This document discusses input/output streams, error handling, and passing command line arguments in Java. It covers the basics of reading from and writing to files, the console, and networks using input/output streams. It also discusses how to handle exceptions using try/catch blocks and how to pass command line arguments to a Java program that will be stored in the main method's String array.




![UCSC 2003. All rights reserved.No parts of this material ma
• When an application is run with arguments,
Java stores the arguments as an array of as
strings & passes the array to the application’s
main() method.
eg:
public static void main(String arguments[]) {
// body of method
}
In here, arguments is the name of the array of strings that
contains list of arguments.
Handling Arguments in Java Application](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7-streamsanderrorhandlinginjava-161216133150/75/7-streams-and-error-handling-in-java-6-2048.jpg)
![UCSC 2003. All rights reserved.No parts of this material ma
Handling Arguments in Java Application…
• Inside the main() method, you can handle the
arguments your program was given,
– By iterating.
And
– Handling them in some manner.
eg:
class EchoArgs {
public static void main (String arguments[]) {
for (int i=0; i<arguments.length; i++) {
System.out.println(“Argument” + i + “:” +
arguments [i]);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7-streamsanderrorhandlinginjava-161216133150/75/7-streams-and-error-handling-in-java-7-2048.jpg)

![UCSC 2003. All rights reserved.No parts of this material ma
• All arguments passed to a Java
application are stored in an array of
strings.
• To treat them as something other than
strings, you must convert them.
• The following program takes any number of
numeric arguments & returns the sum & the
average of those arguments.
class SumAverage {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int sum = 0;
for (int I = 0; i<args.length; i++) {
Sum += args[i];
}
Handling Arguments in Java Application…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7-streamsanderrorhandlinginjava-161216133150/75/7-streams-and-error-handling-in-java-9-2048.jpg)
![UCSC 2003. All rights reserved.No parts of this material ma
System.out.println(“Sum is;” + sum);
System.out.println(“Average is:” +
(float) sum / args.length);
}
}
Output
SumAverage.java.6: Incompatible type for +=. Can’t convert
java.lang.String to int.
Sum += args[i];
• This error occurs the argument array is an array
of strings.
Handling Arguments in Java Application…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7-streamsanderrorhandlinginjava-161216133150/75/7-streams-and-error-handling-in-java-10-2048.jpg)
![UCSC 2003. All rights reserved.No parts of this material ma
• You have to convert them from strings to
integers using a class method for the
Integer class called parseInt.
Sum += Integer.parseInt(args[i]);
• By applying the following inputs to the
example we can run the program.
• Input
Java SumAverage 123
• Output
Sum is : 6
Average is : 2
Handling Arguments in Java Application…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7-streamsanderrorhandlinginjava-161216133150/75/7-streams-and-error-handling-in-java-11-2048.jpg)











![UCSC 2003. All rights reserved.No parts of this material ma
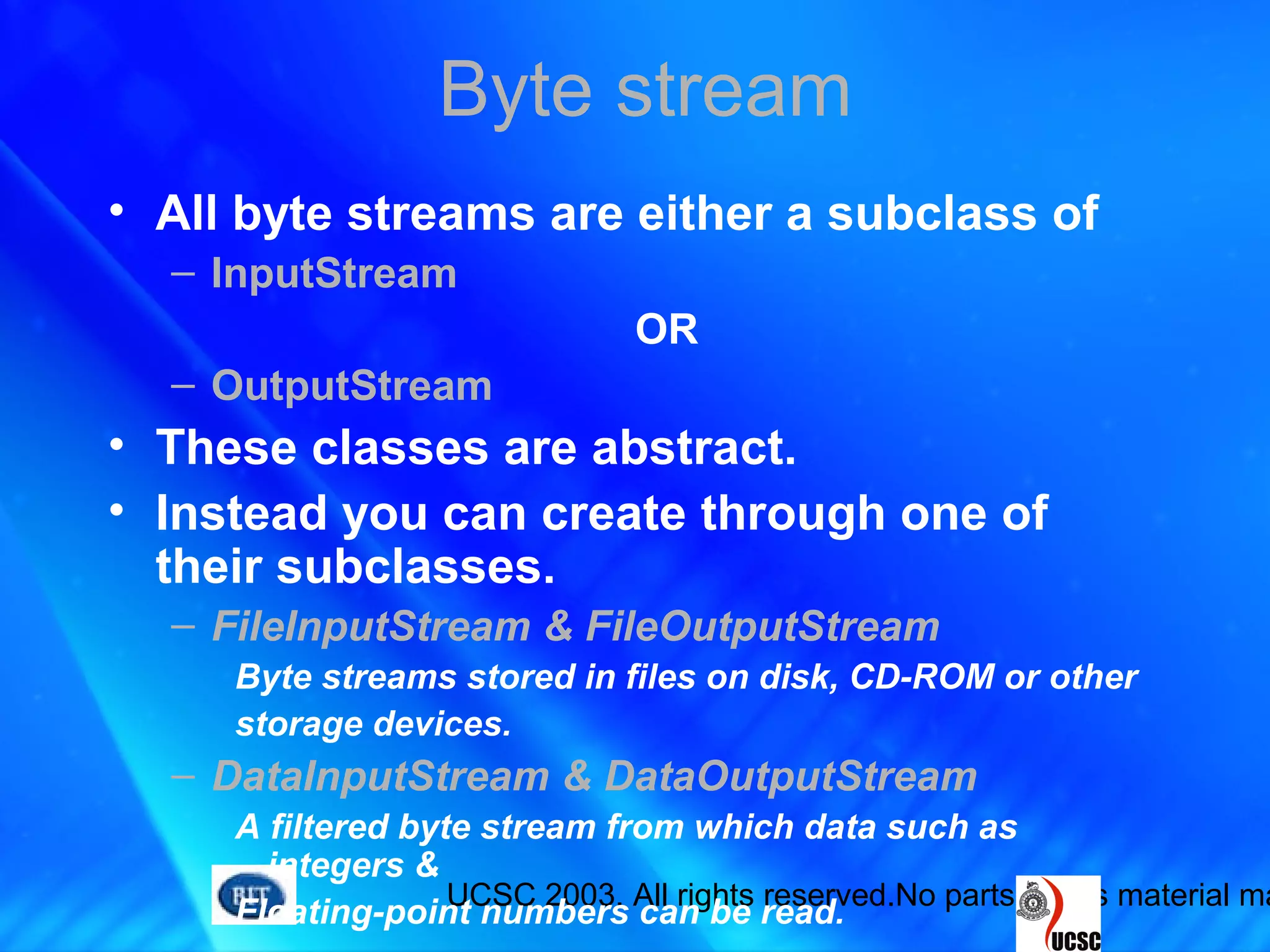
• To read more than one byte of data from
the stream, call its read(byte[], int, int)
method.
Byte stream……….](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7-streamsanderrorhandlinginjava-161216133150/75/7-streams-and-error-handling-in-java-25-2048.jpg)
![UCSC 2003. All rights reserved.No parts of this material ma
• File Output Streams
– A file output stream can be created with the
FileOutputStream(String) constructor.
– You can create a file output stream that
appends data after the end of an existing file
with the FileOutputStream(String, boolean)
constructor.
– The file output stream’s write(int) method is
used to write bytes to the stream.
– To write more than one byte, the
write(byte[],int,int) method can be used.
Byte stream……….](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7-streamsanderrorhandlinginjava-161216133150/75/7-streams-and-error-handling-in-java-26-2048.jpg)