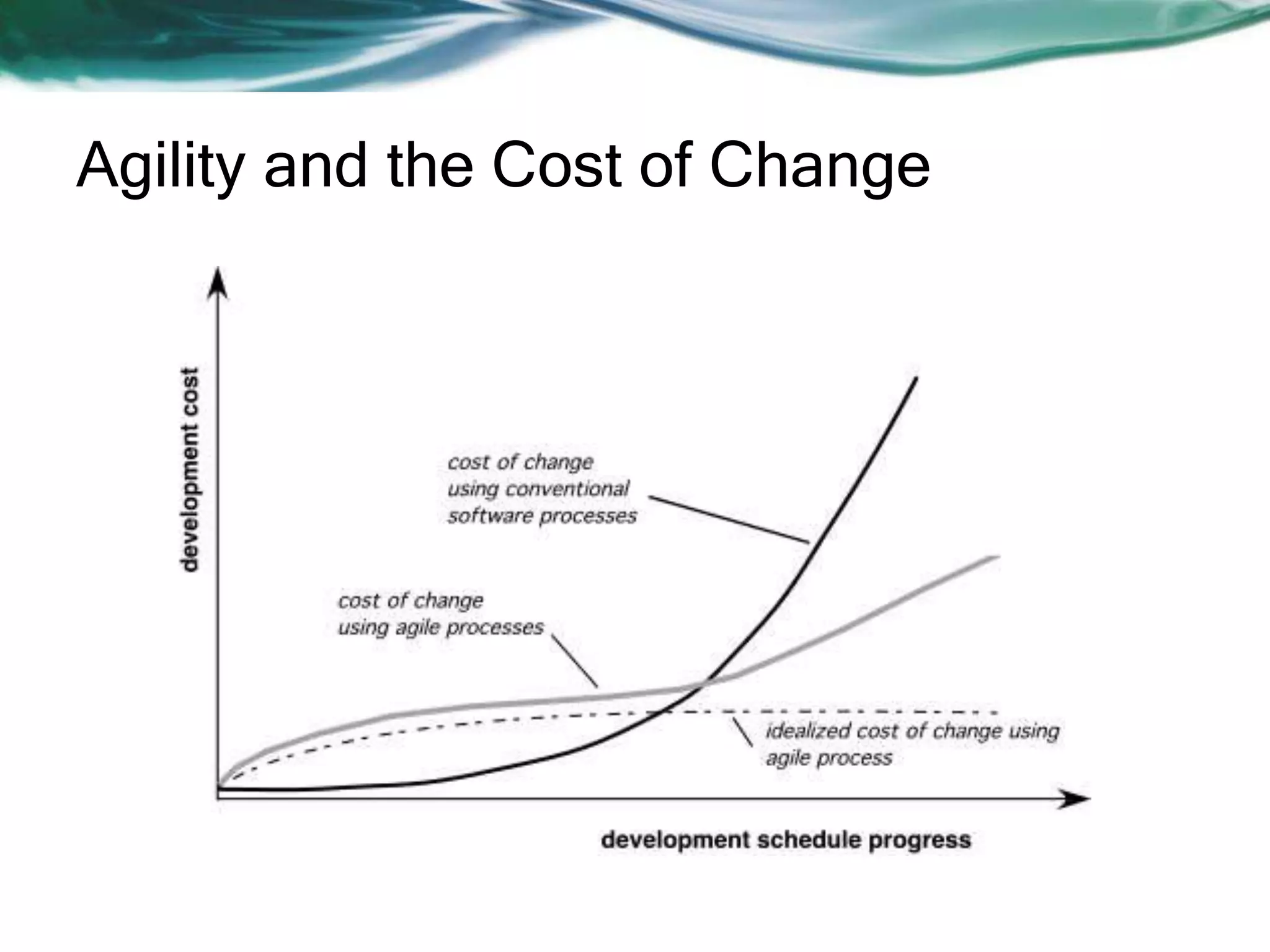
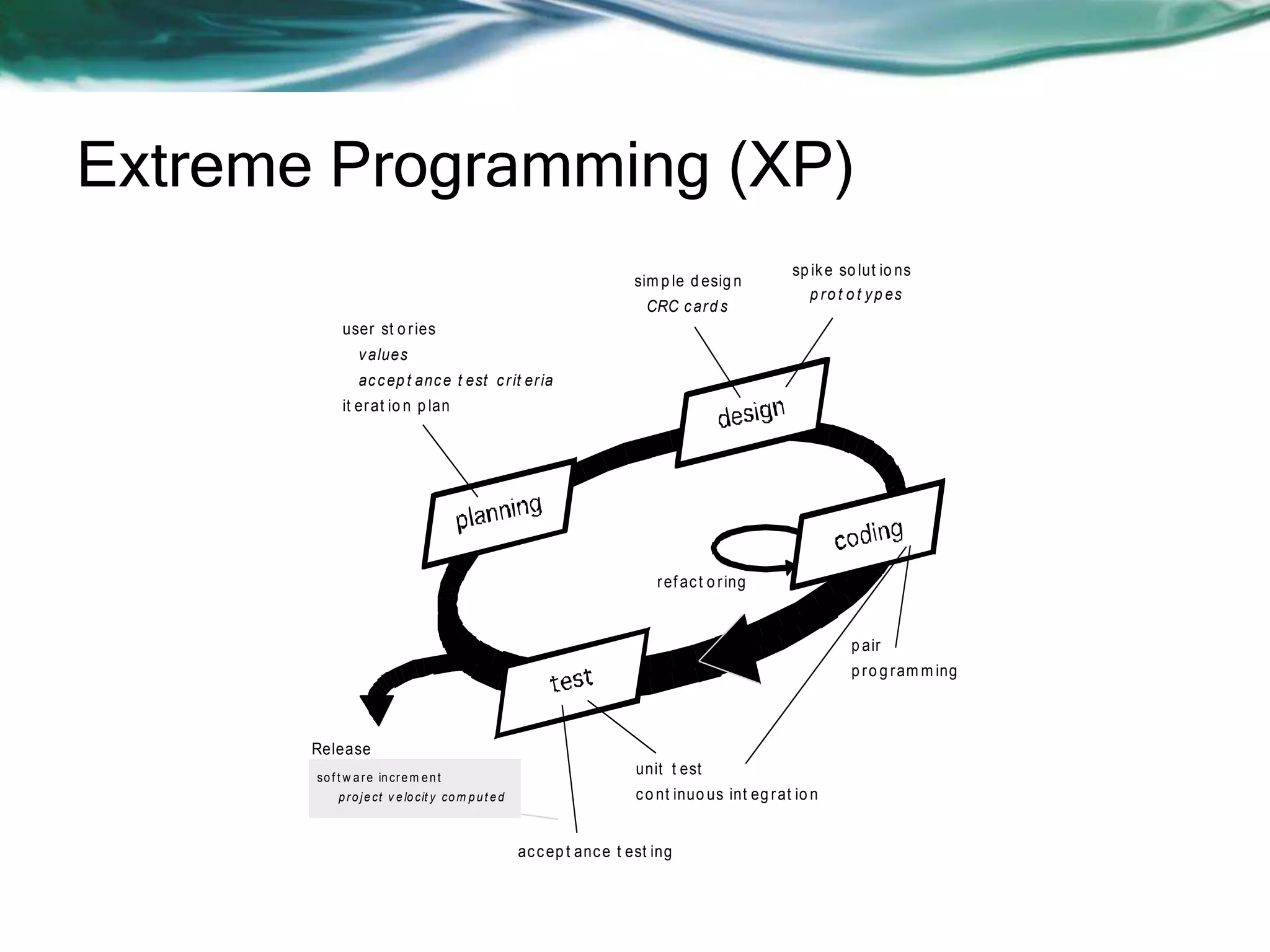
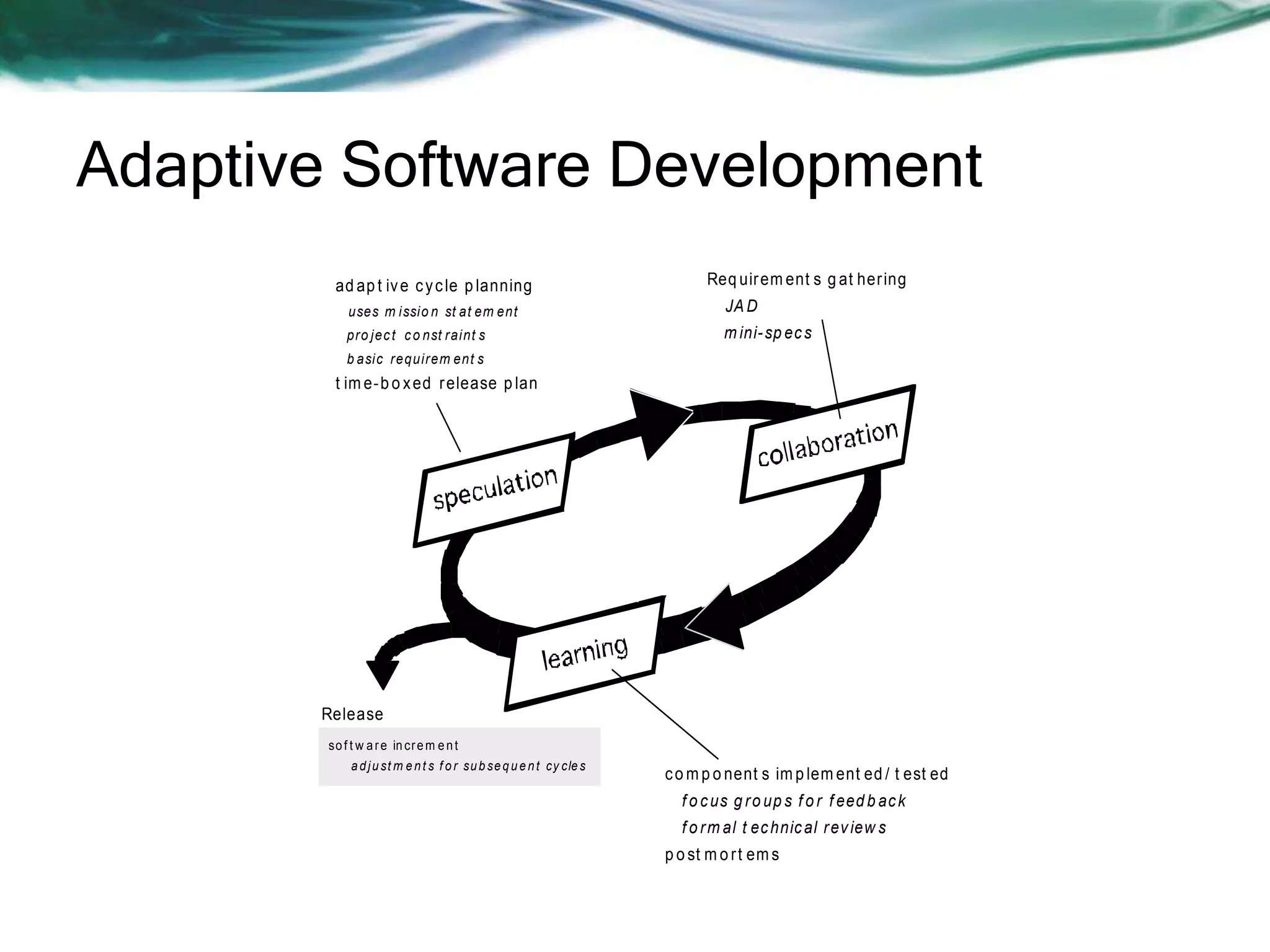
