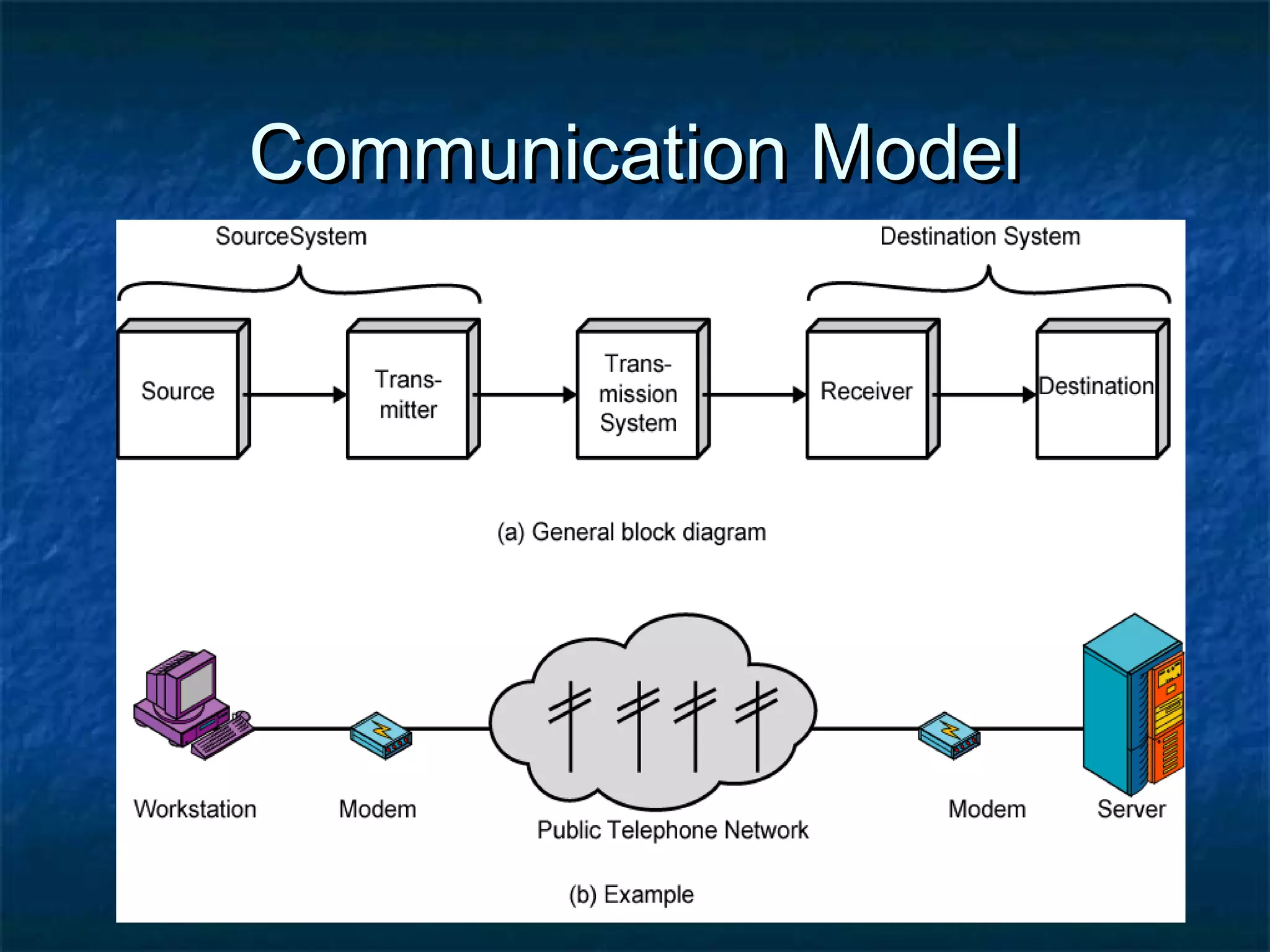
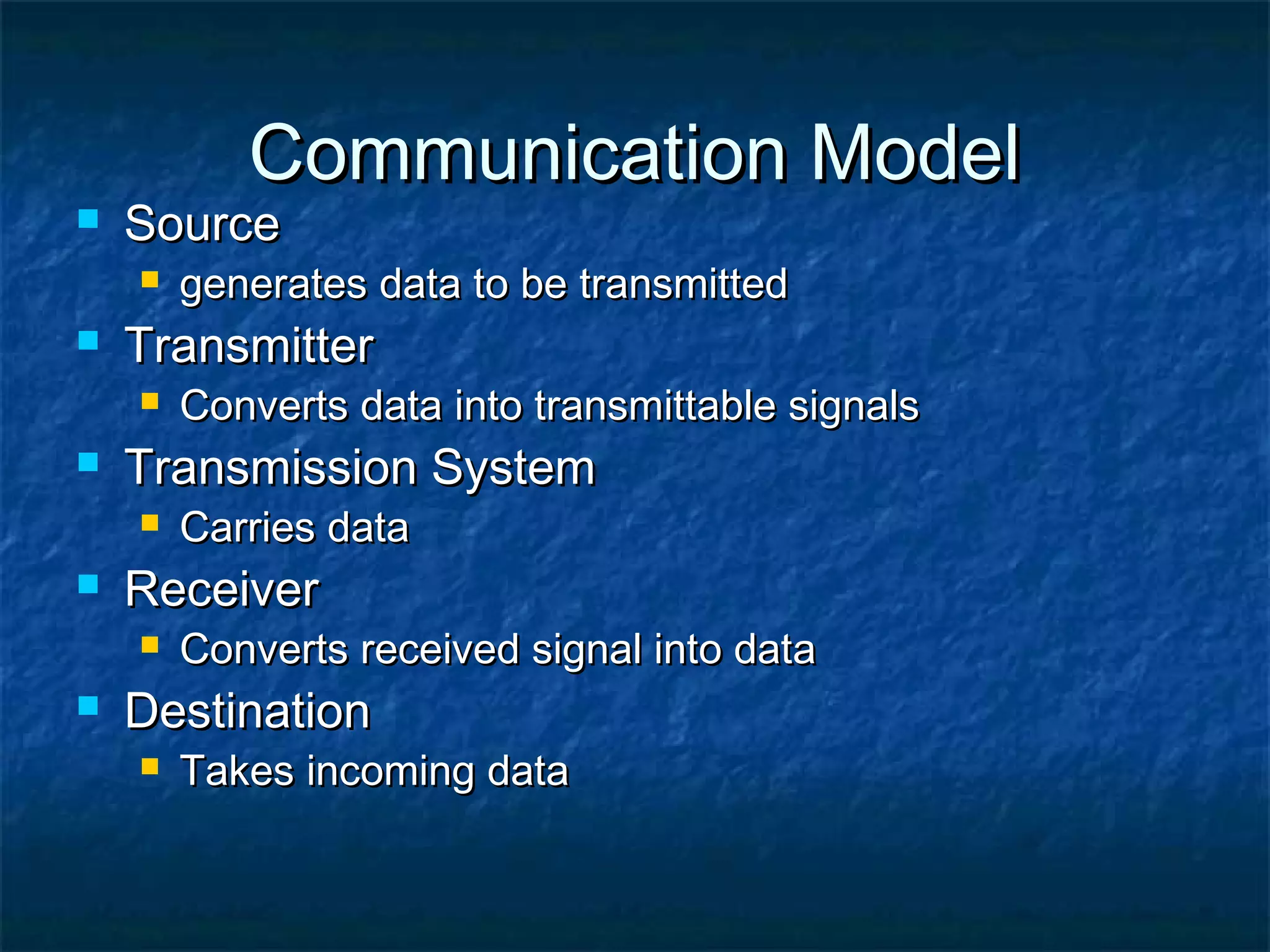
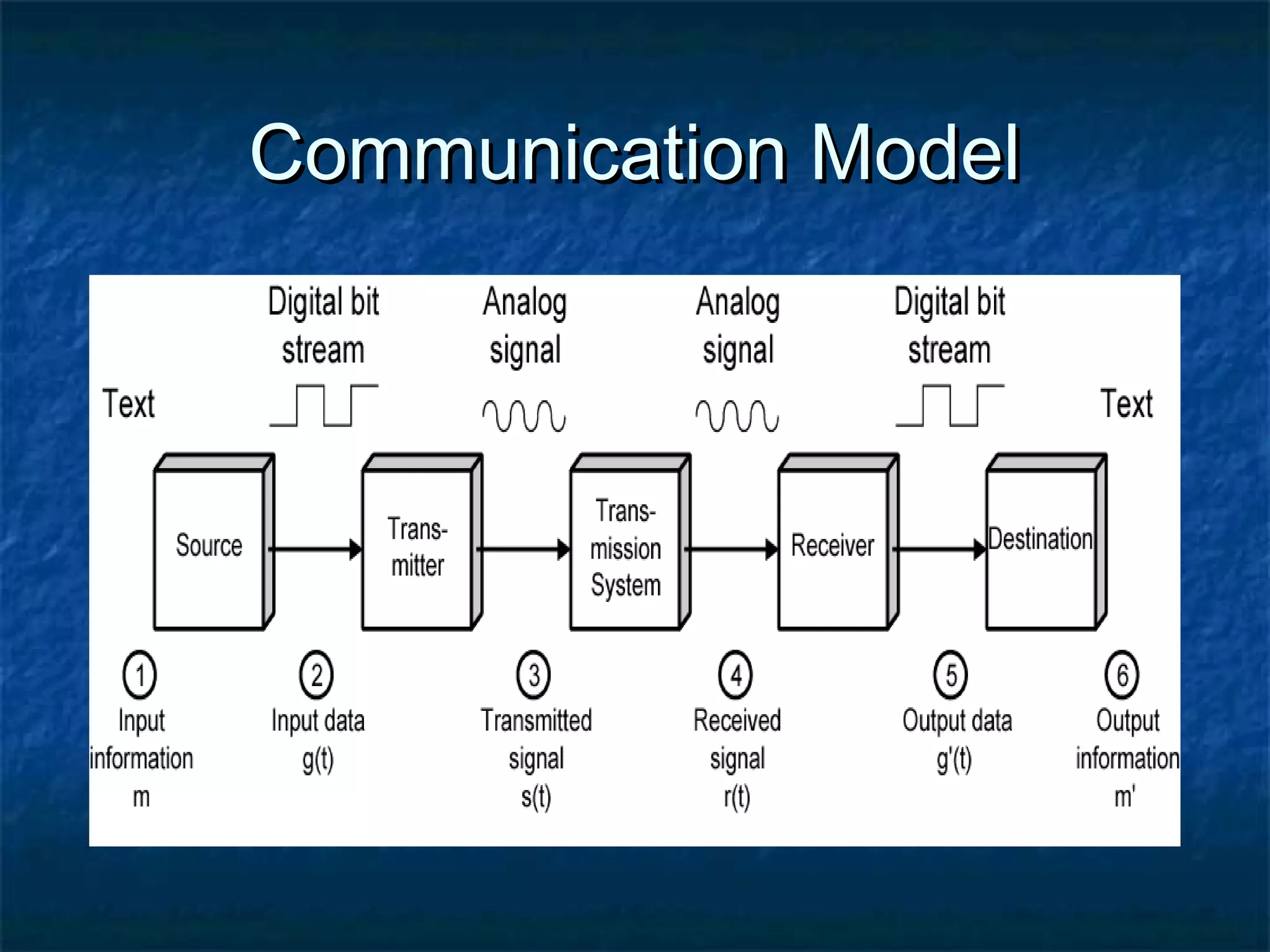
