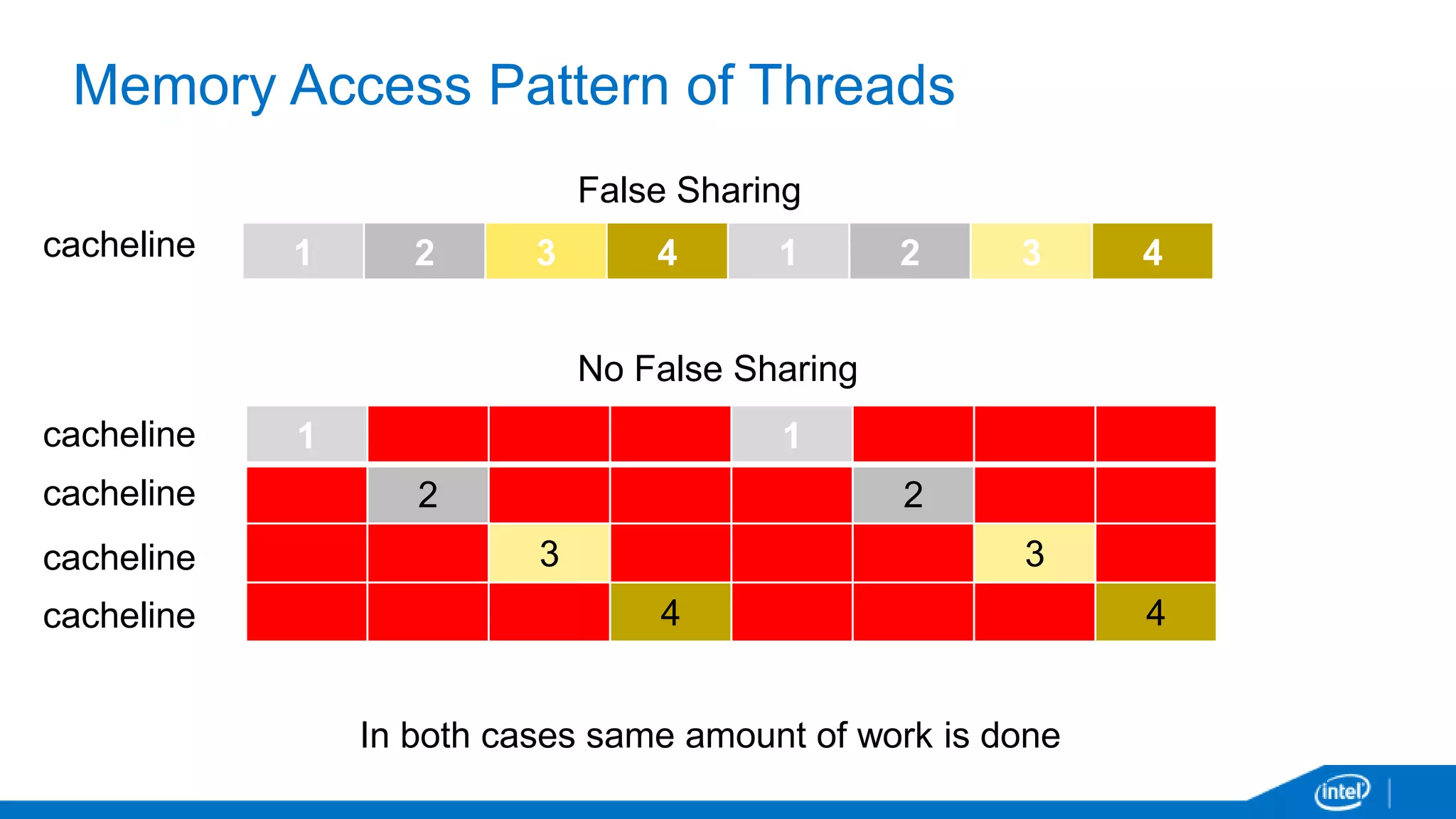
