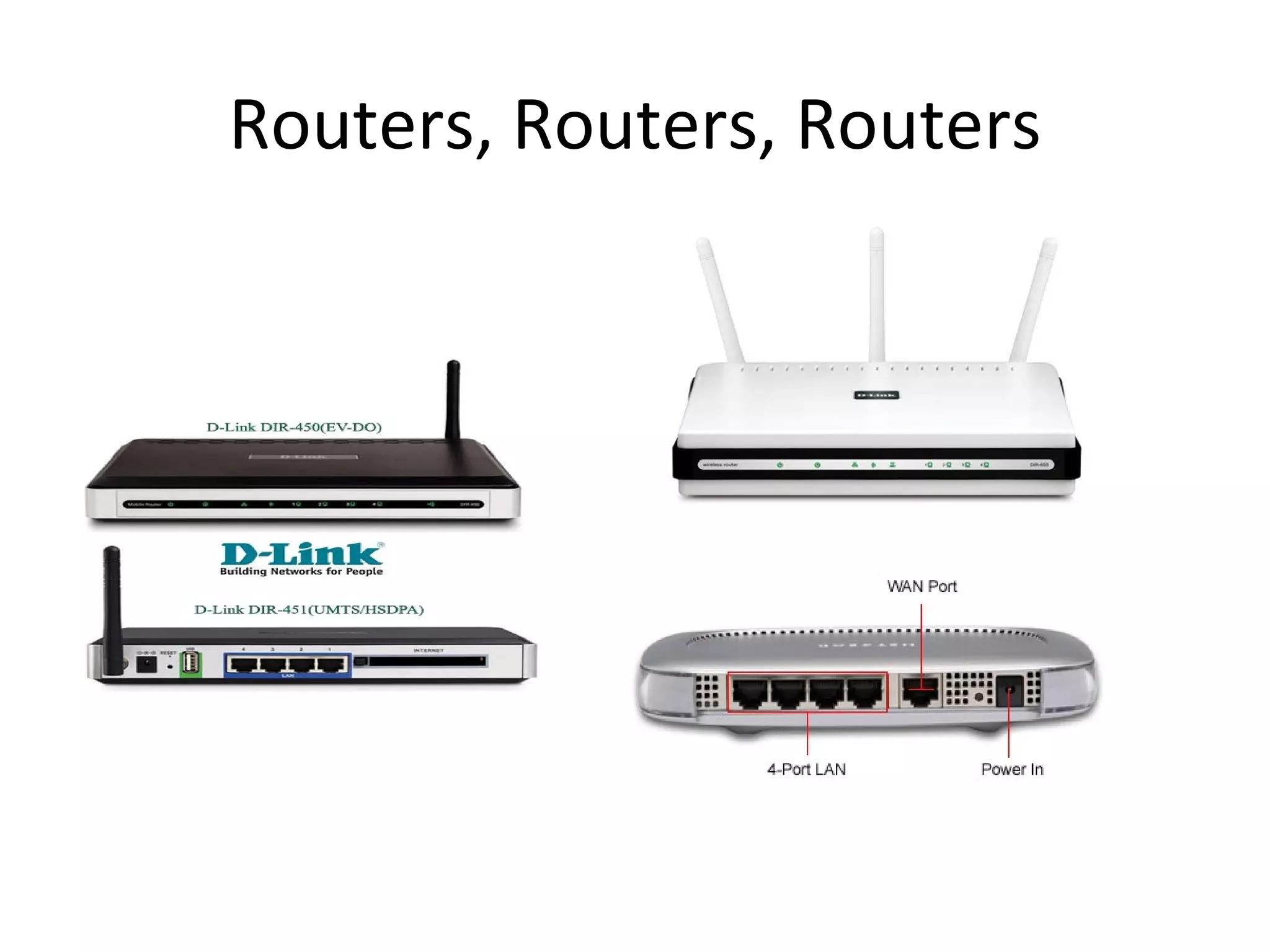
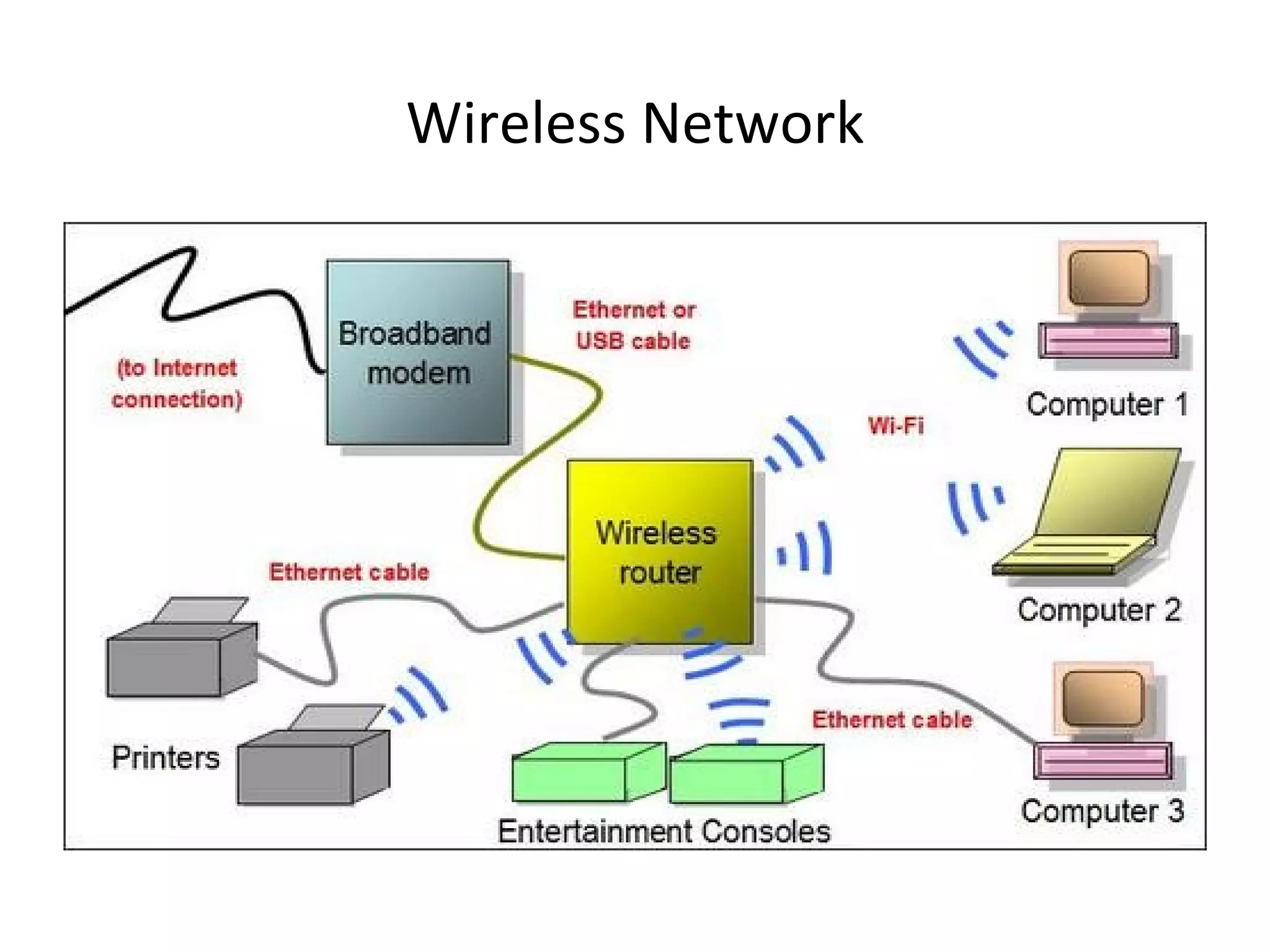
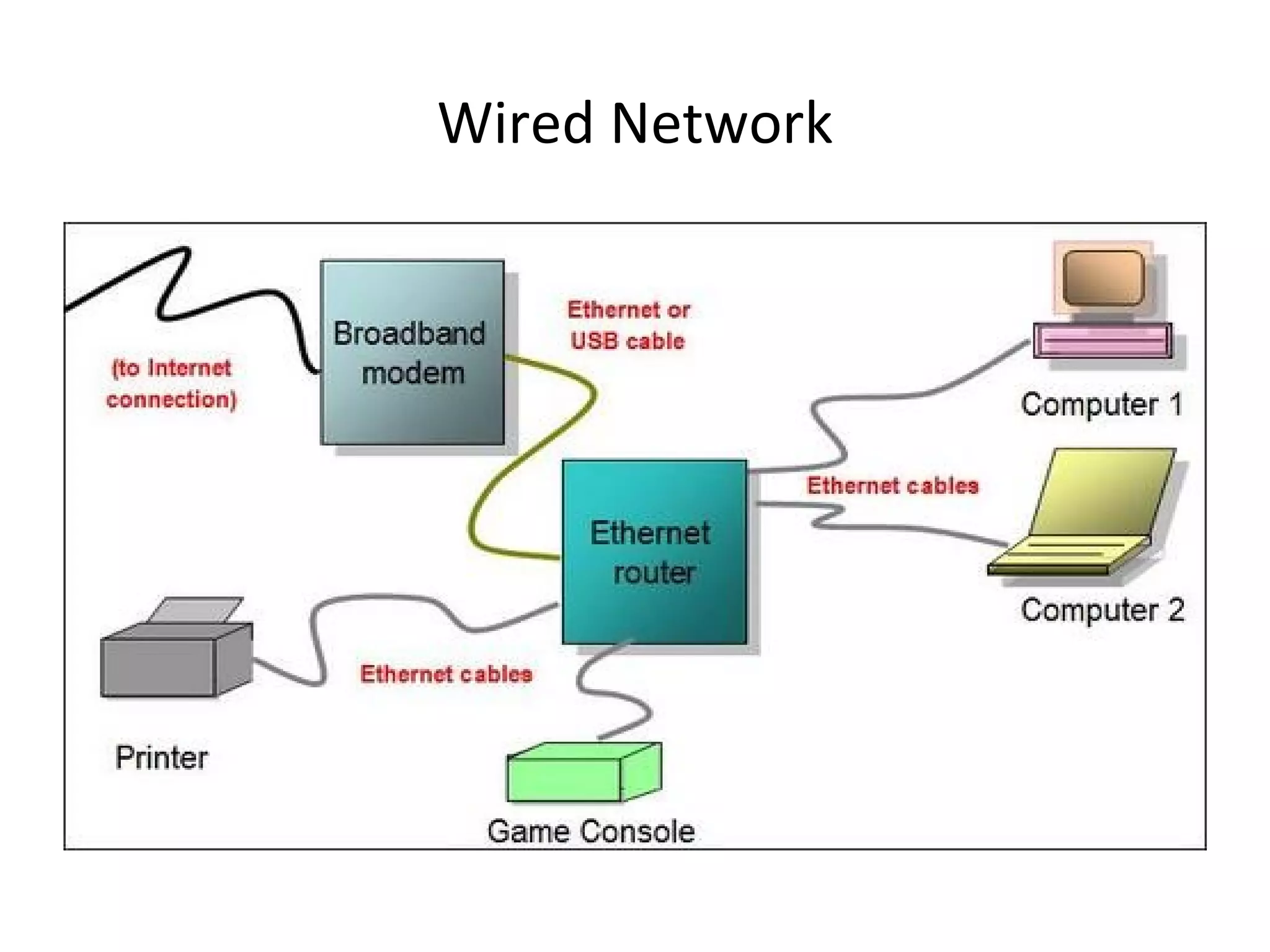
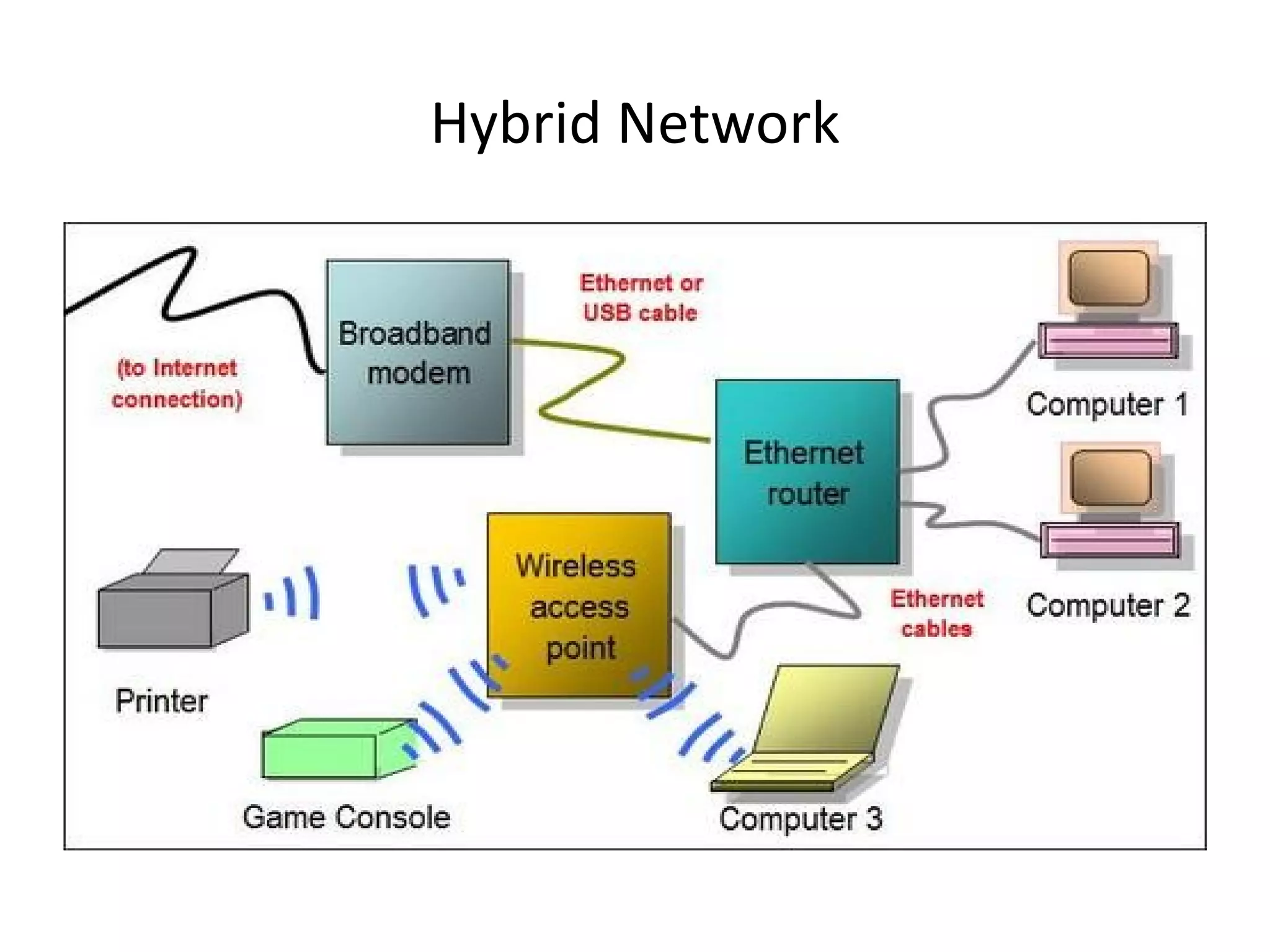
