Downloaded 26 times













































































The document covers an introduction to computers and problem-solving techniques. It discusses the functionalities, characteristics, types, and applications of computers, as well as the steps and methods involved in problem solving, including algorithms and flowcharts. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of precise instruction and understanding in effectively programming computers.
Introduction to the course 20CST11. Overview of syllabus and topics related to computers.
Usage of computers in workplaces, schools, and home; various activities from emails to online shopping.
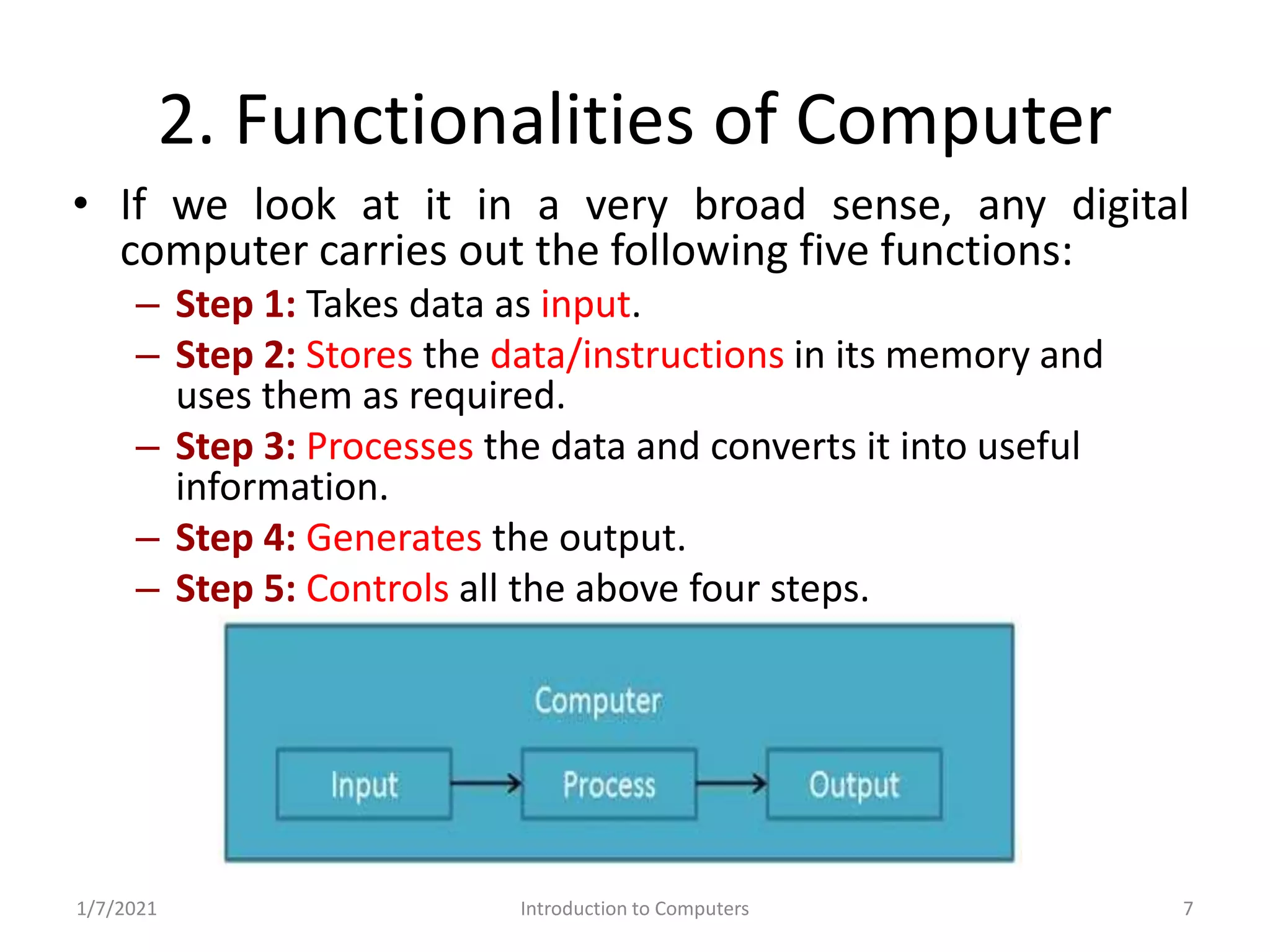
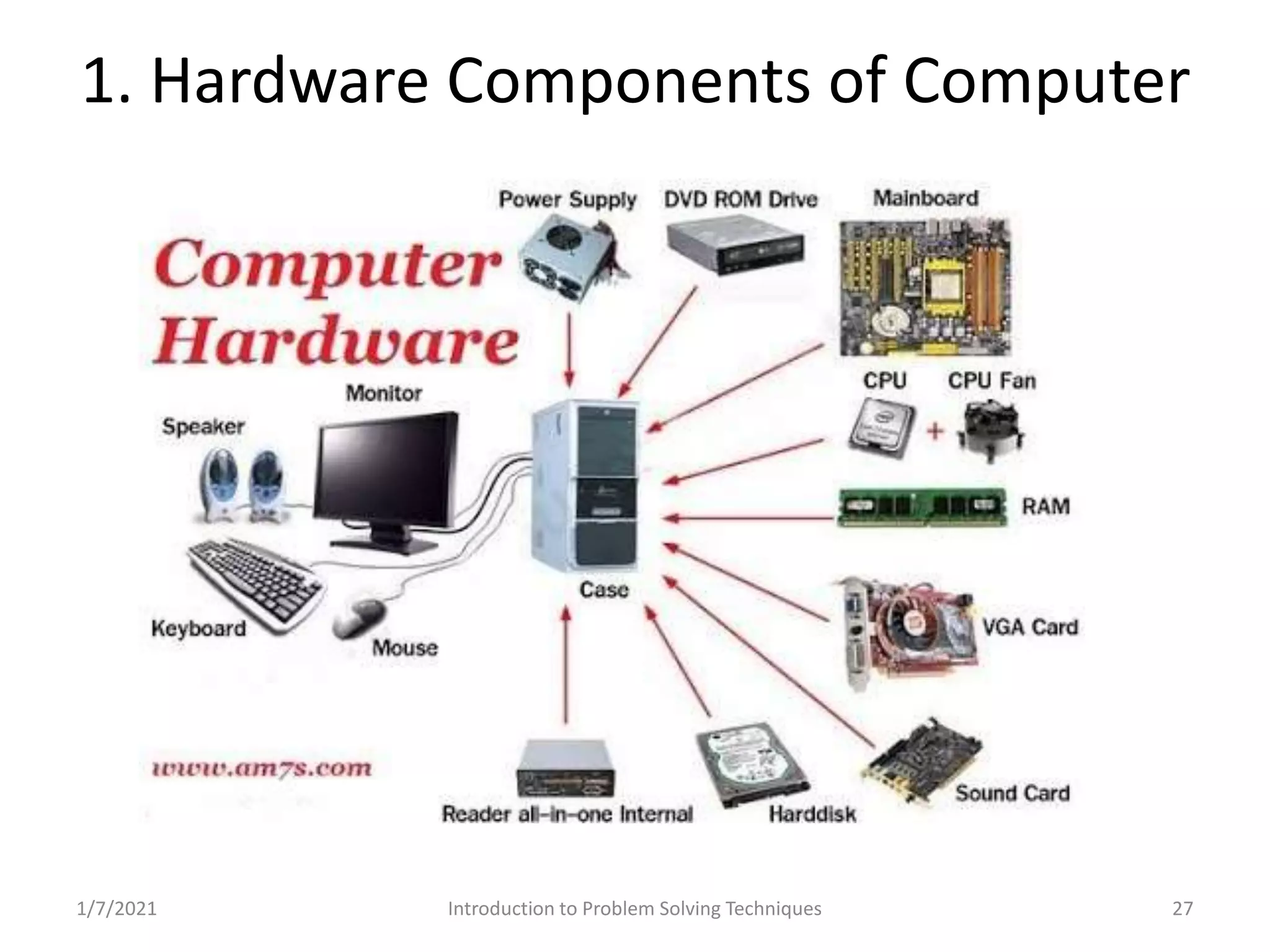
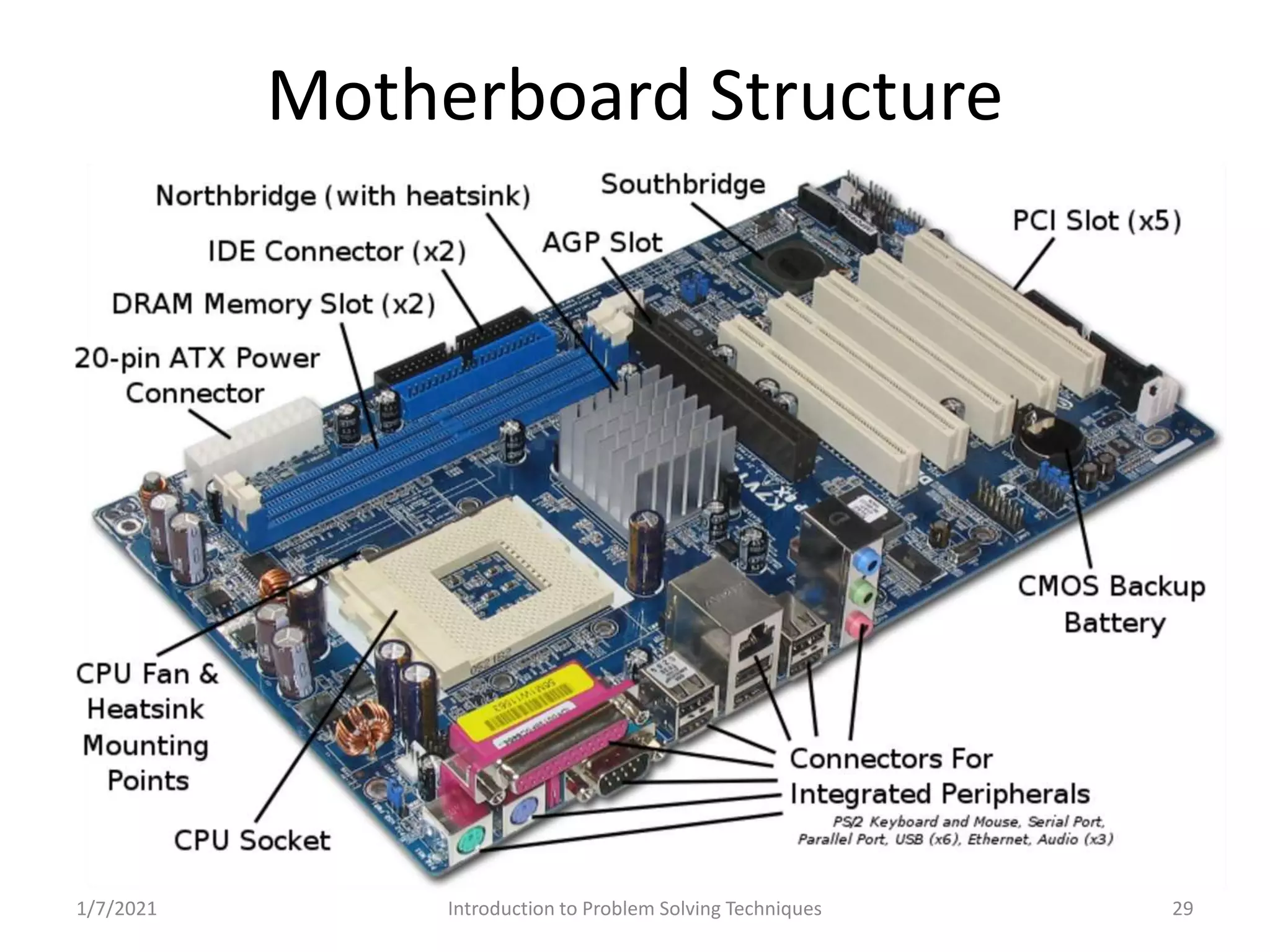
Overview of computer functionalities: input, processing, output, and storage. Classification of hardware components.
Key characteristics include speed, accuracy, versatility, and storage capacity.
Drawbacks of computers such as lack of intelligence, feelings, dependency on humans, and environmental requirements.
Applications of computers across sectors like science, business, medicine, and education.
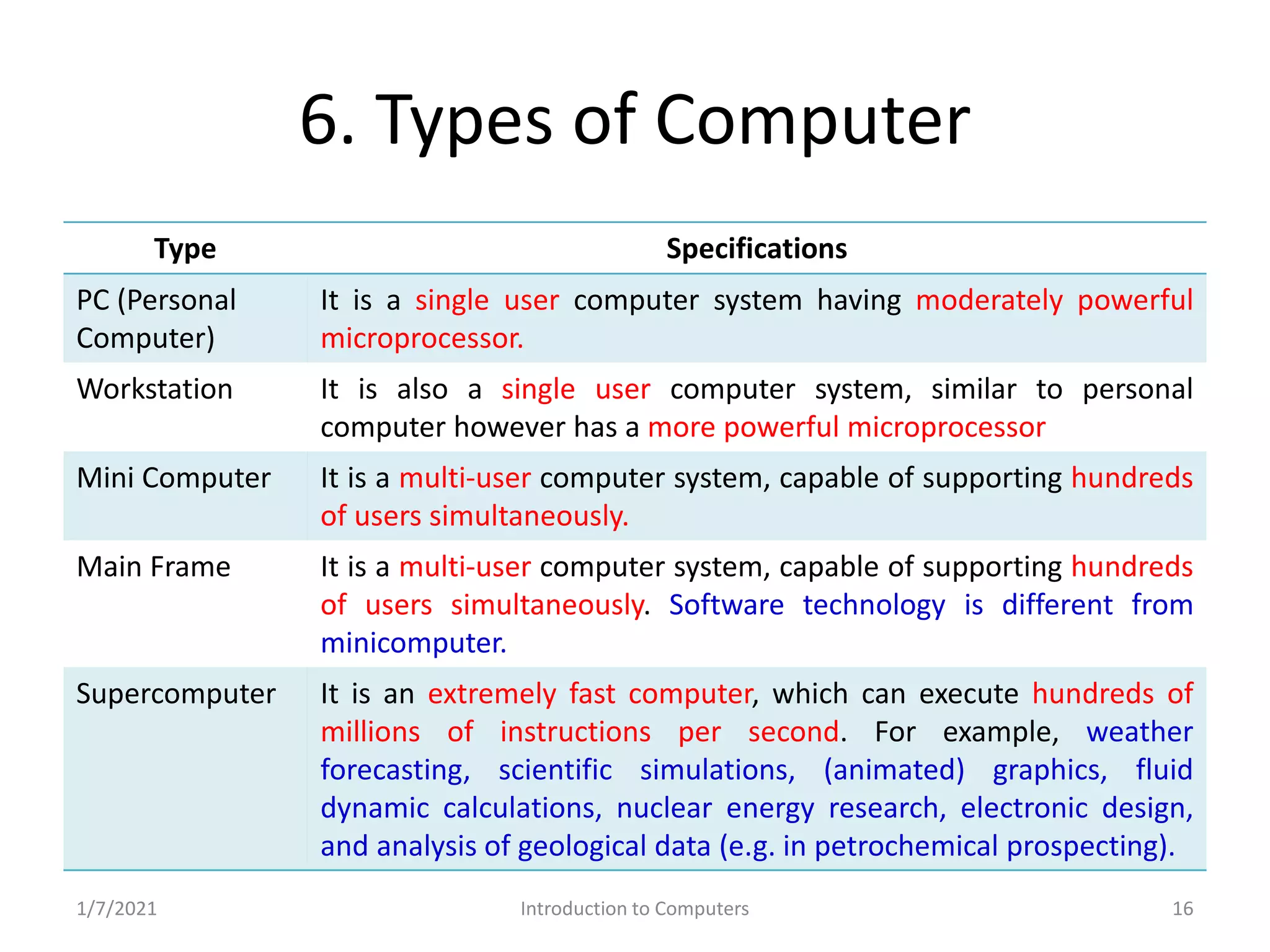
Different types of computers: PCs, workstations, mini computers, mainframes, and supercomputers.