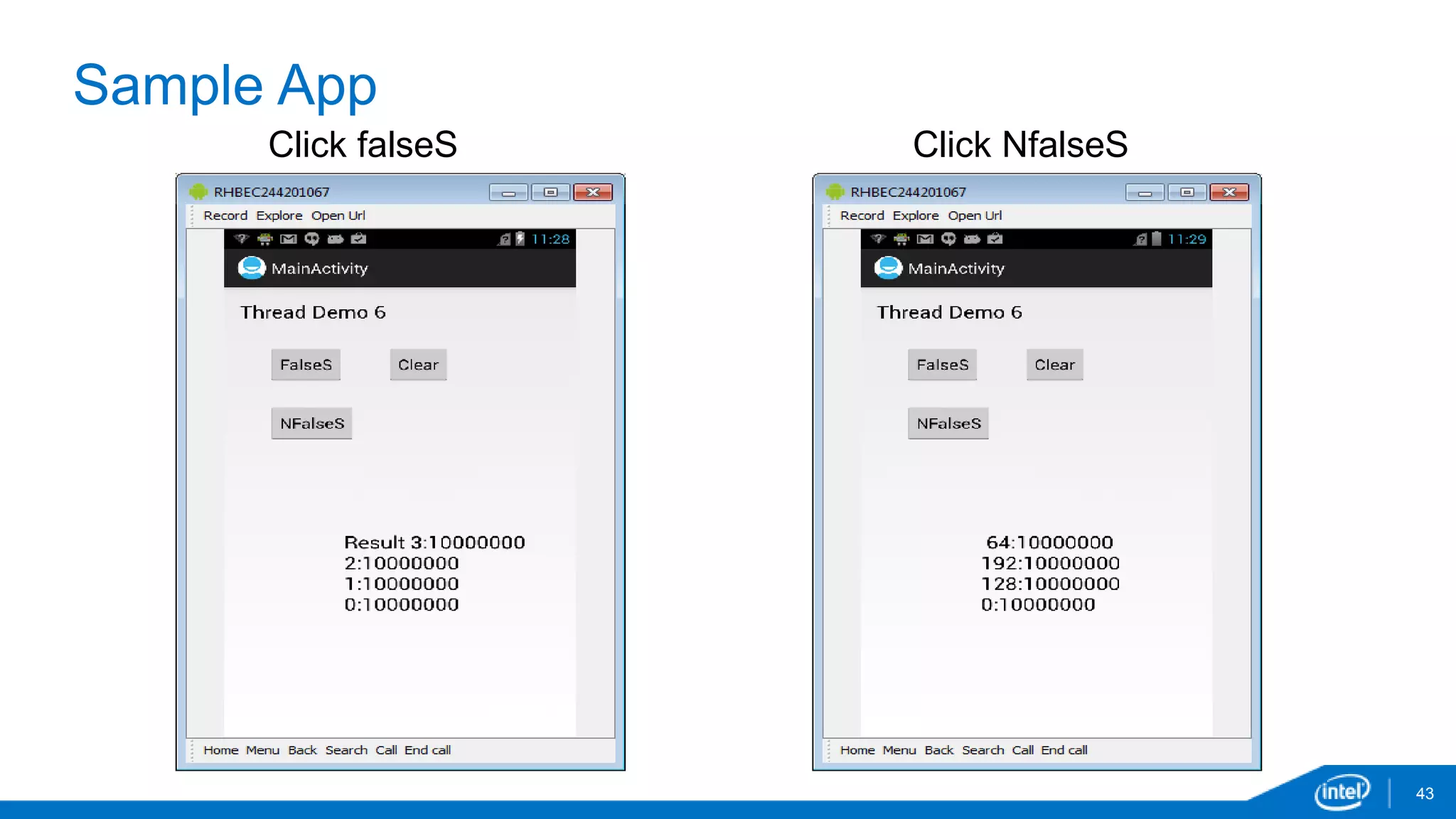
