The document discusses Java I/O and provides an overview of key concepts like streams, readers/writers, files, serialization, and tokenization. It describes the different types of input/output streams, readers, and writers in Java and best practices for working with them. Examples are provided to demonstrate reading from and writing to files, streams, and using serialization and tokenization.




![Standard IO Reading from StandardInput (see Echo.java) System.in (Raw IOStream) Writing to Standard Output System.out (PrintStream) Standard Error System.err (PrintStream) Redirecting standard IO [see: Redirecting.java]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handling-io-in-java-12663/75/IO-In-Java-5-2048.jpg)
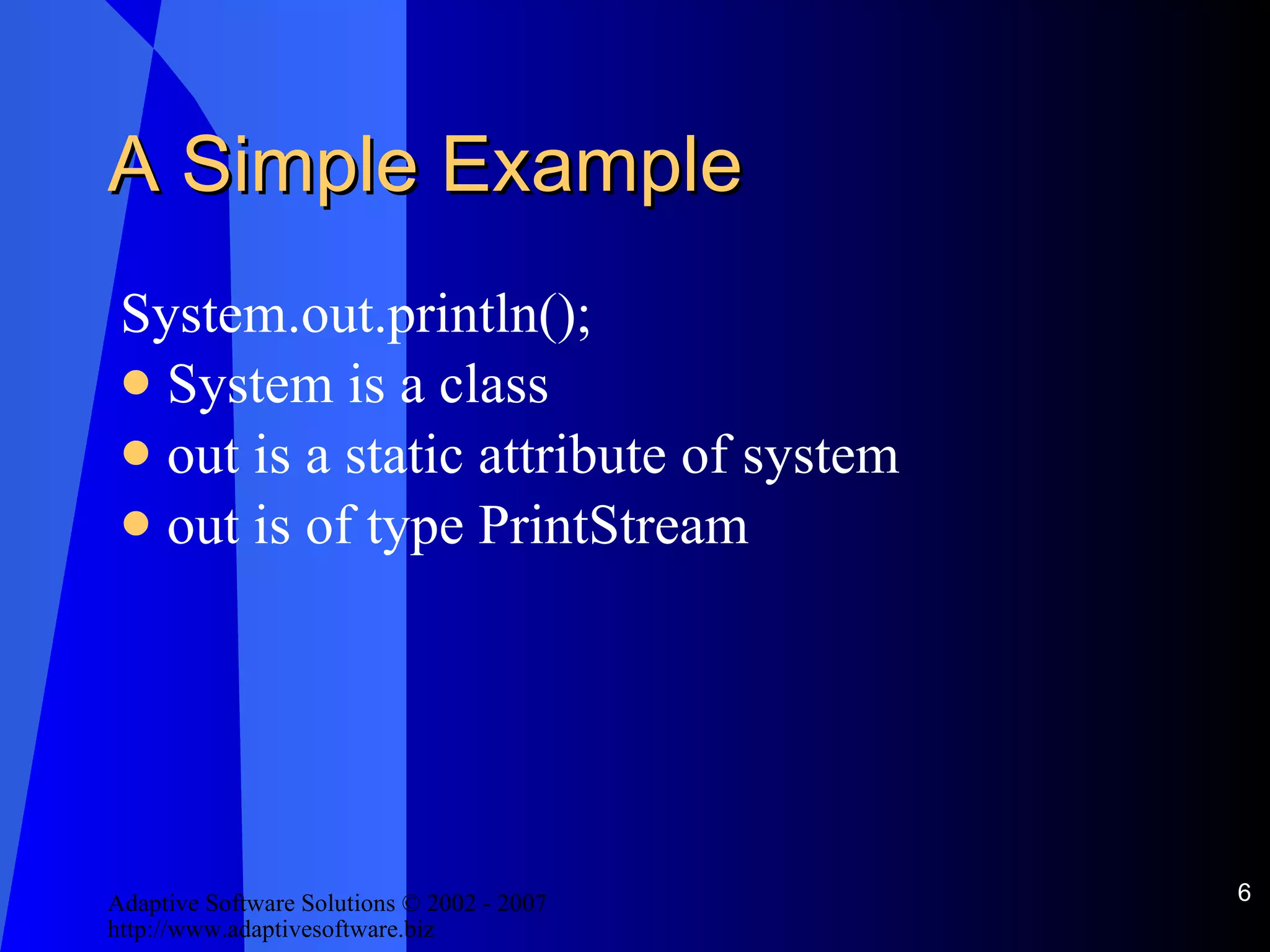
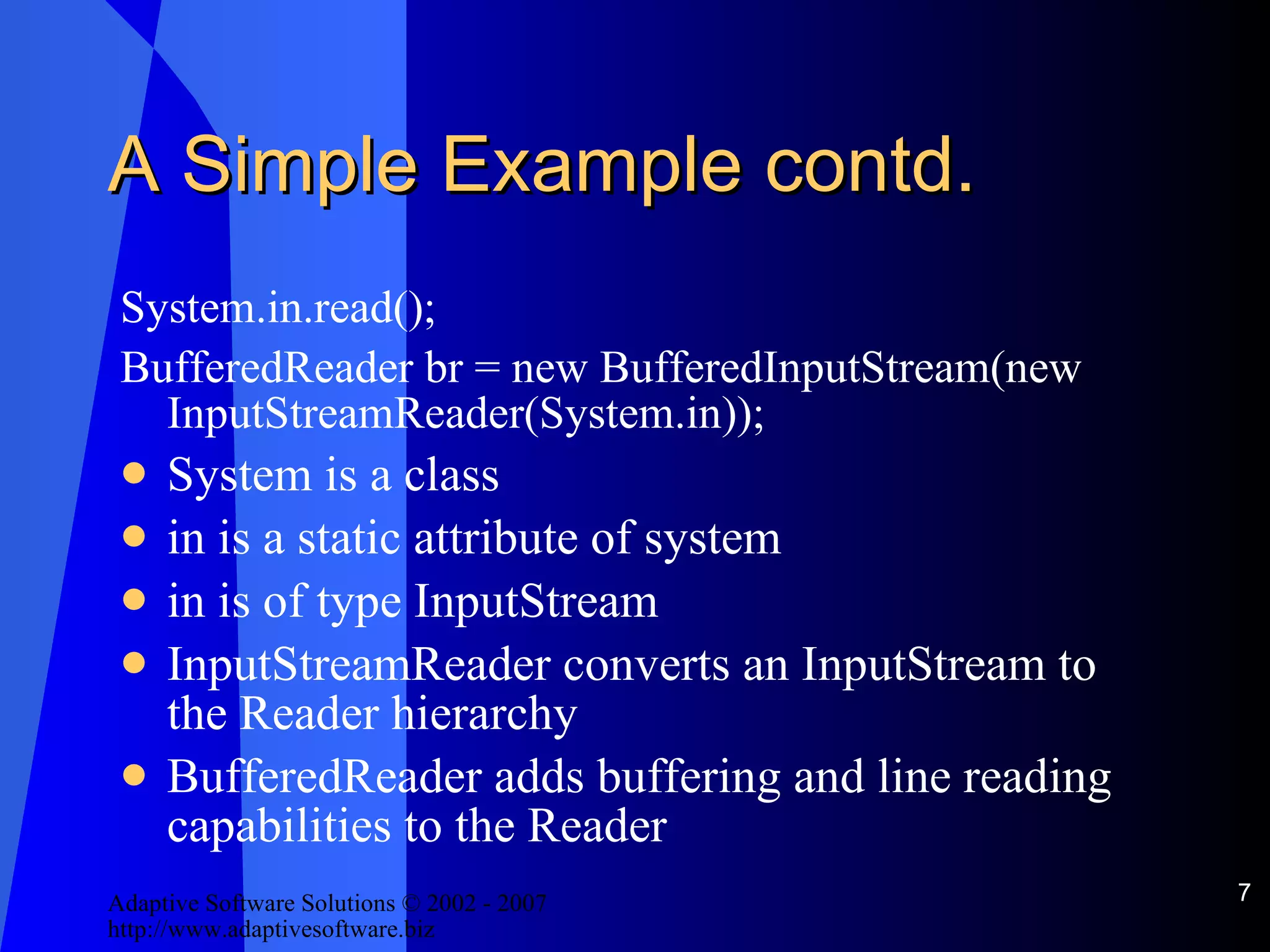


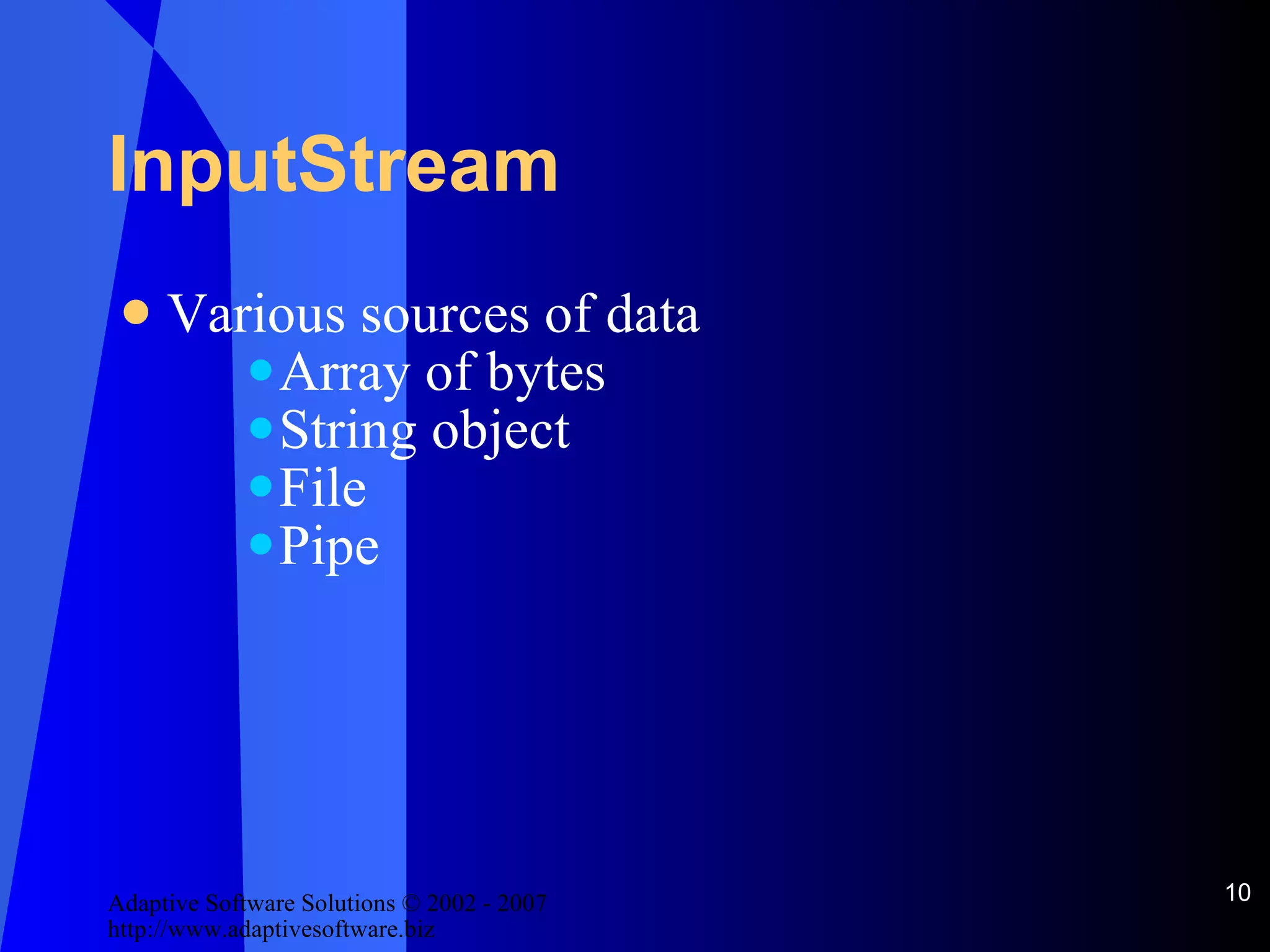
![InputStream See [StreamExample.java]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handling-io-in-java-12663/75/IO-In-Java-11-2048.jpg)
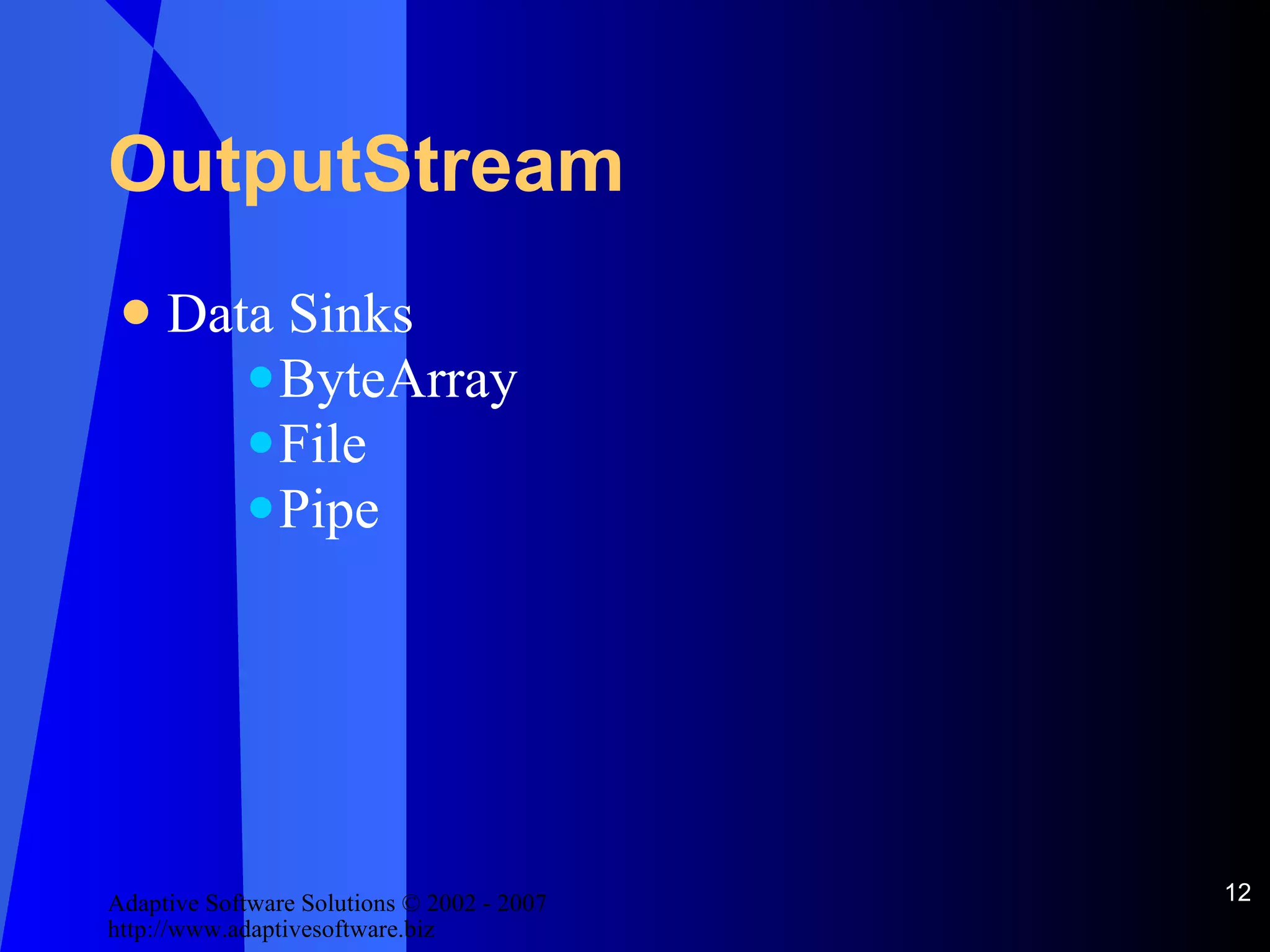
![OutputStream See [StreamExample.java]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handling-io-in-java-12663/75/IO-In-Java-13-2048.jpg)





![Object Serialization - 2 Serializing objects ObjectOutputStream Deserializing objects ObjectInputStream Remember no constructors are called see [SerializationExample.java]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handling-io-in-java-12663/75/IO-In-Java-21-2048.jpg)


![String Tokenizer Tokenizes a String We must define delimiting characters Throws an Exception if we go beyond the String size. See [StringTokenizingExample.java] It is recommended to use the split() method in String See [StringSplitExample.java]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handling-io-in-java-12663/75/IO-In-Java-24-2048.jpg)



![Using Stream Tokenizer Create an instance of StreamTokenizer Set up tables and flags Loop through the stream calling nextToken until a TT_EOF is returned. See [StreamTokenizingExample.java]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handling-io-in-java-12663/75/IO-In-Java-28-2048.jpg)