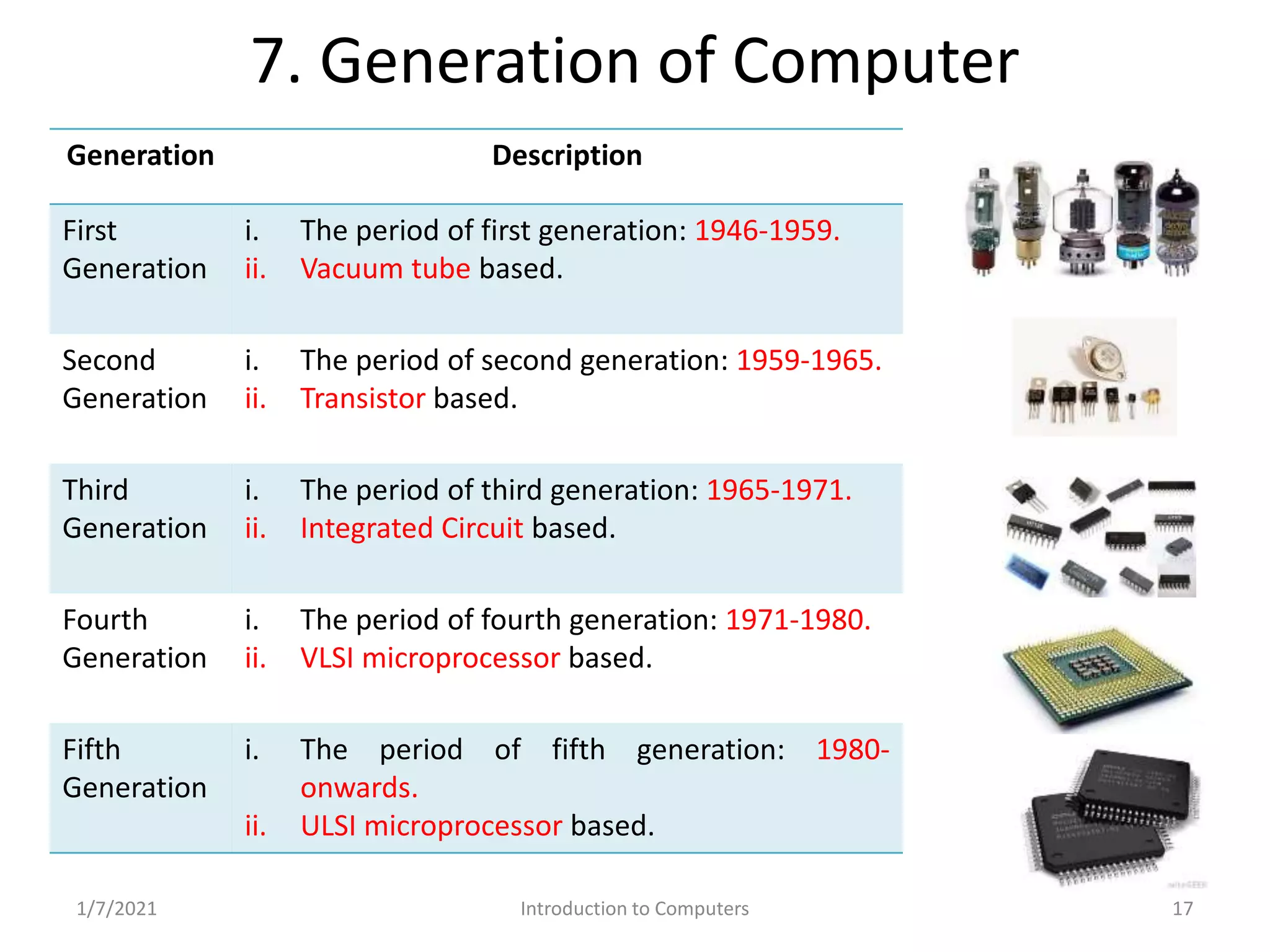
Evolution of computers from vacuum tubes in the first generation to ULSI microprocessors in the fifth generation.
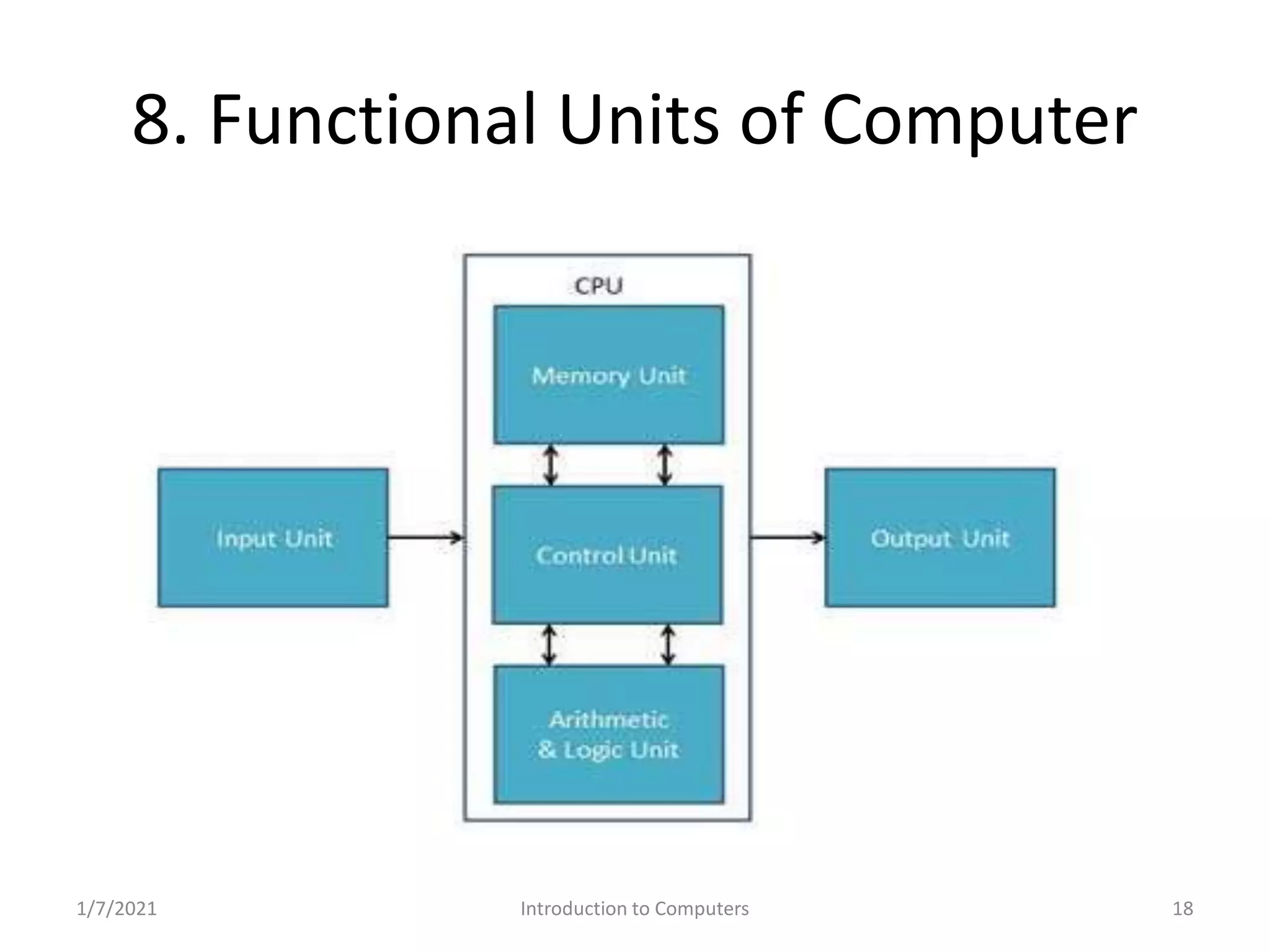
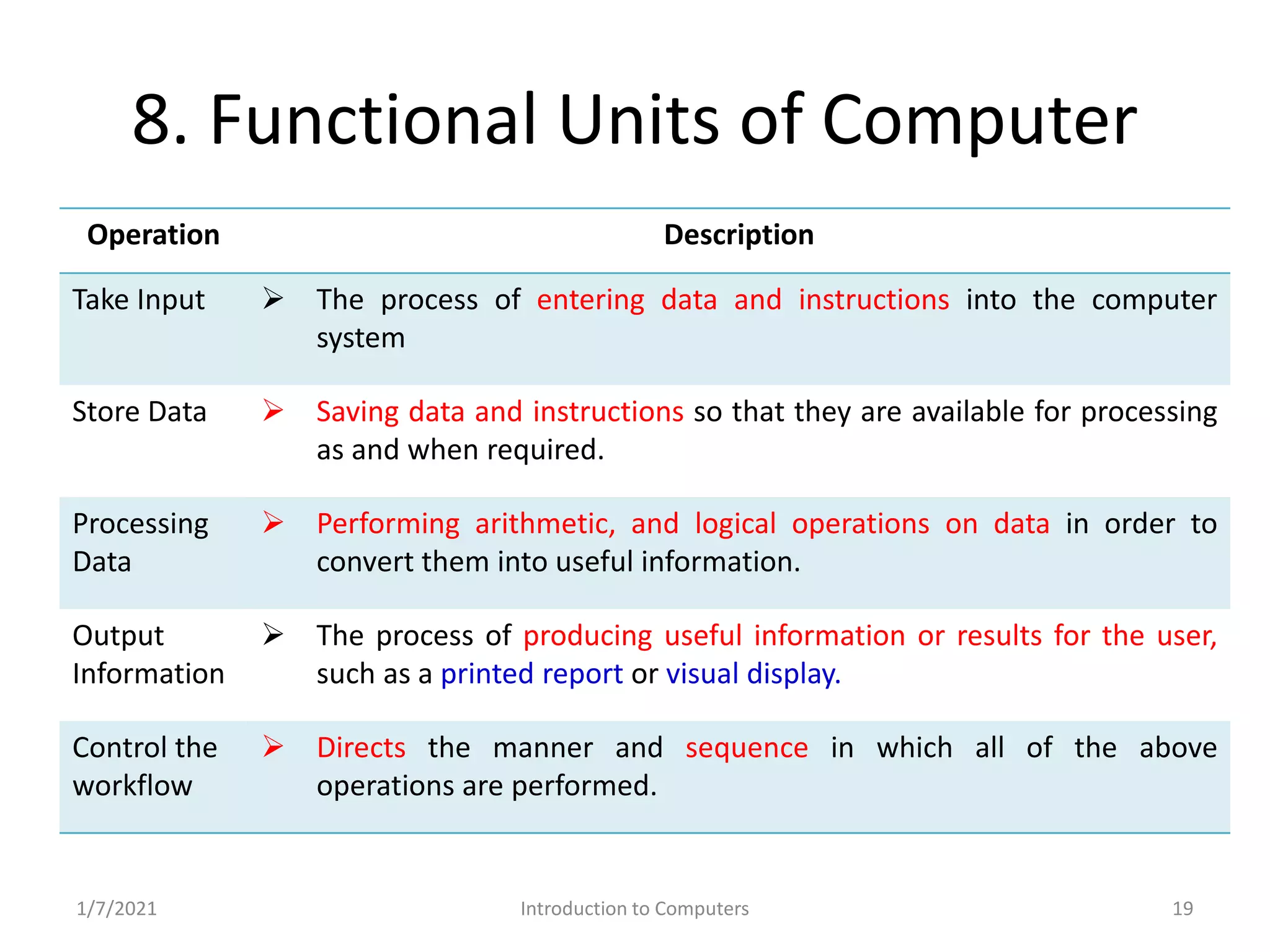
Key operations within computers: input, storage, processing, output, and control.
Distinction between hardware (physical components) and software (programs) in computing.
Types of software: system software for operating computers and application software for specific tasks.
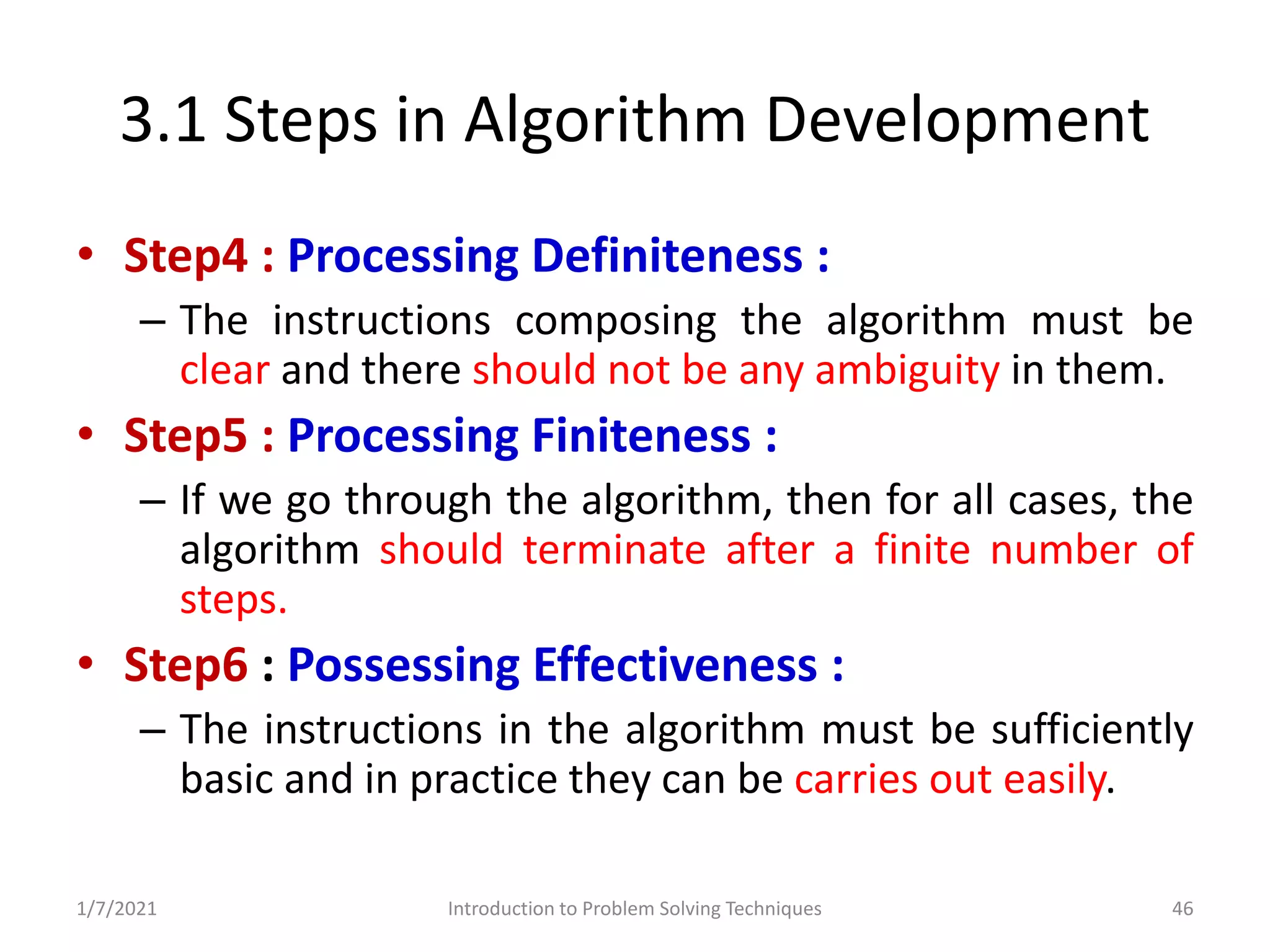
Overview of problem-solving techniques, including steps from understanding to implementing solutions.
Stepwise approach to problem-solving: understanding, analyzing, developing solutions, coding.
