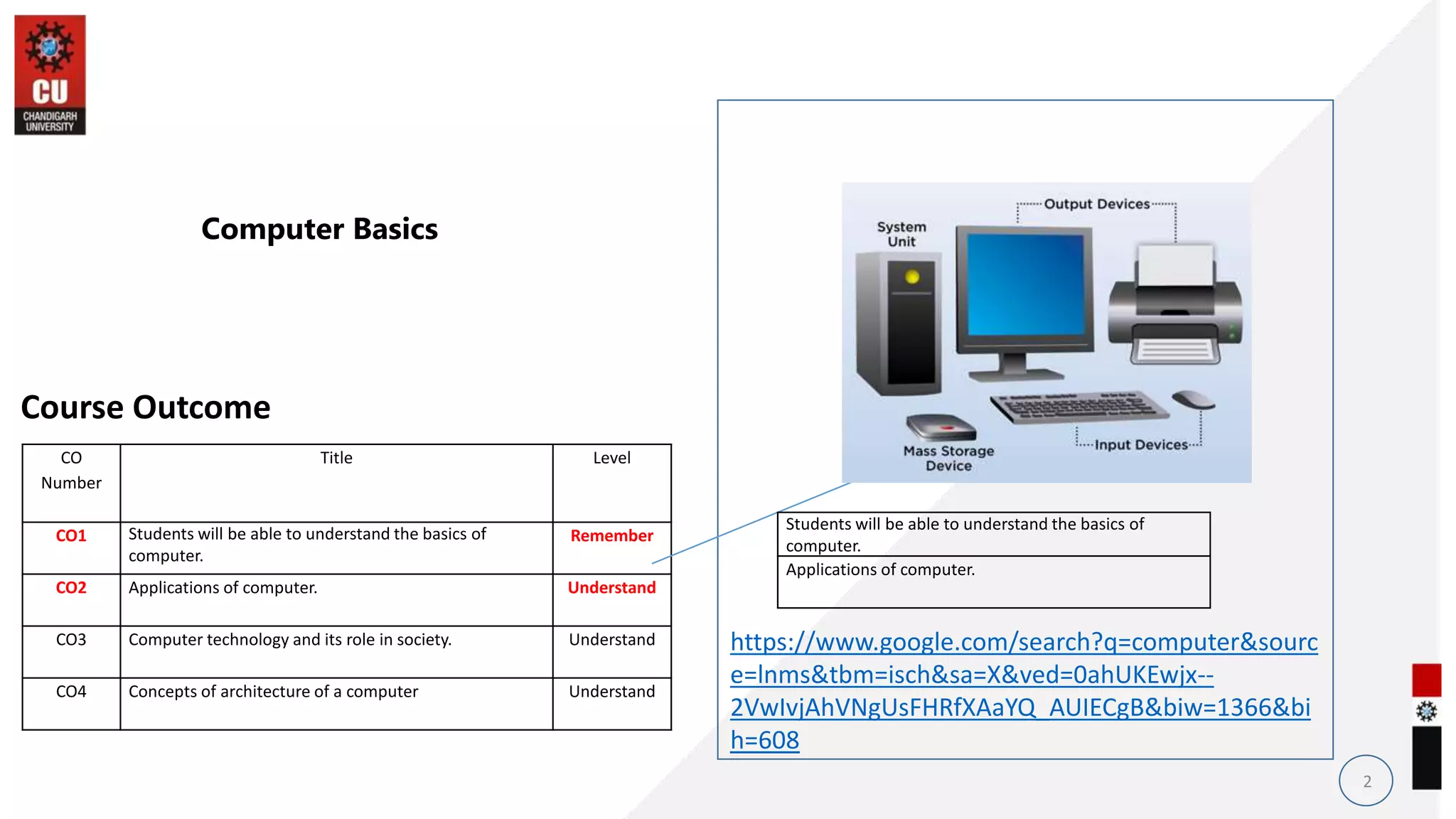
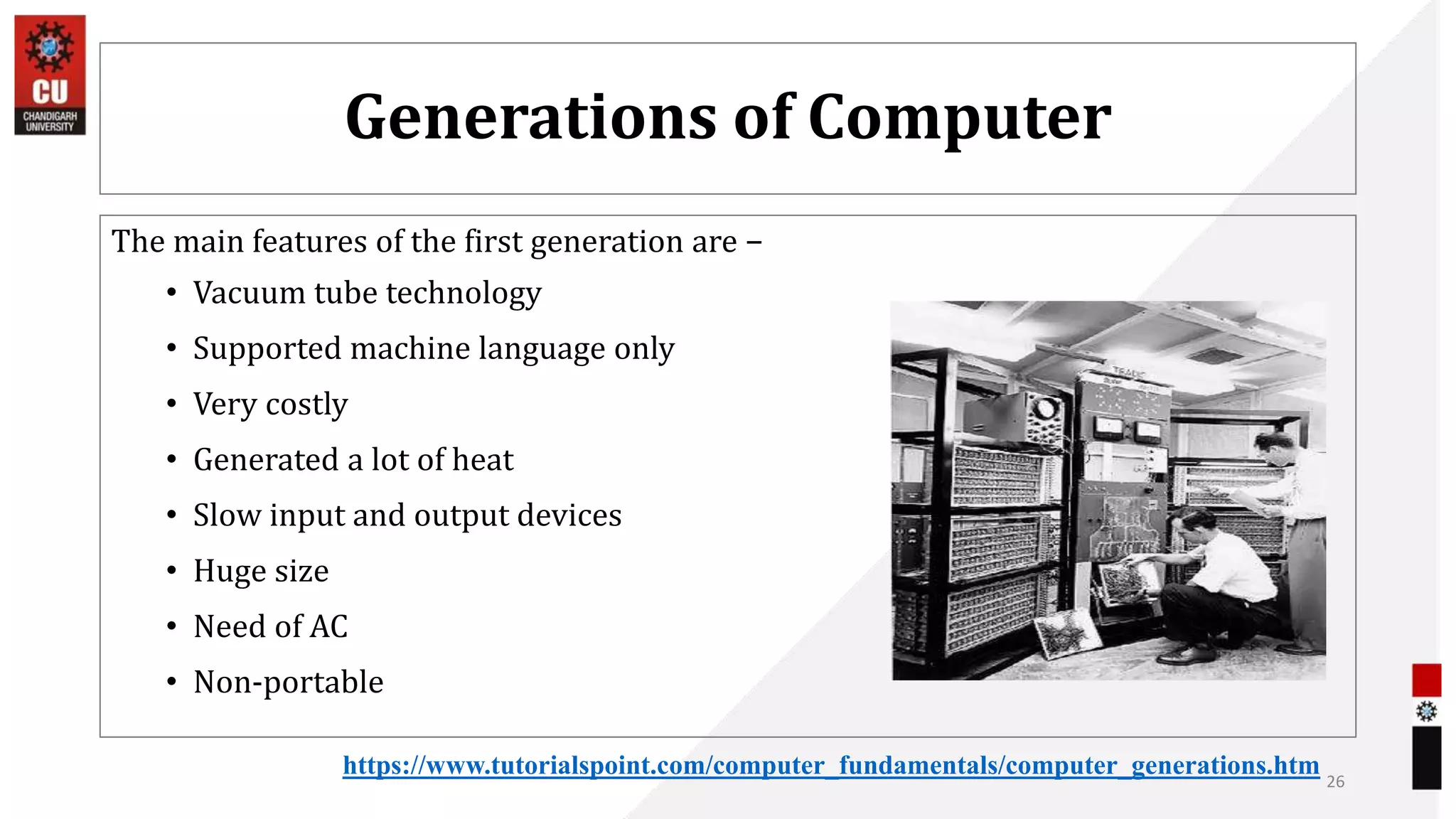
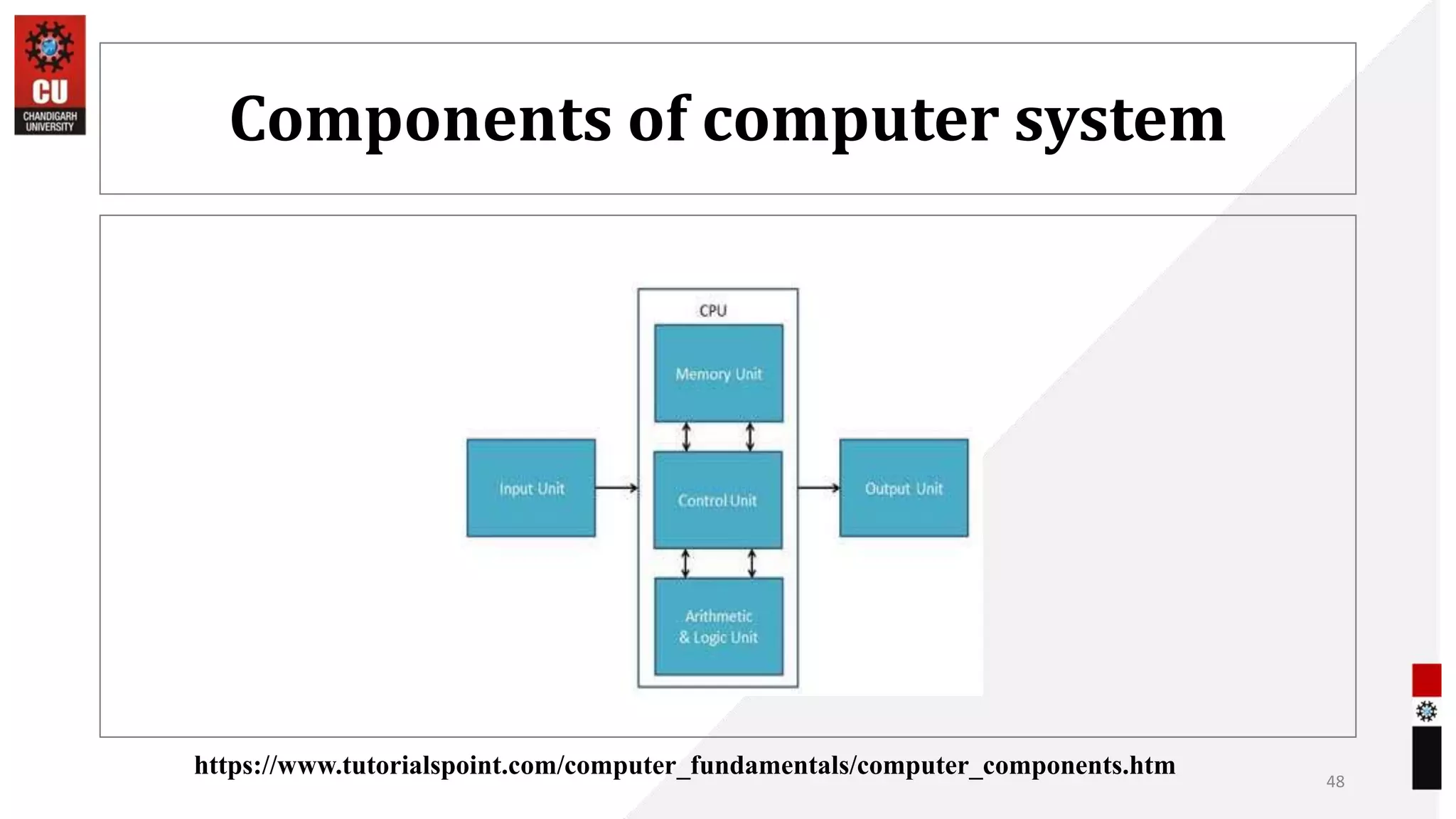