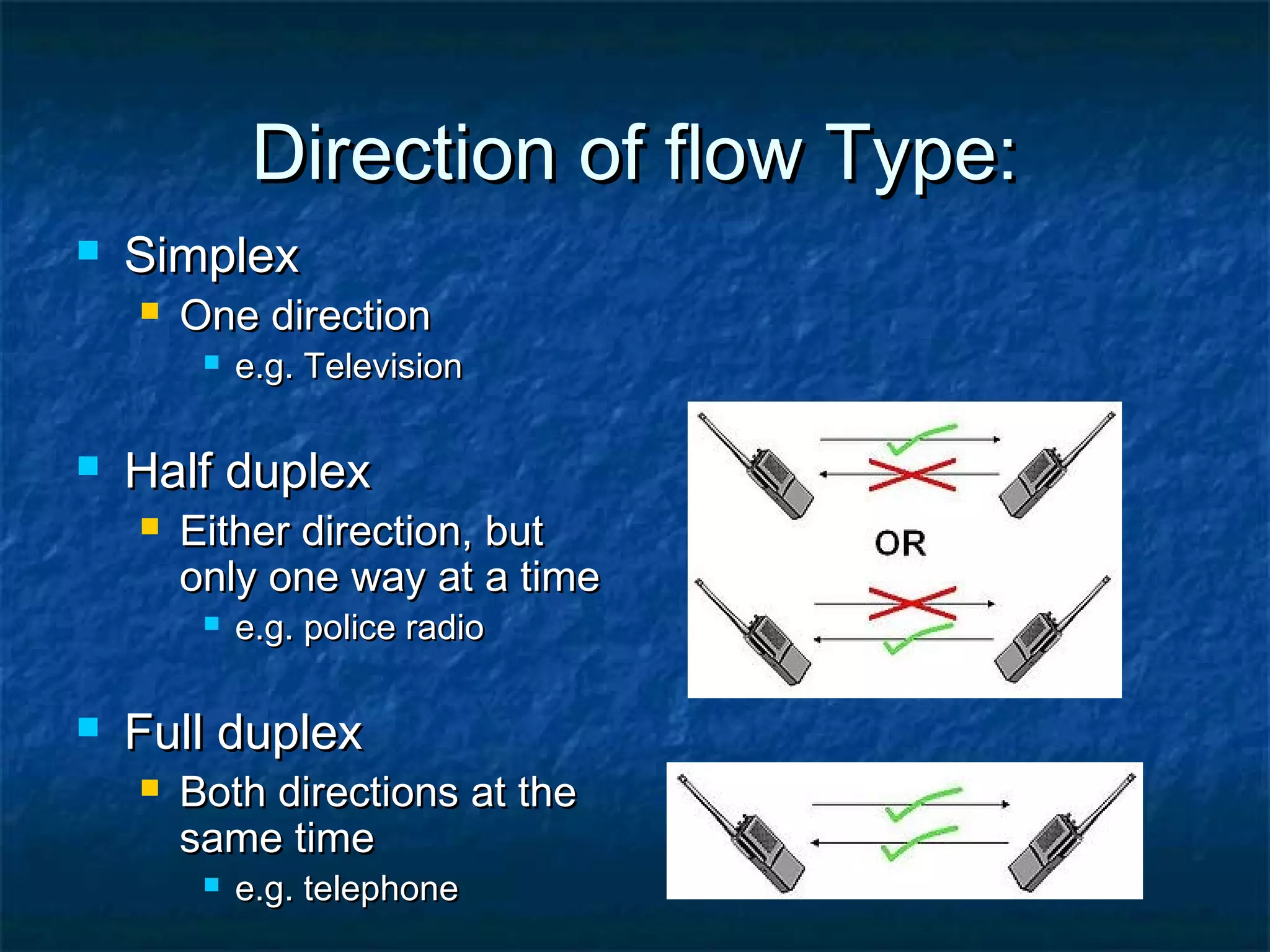
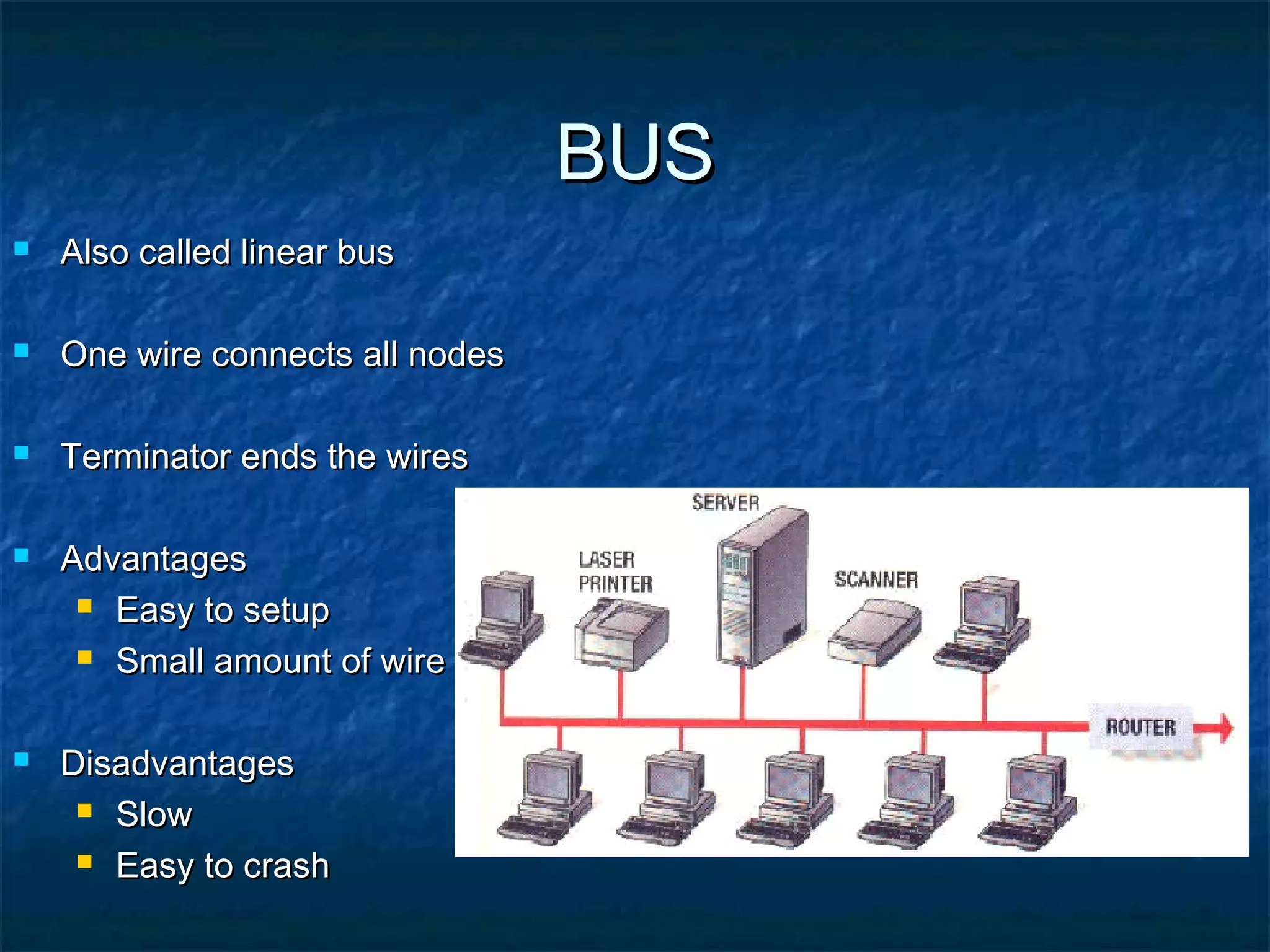
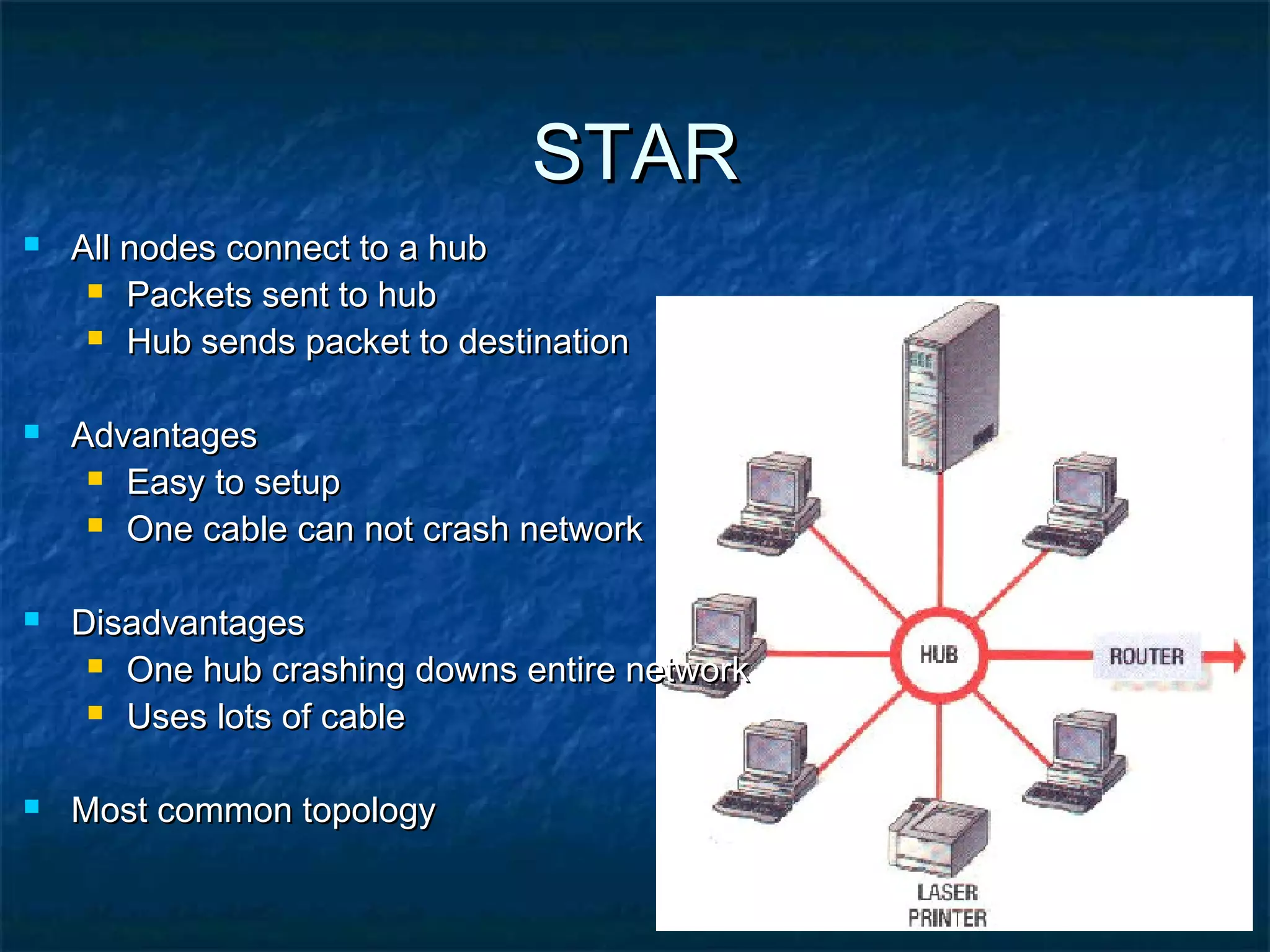
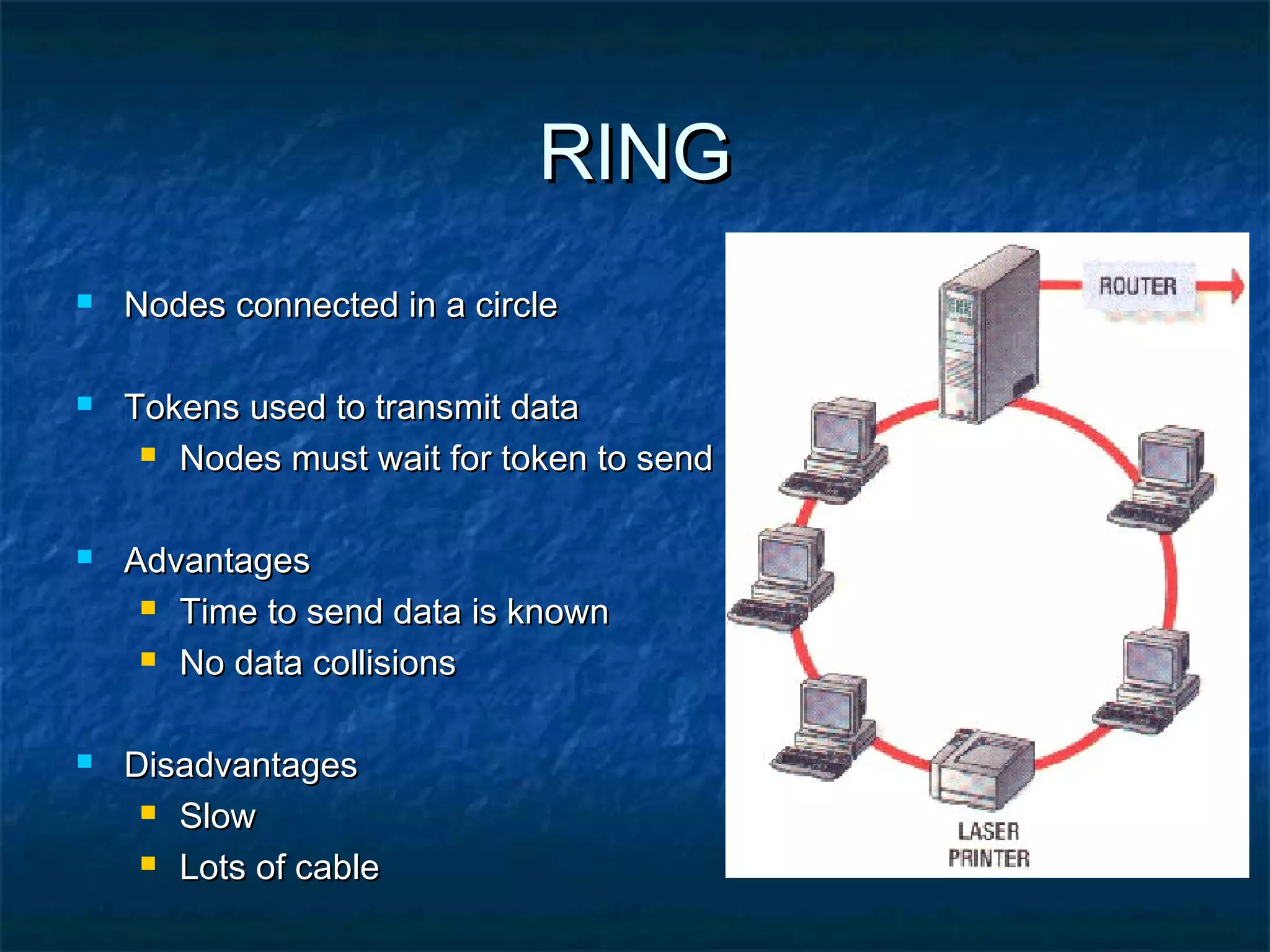