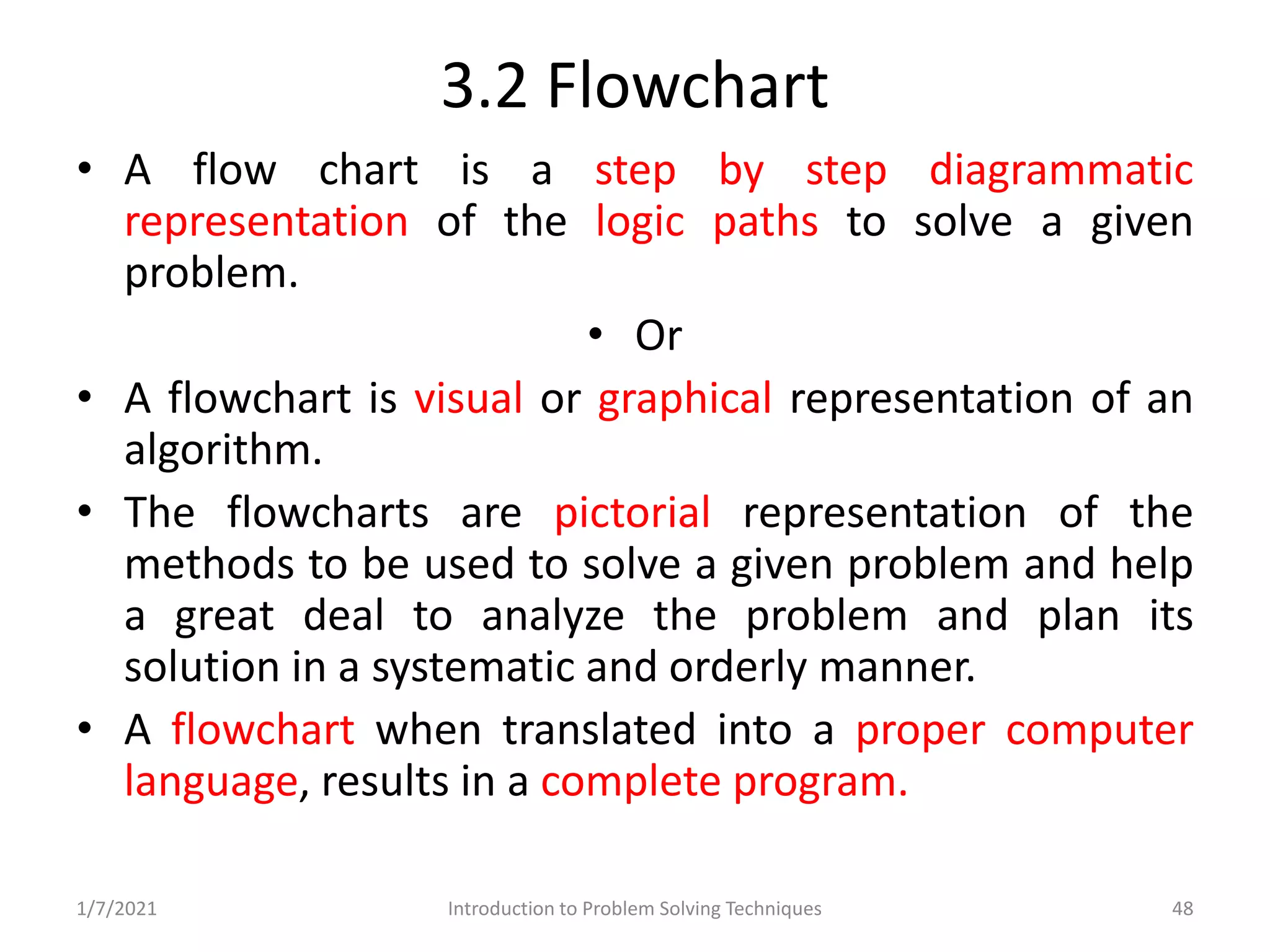
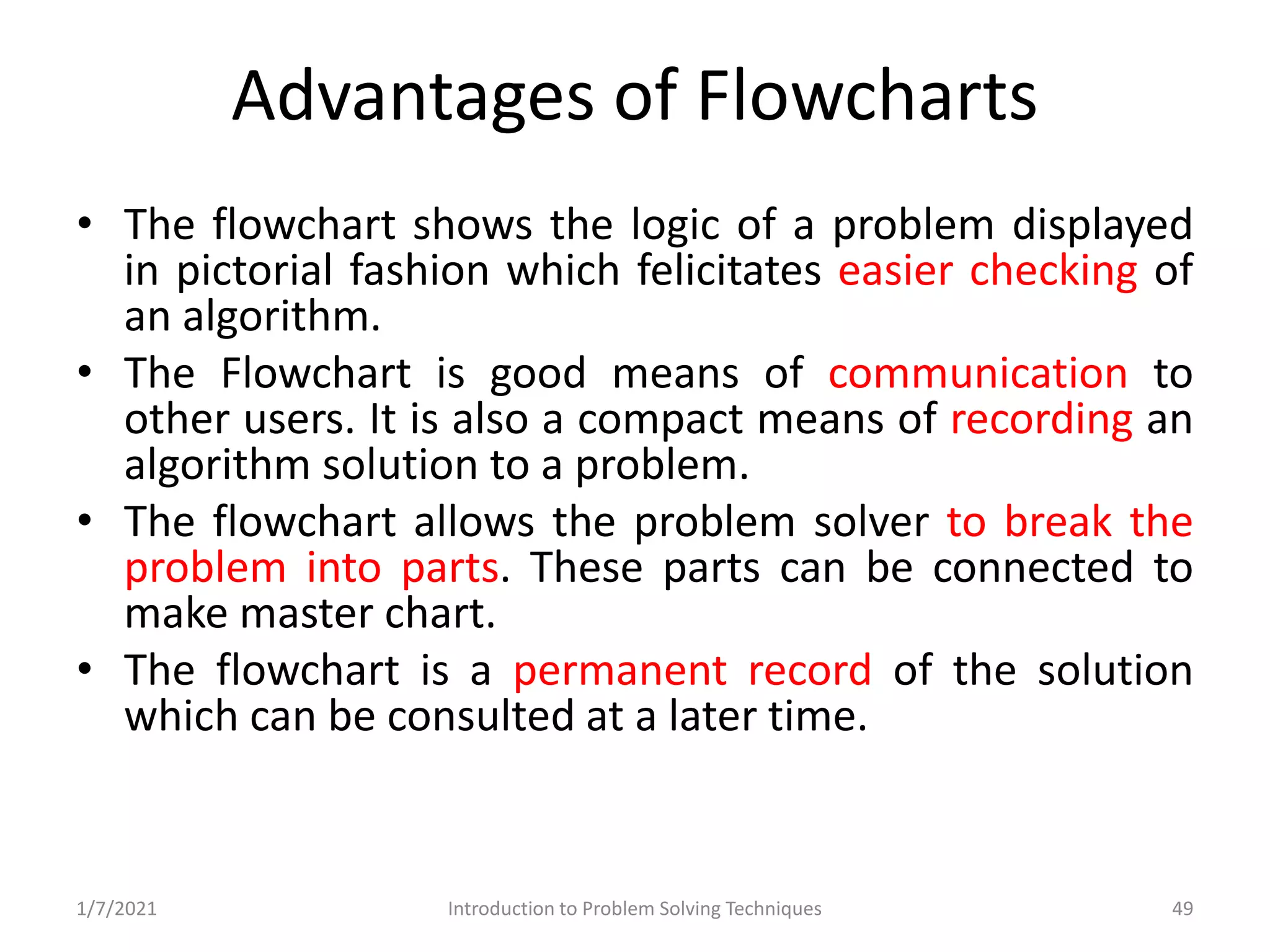
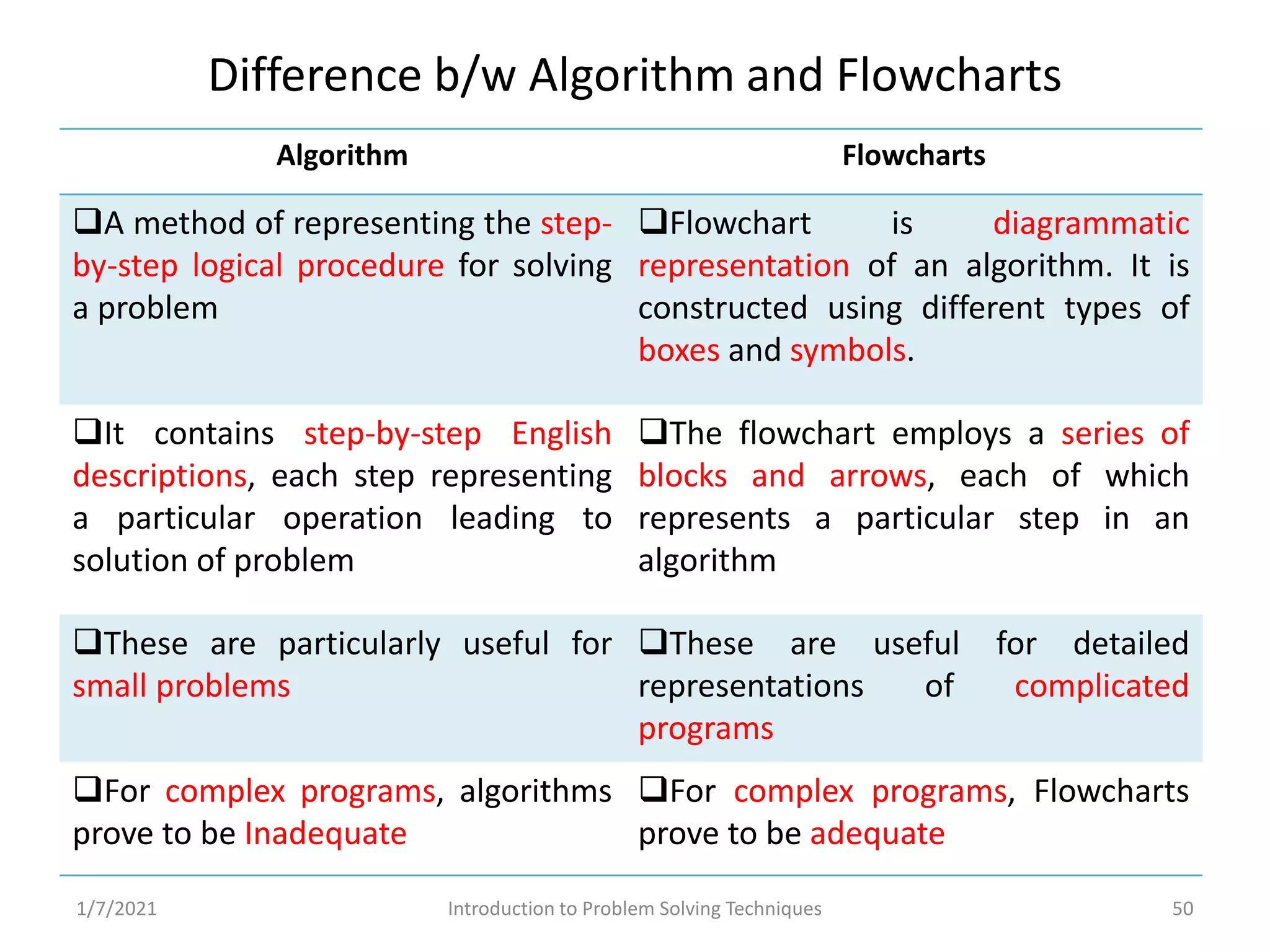
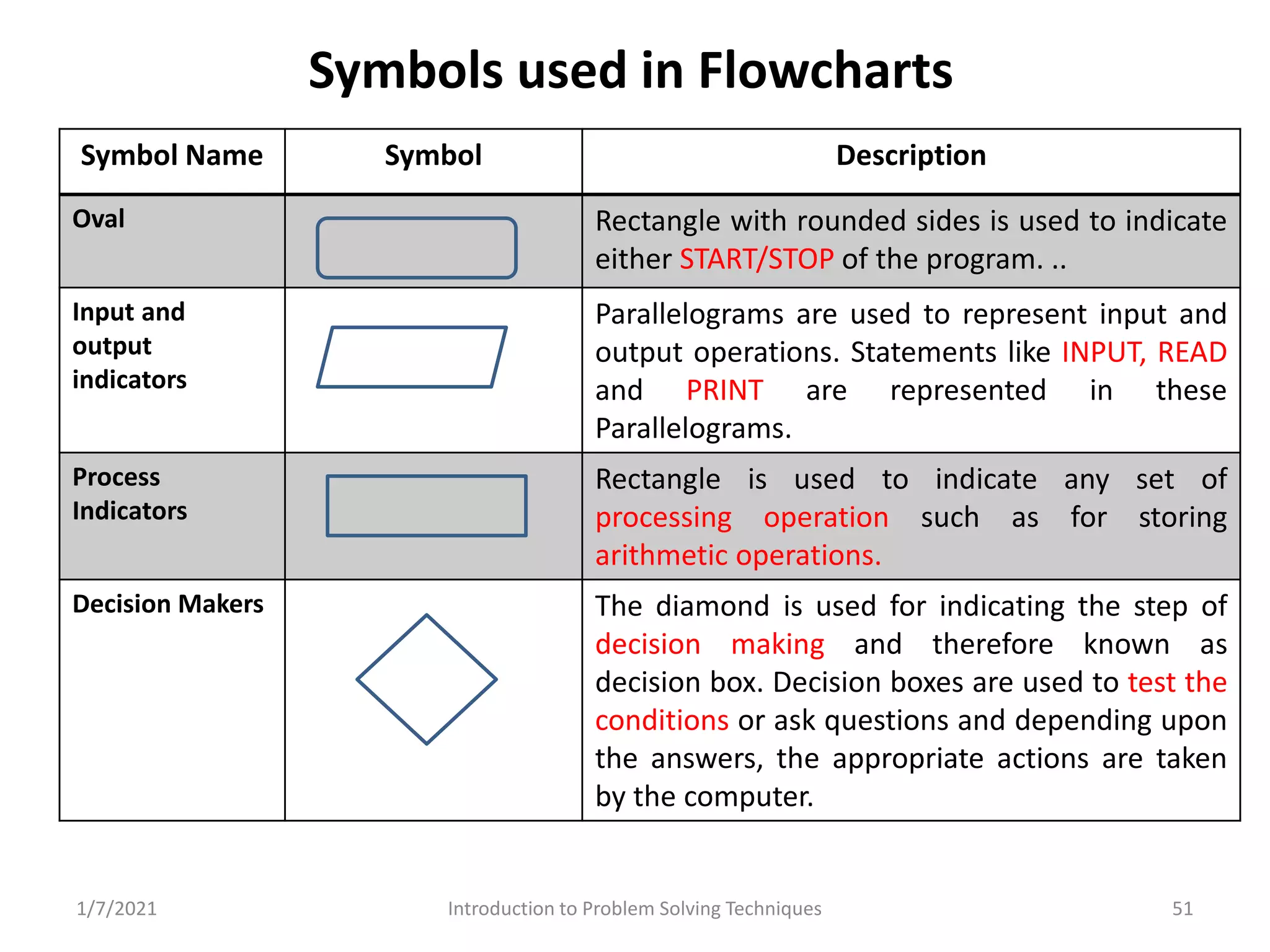
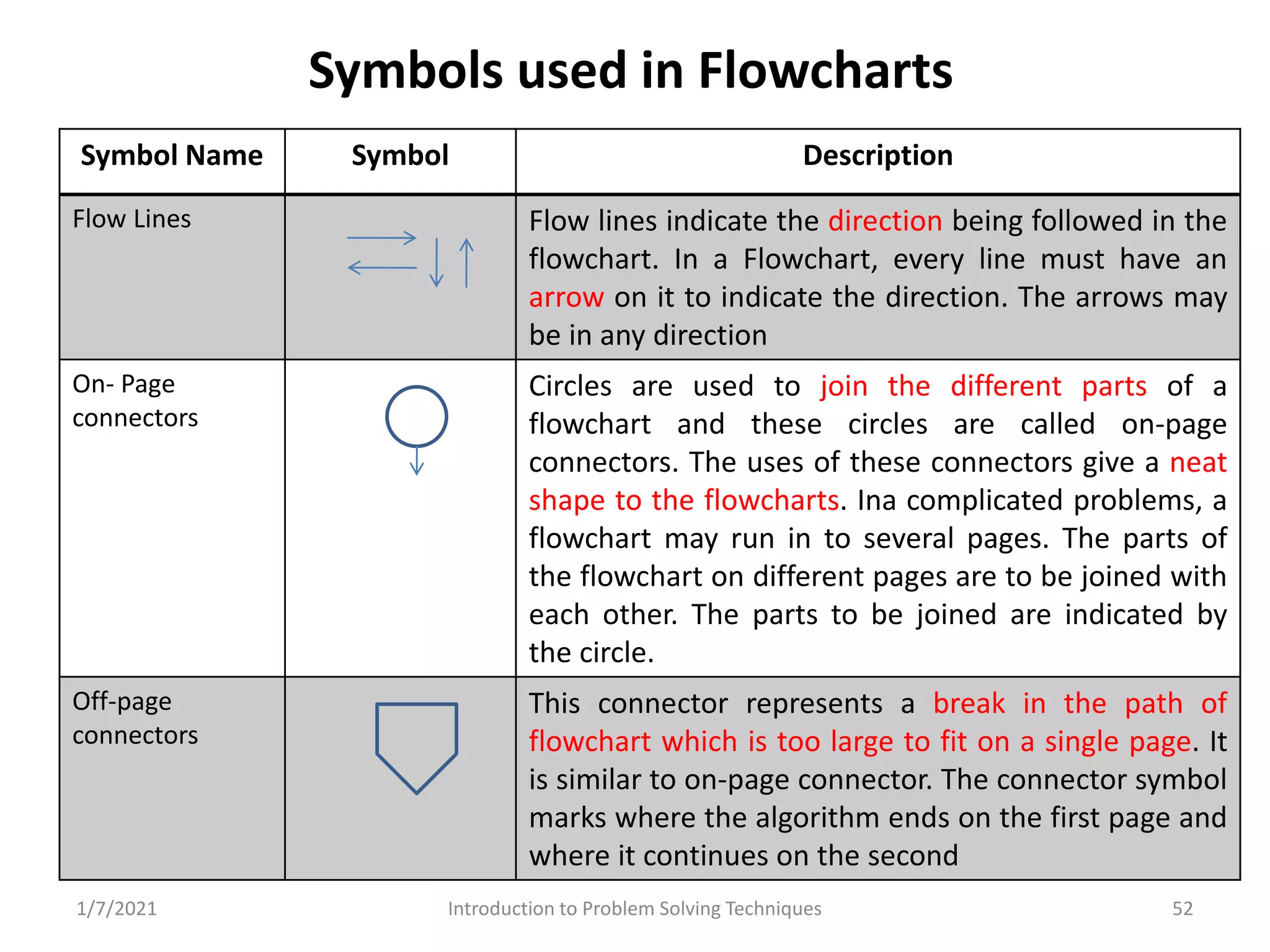
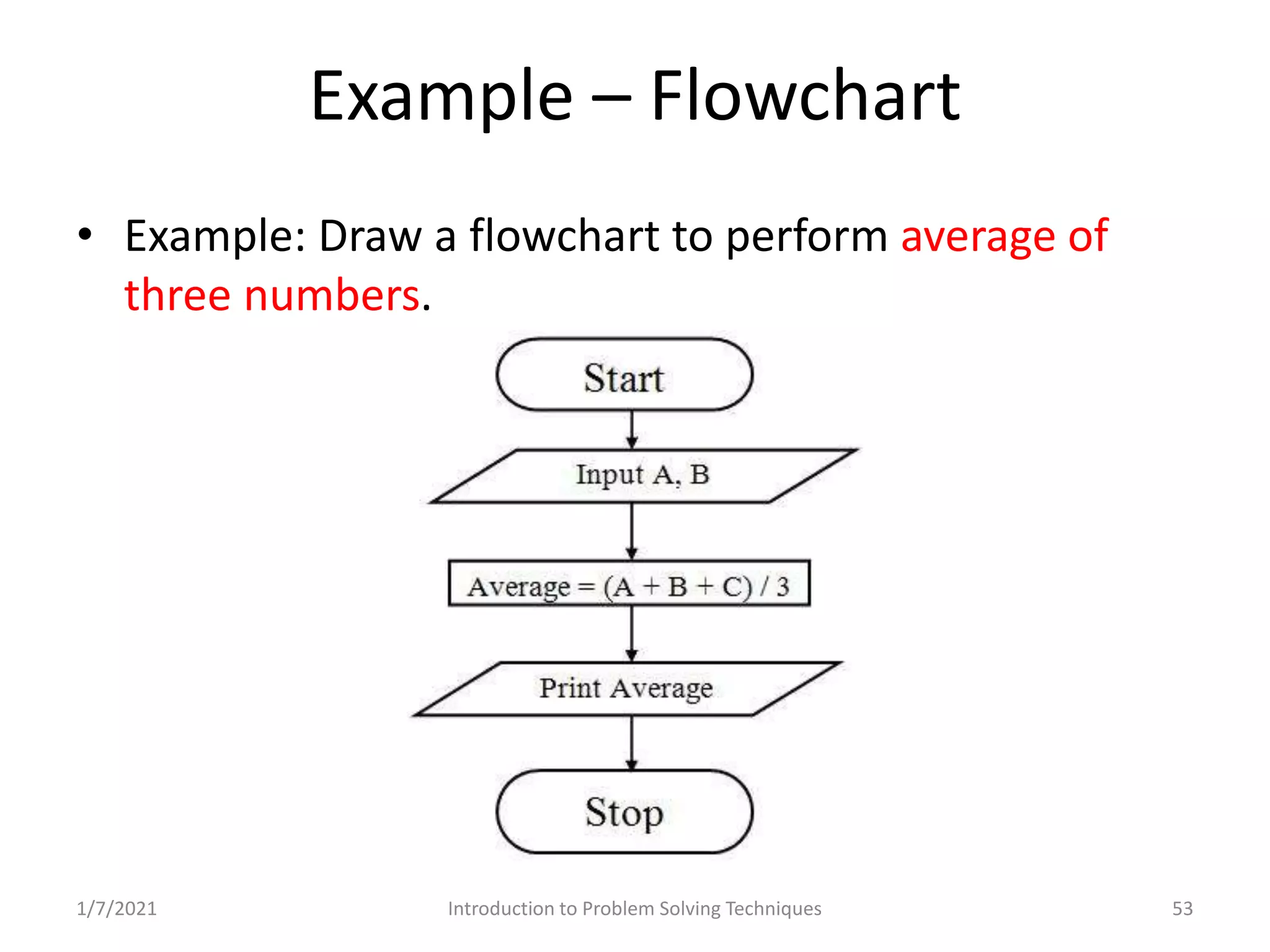
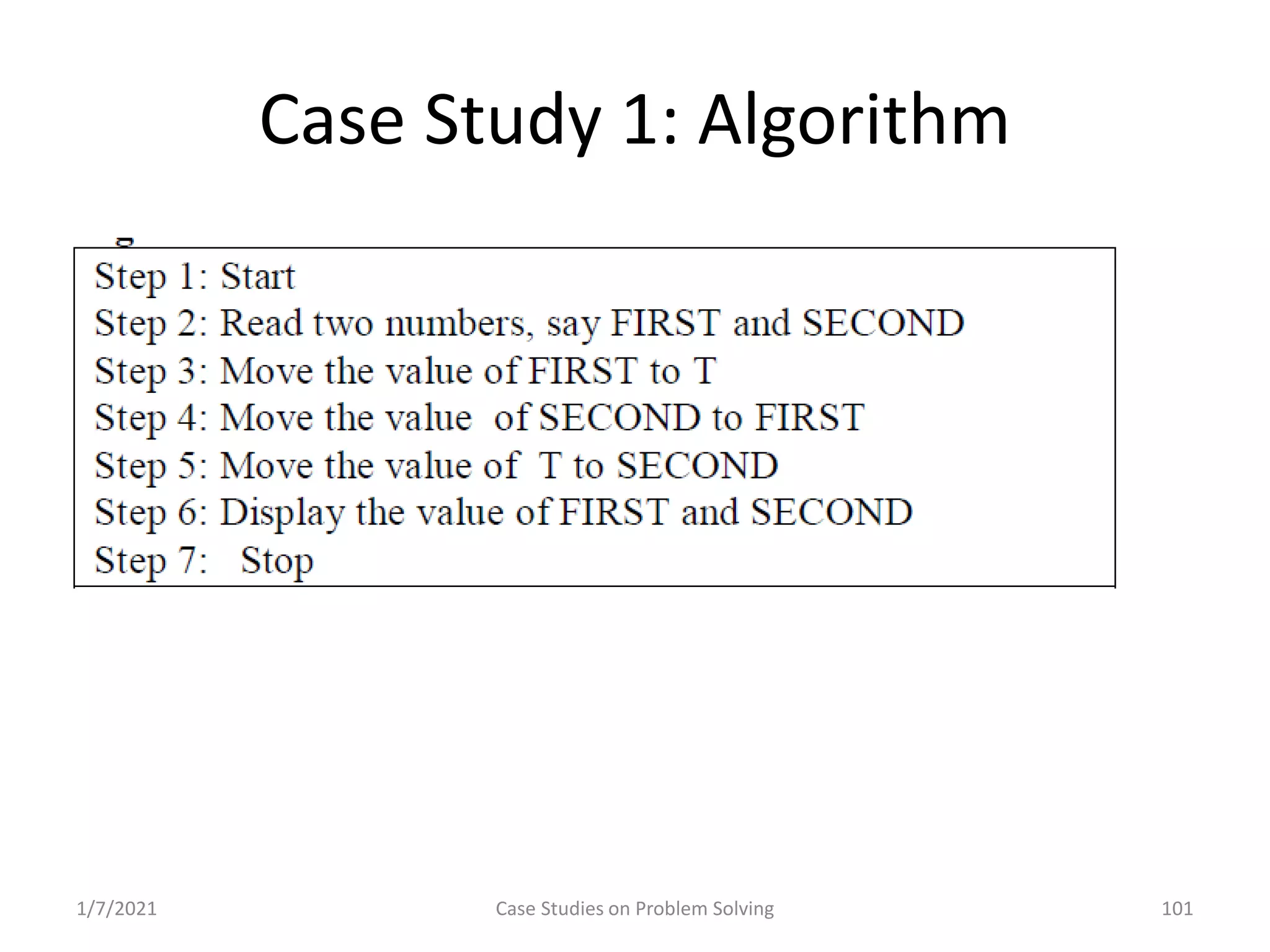
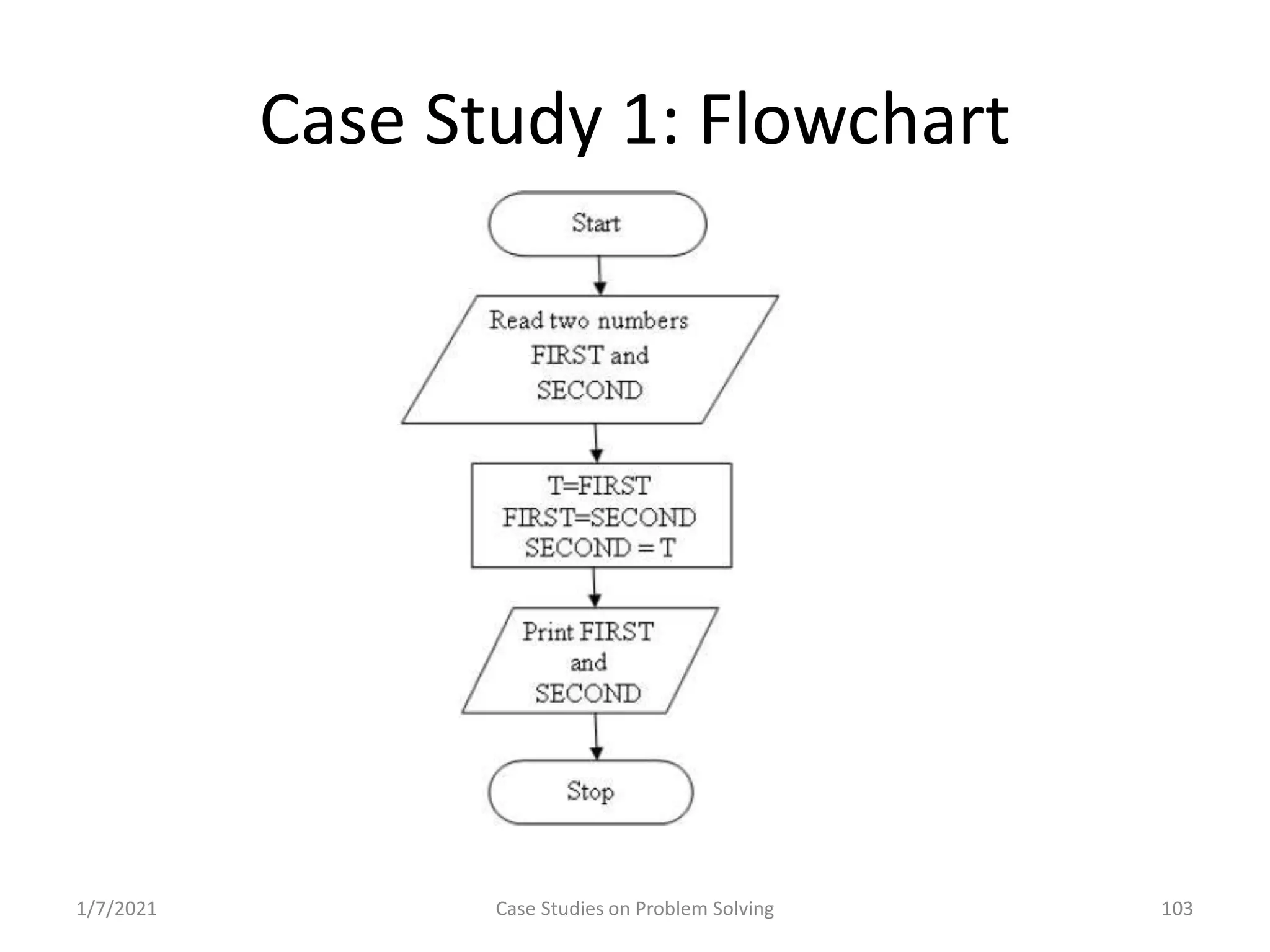