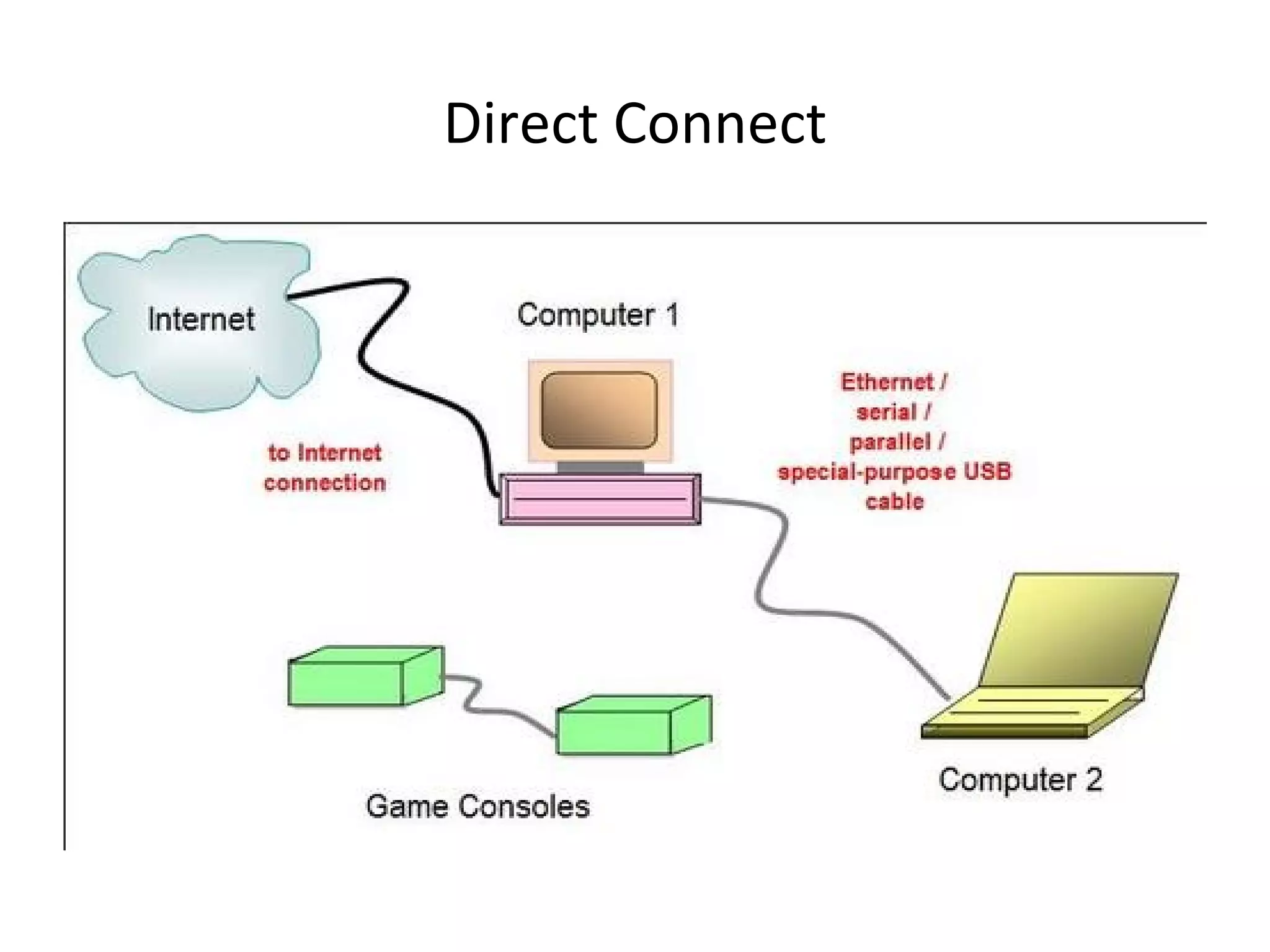
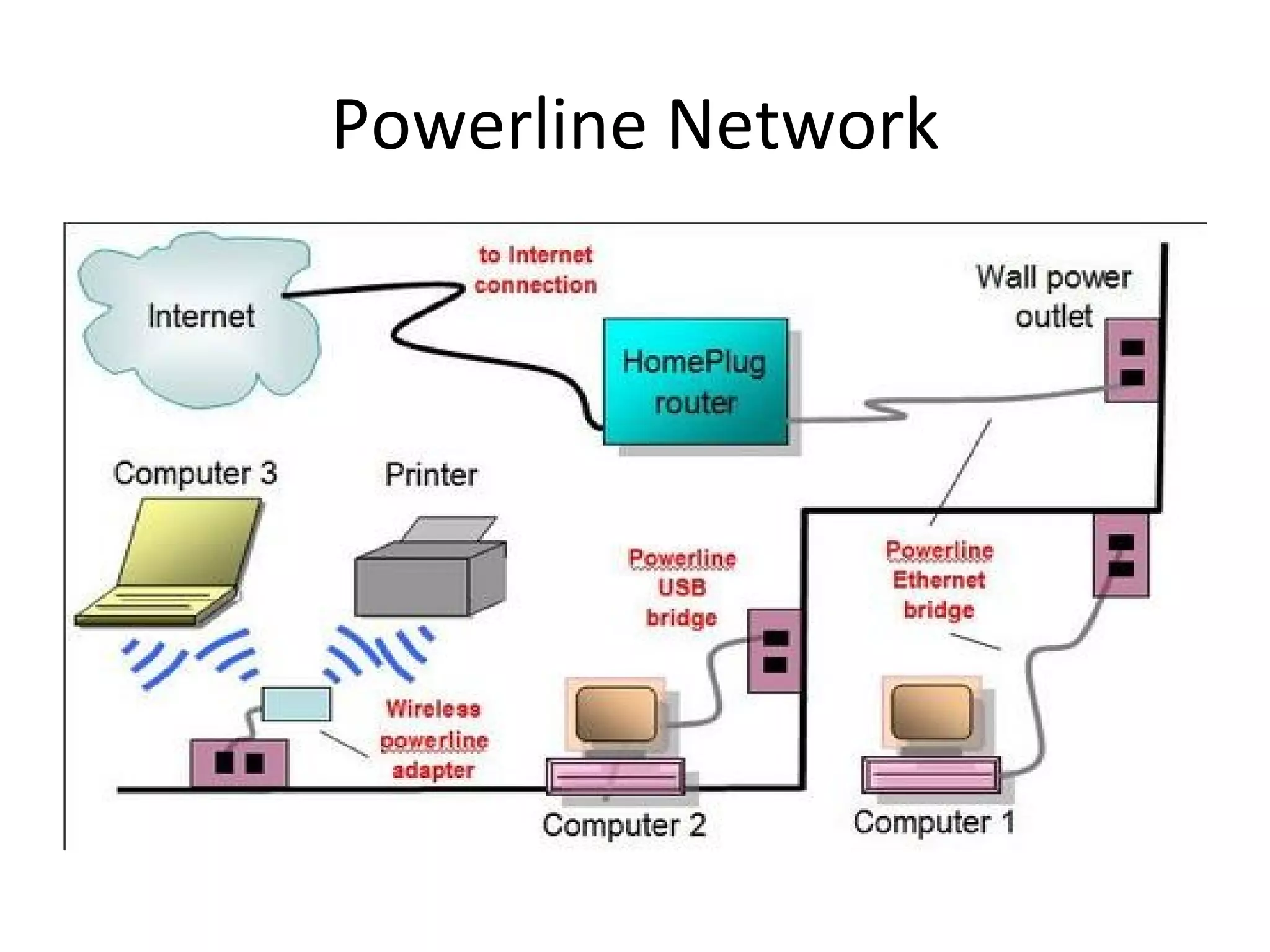
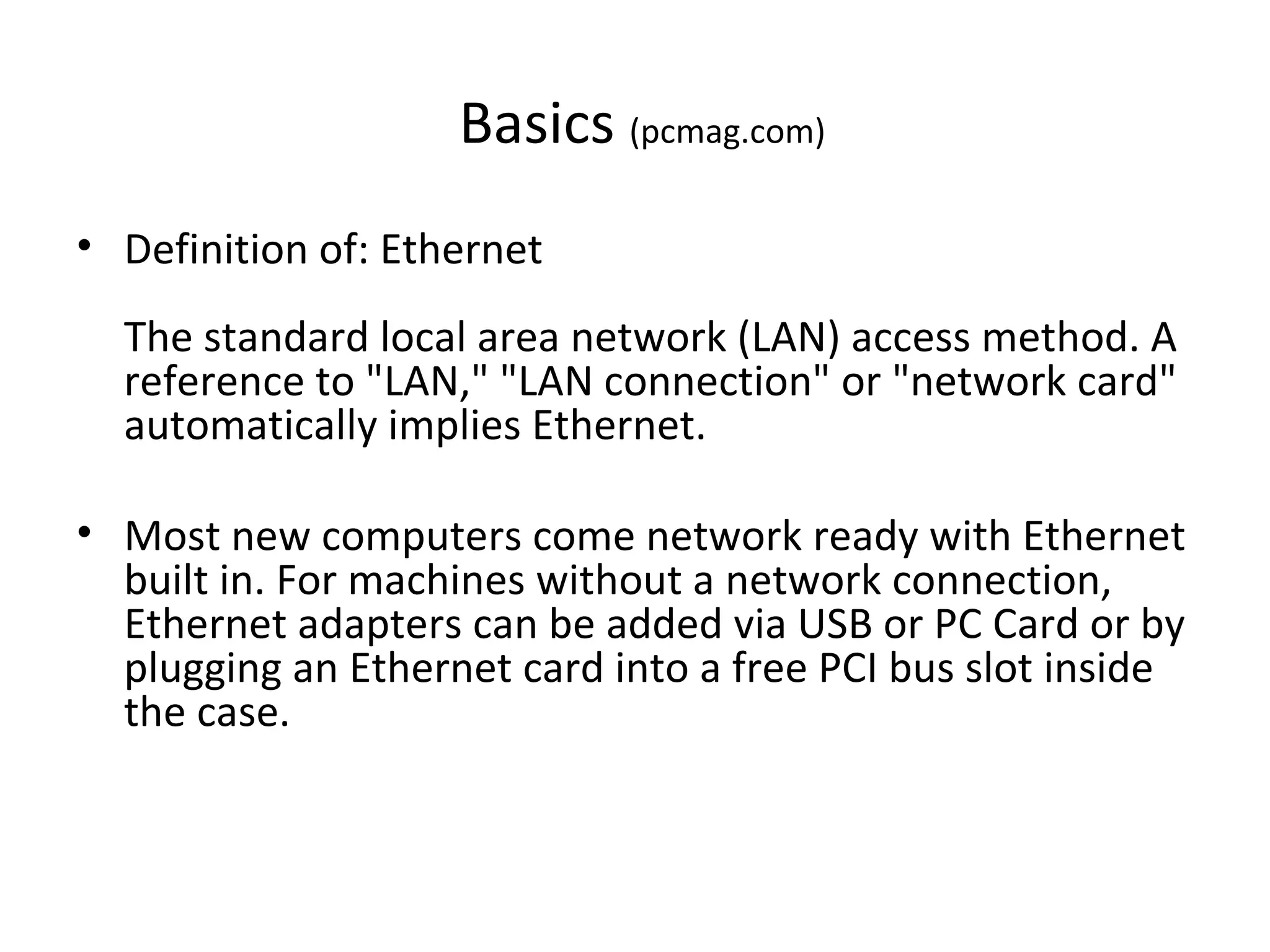
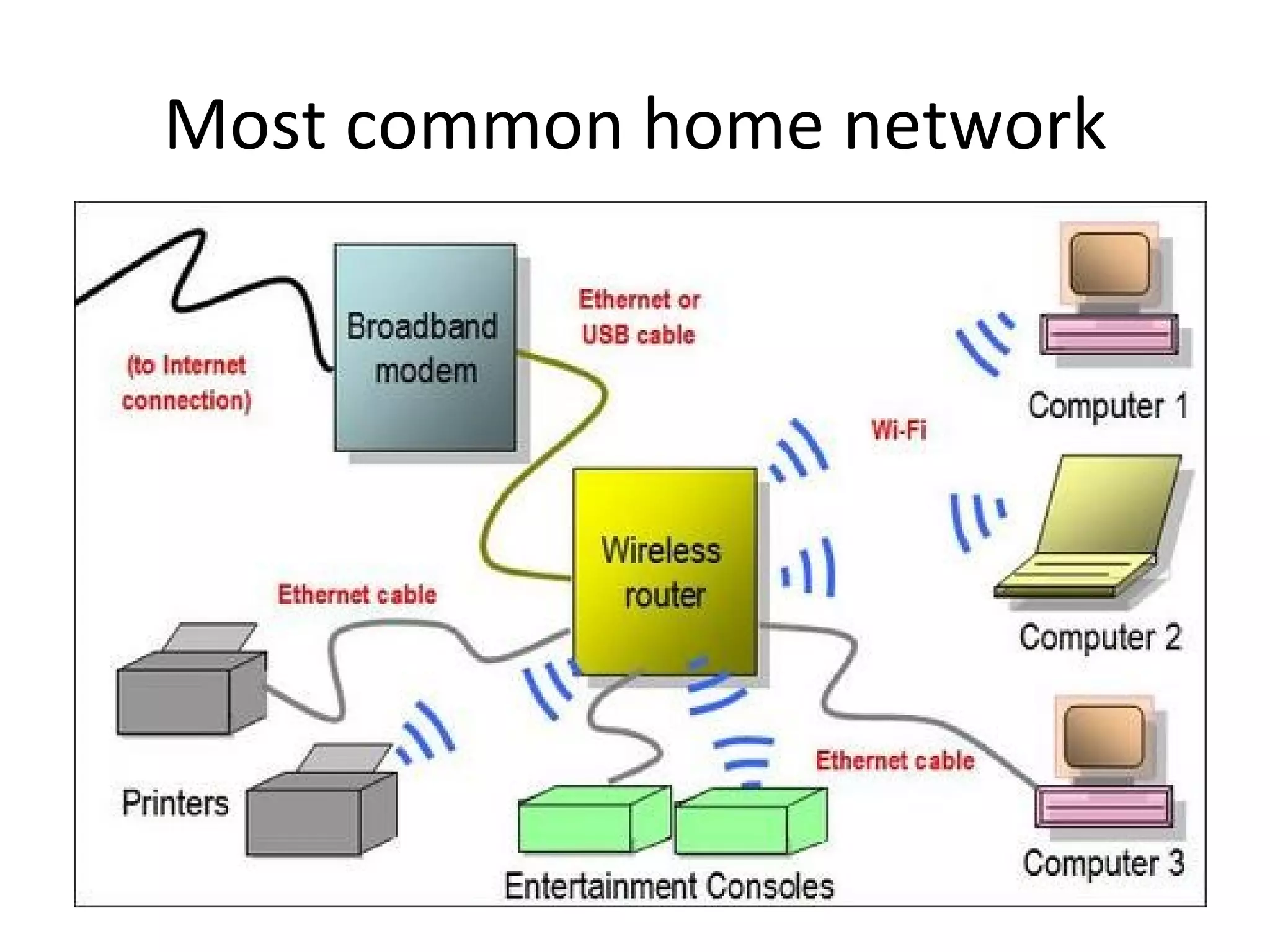
