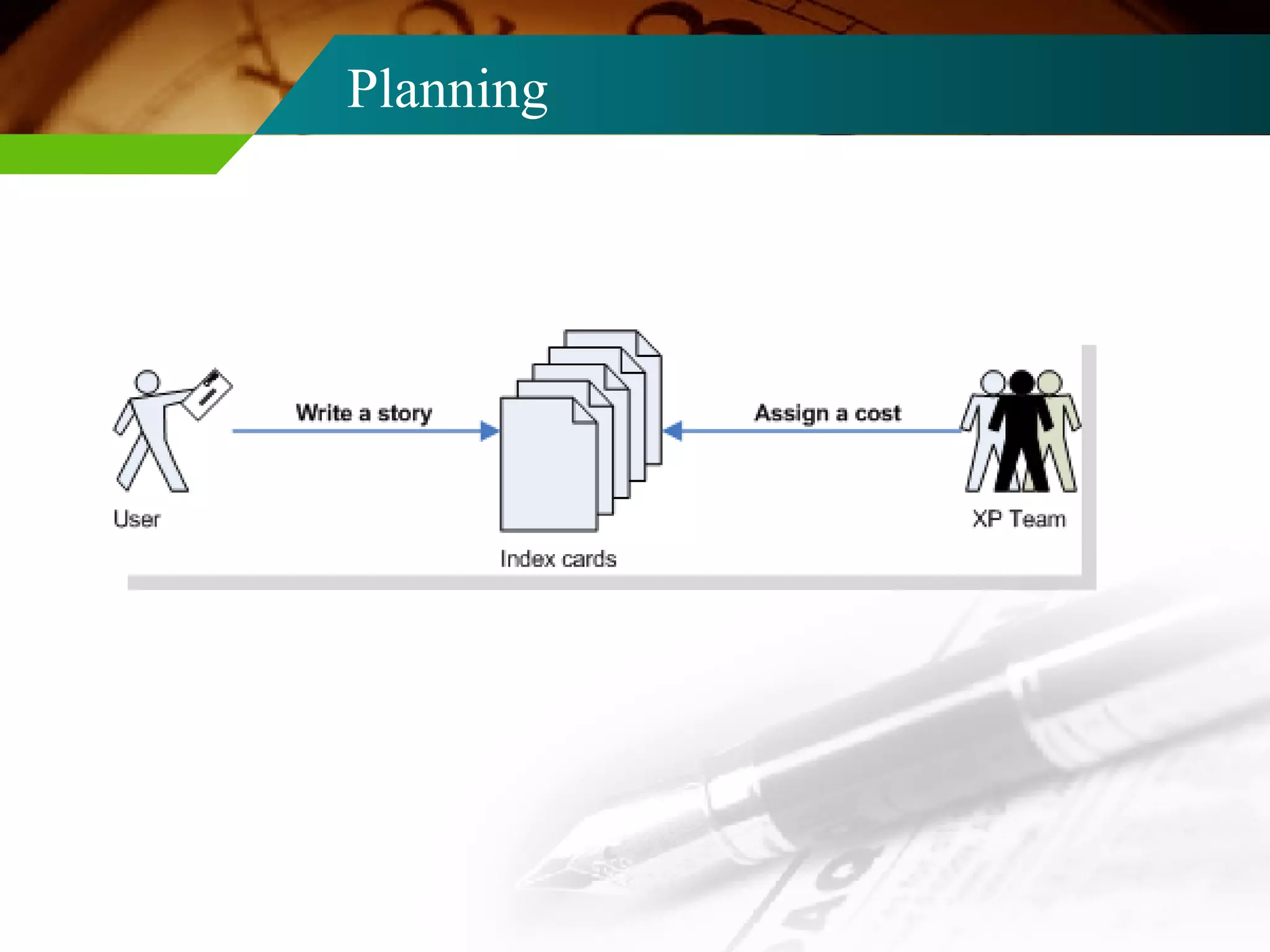
The document provides an overview of Extreme Programming (XP), the most widely used agile development process originally proposed by Kent Beck. It discusses the key practices of XP including planning with user stories, small iterative releases, simple design practices like CRC cards, test-driven development, pair programming, continuous integration, and collective code ownership. The document notes that XP works well for projects with dynamically changing requirements, risky projects, or small development groups of up to 100 people.
![Agile development Extreme Programming (XP) Abder-Rahman Ali M.S.Software Engineering DePaul CTI [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/agile-development-ultimate-slides-1198295615697276-4/75/Agile-Development-Ultimate-Slides-1-2048.jpg)