Different methods including algorithms, flowcharts, pseudo code, and programming.
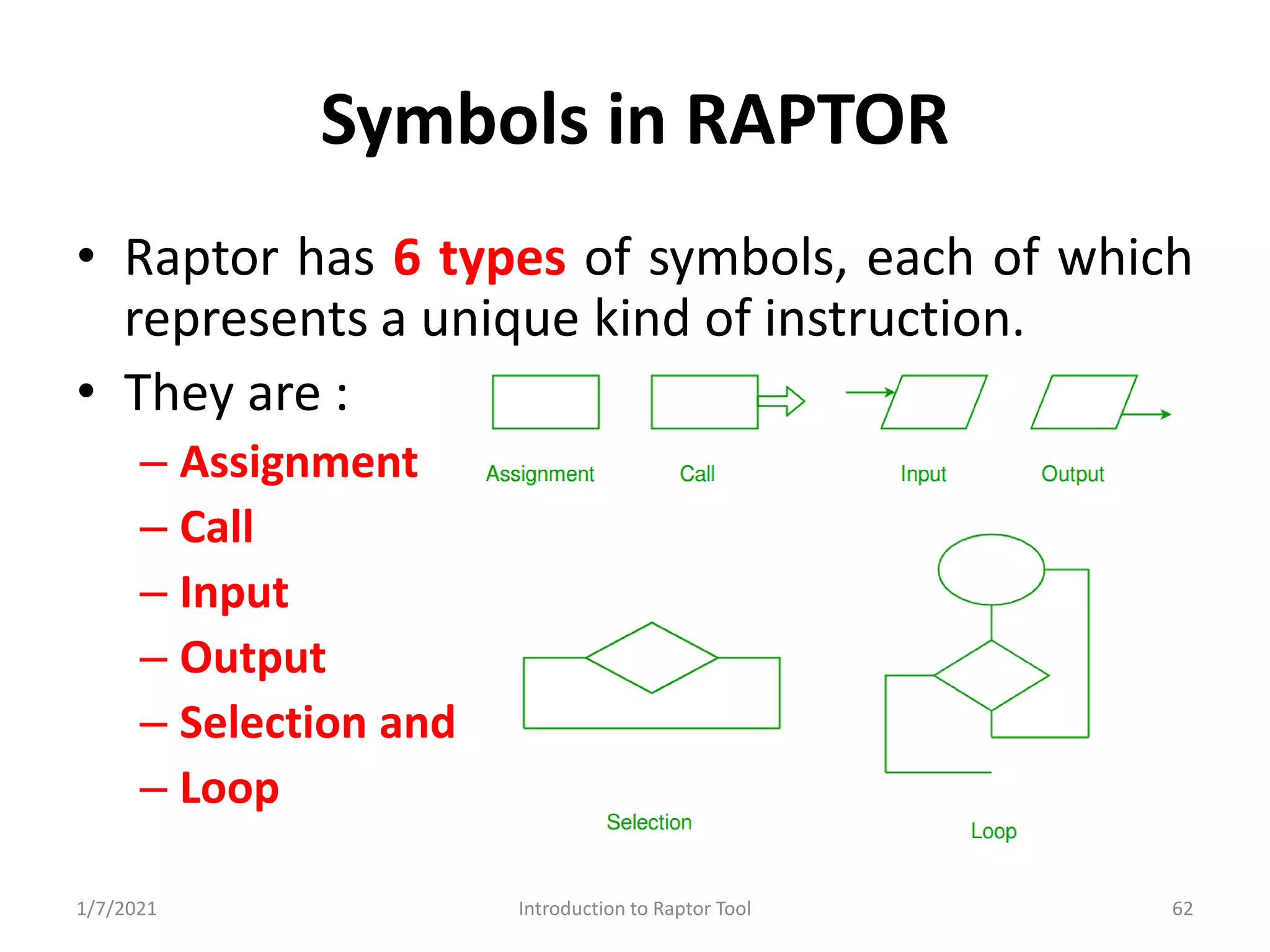
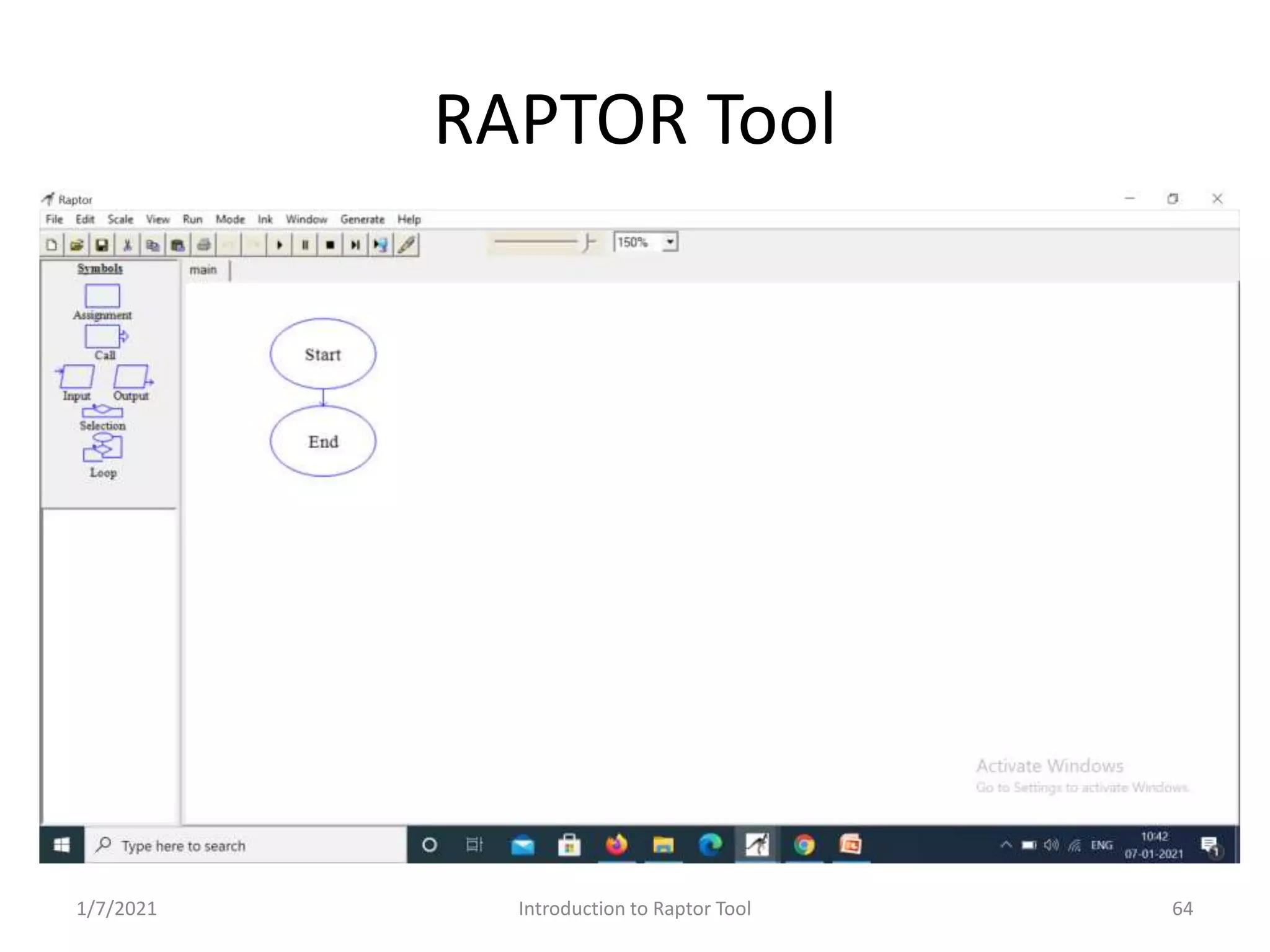
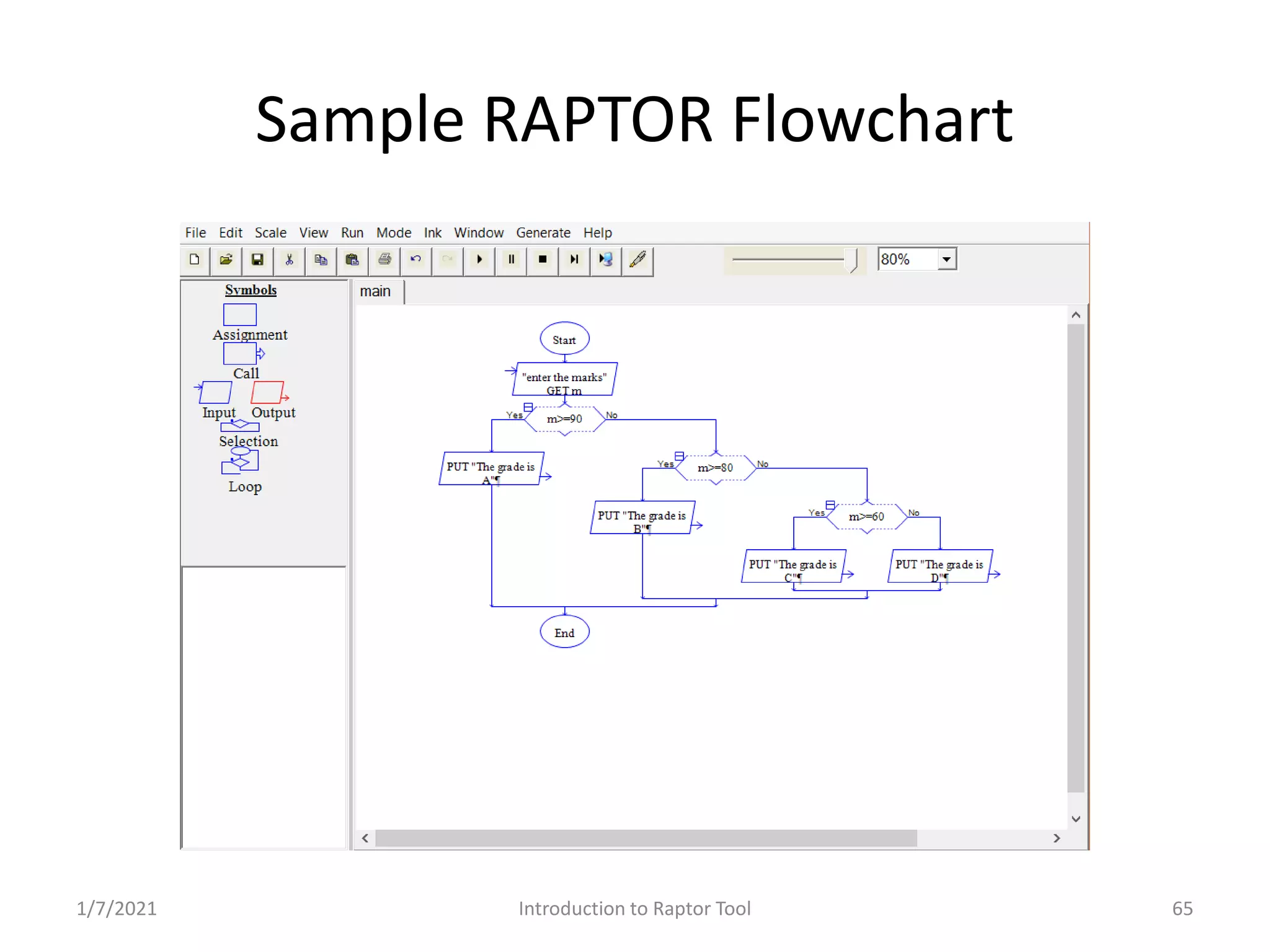
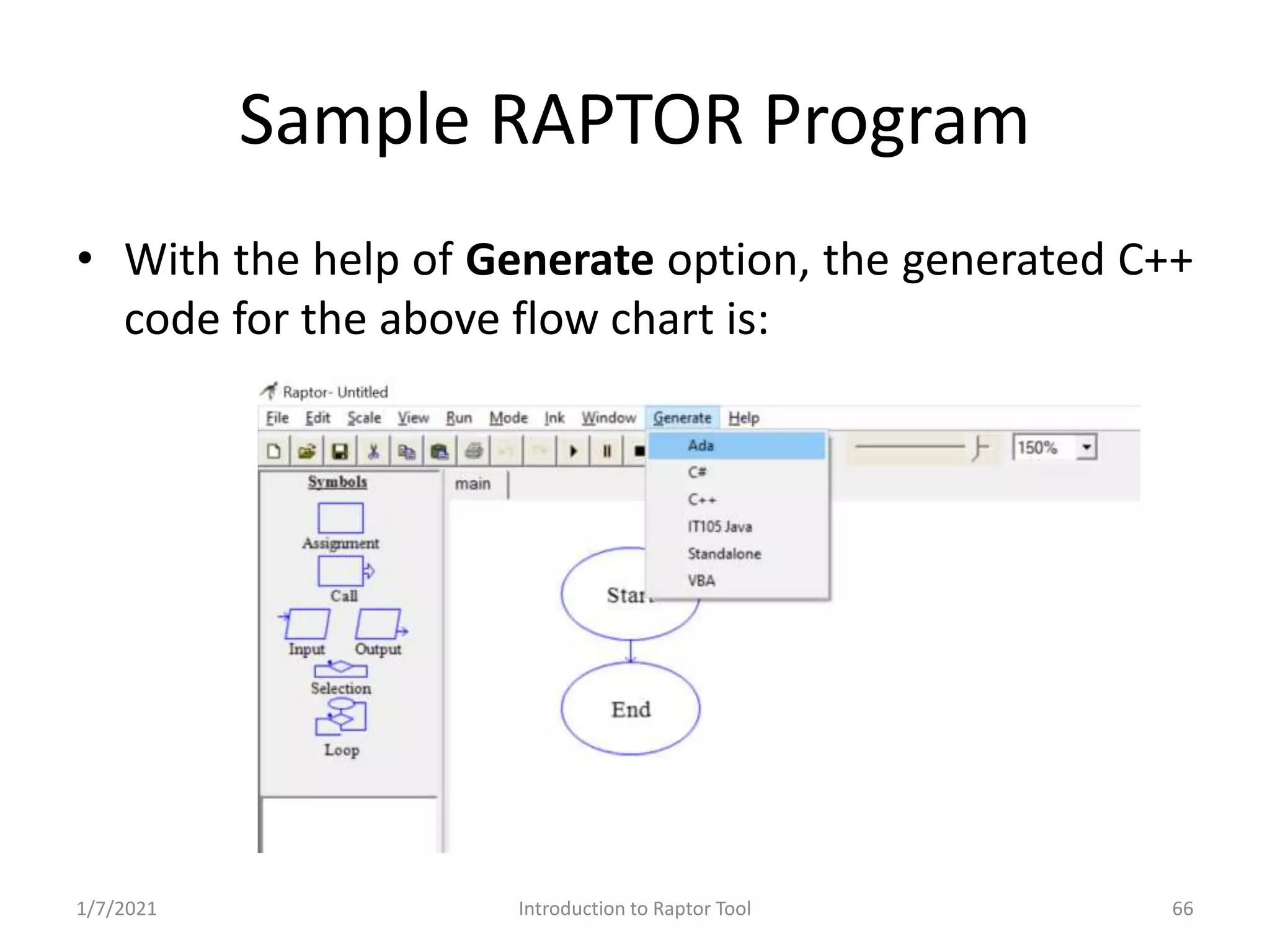
RAPTOR Tool for graphic representation of algorithms; utilizes graphical symbols for programming. Structure of programs in RAPTOR; execution flow and sample code generation.