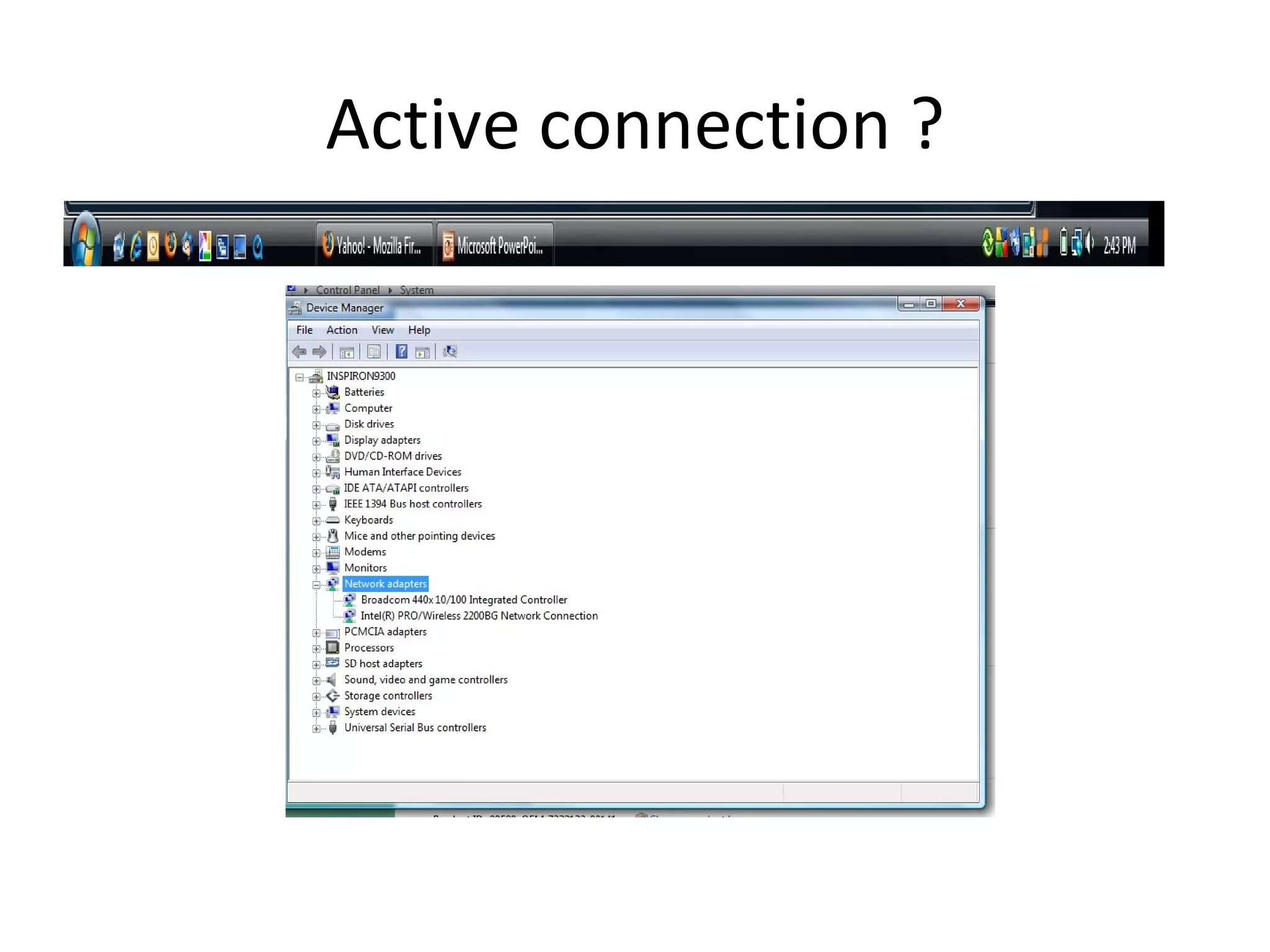
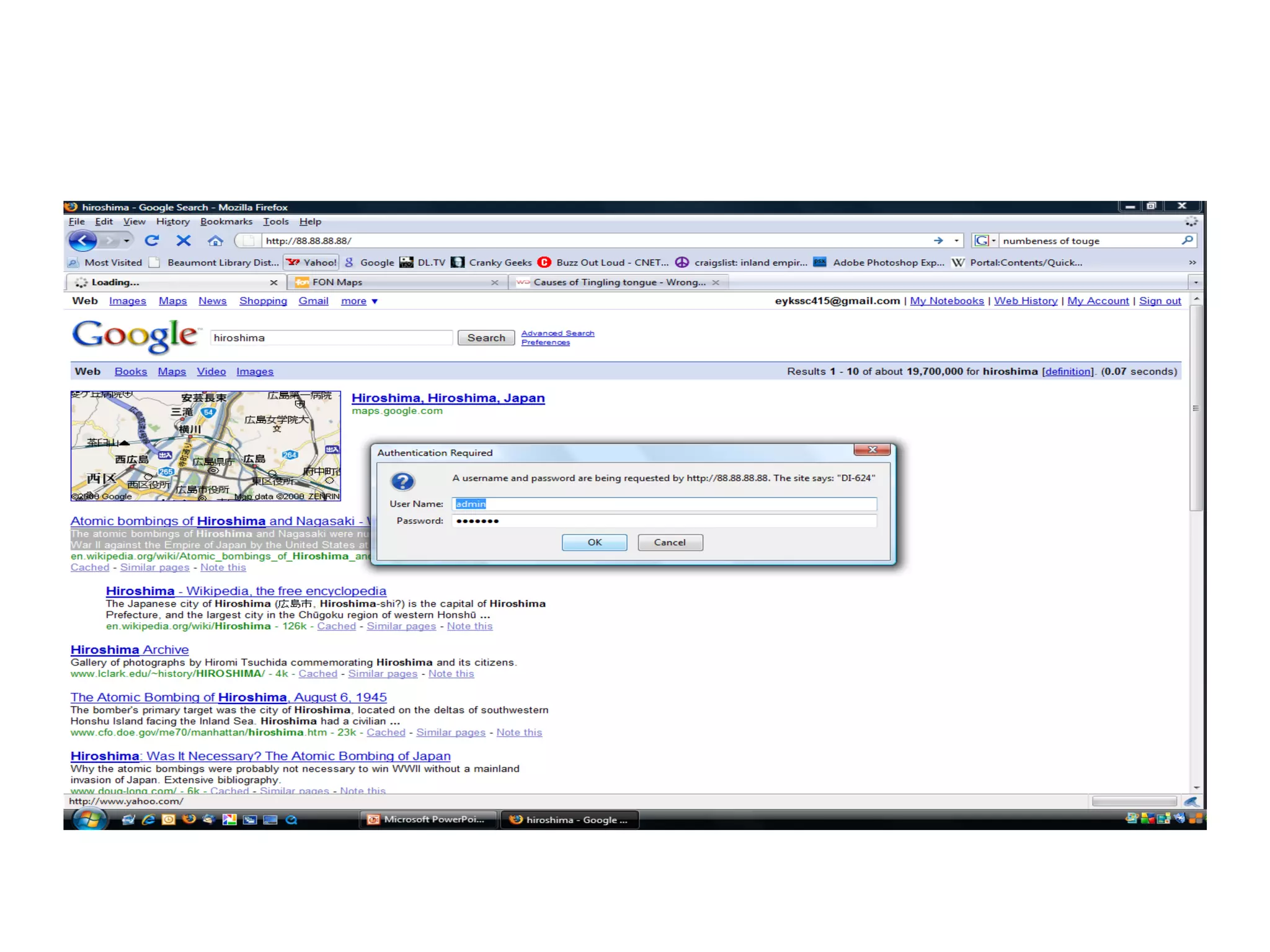
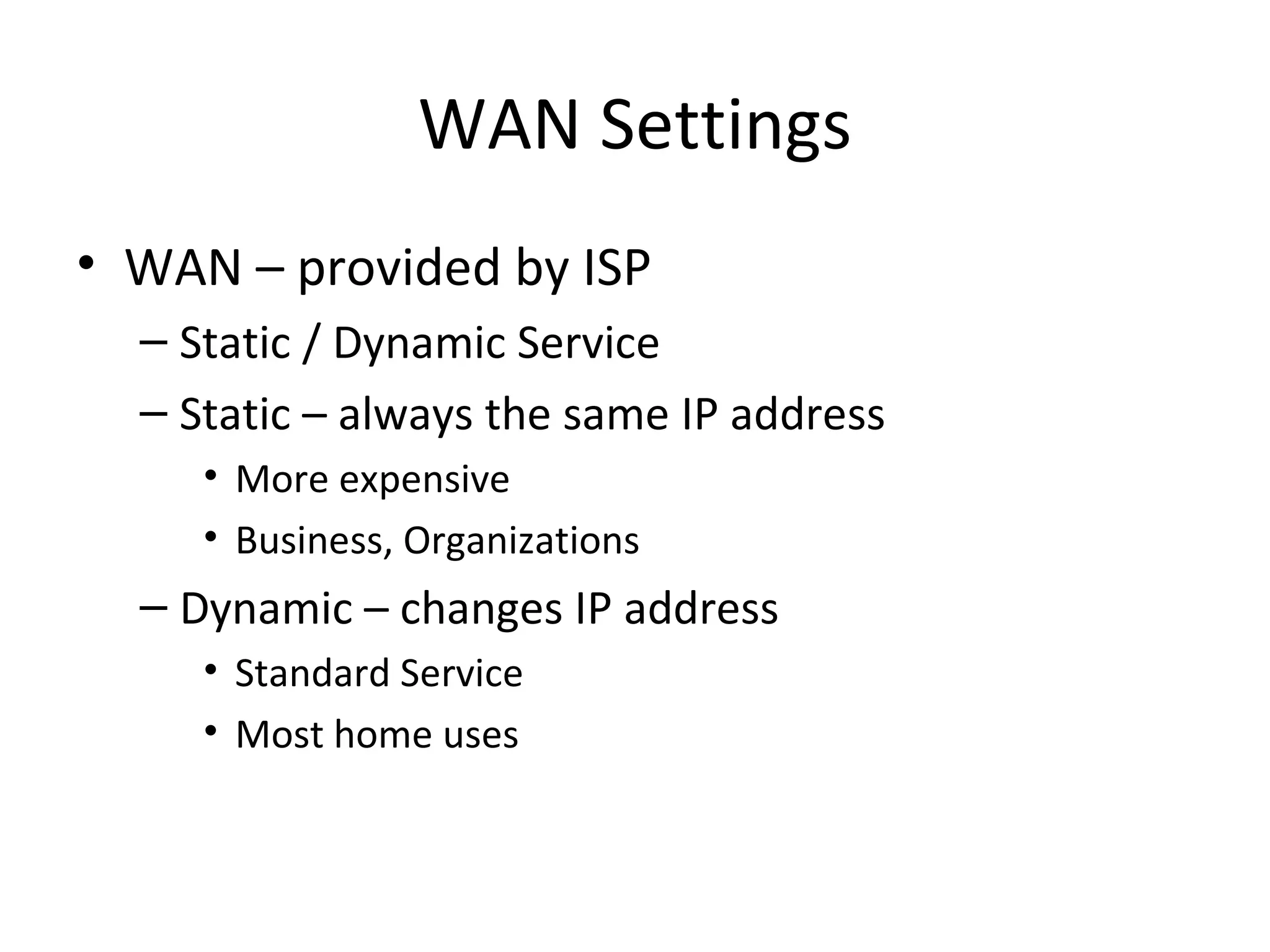
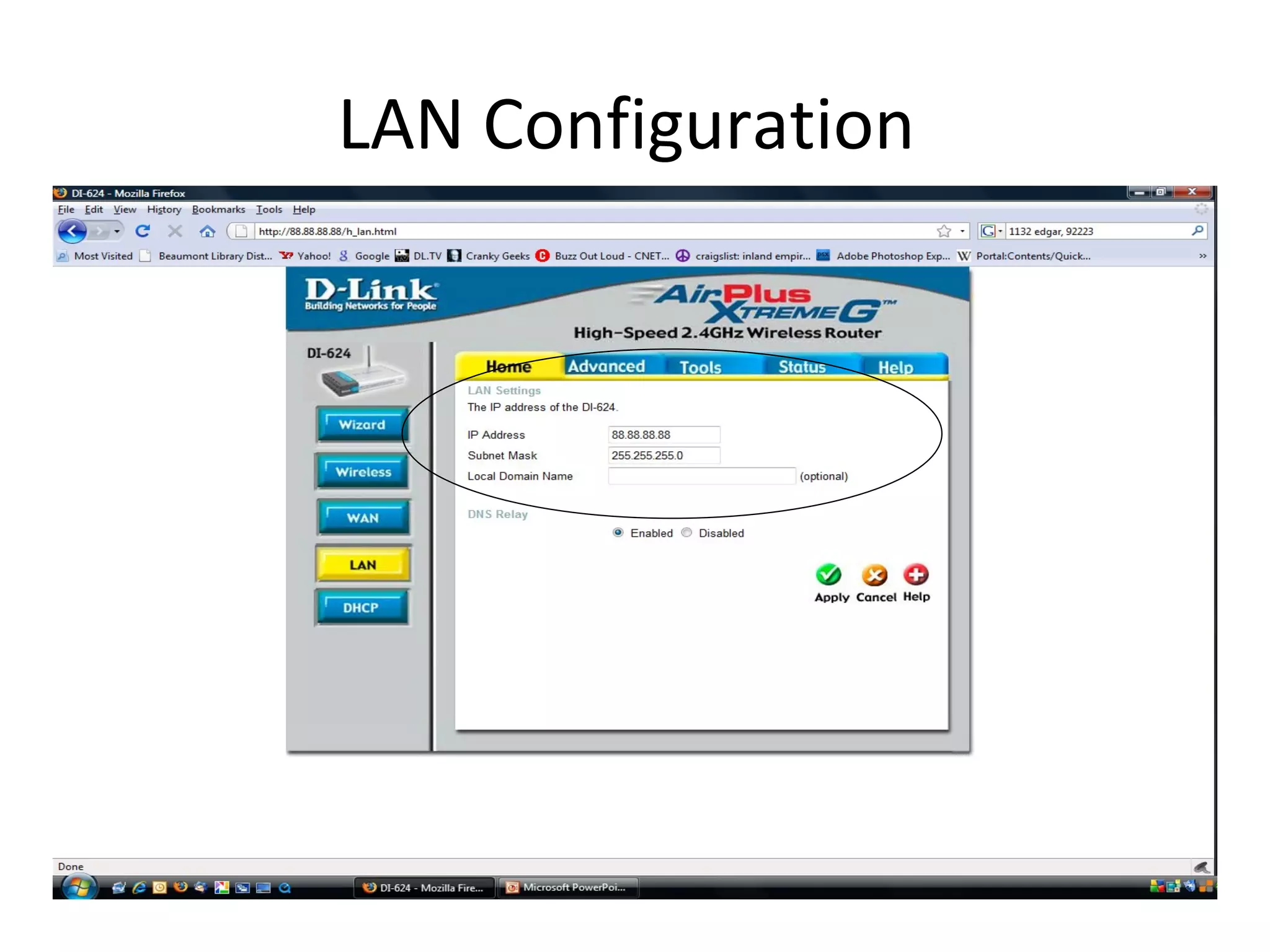