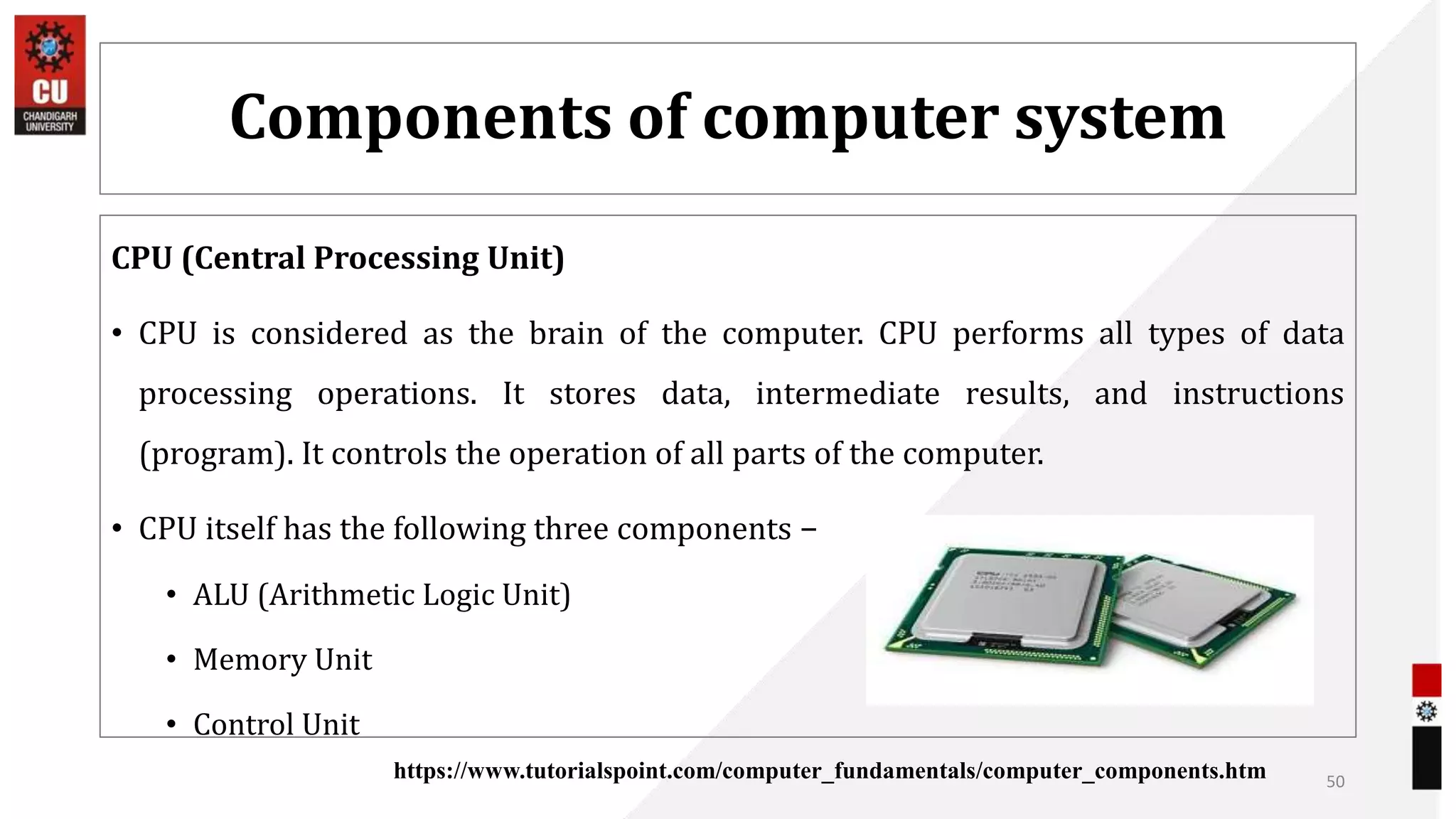
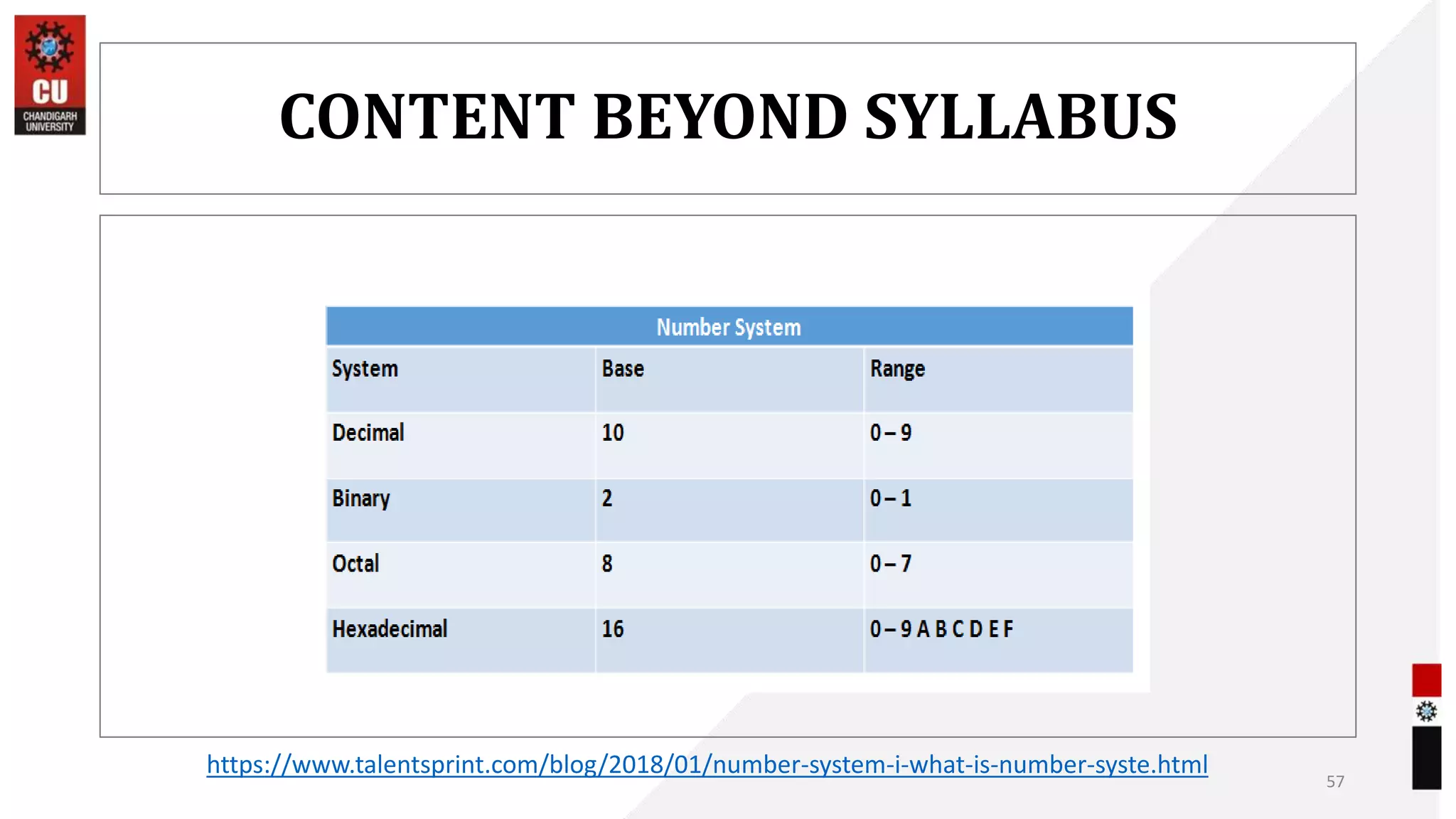