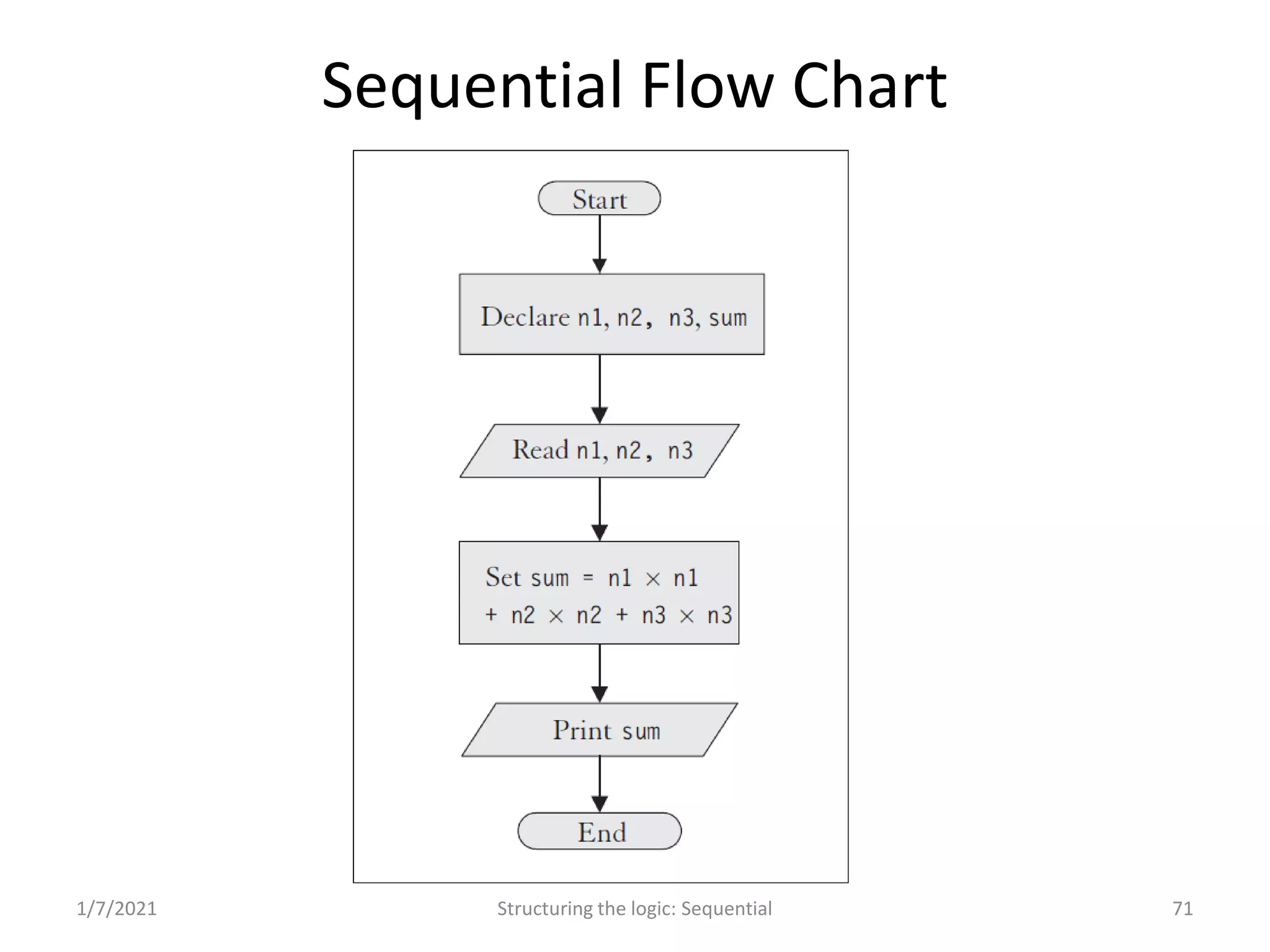
Concept of sequencing in programming; includes simple examples and sample problems for practice.
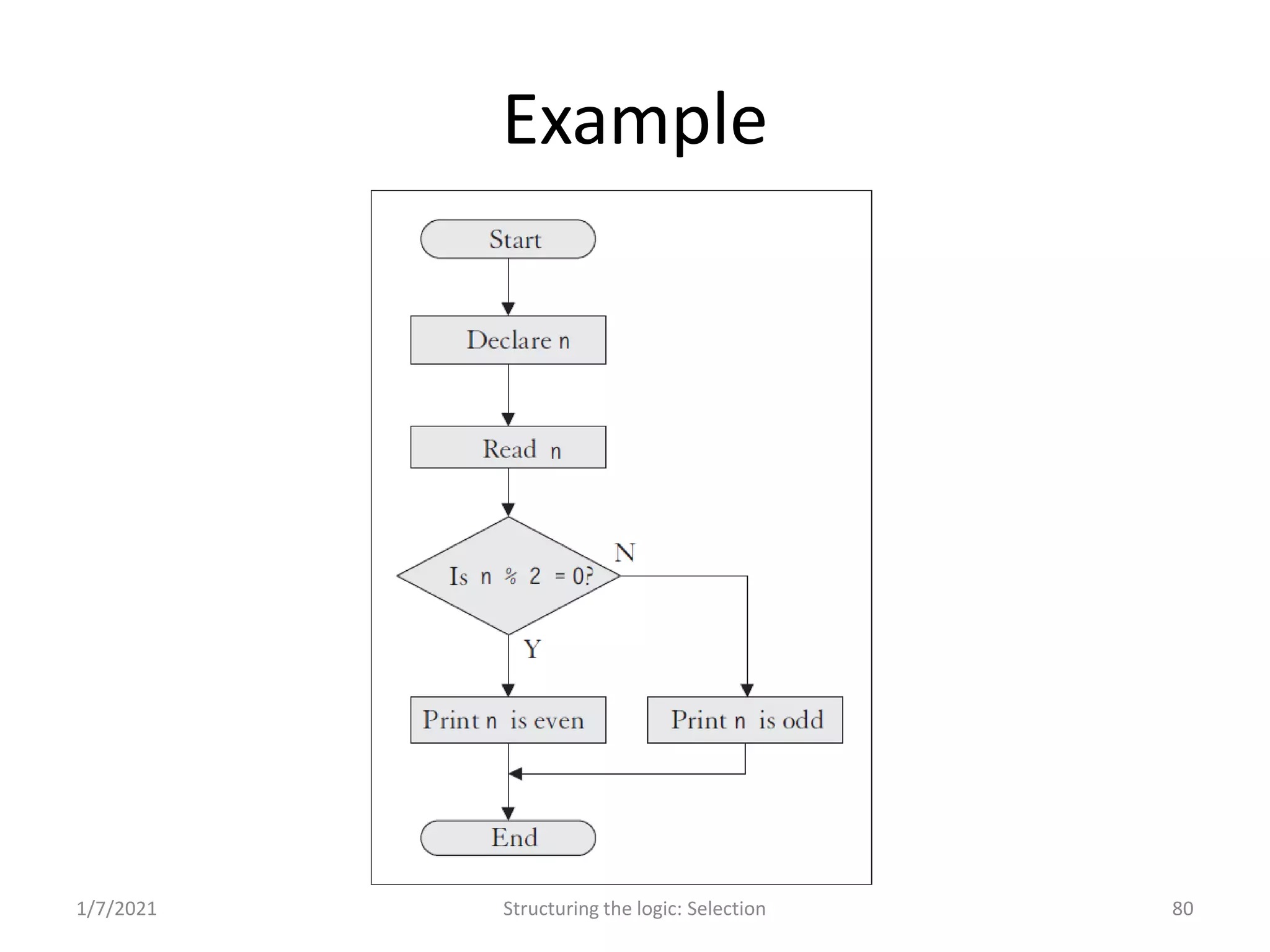
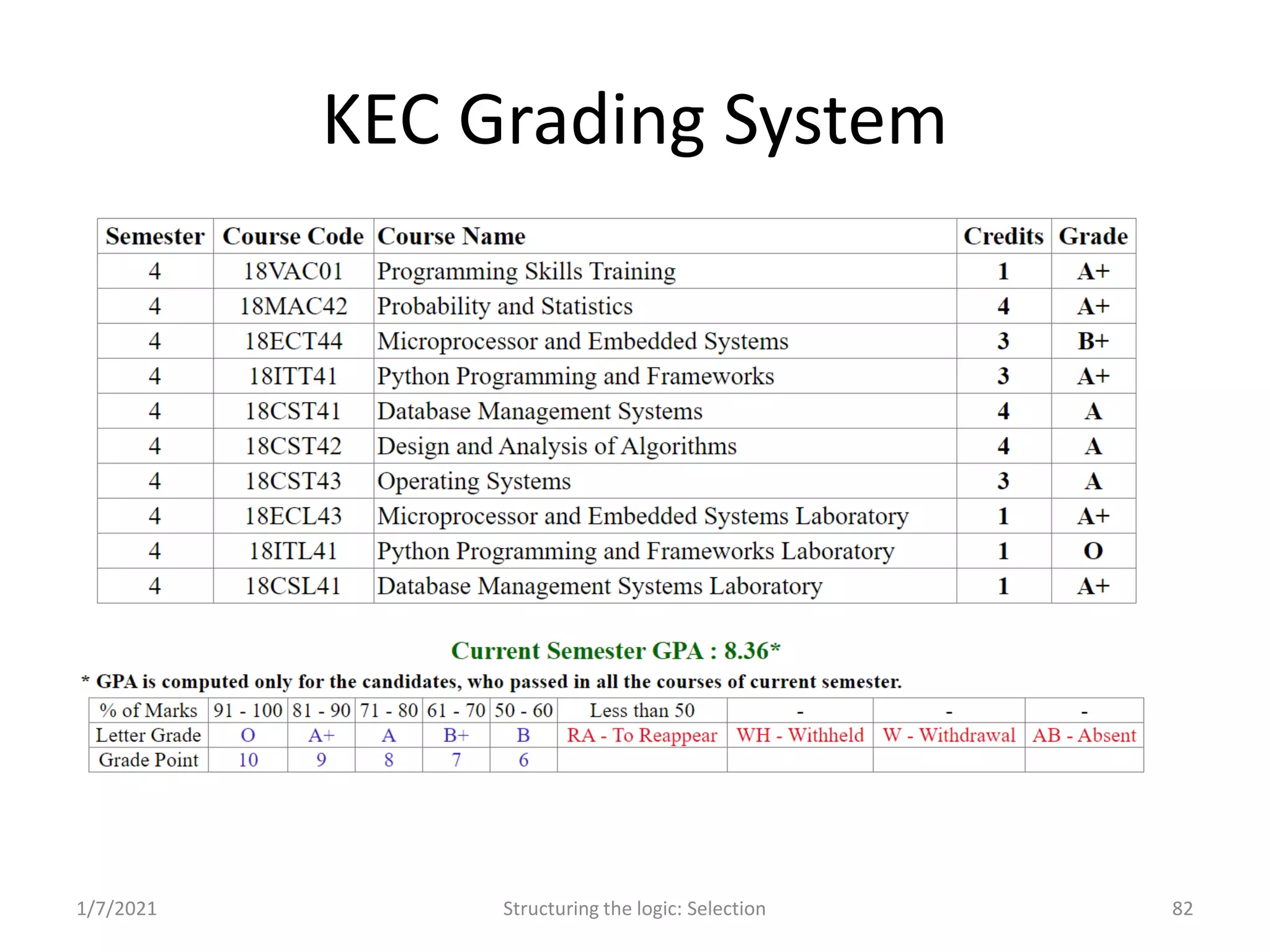
Decision making in programming; using flowcharts and examples to demonstrate selection logic.