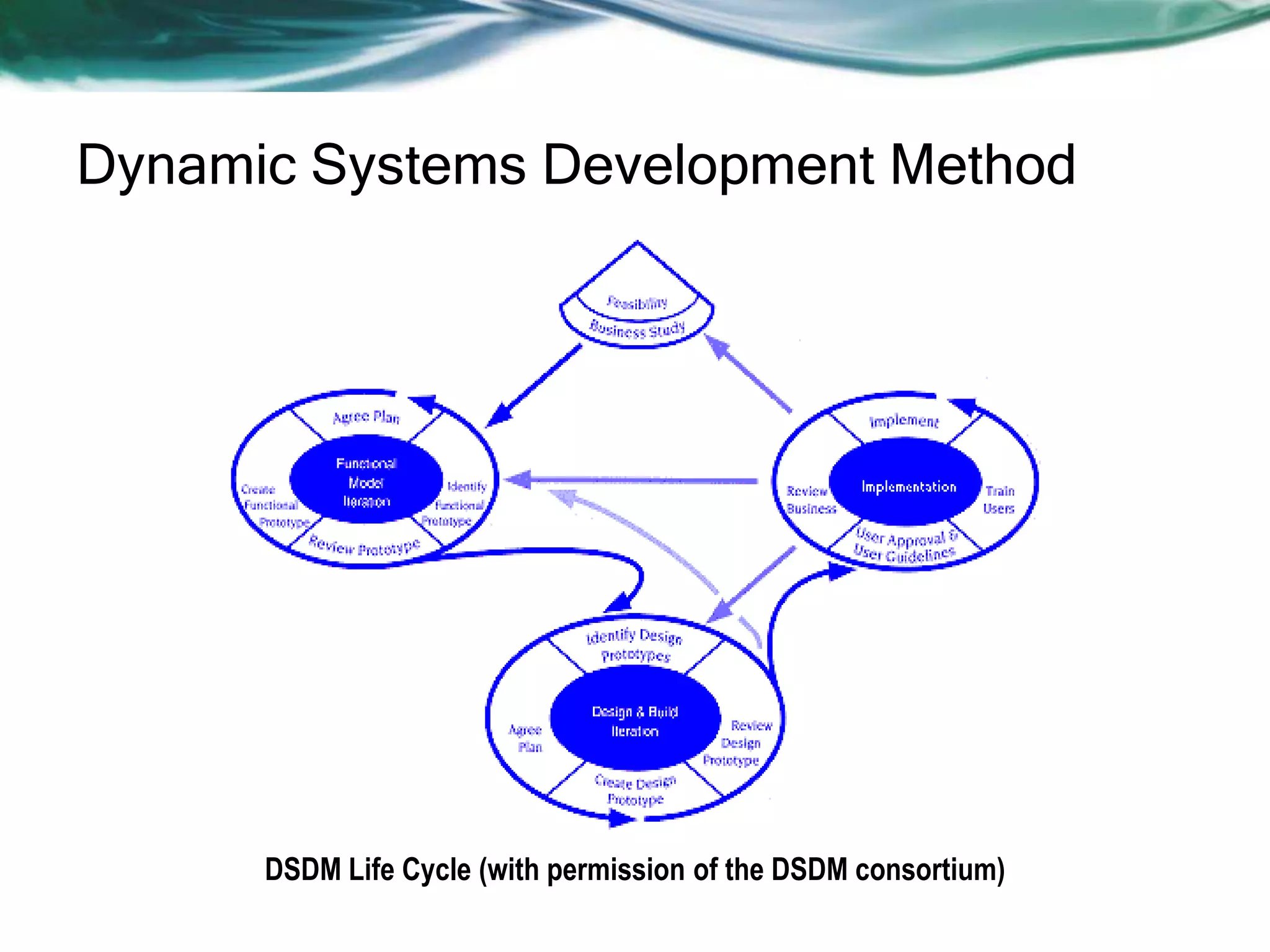
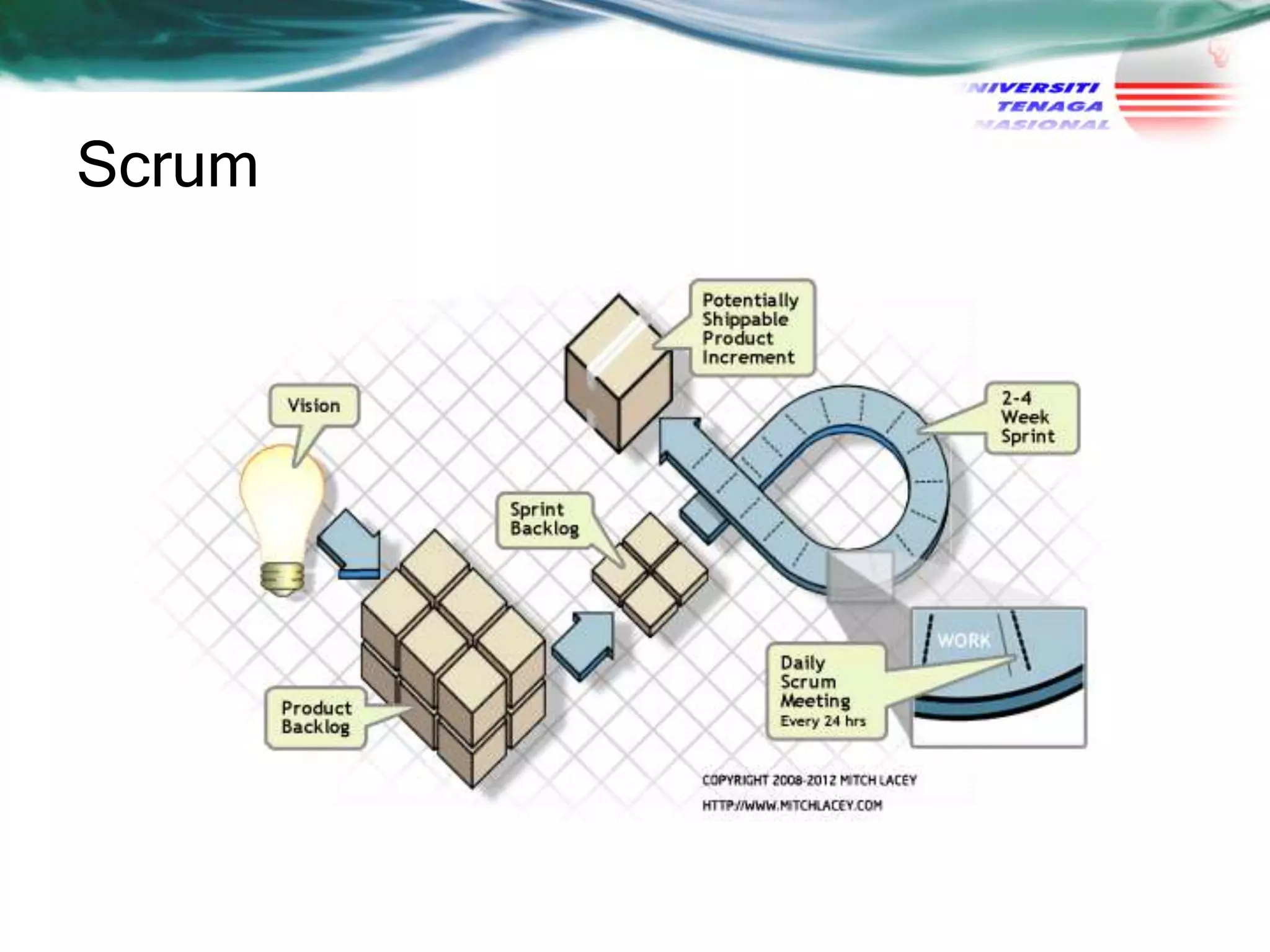
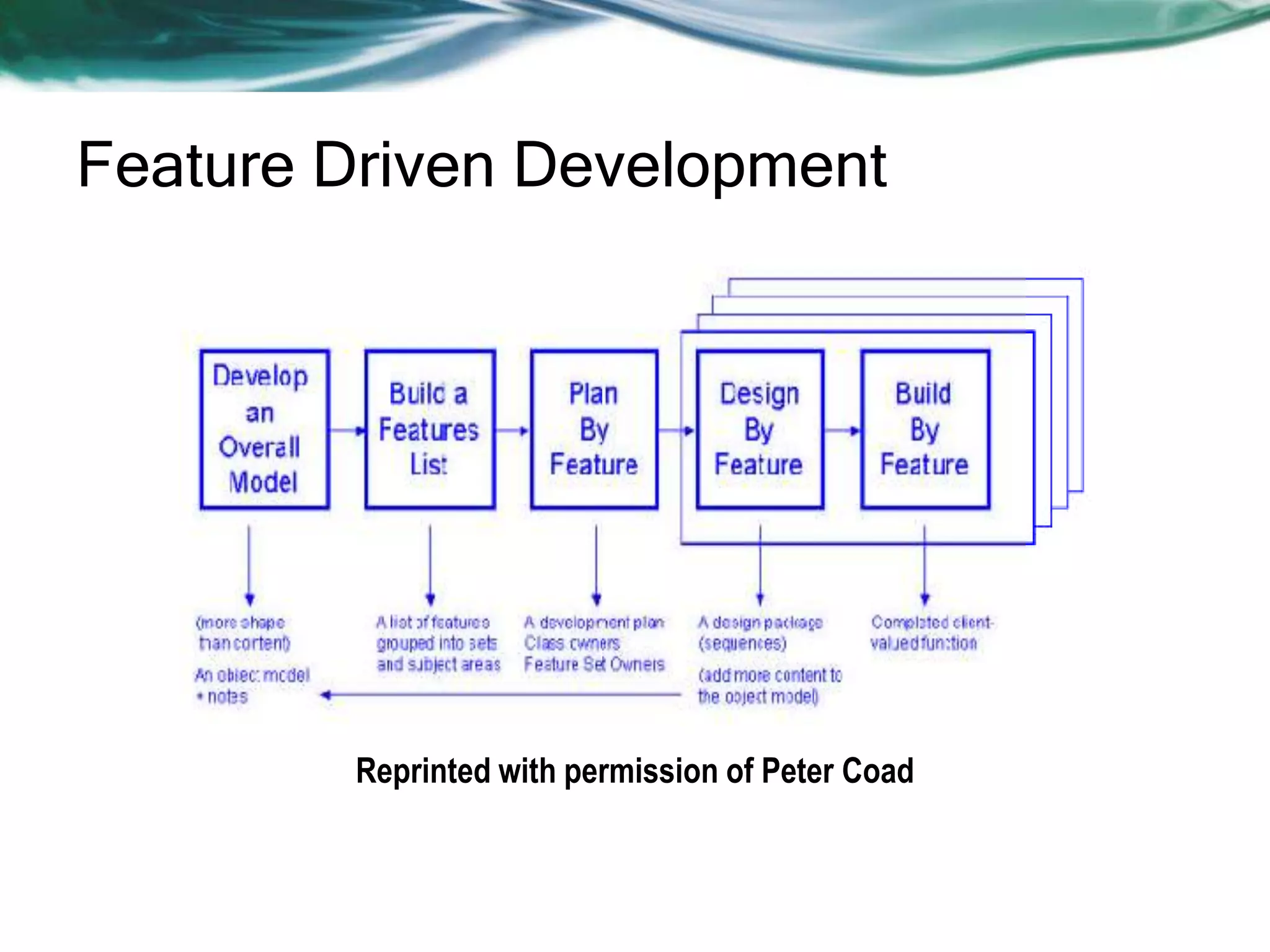