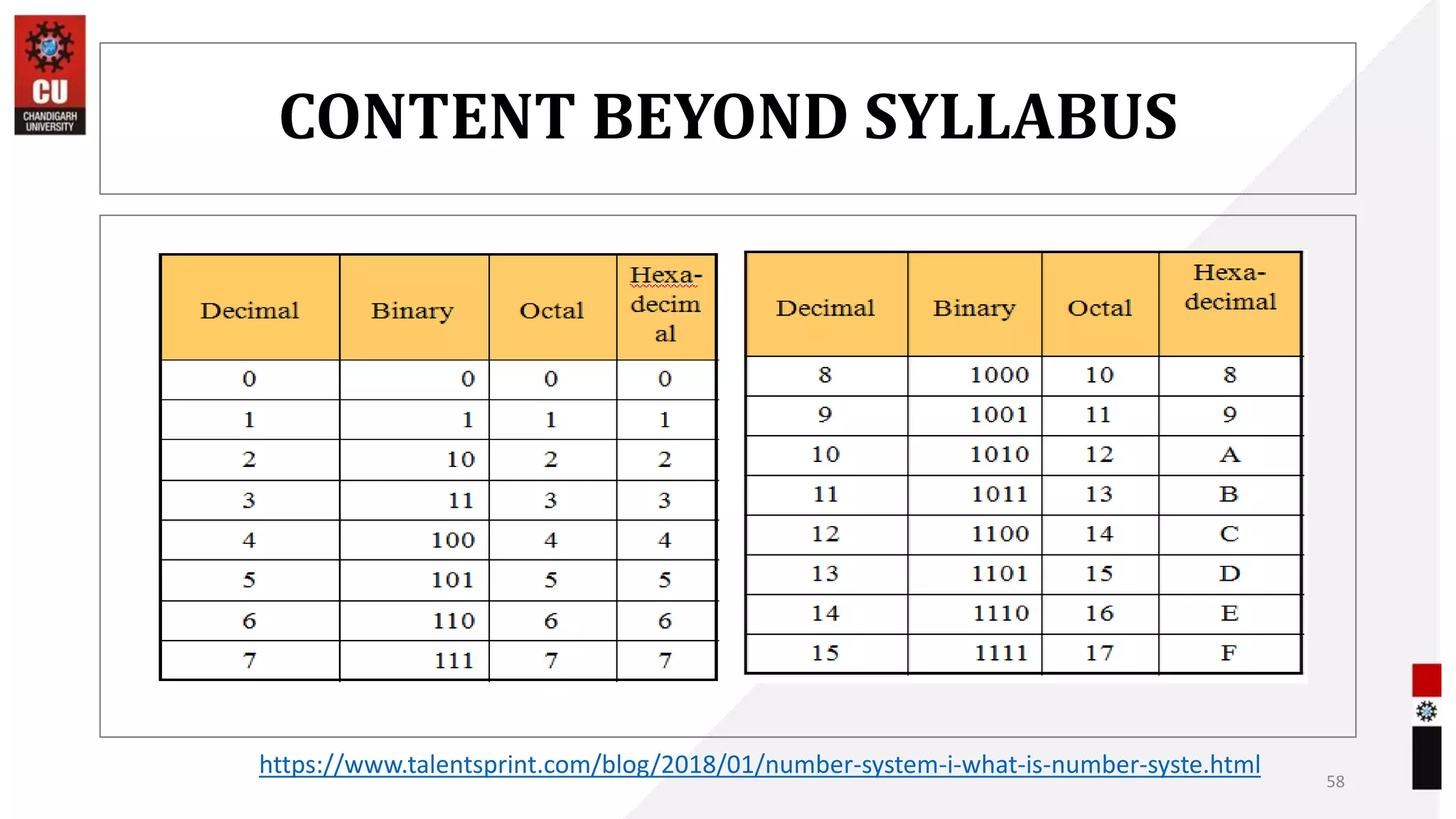
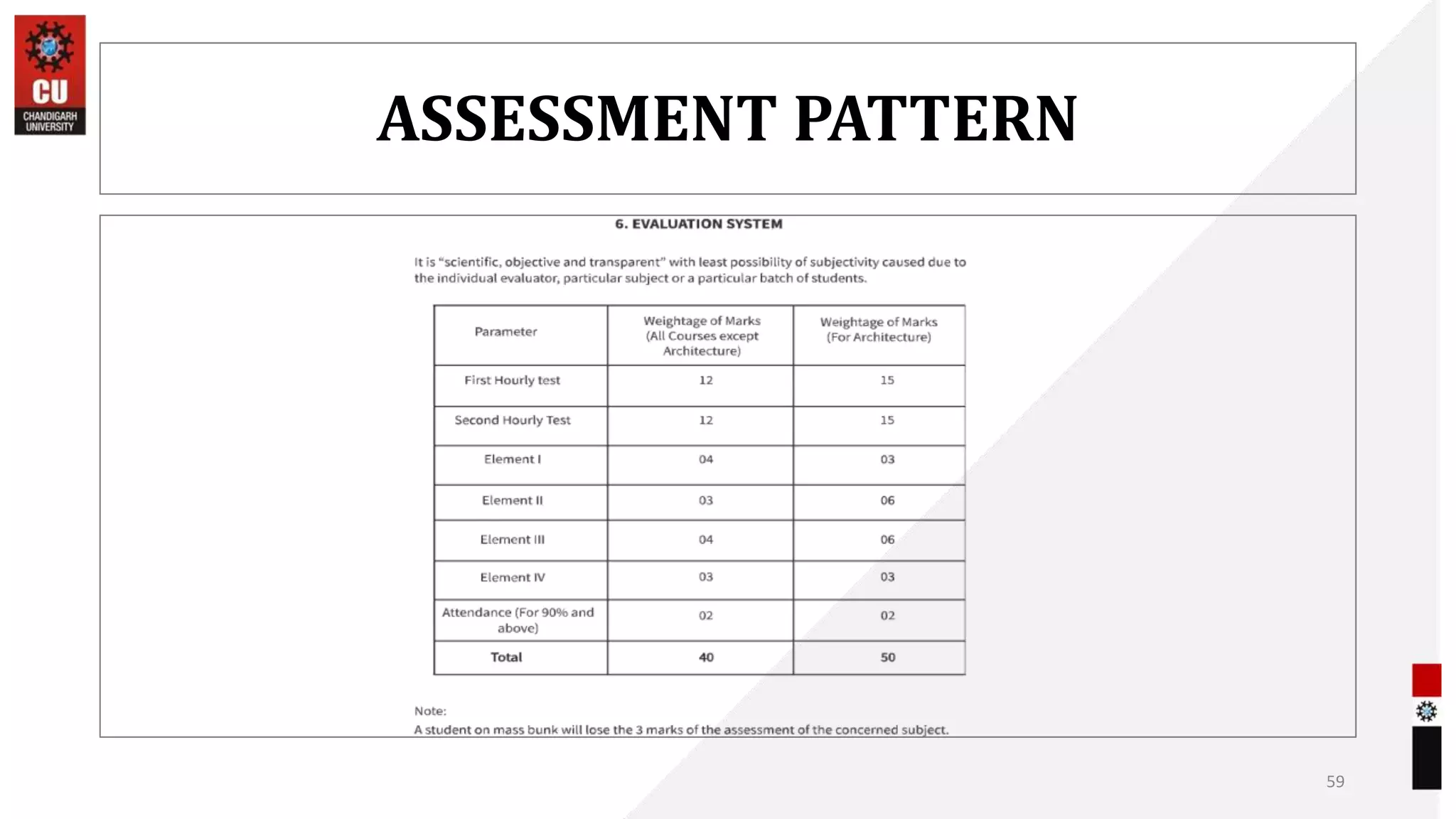
The document provides information about the B.Sc. TTM/AAM Computer Applications course offered at Chandigarh University, including the course objectives to introduce students to computers, expose them to recent computer applications and software, and provide an understanding of computer systems. The syllabus covers topics like computer basics, hardware, software, and the relevance of learning about fundamentals of computers for further education and knowledge in related fields.