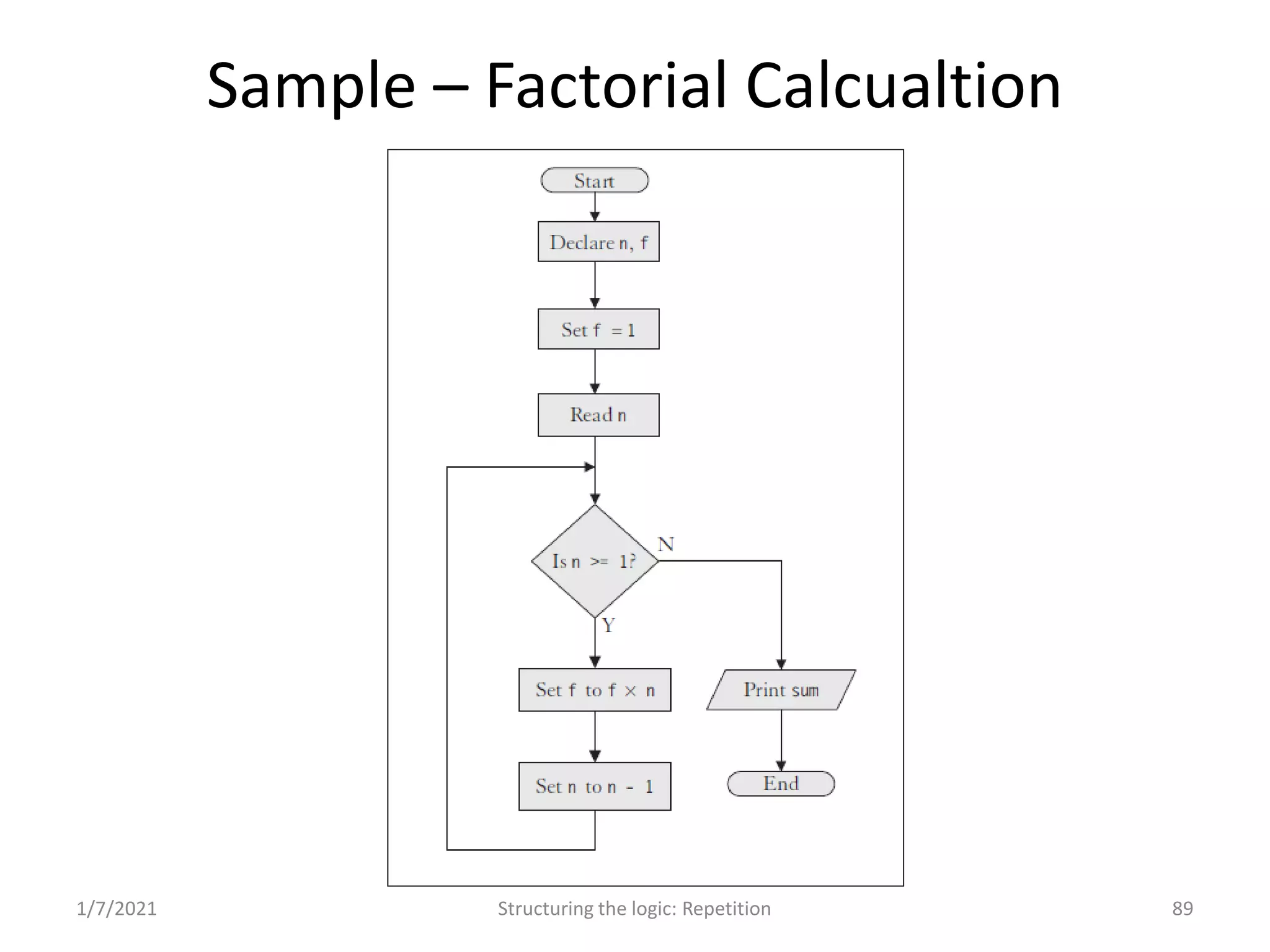
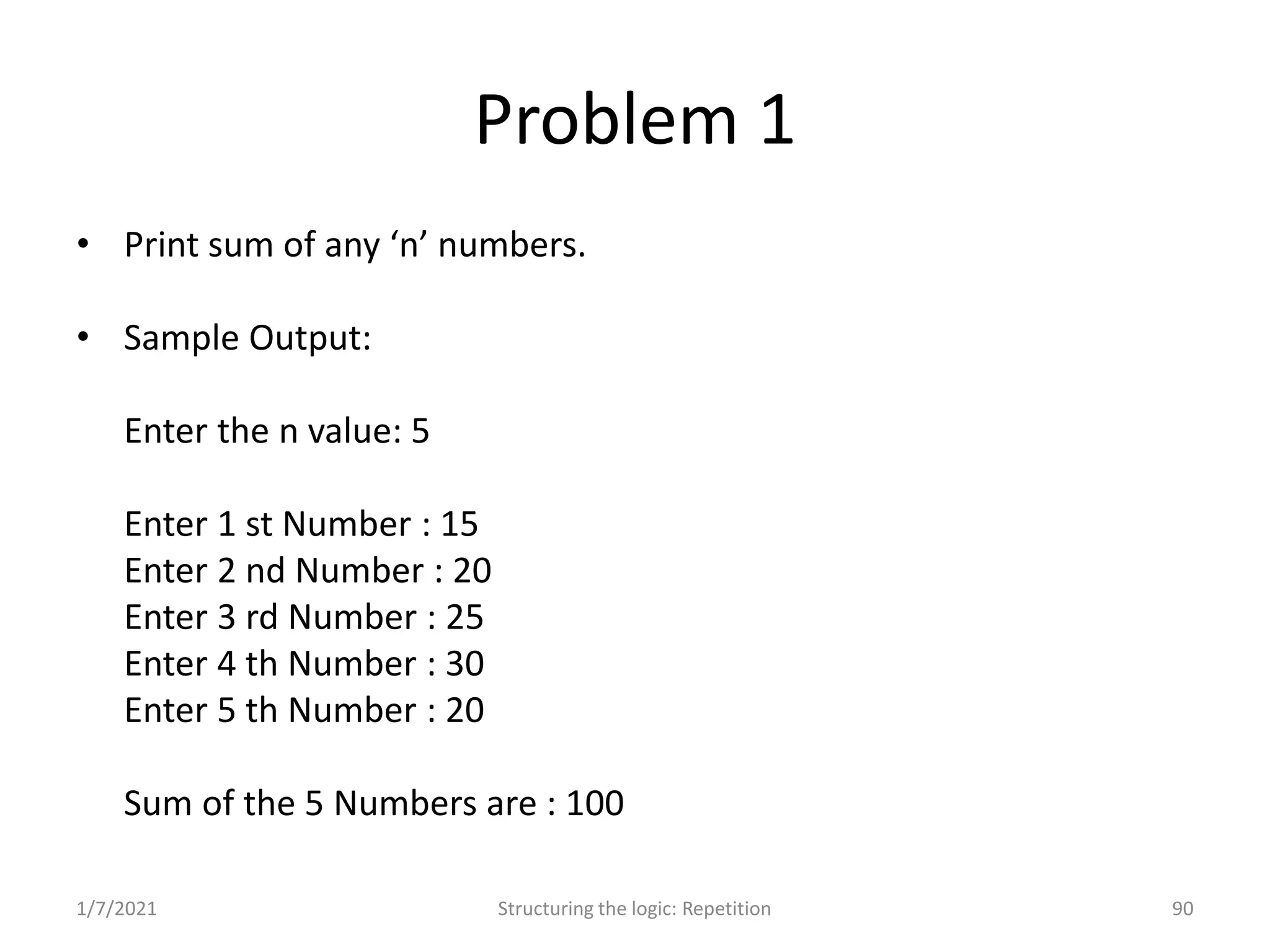
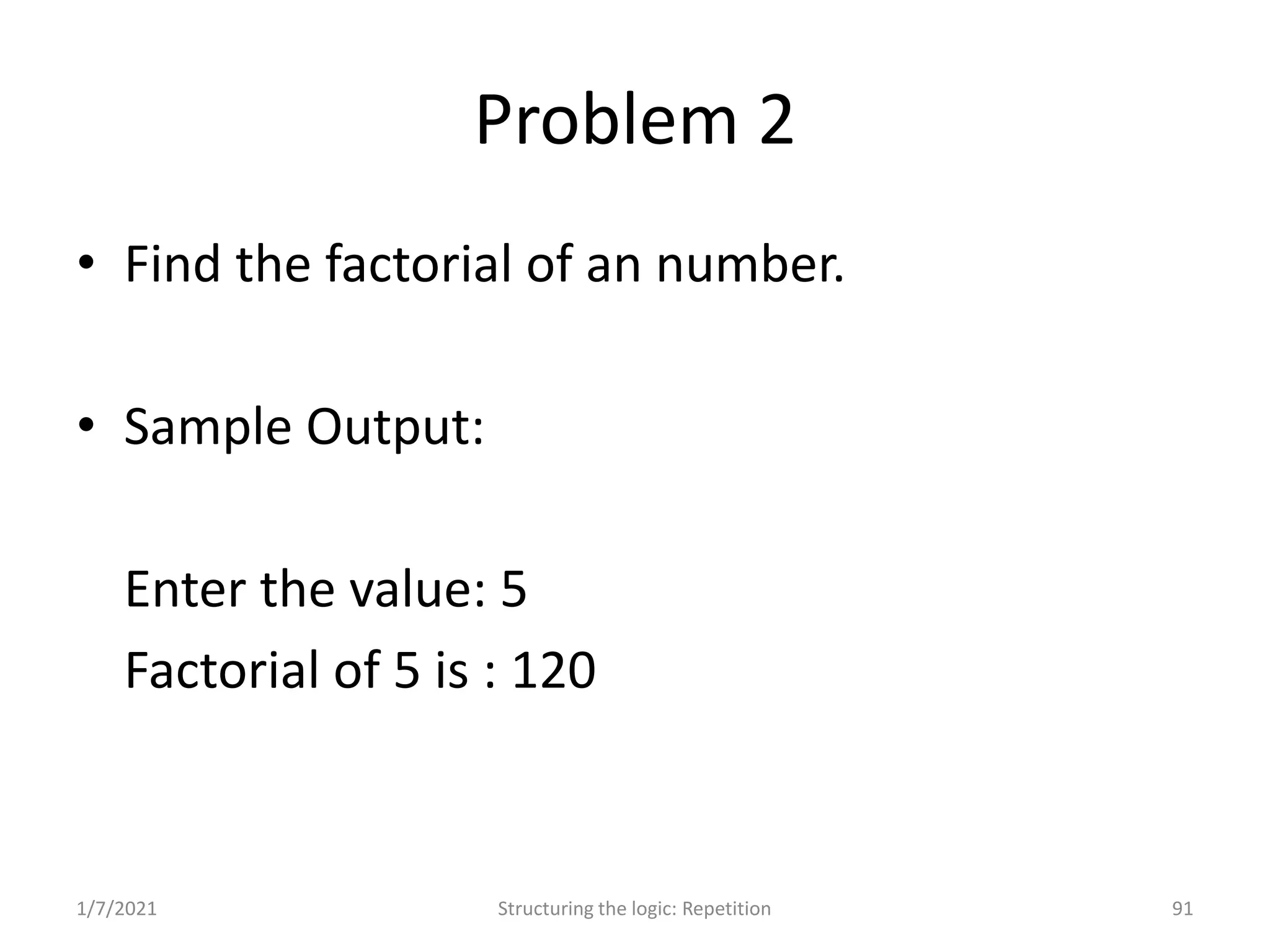
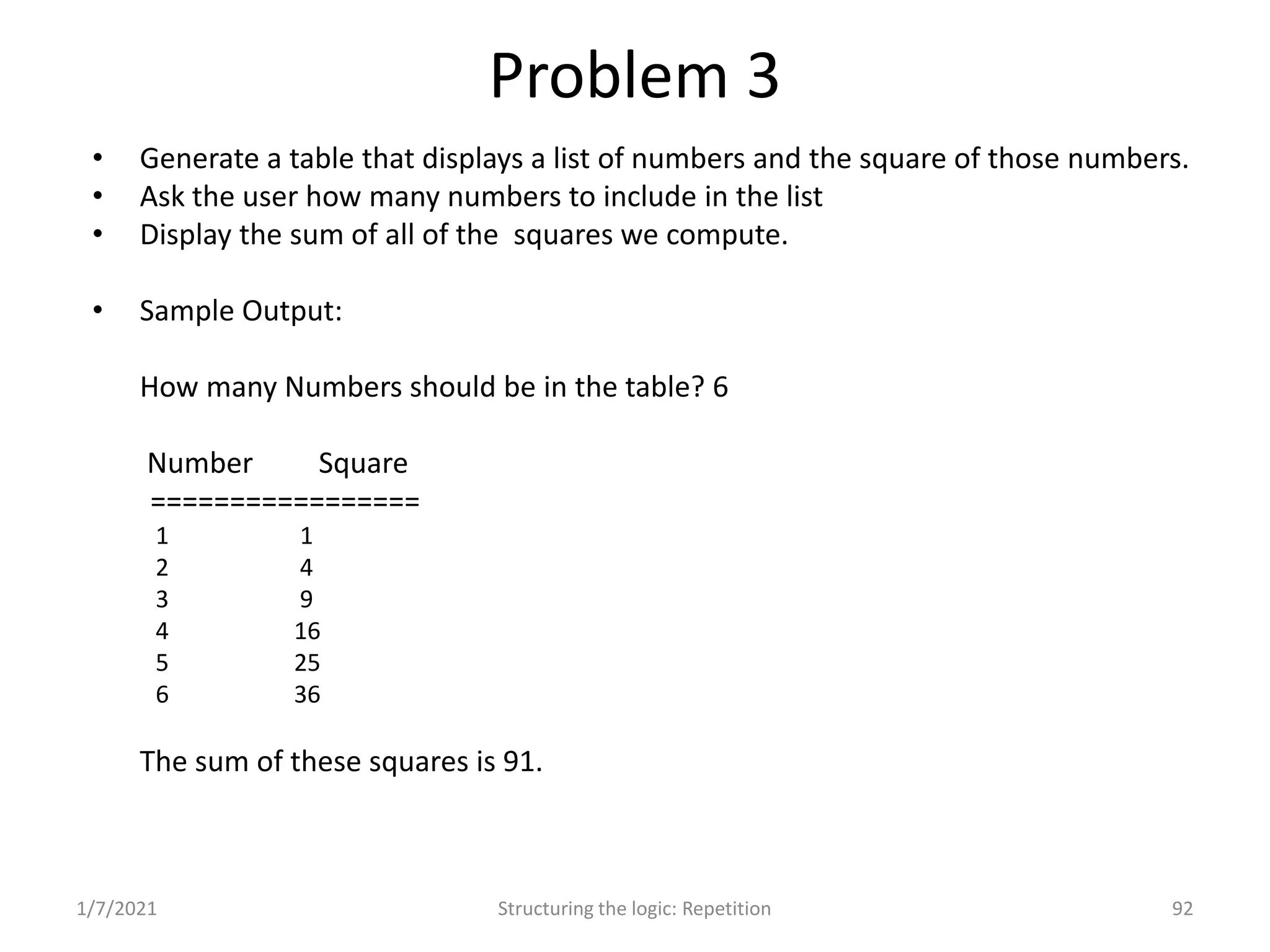
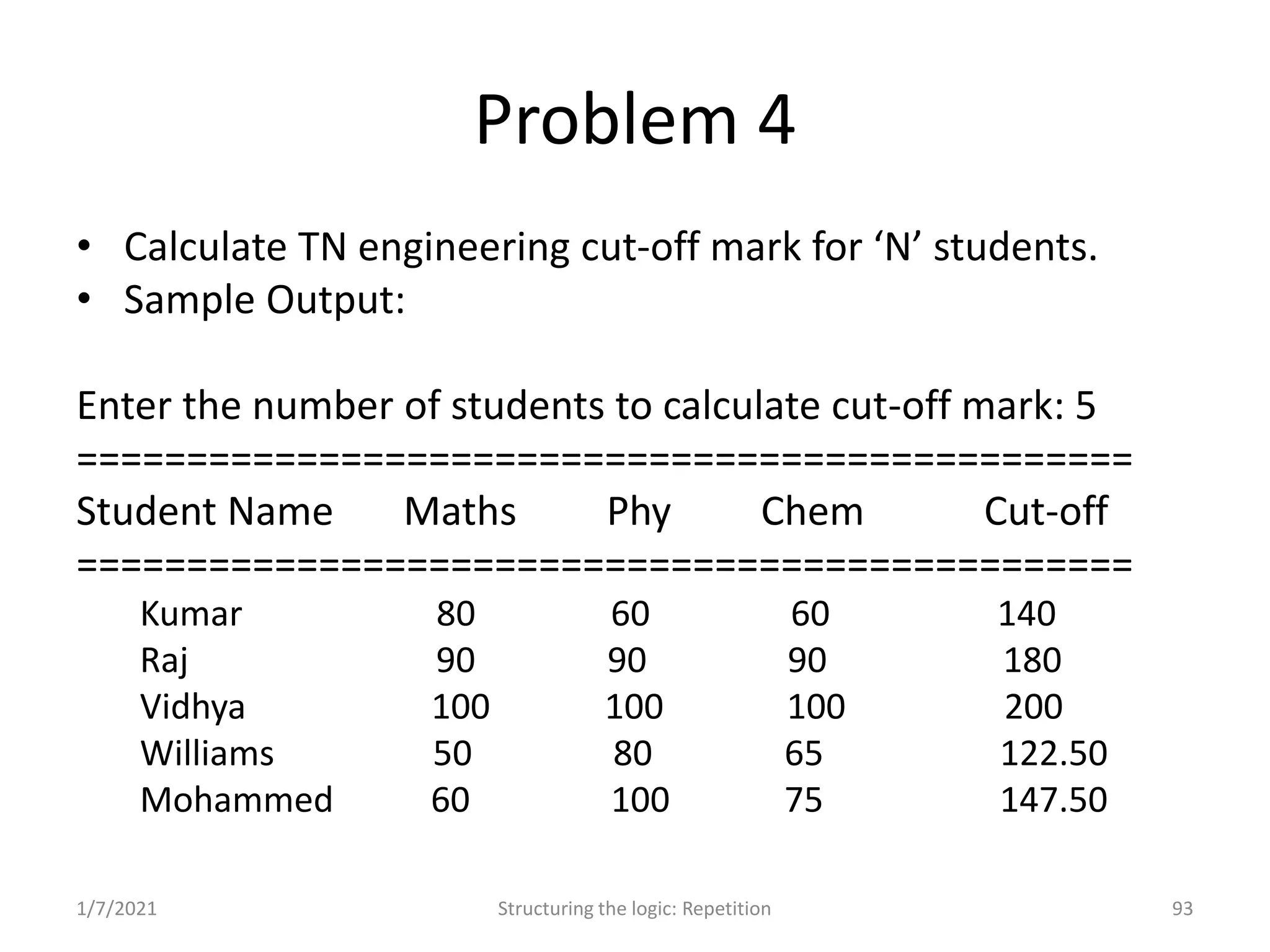
Understanding repetition constructs; sample problems demonstrating the loop constructs.