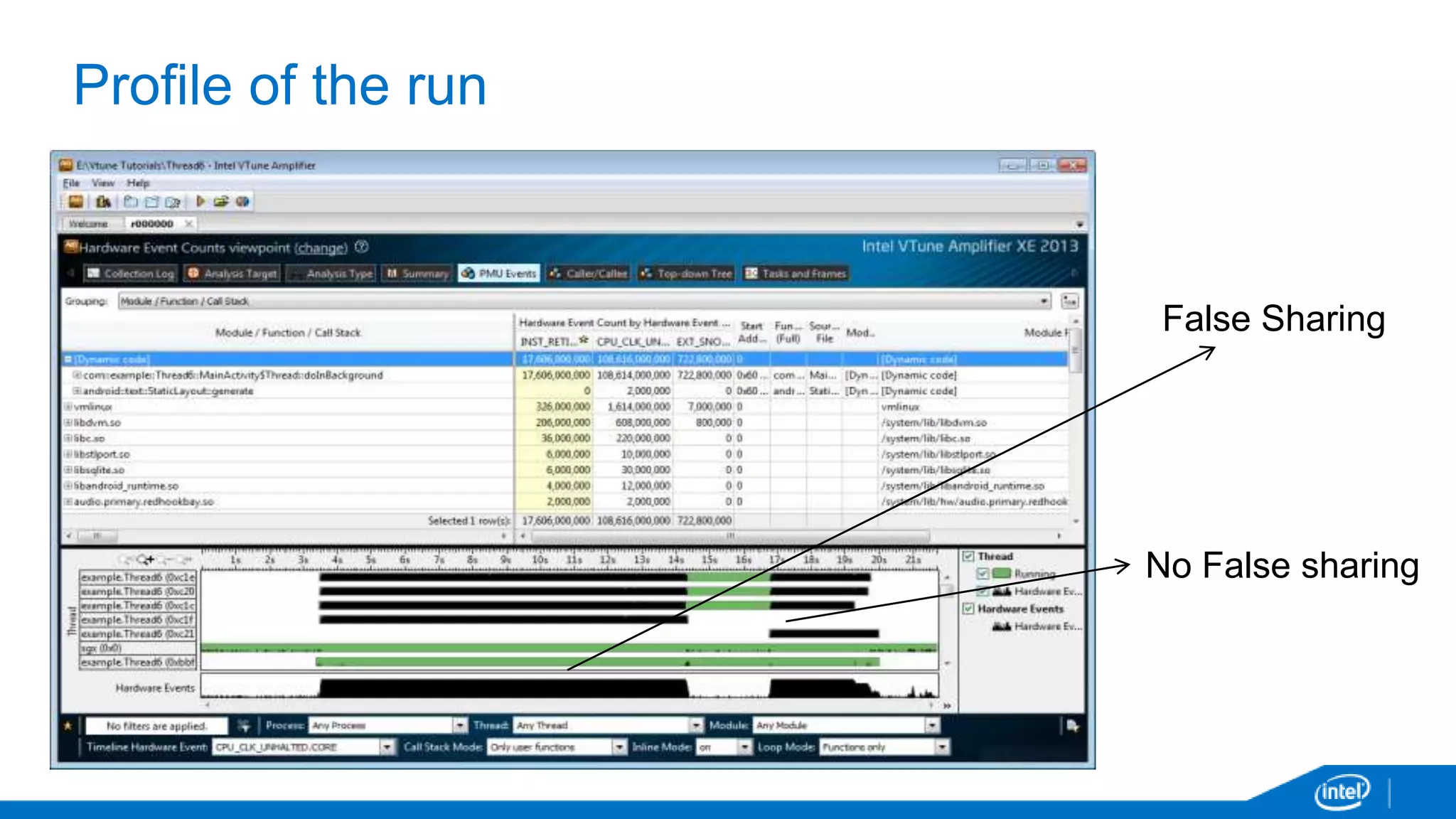
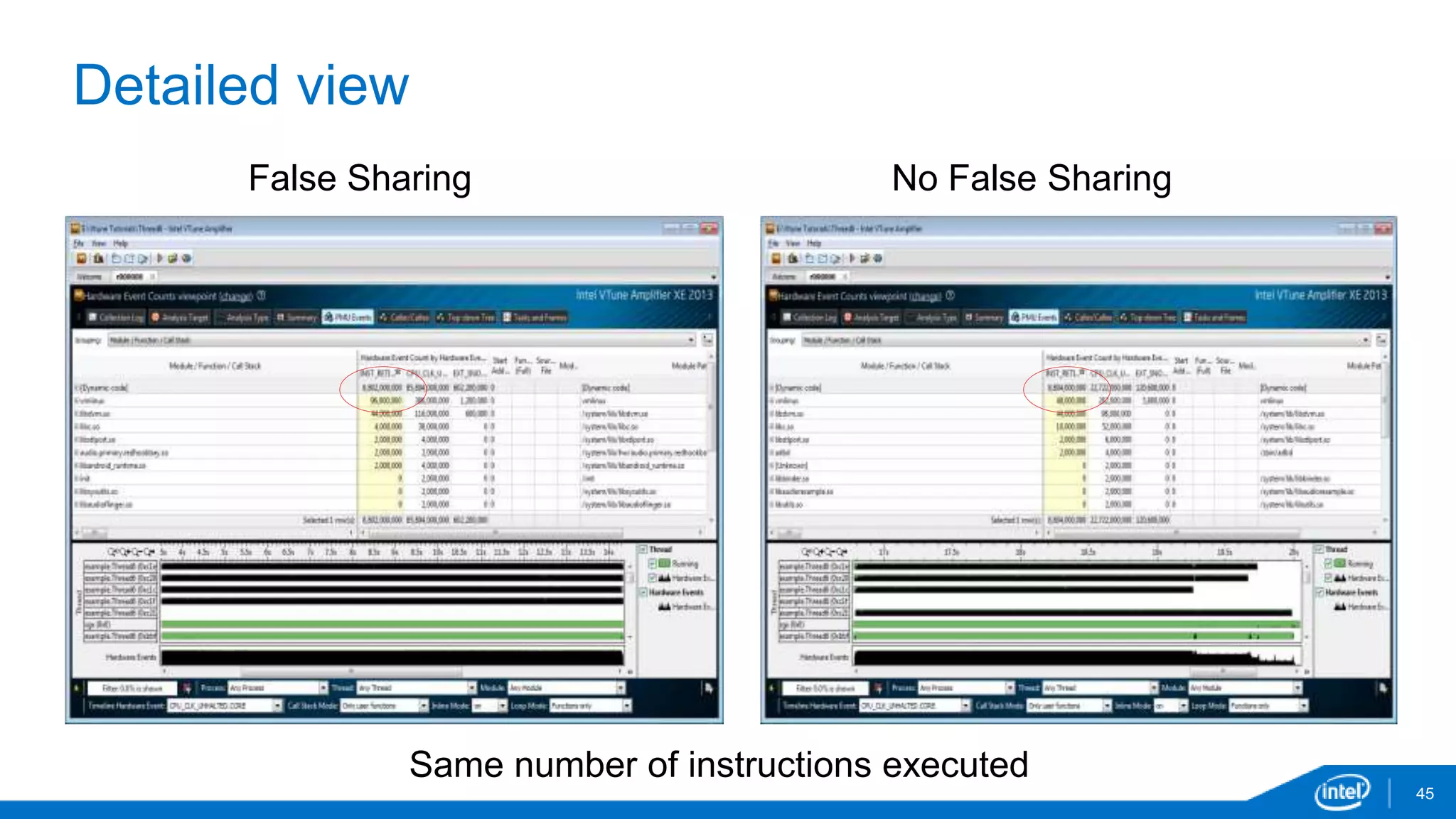