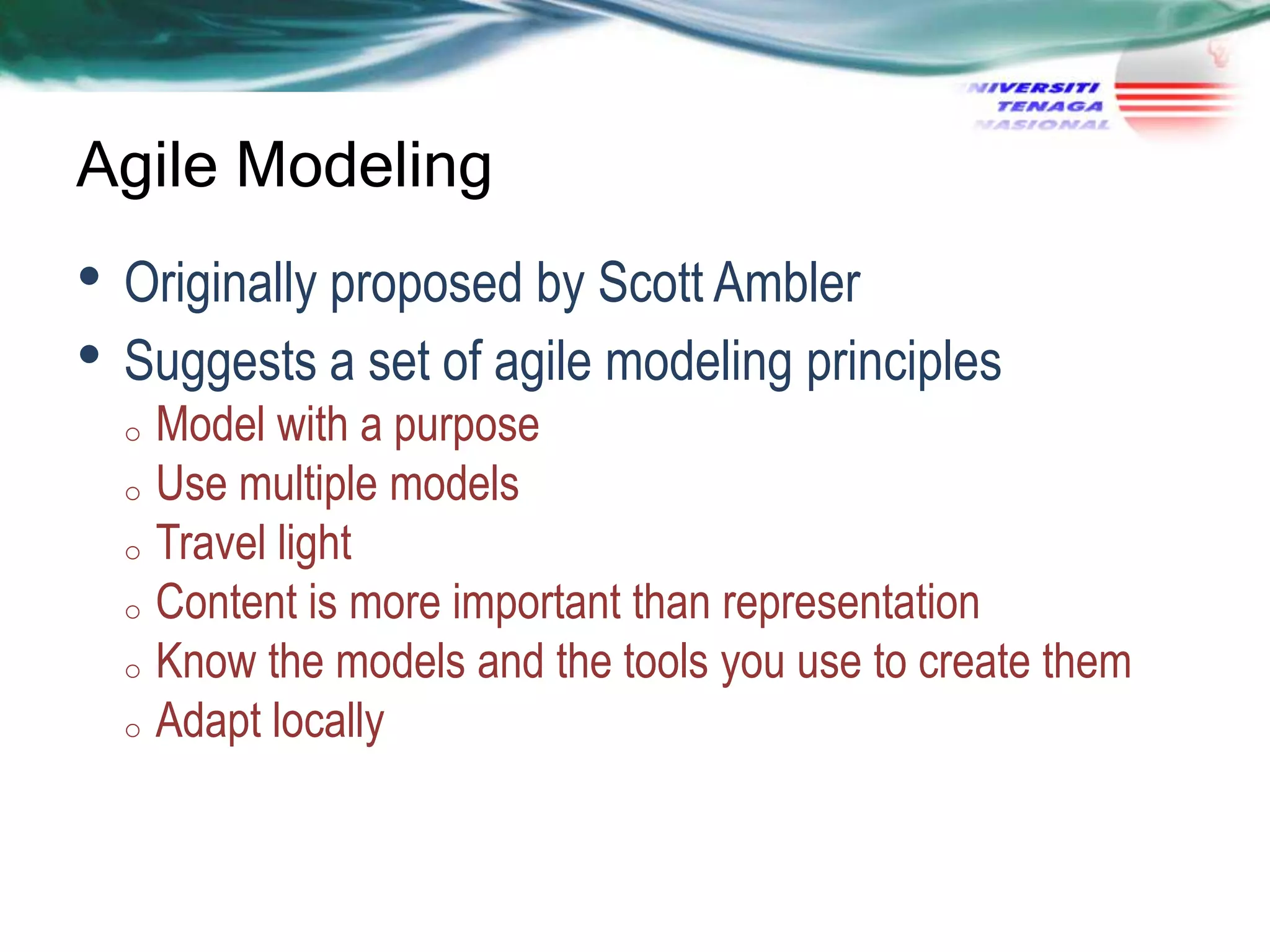
This document discusses various agile software development approaches. It begins by outlining the objectives of discussing agile development and explaining the Extreme Programming approach. It then summarizes the Manifesto for Agile Software Development. The rest of the document describes key concepts of agile development such as agility, principles of agility, and human factors important for agile teams. It also provides details on other agile processes including Adaptive Software Development, Dynamic Systems Development Method, Scrum, Crystal, Feature Driven Development, and Agile Modeling.