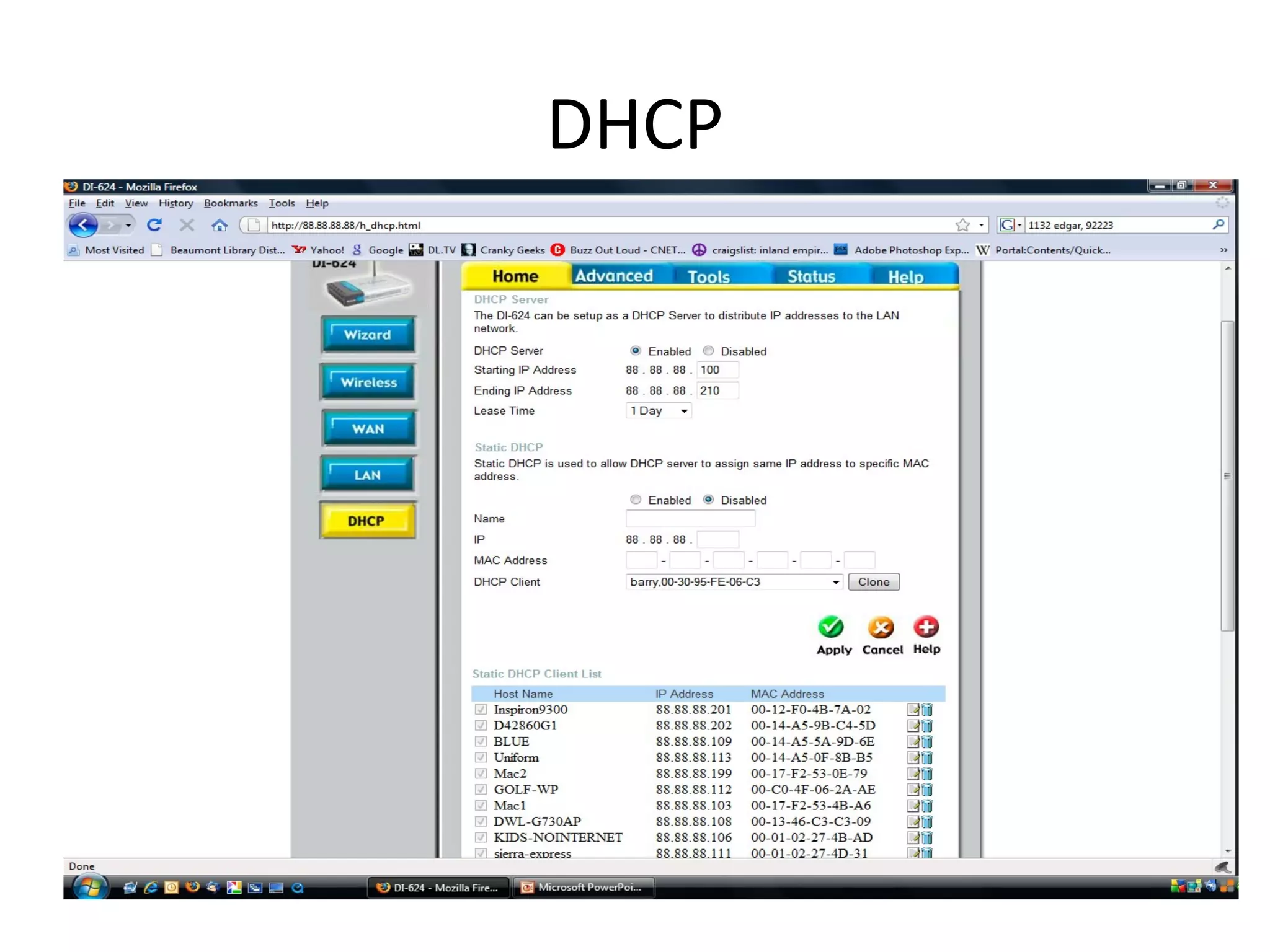
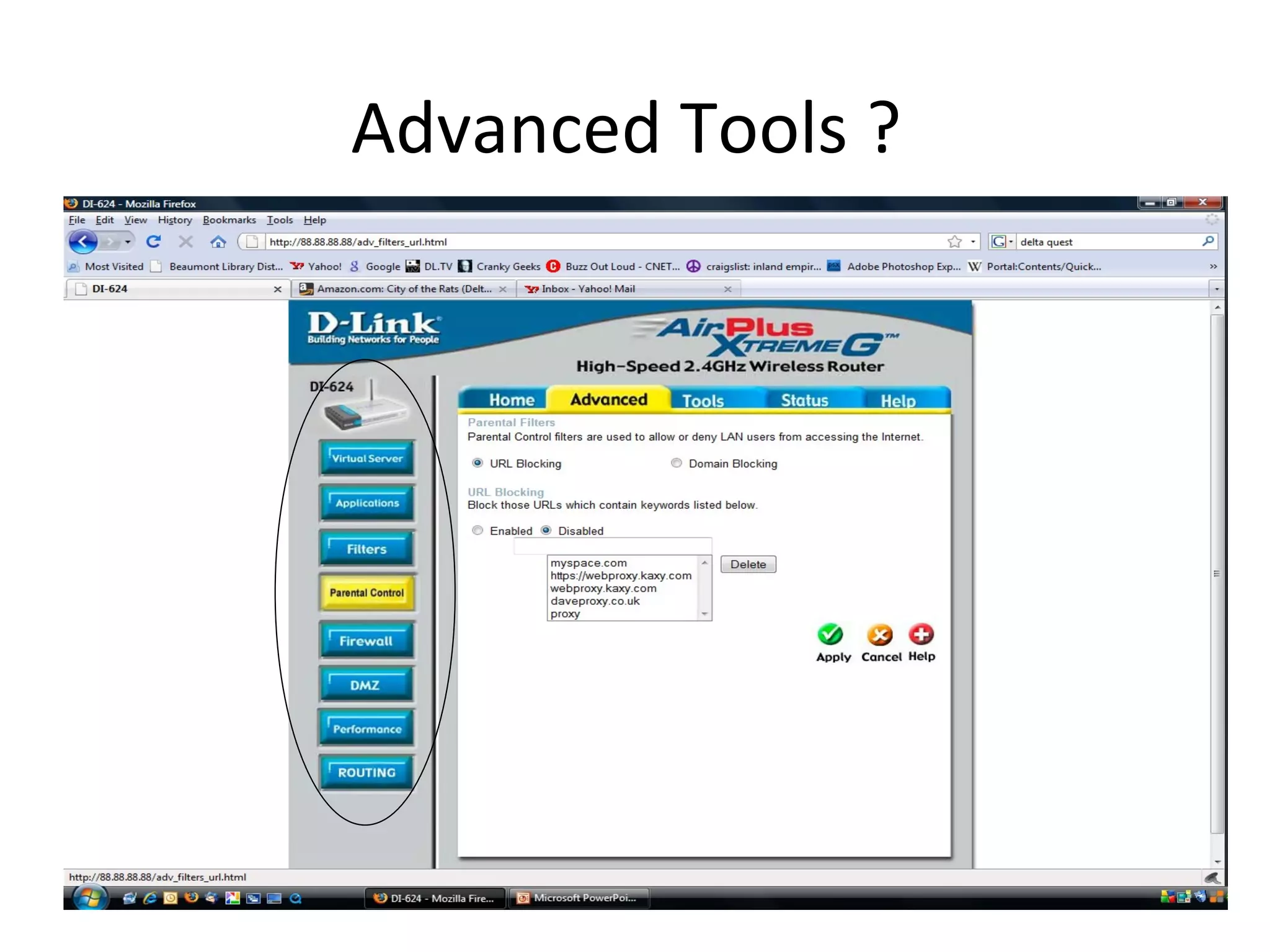
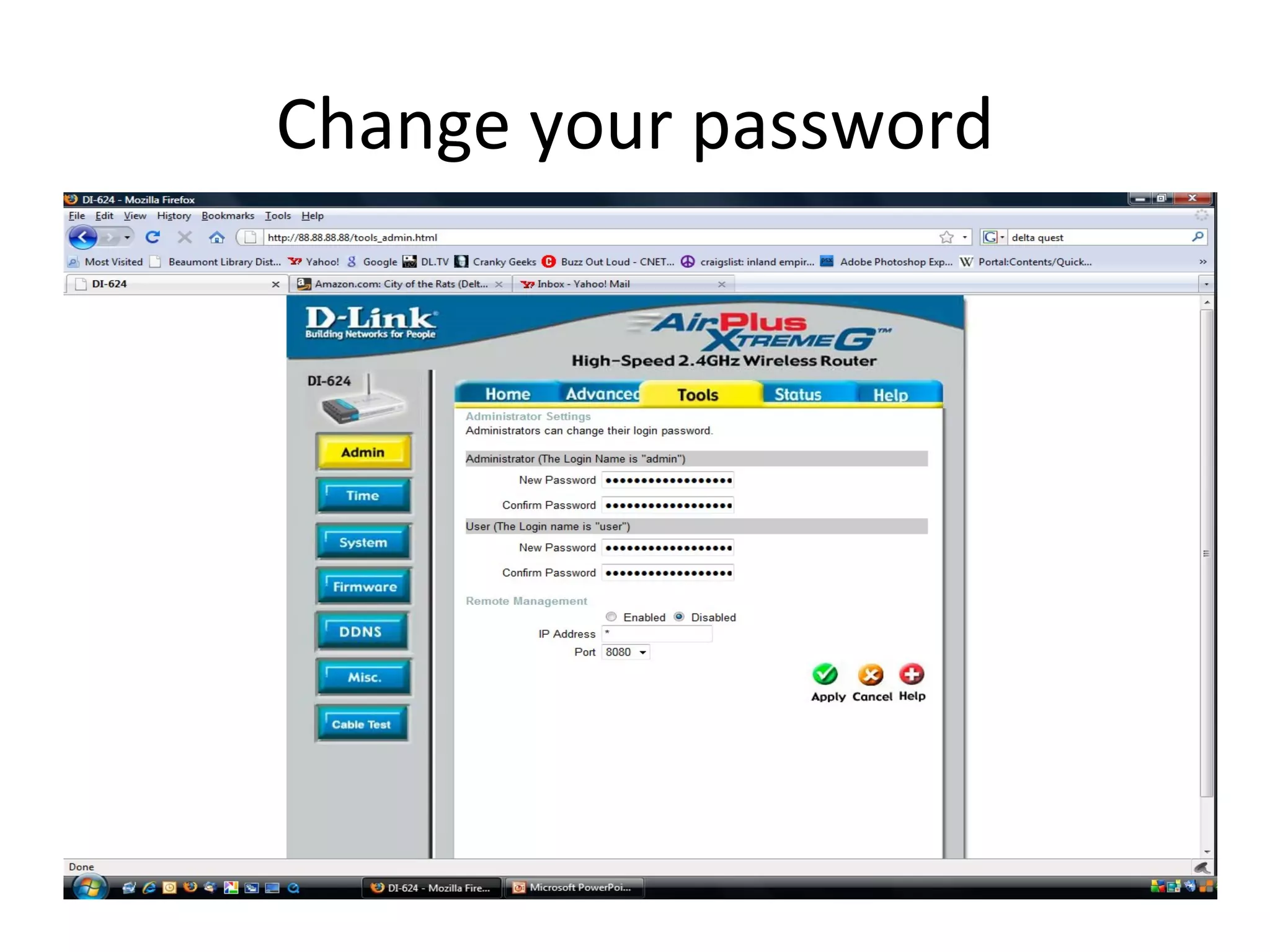
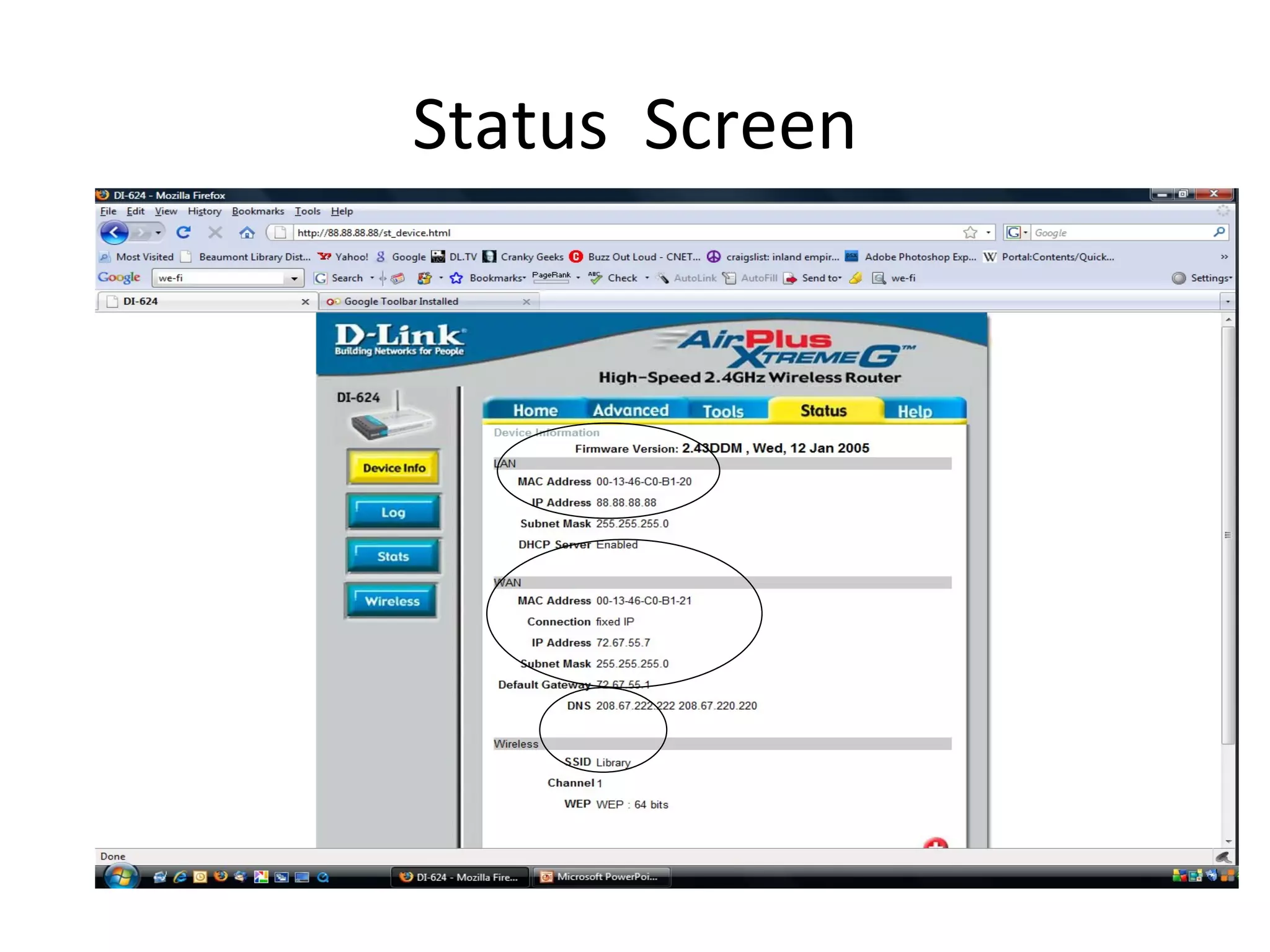