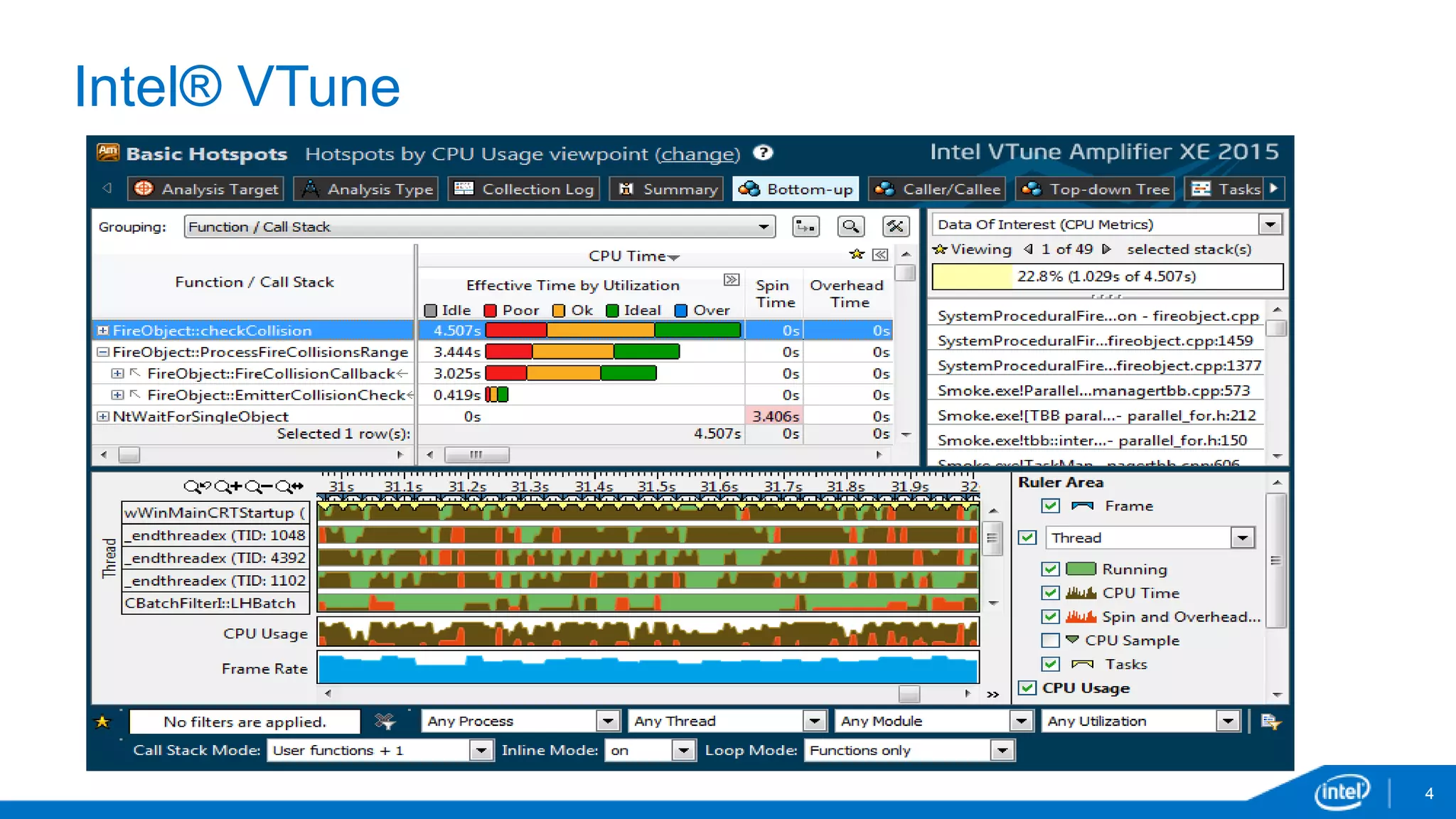