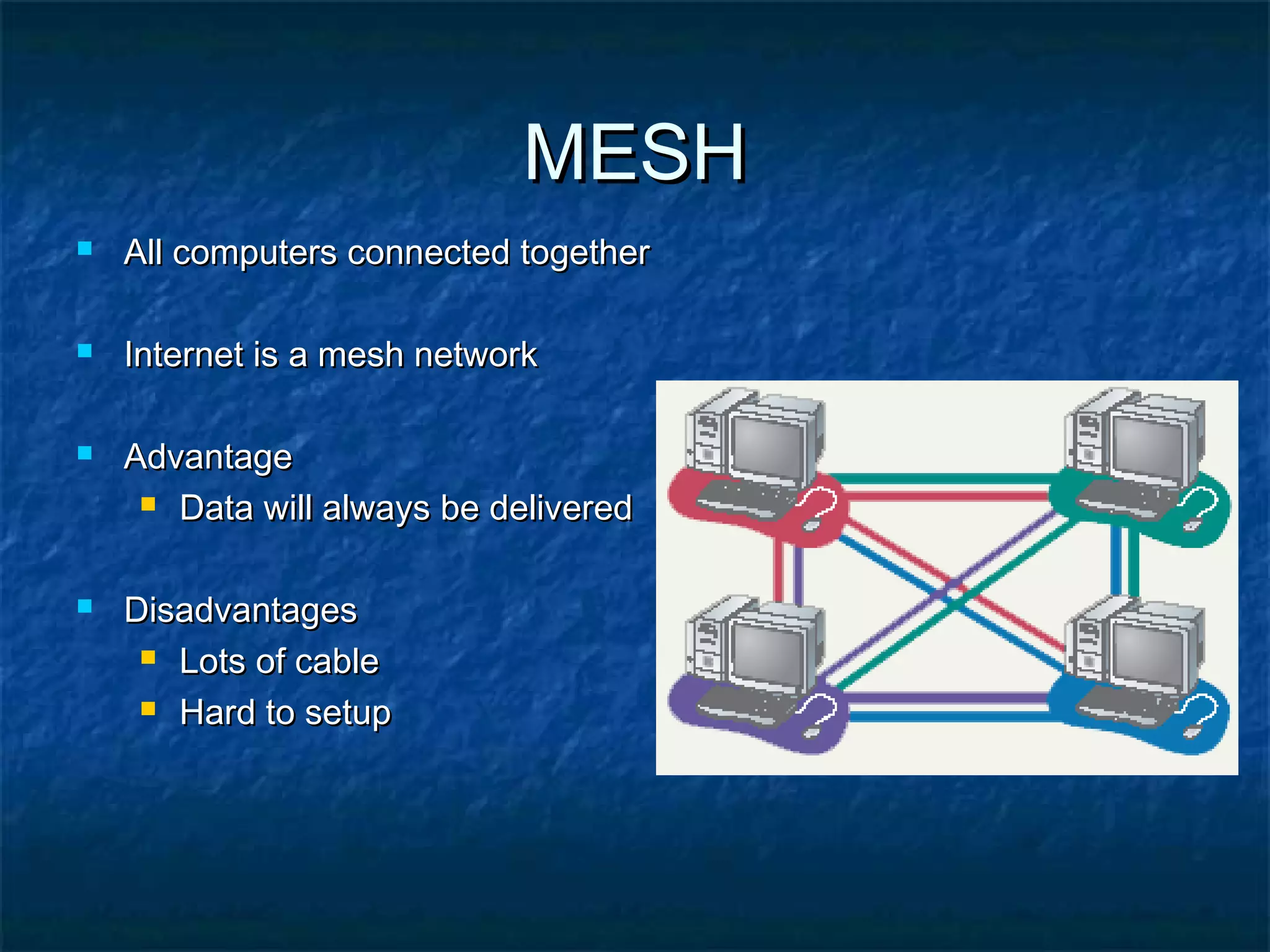
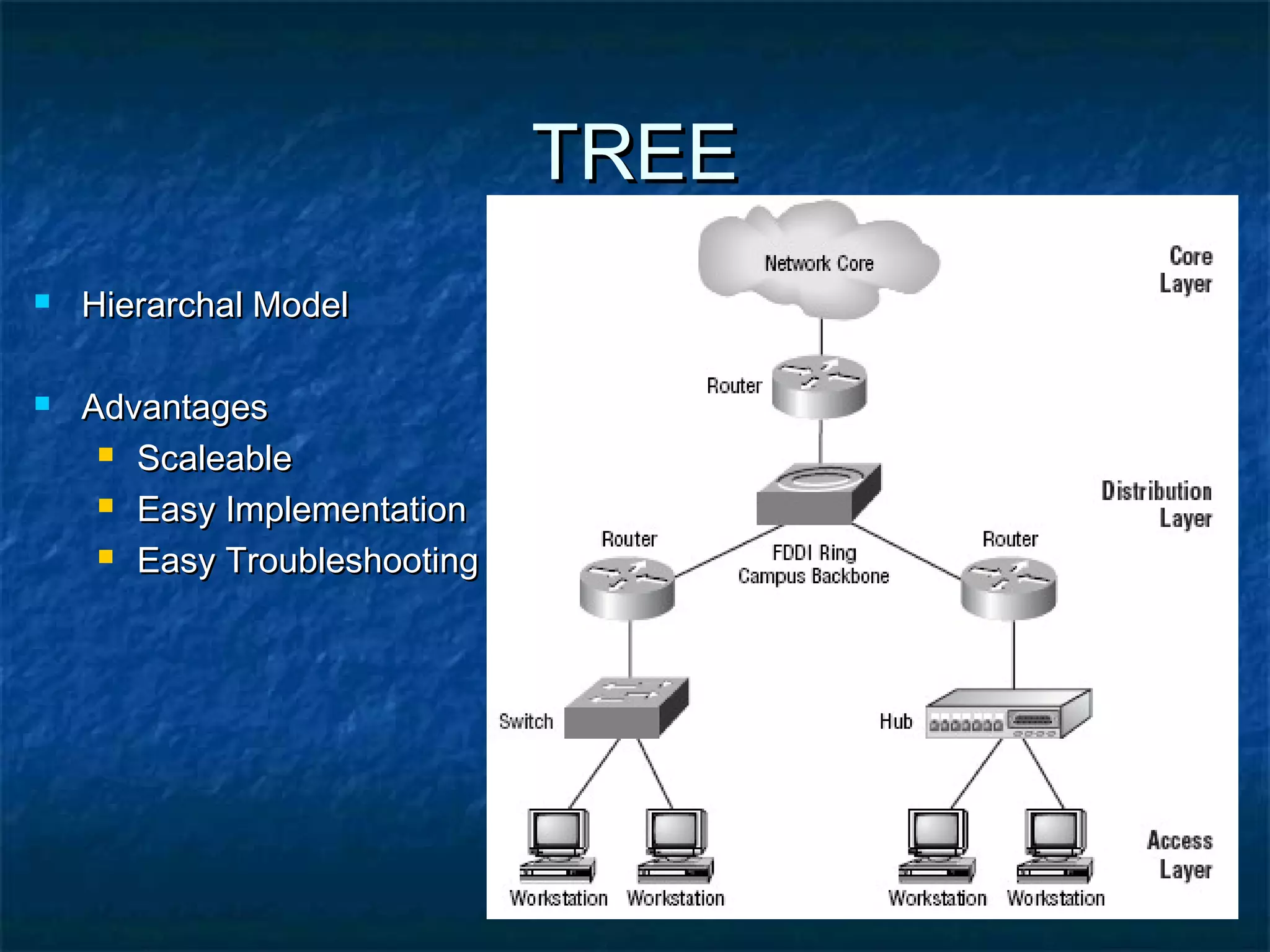
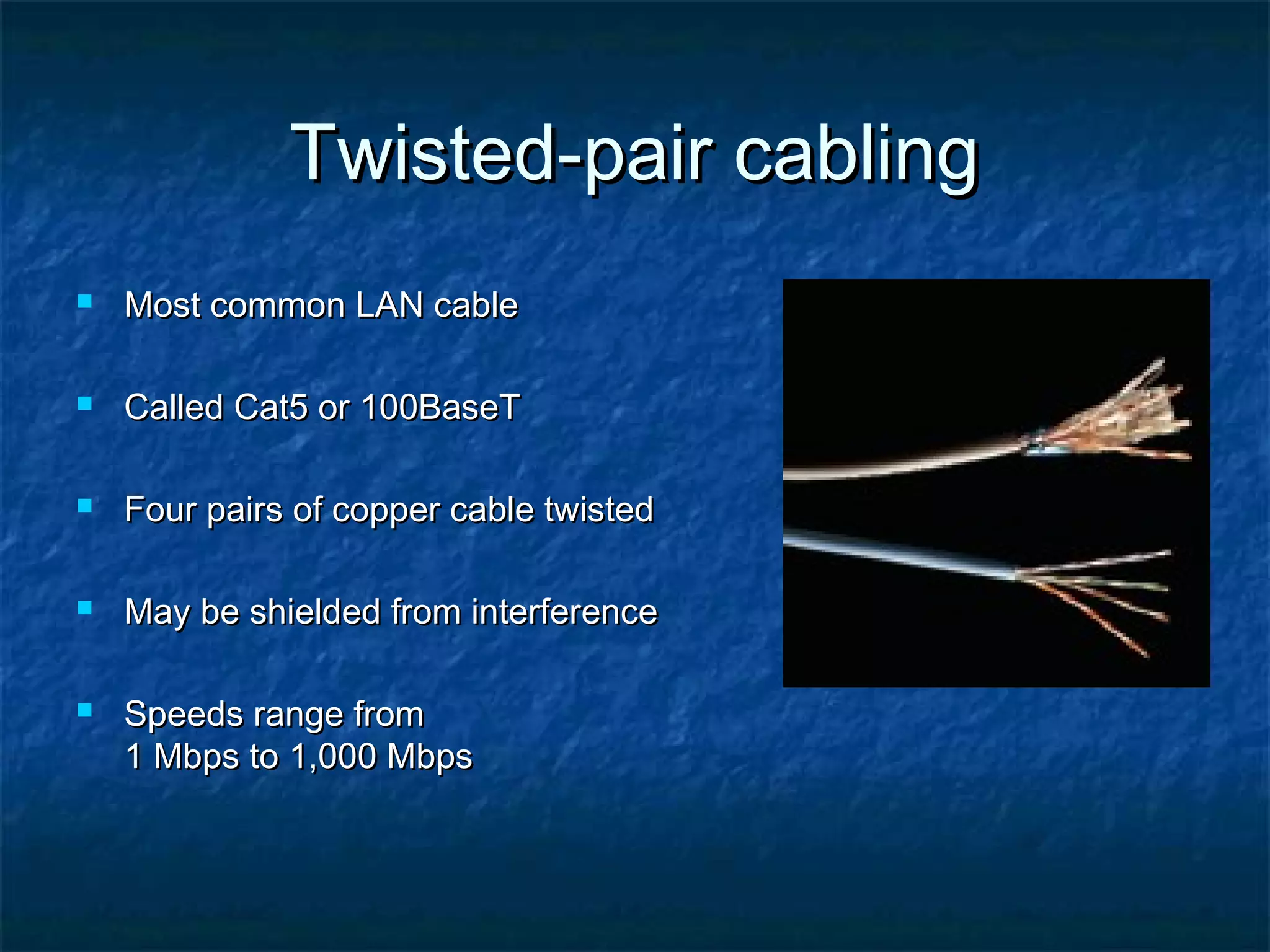