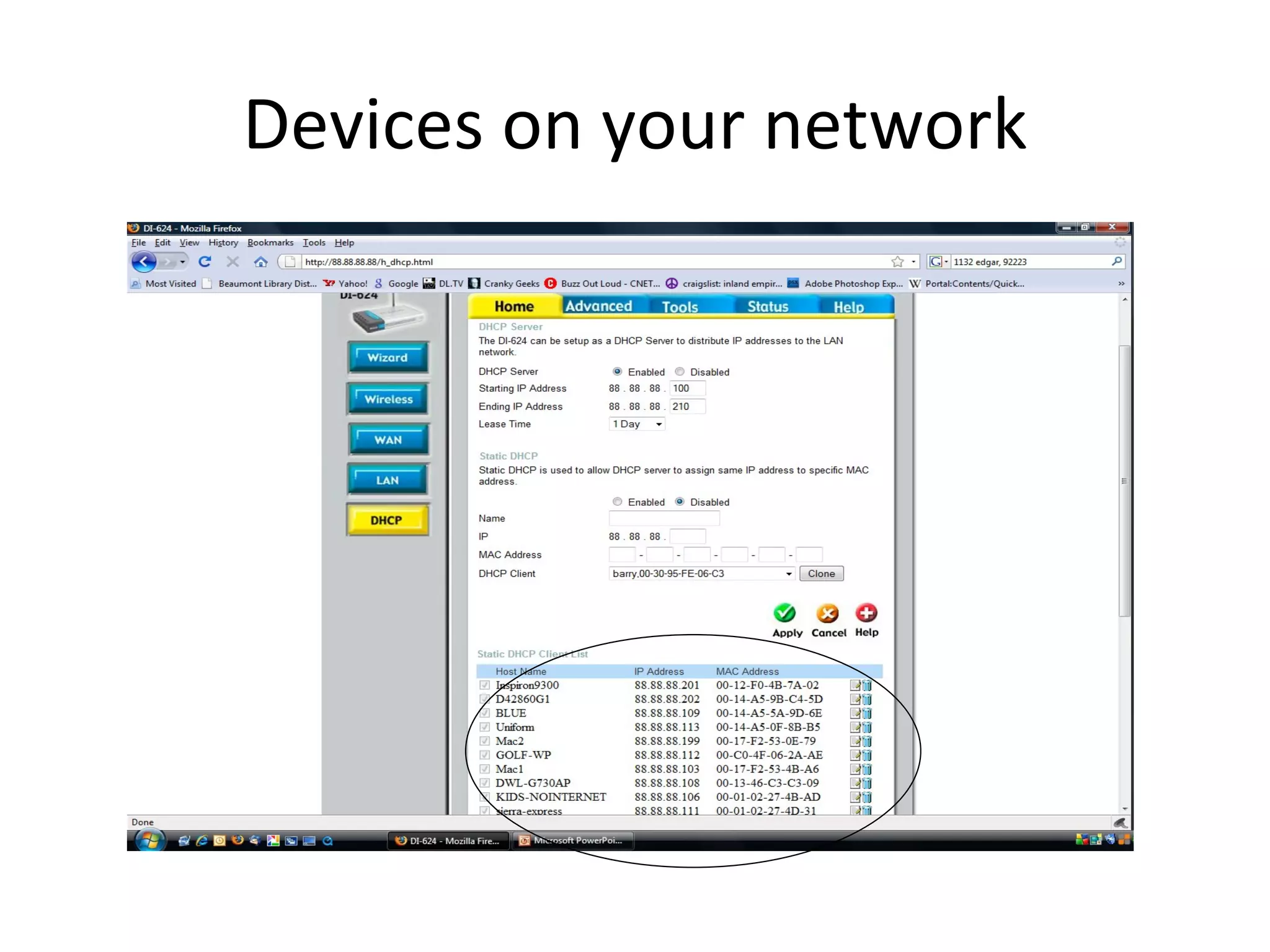
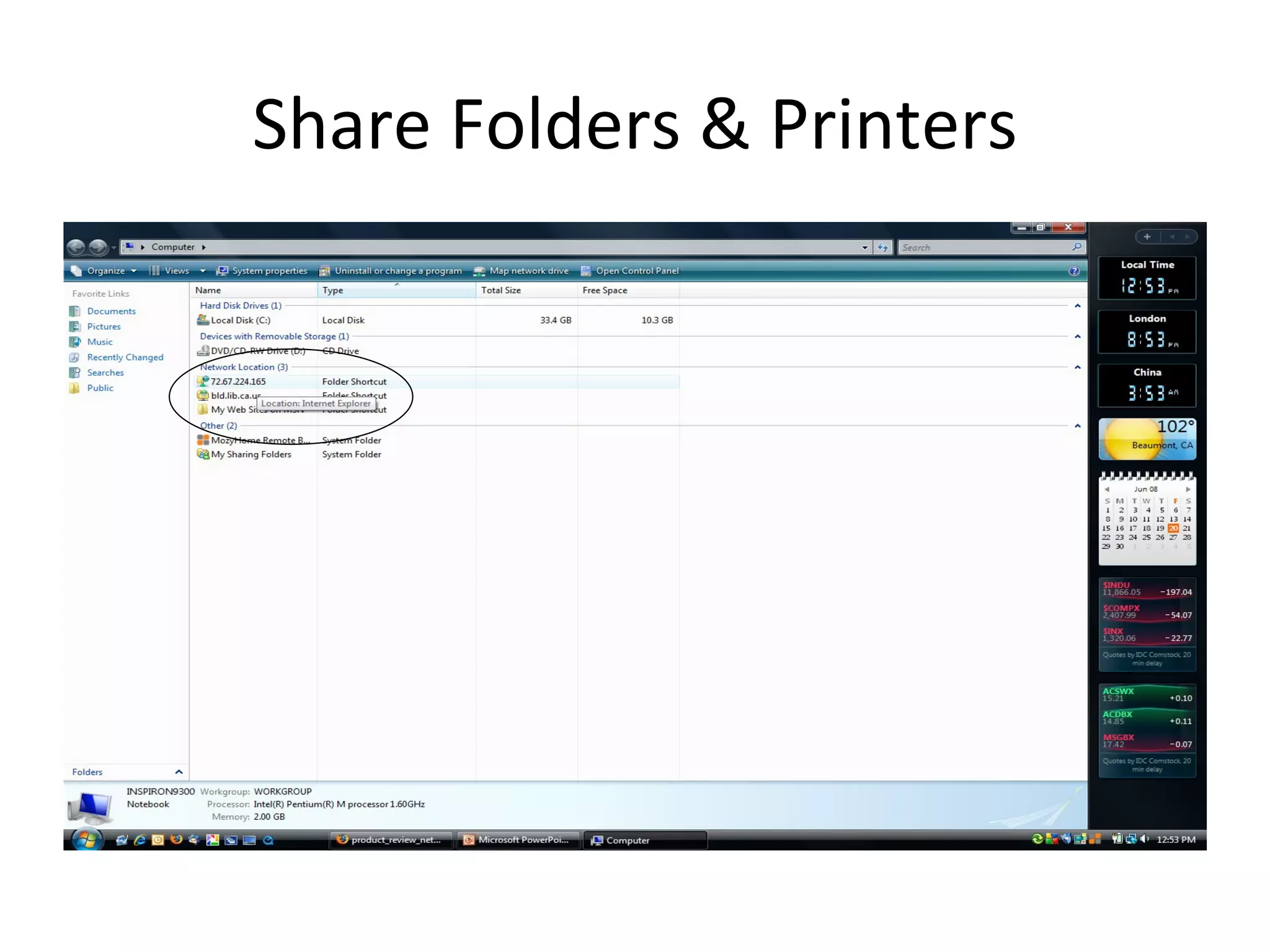
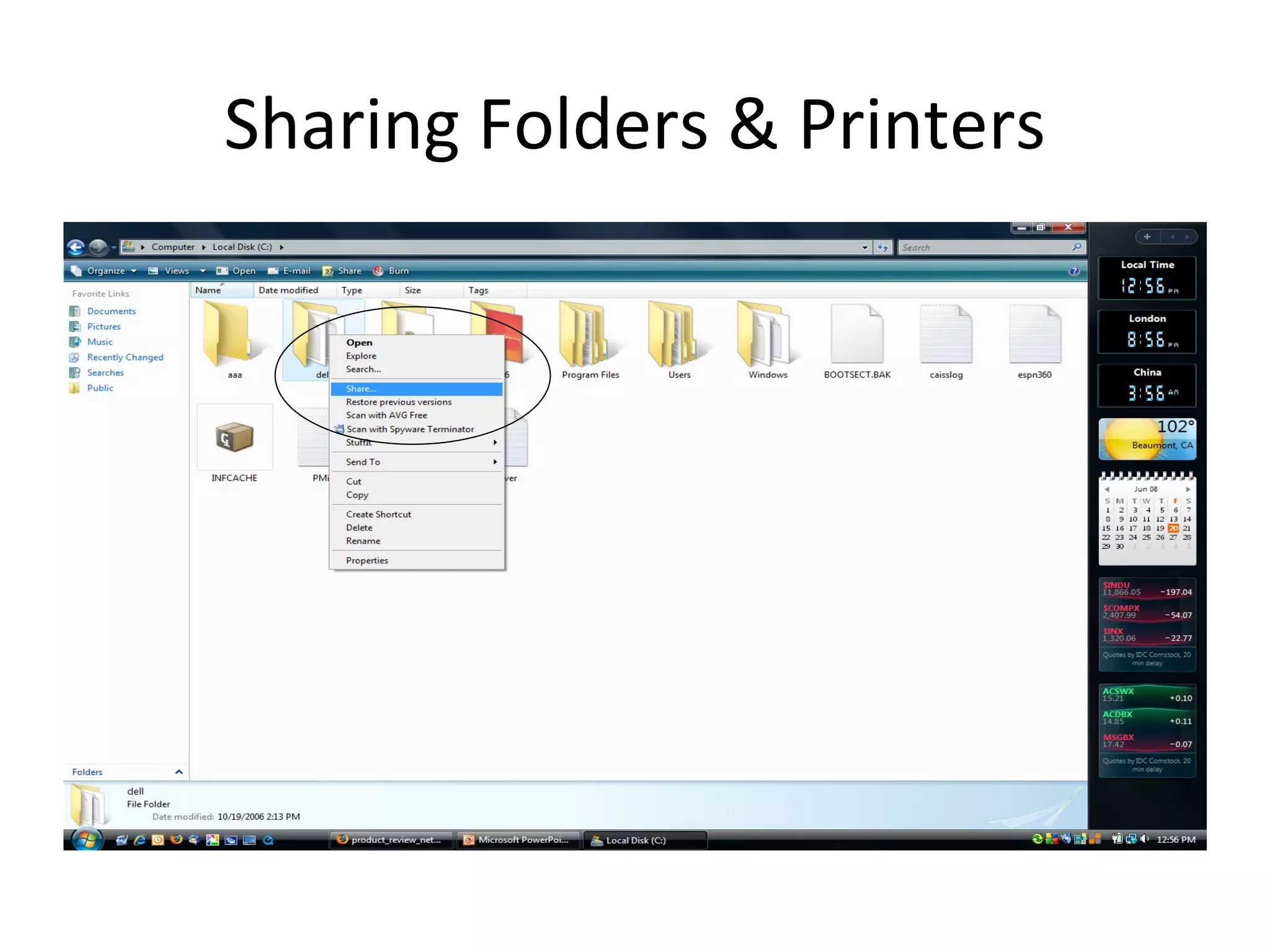
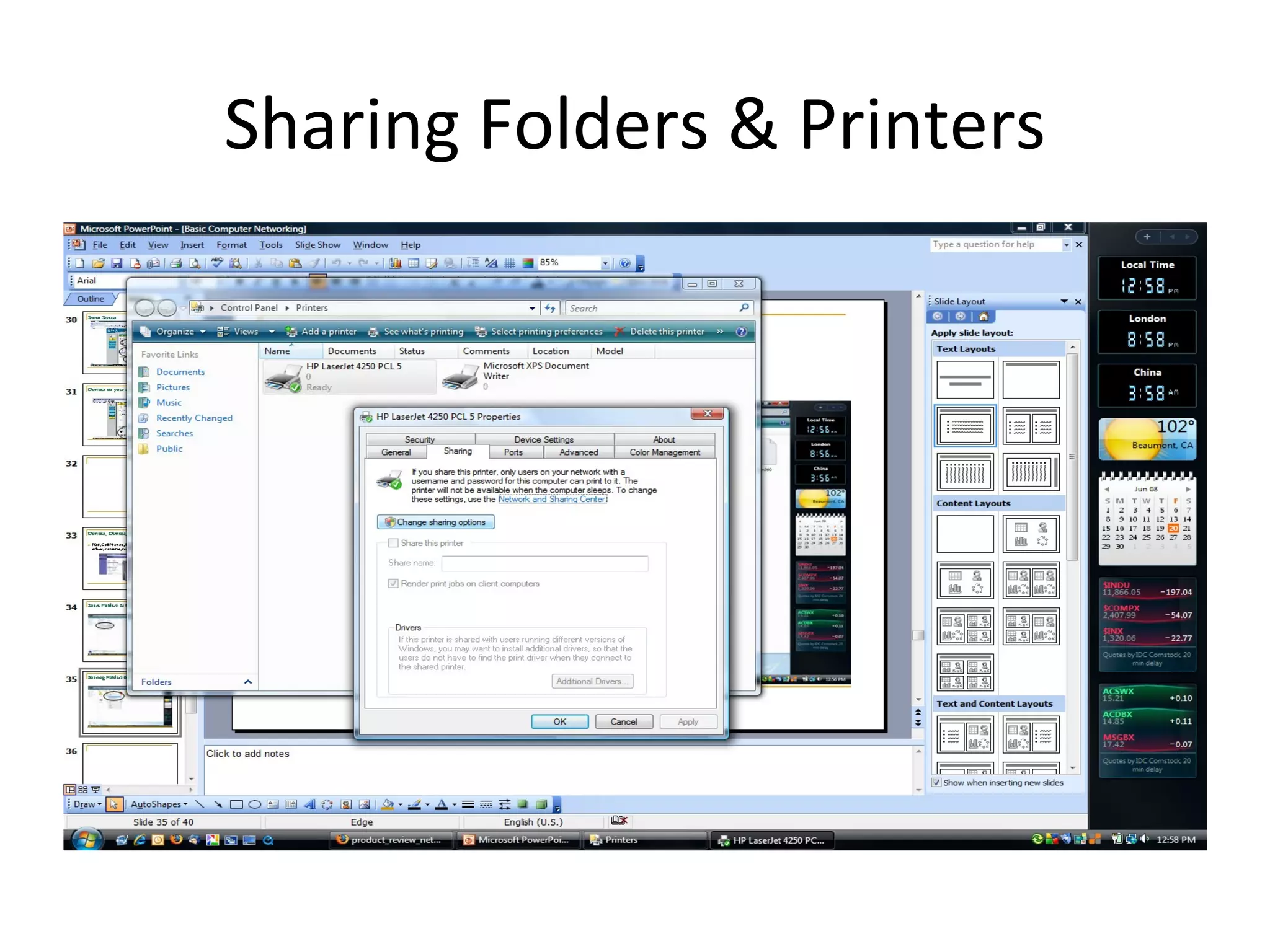
