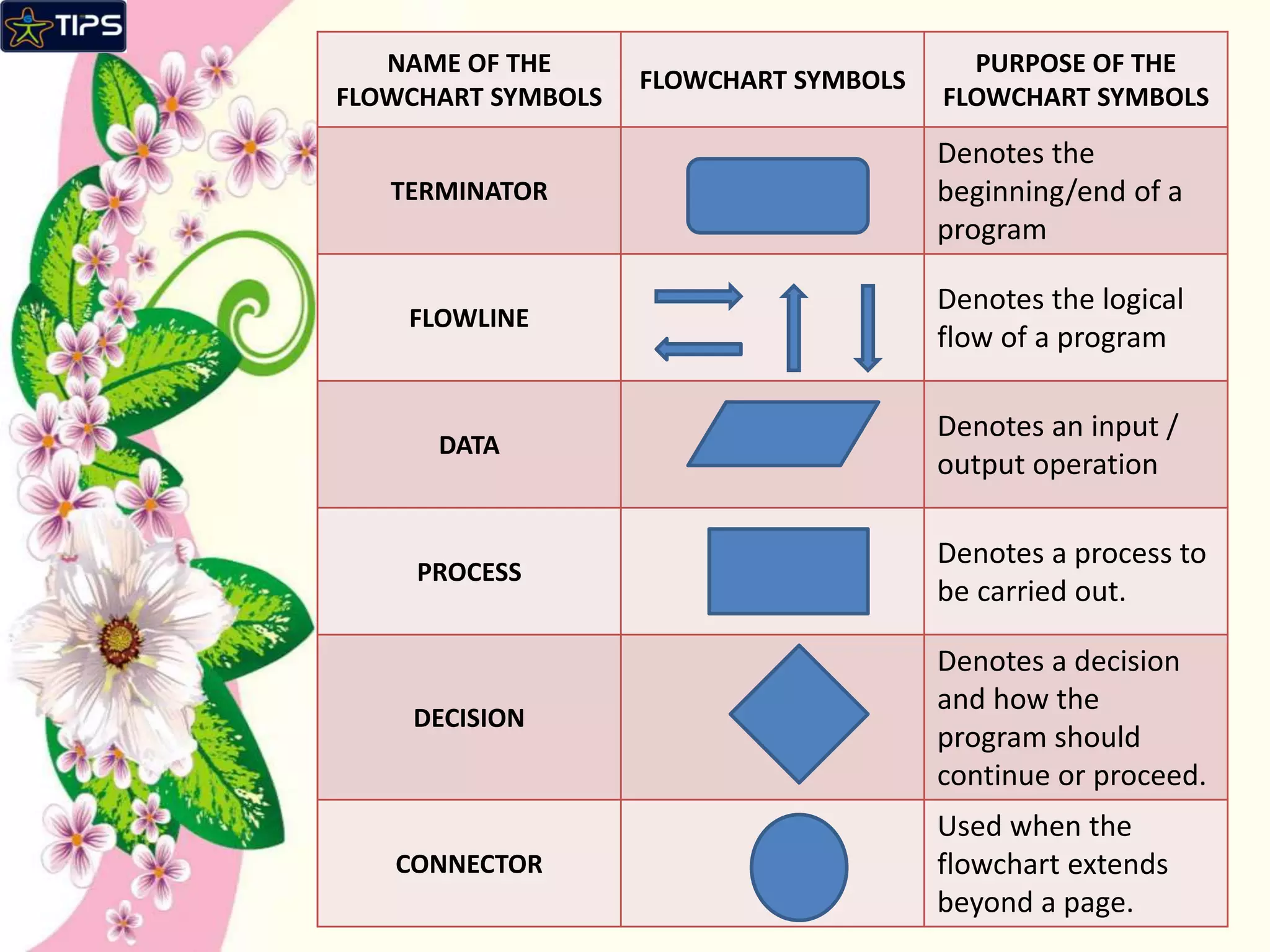
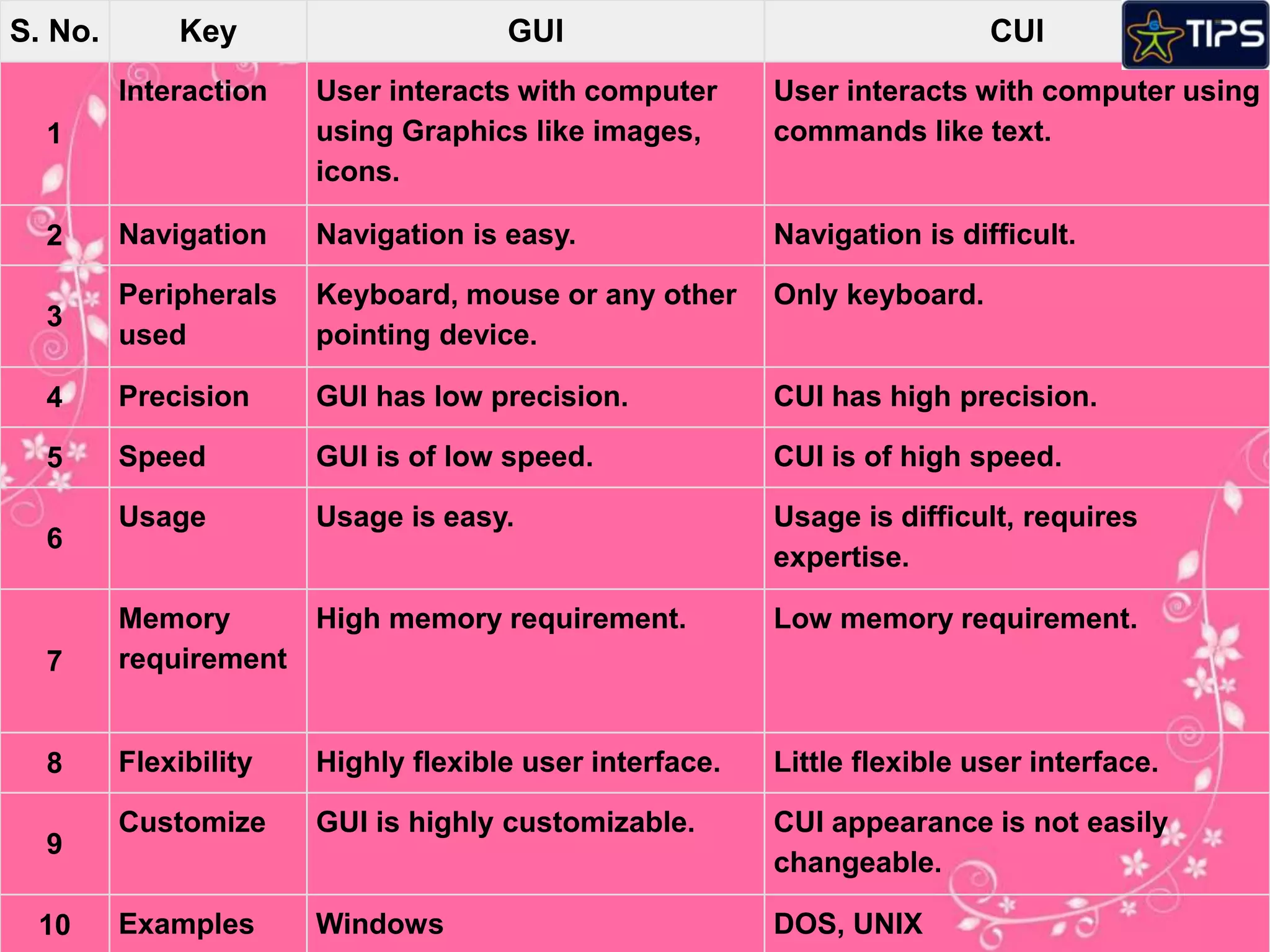
The document defines key computer science concepts. It explains that an algorithm is a set of steps to solve a problem, and a flowchart graphically shows algorithm steps in boxes and arrows. Conditions are statements that evaluate actions as true or false. A computer program is a collection of instructions that can be executed by a computer to perform a task. Graphical user interfaces (GUI) use graphics and icons for interaction, while character user interfaces (CUI) use only text-based commands.