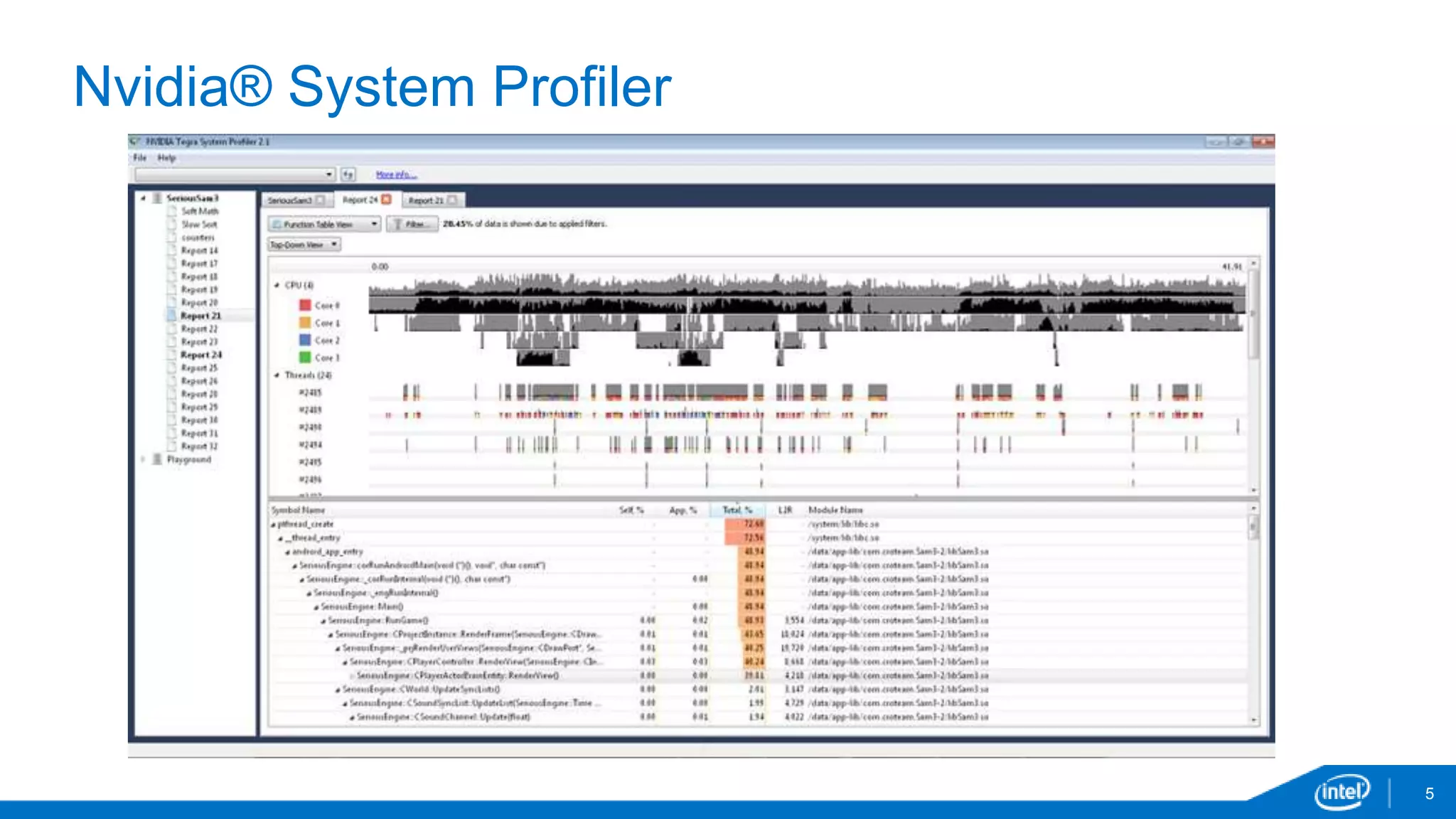