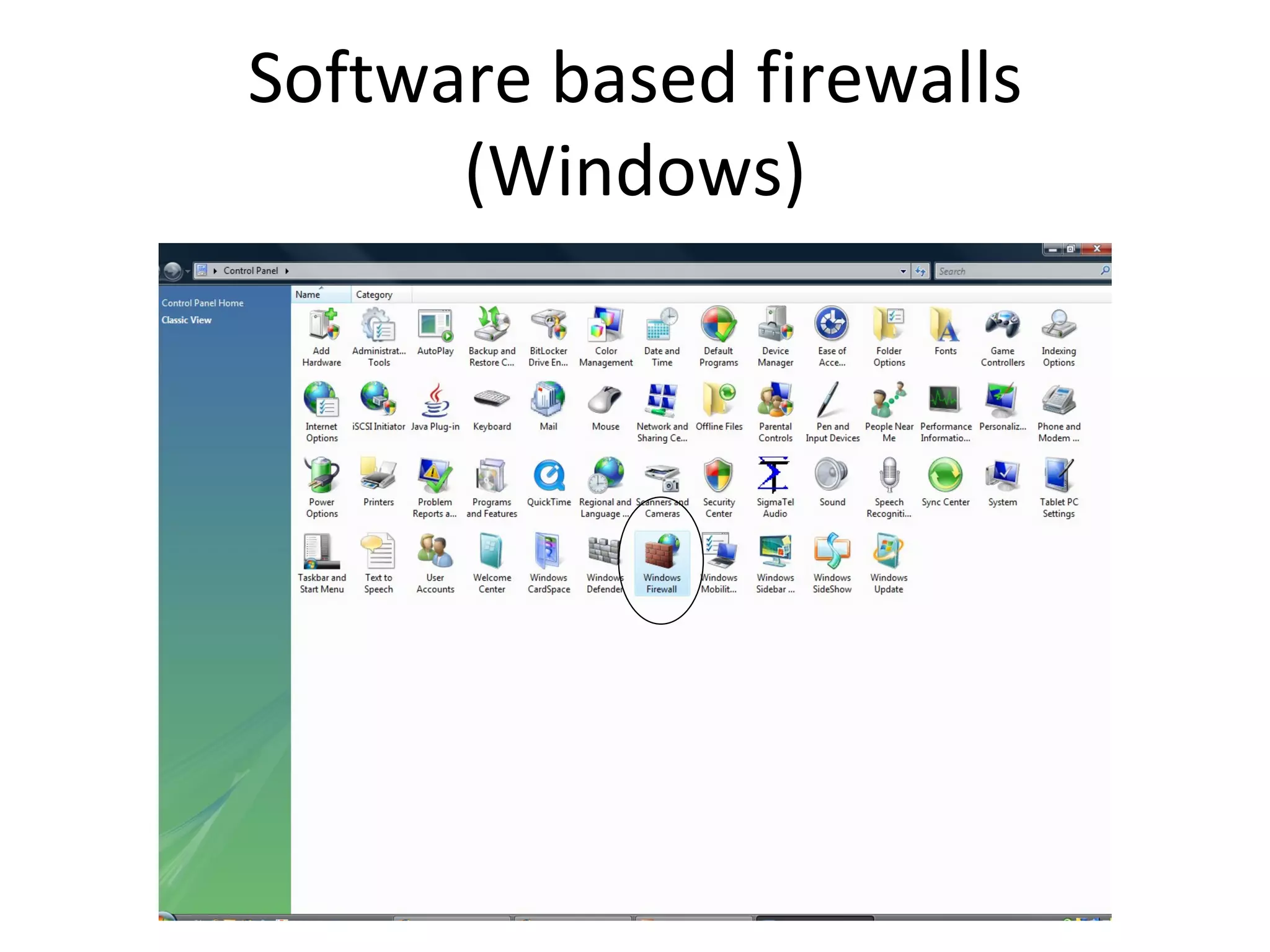
The document provides an overview of computer networking basics, including definitions of common networking terms like Ethernet, switches, routers, and IP addresses. It also describes typical home networking setups and configurations, such as connecting multiple computers to a router, setting up a wireless network, and sharing folders and printers on the local network. Basic network troubleshooting and security options are also covered.