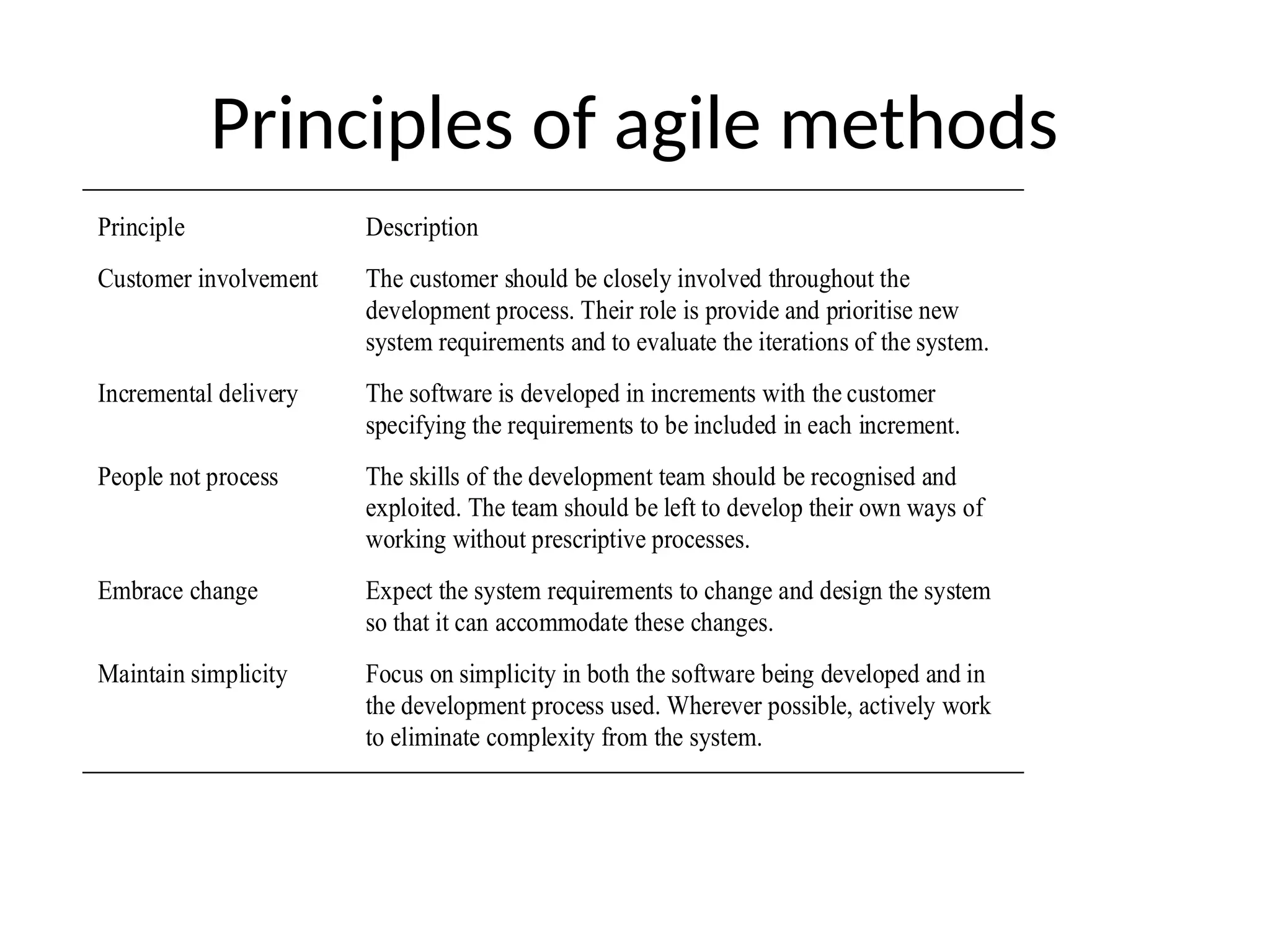
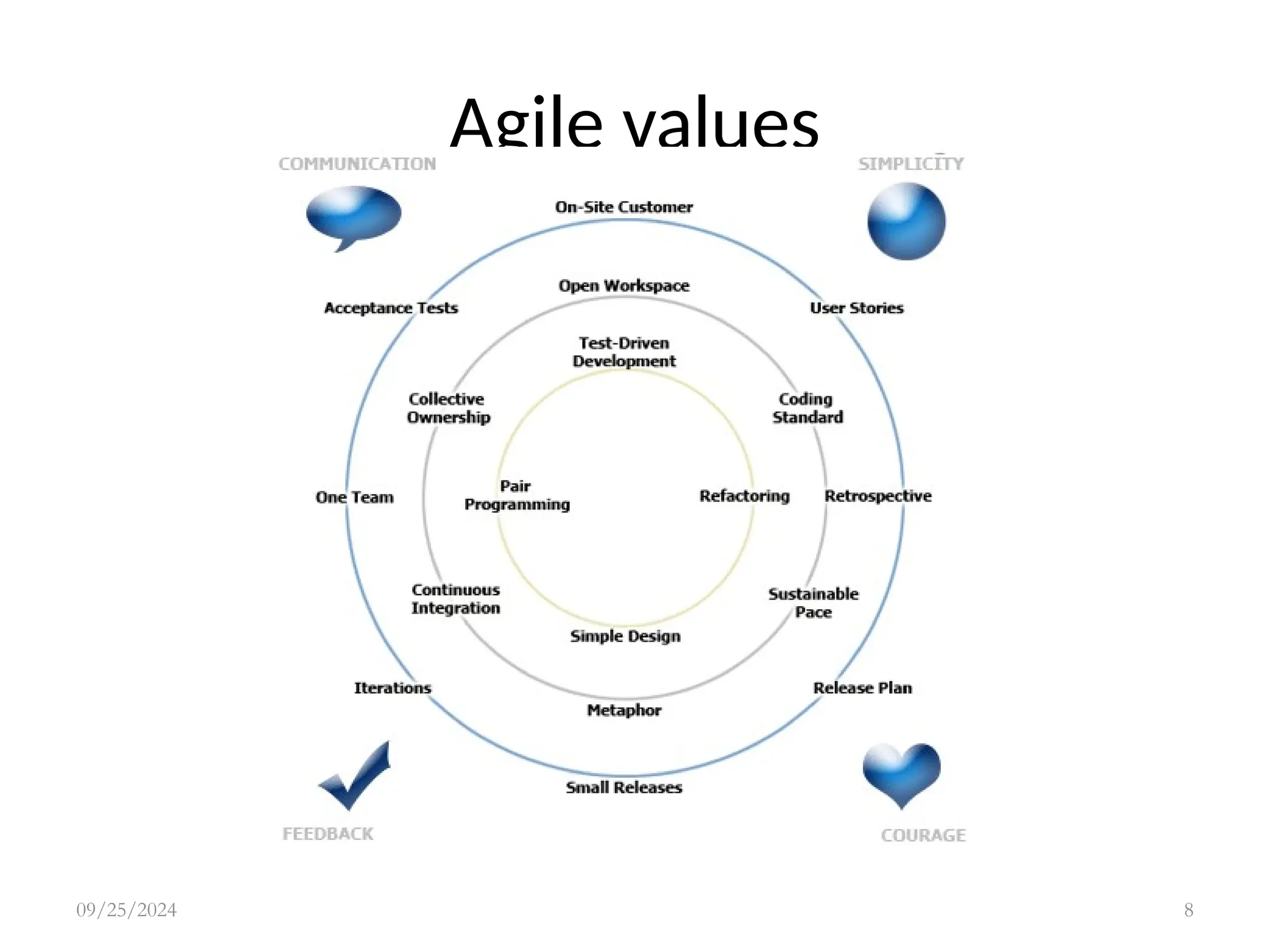
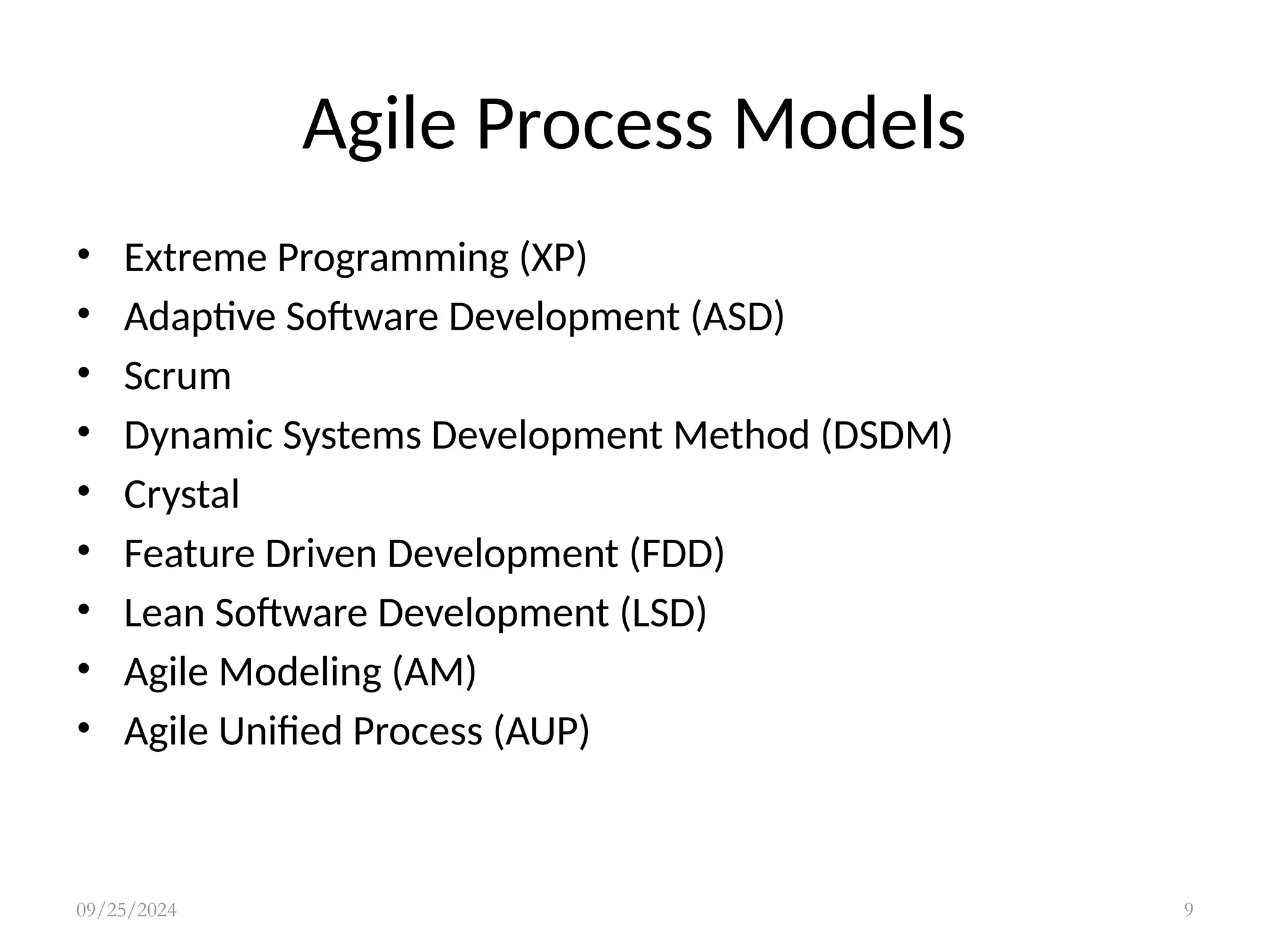
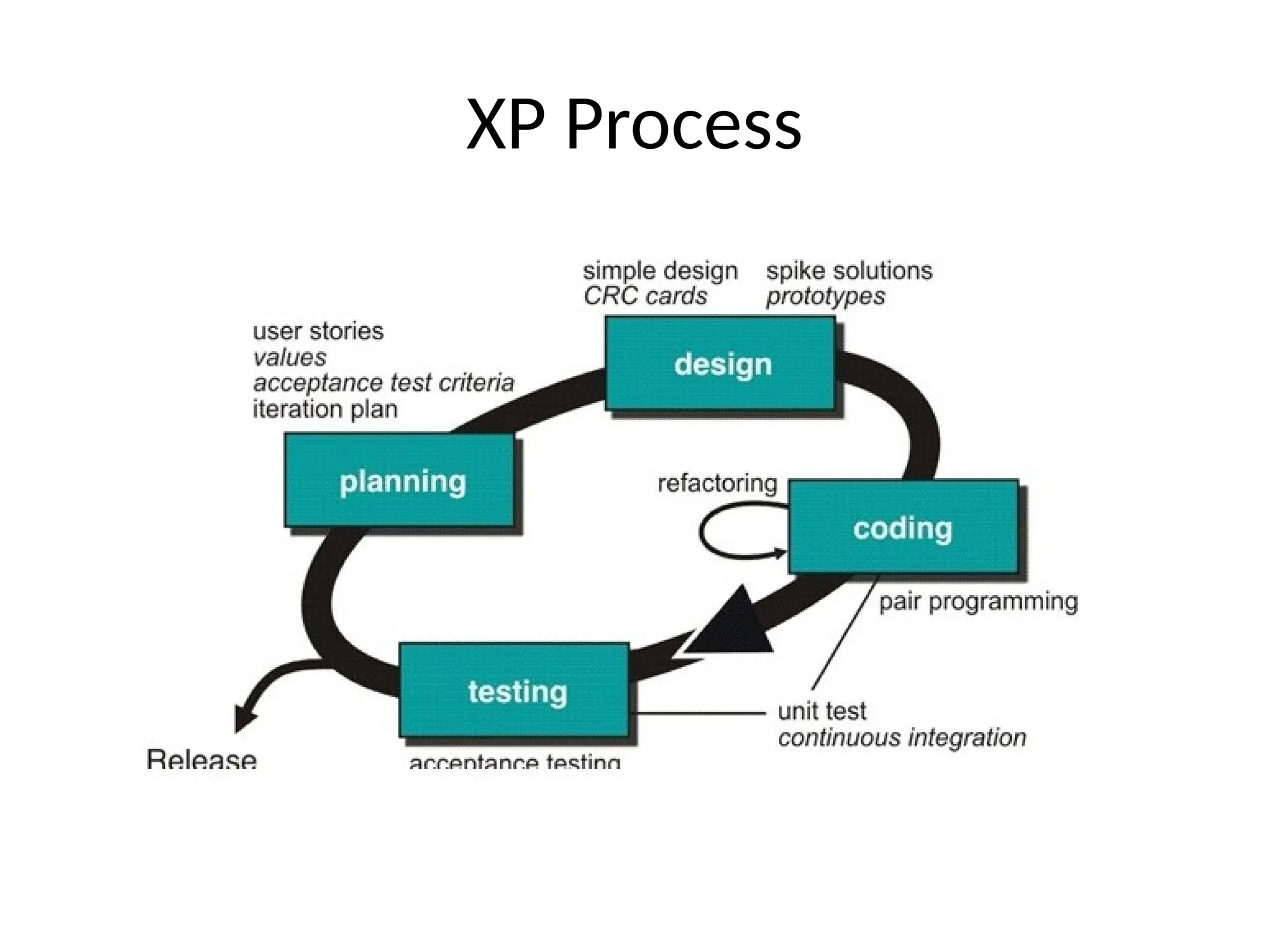
Agile modeling methods focus on delivering working software quickly through iterative development while minimizing design overheads. Key principles include customer involvement, incremental delivery, embracing change, and maintaining simplicity, emphasizing teamwork and flexibility. Although agile methods can enhance responsiveness and efficiency, challenges such as customer engagement and managing multiple stakeholder priorities can arise.