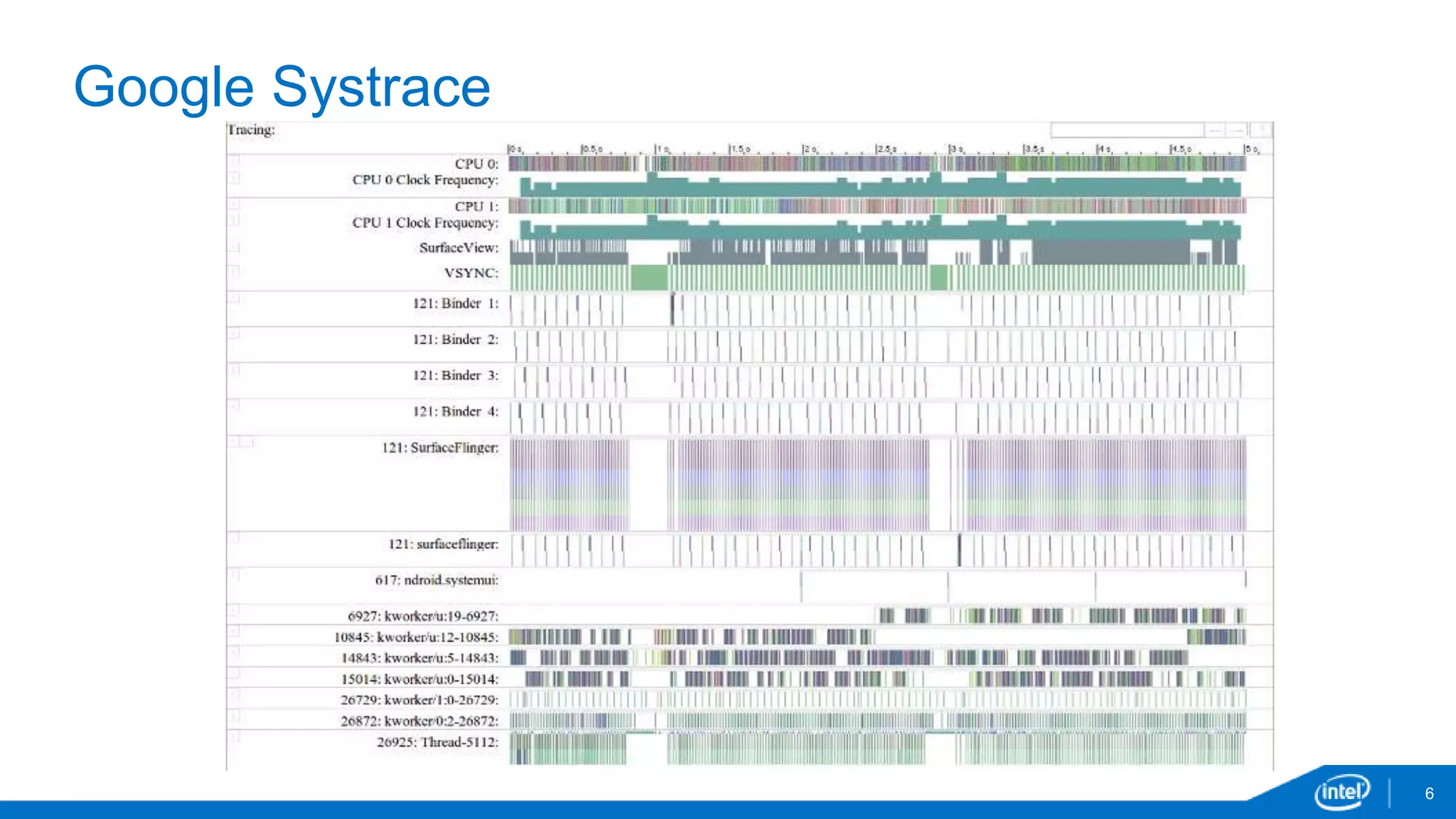
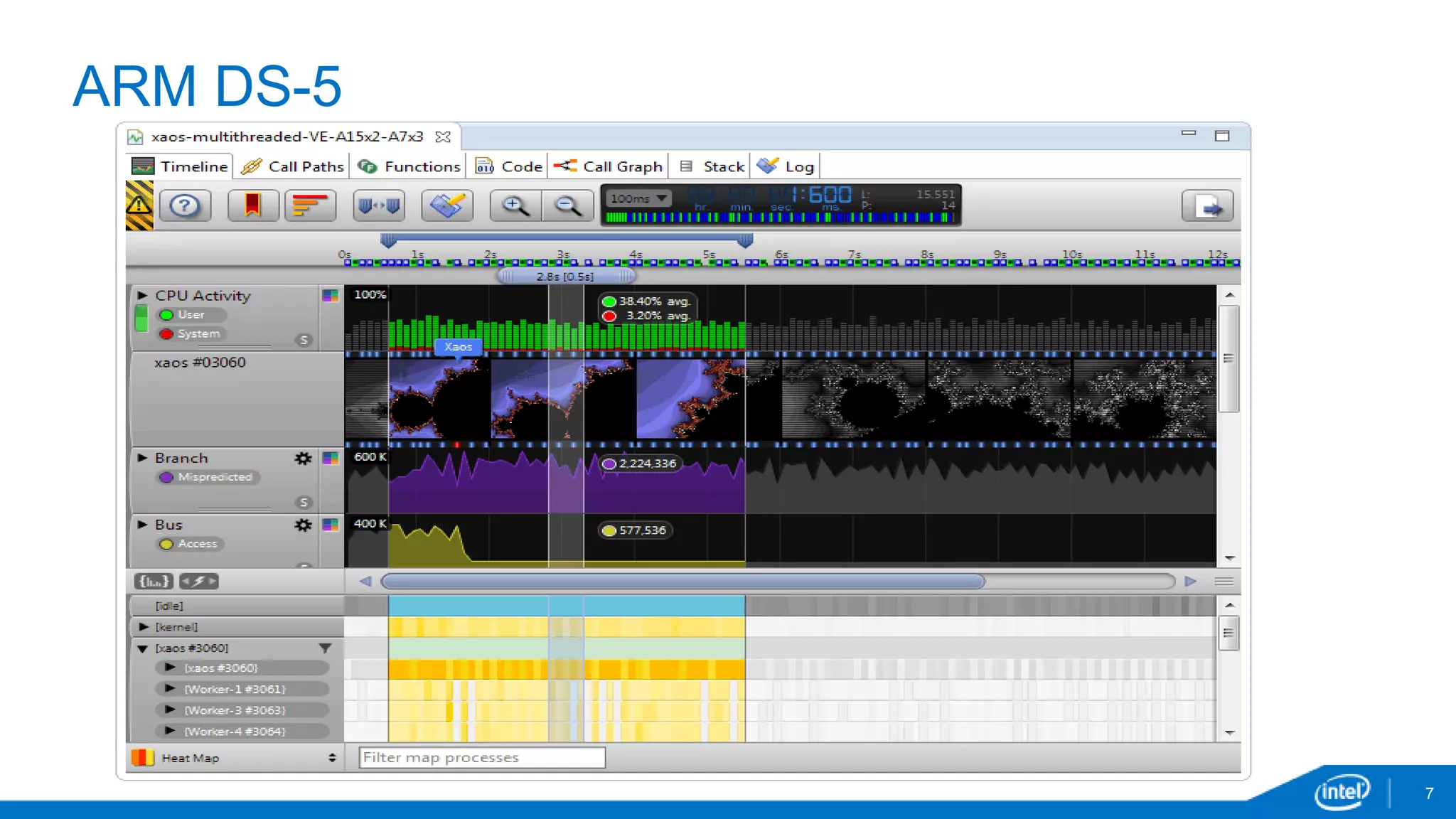