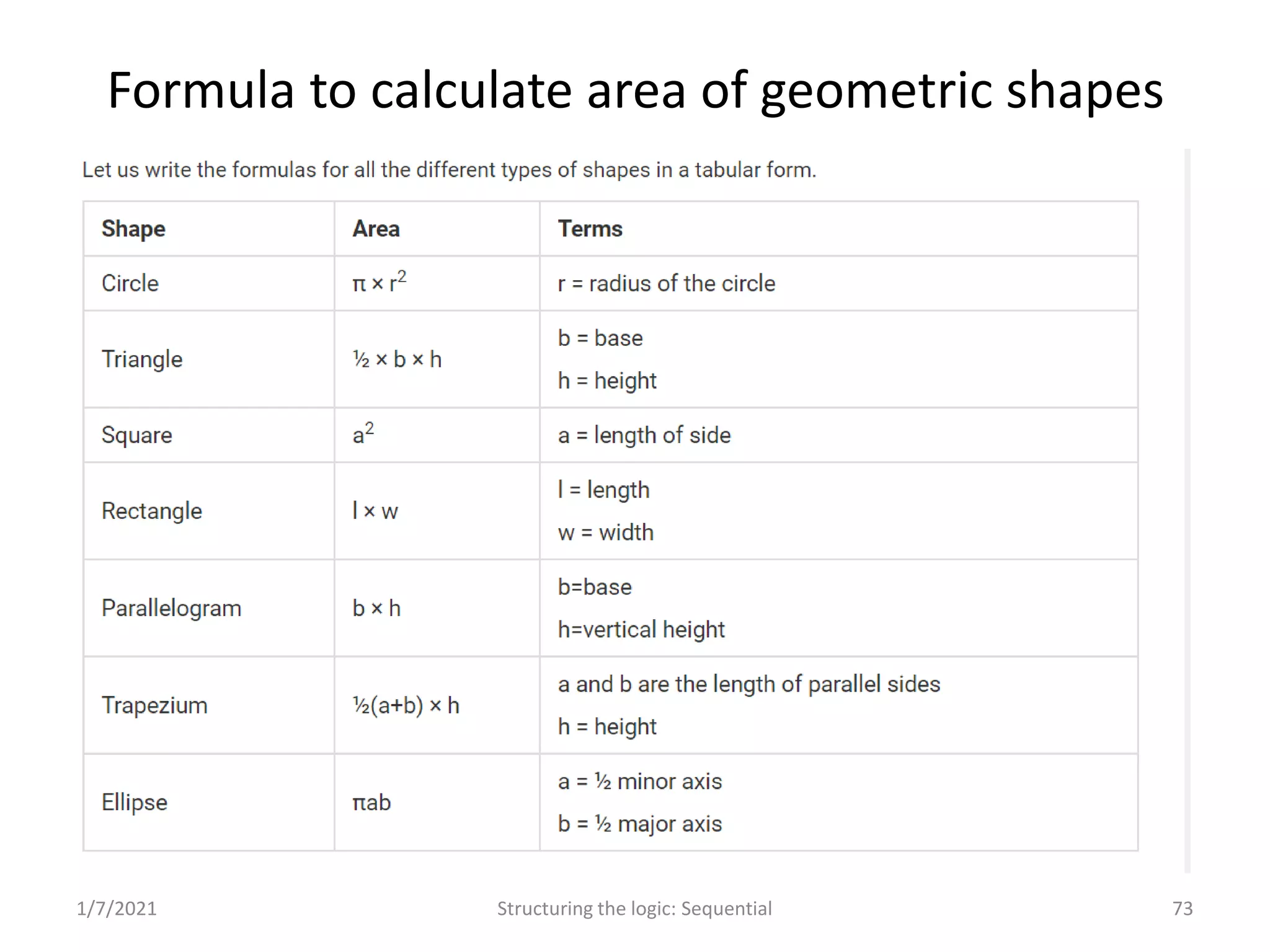
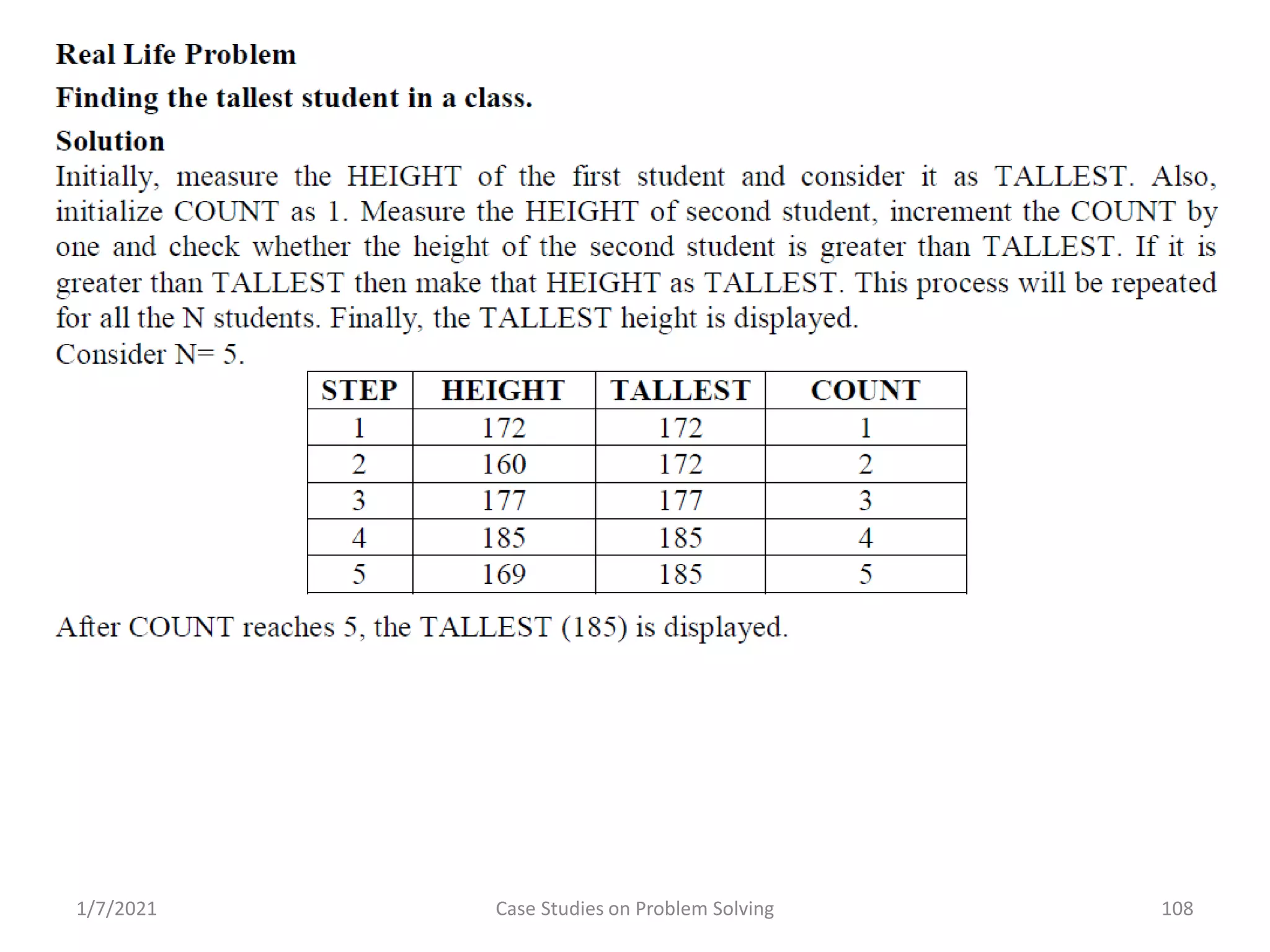
Real-world problems solved through algorithms, flowcharts, and code implementations.
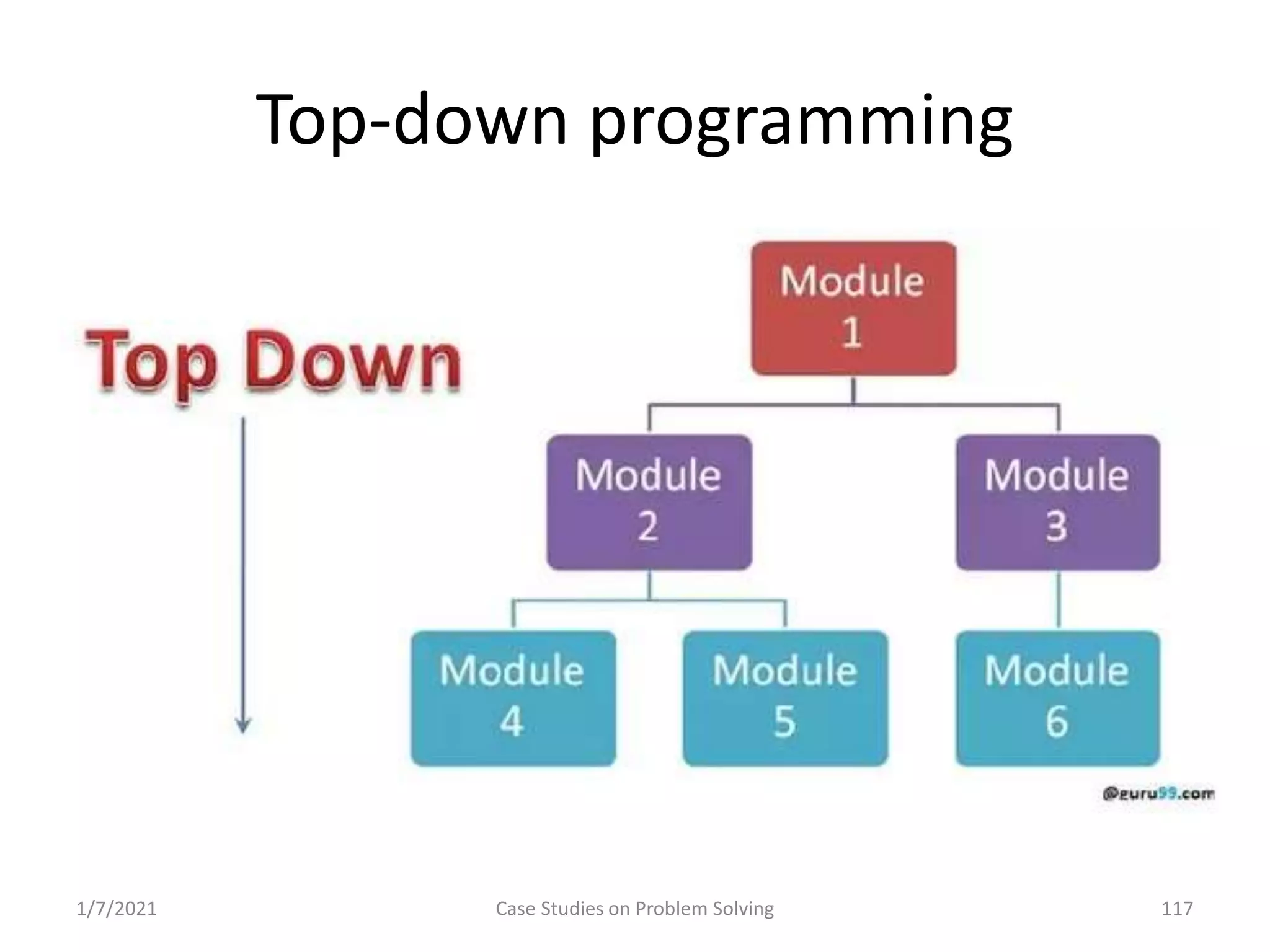
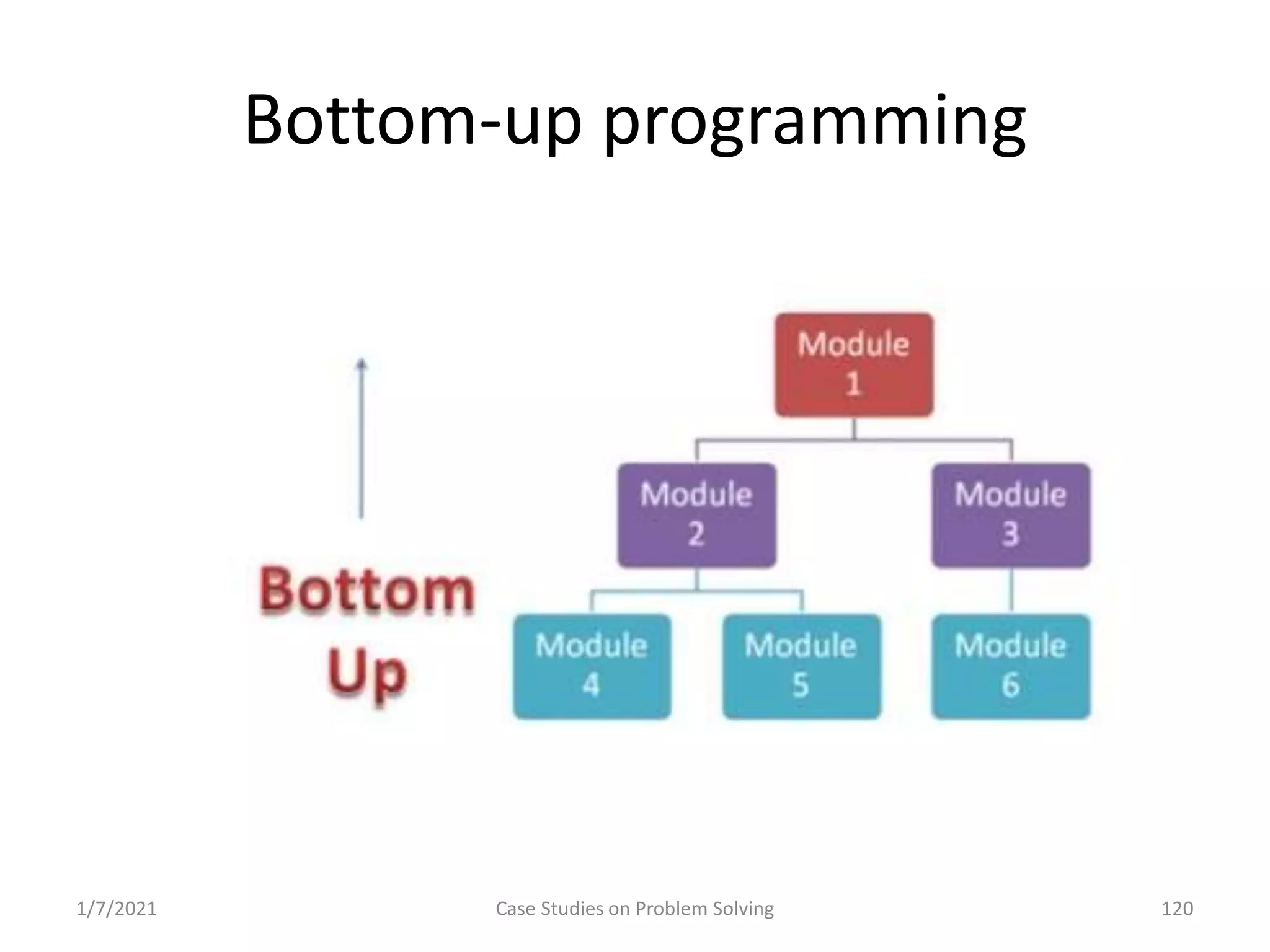
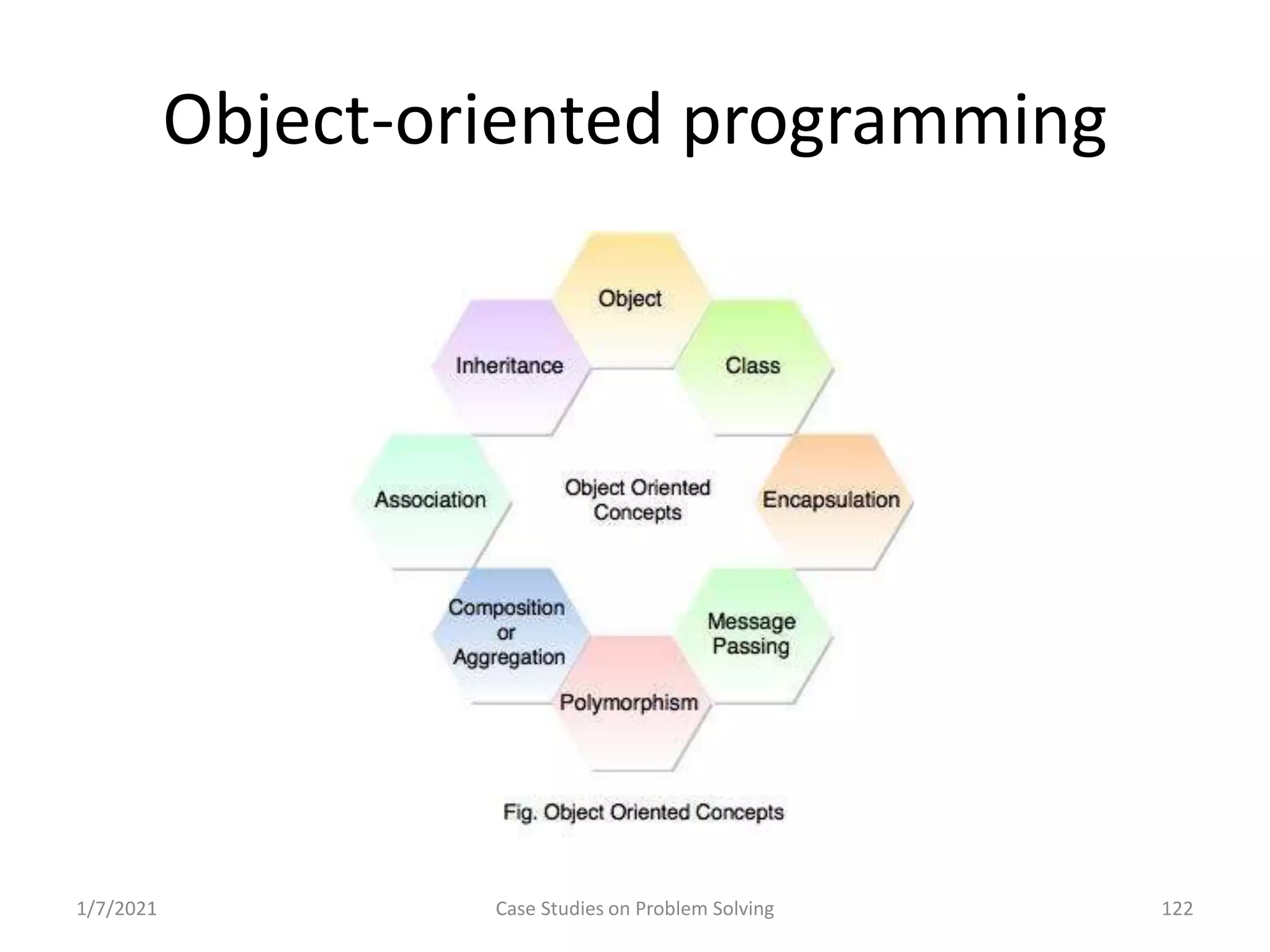
Exploration of programming paradigms: top-down, bottom-up, and object-oriented approaches.