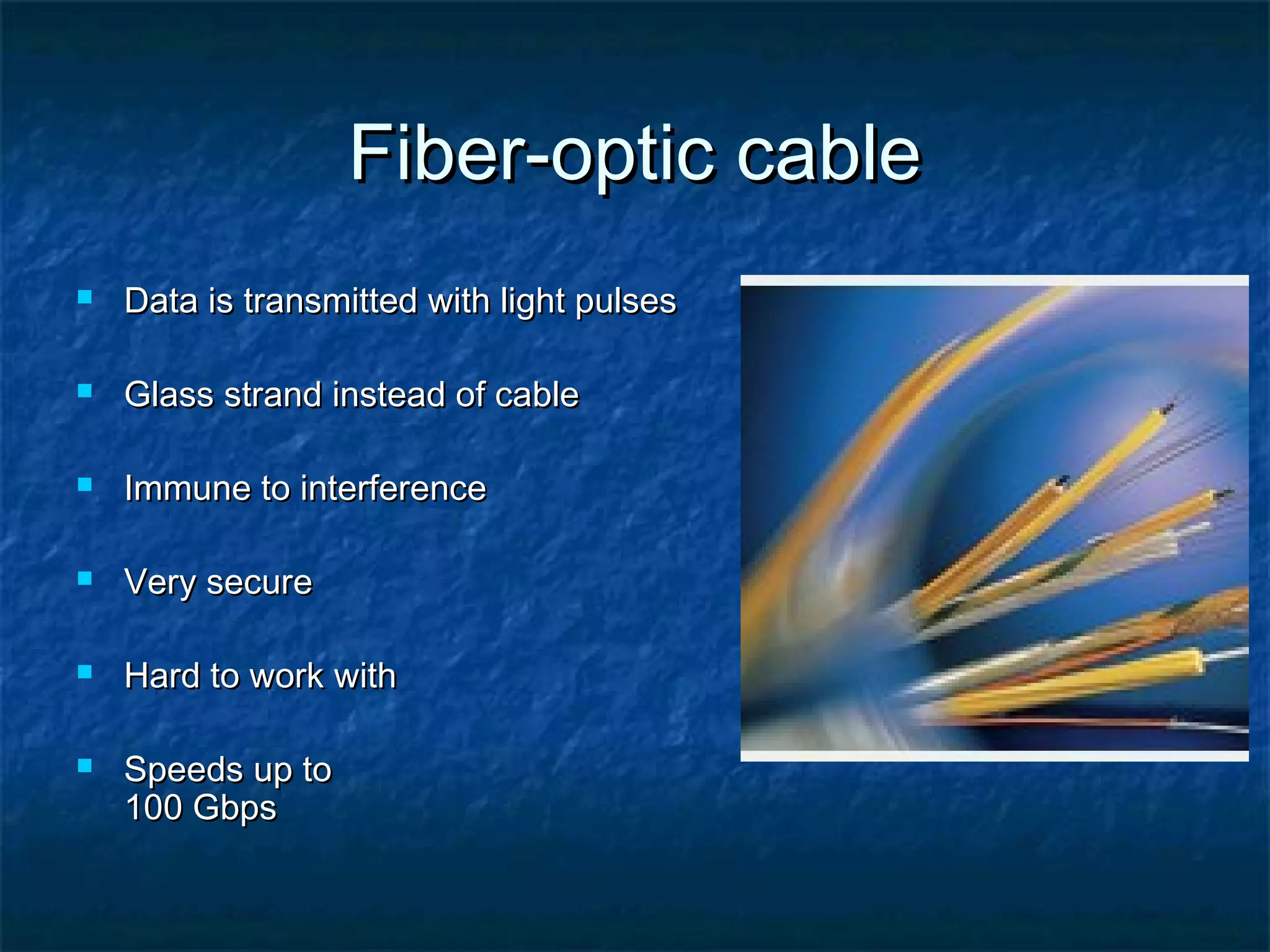
This document provides an overview of computer networks, including basic concepts, communication models, transmission modes, network classifications, topologies, and media. It defines a computer network as a group of interconnected computers that allows sharing of resources and information. The first major network was ARPANET, funded by the US Department of Defense. The document describes common network components, communication types, scales of networks from LAN to WAN to Internet, topologies like bus, star and ring, and media like twisted pair, coaxial and fiber optic cables. It also defines internetworking as connecting two or more networks, and intranets and extranets.