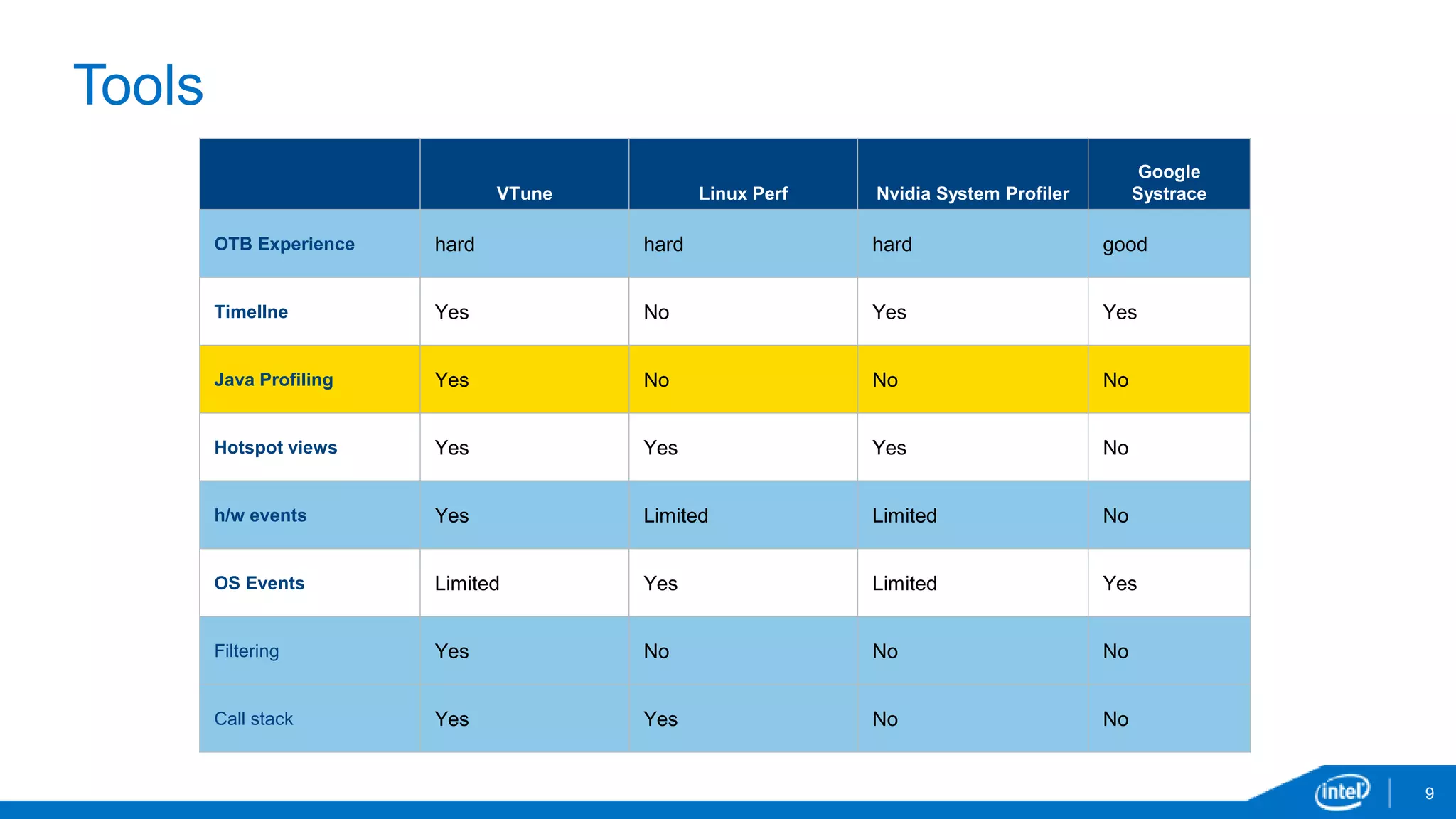