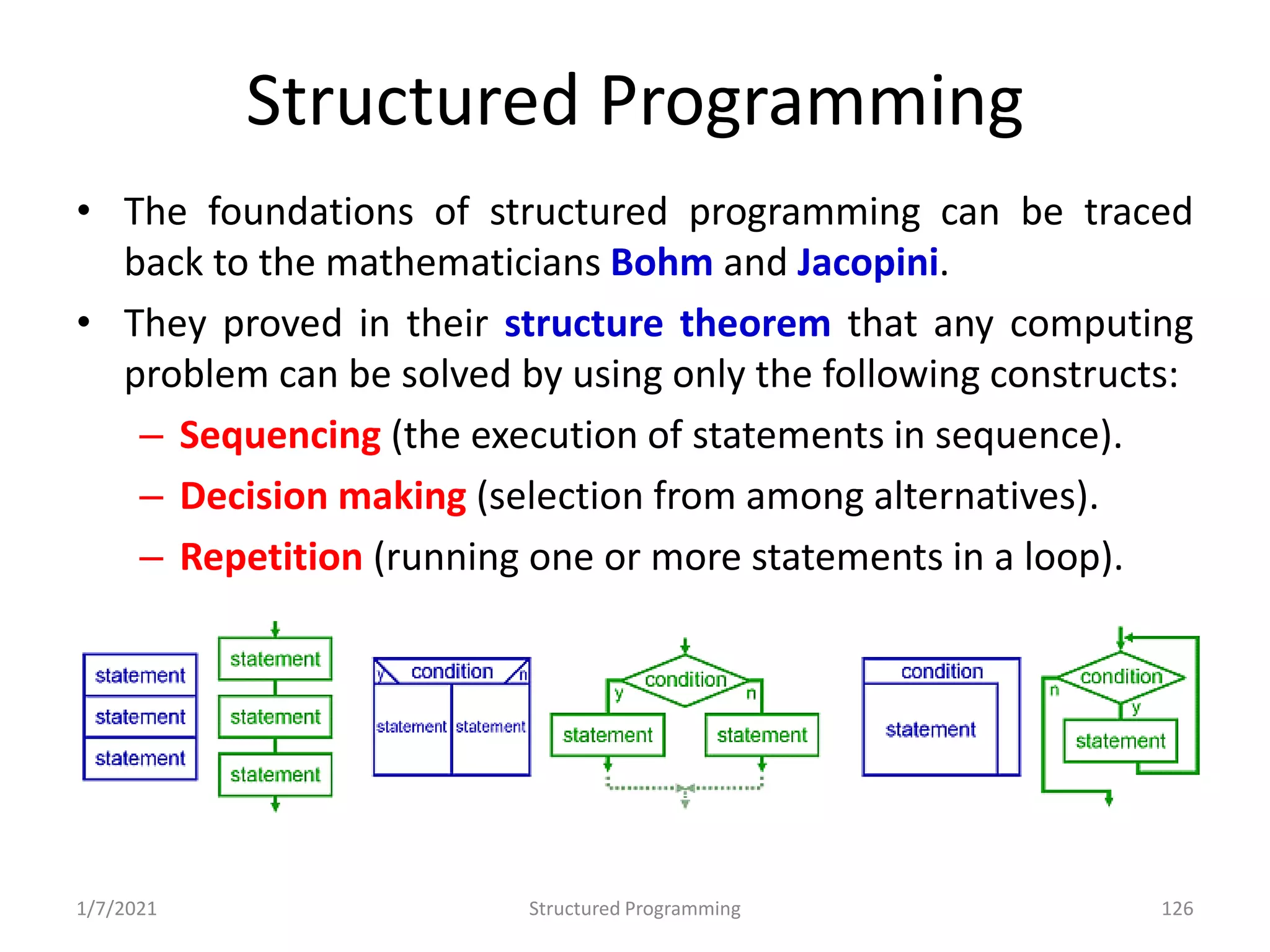
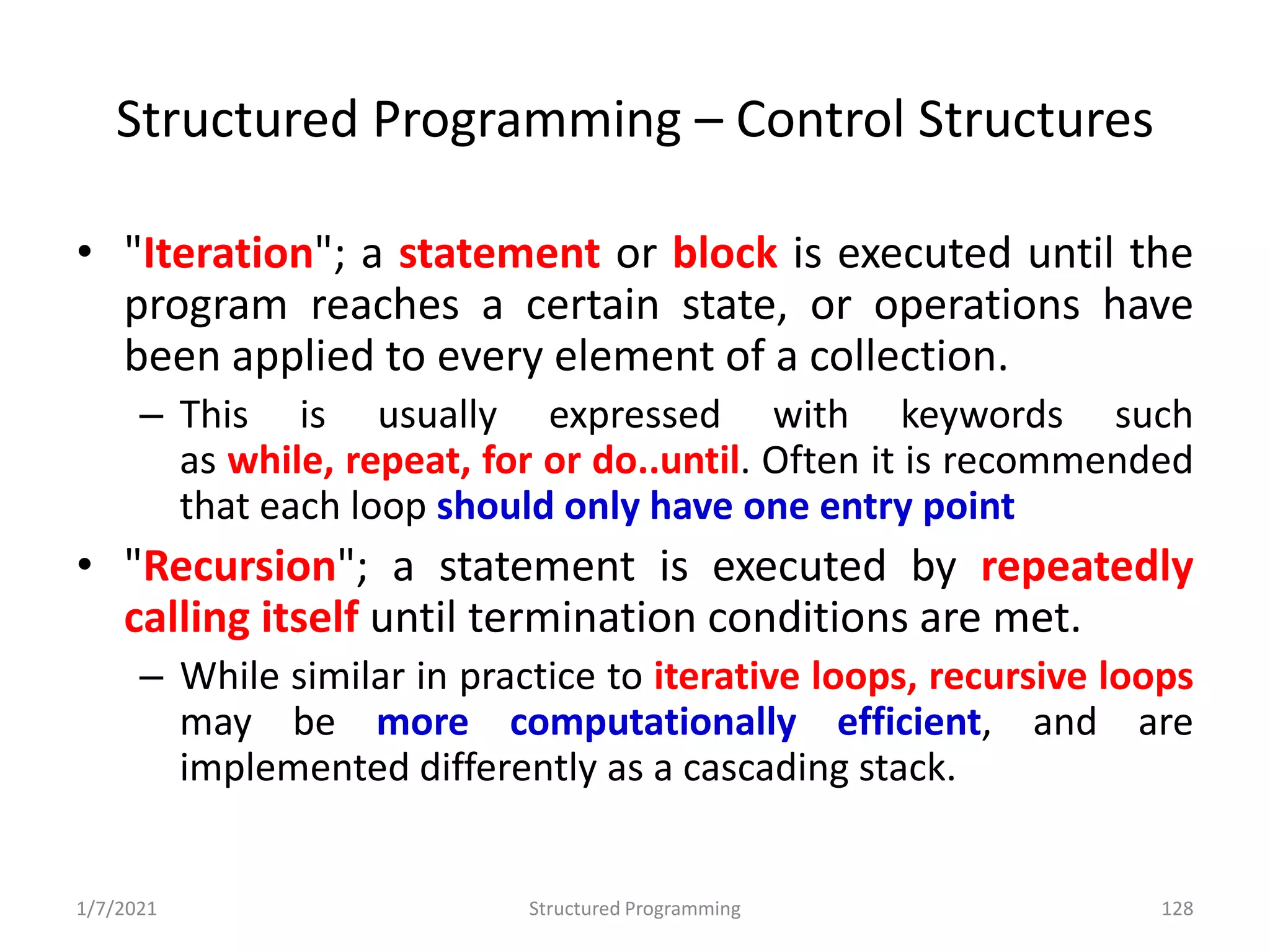
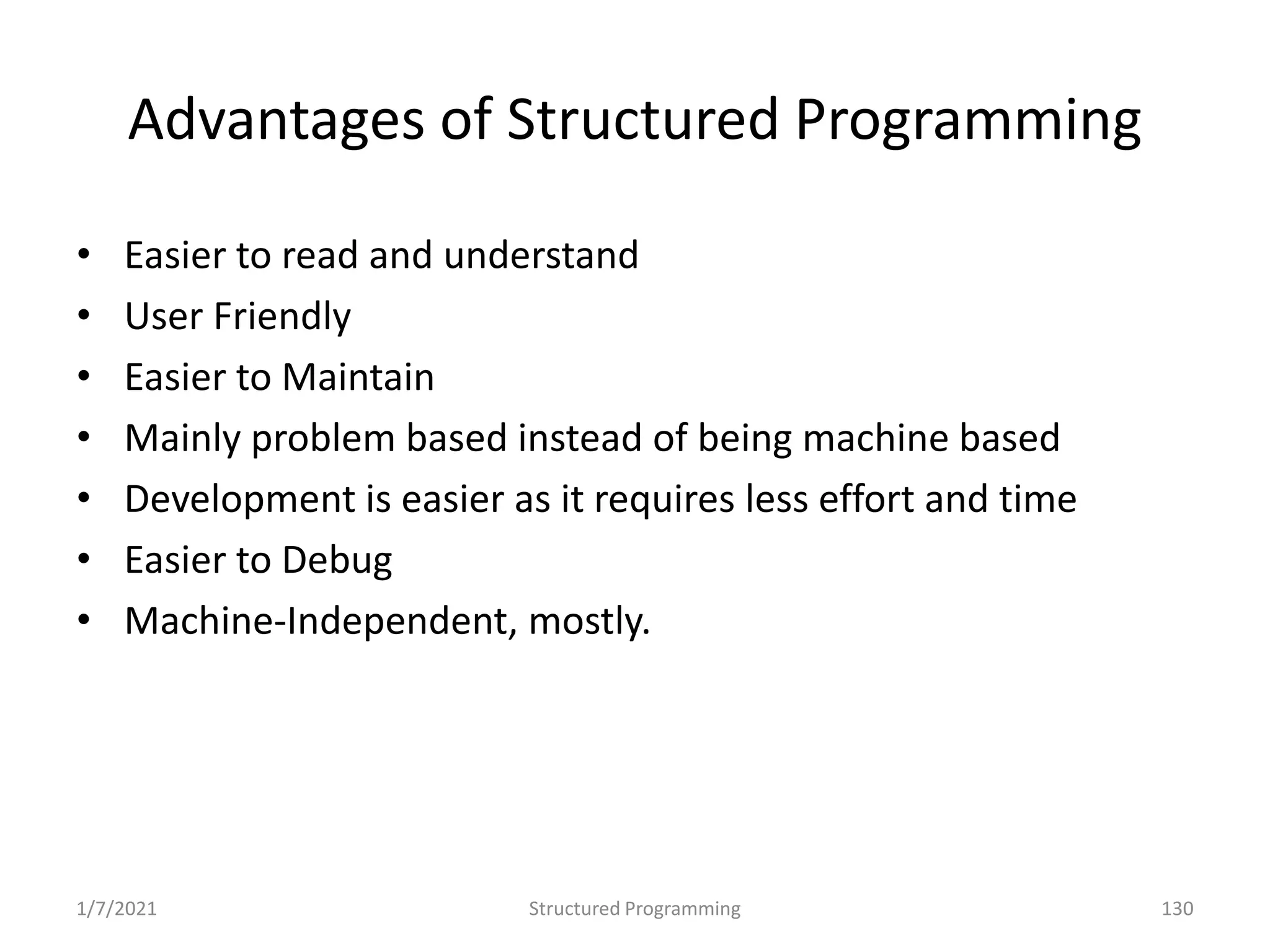
Overview of structured programming: clarity, maintainability, and uses control structures.


































































































































