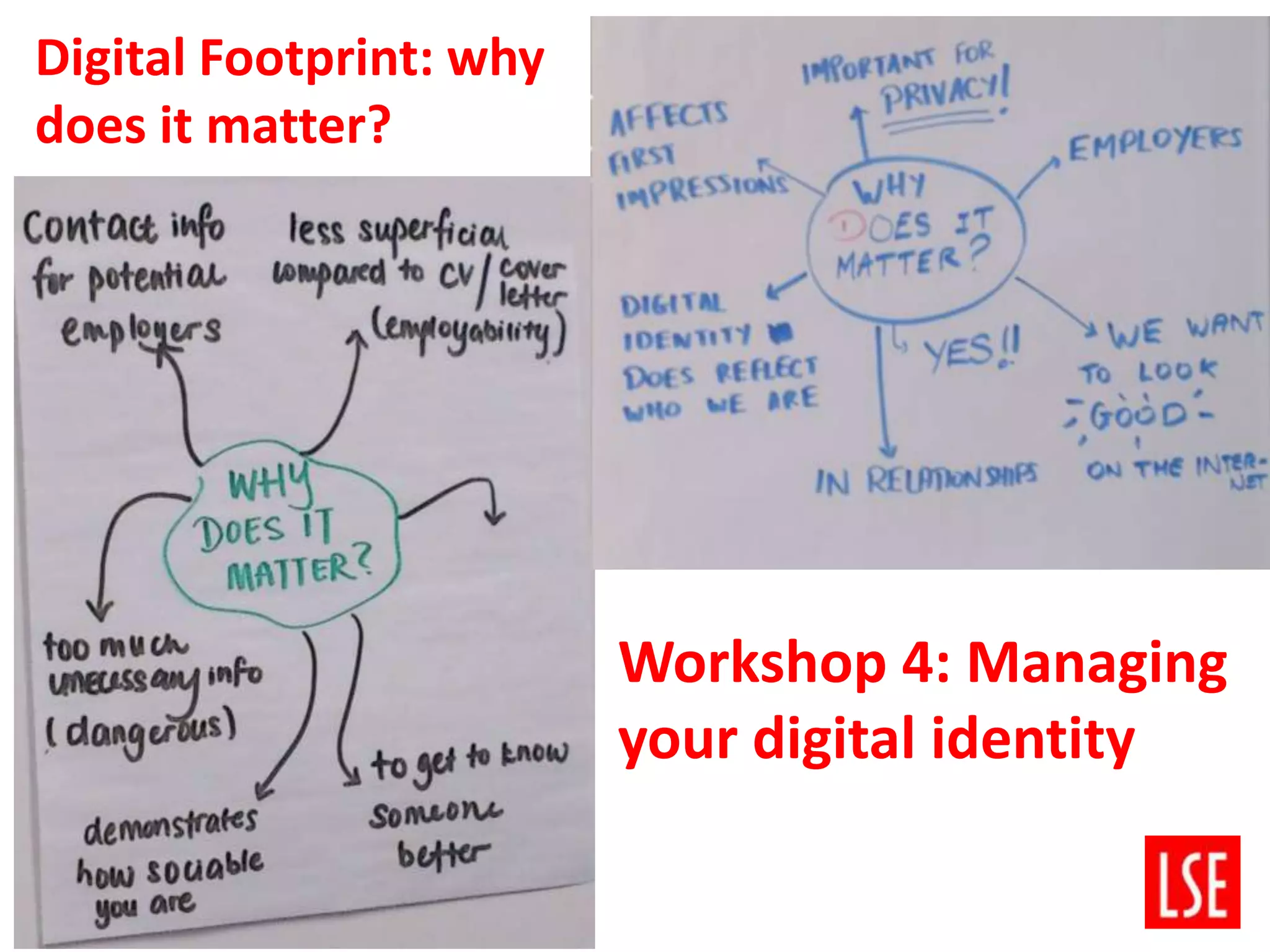
The SADL project at the London School of Economics aimed to improve undergraduate students' digital literacies. It worked with student ambassadors and four academic departments to develop workshops on topics like research skills, reading and writing, and managing digital information and identity. Evaluation found the workshops and ambassador role were valuable but needed more structure. The project also identified challenges in scaling up support and developing peer learning, but provided benefits to students like increased confidence and skills. Moving forward, the project aims to further student partnerships and embed digital literacy into the curriculum.