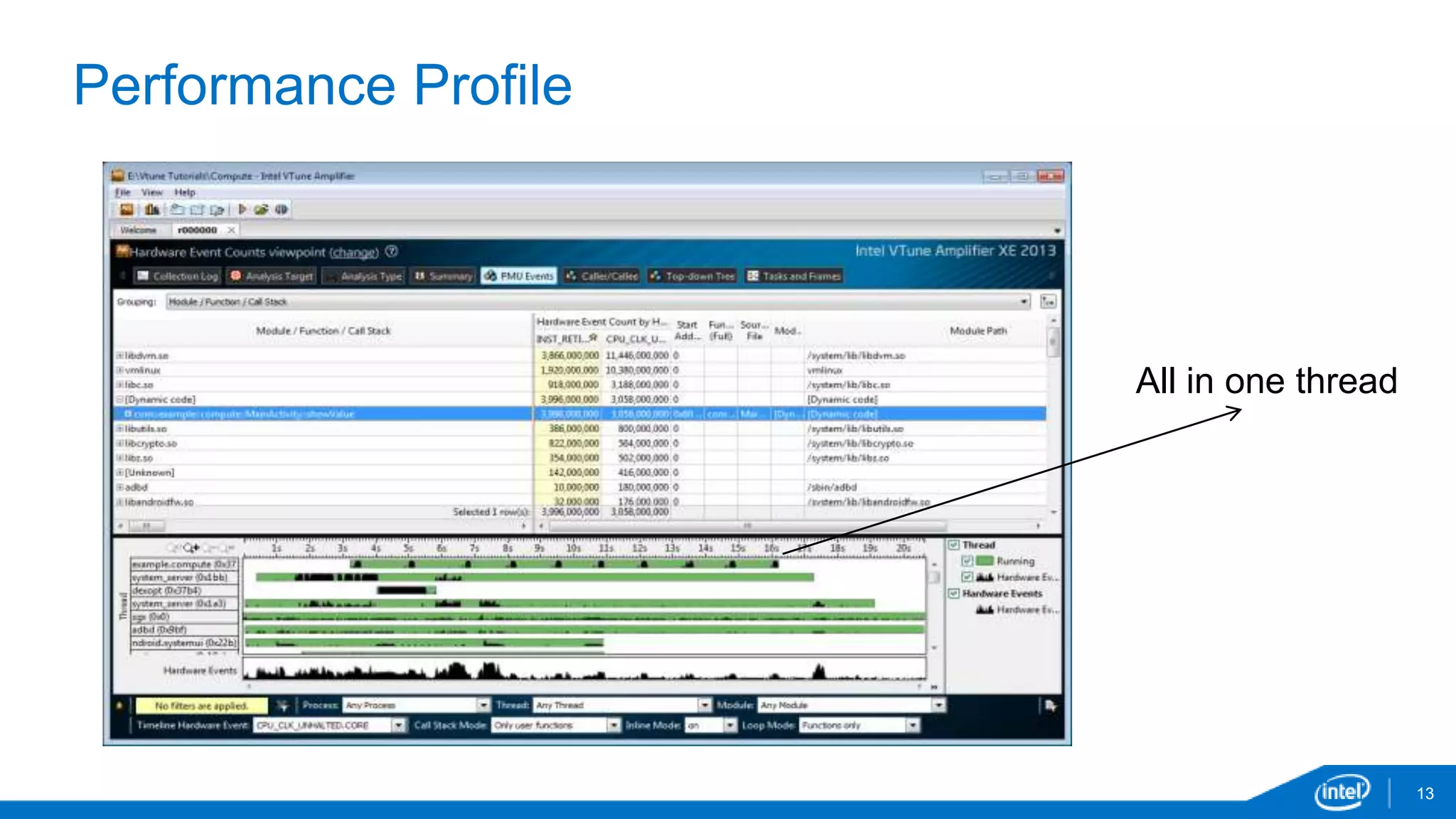
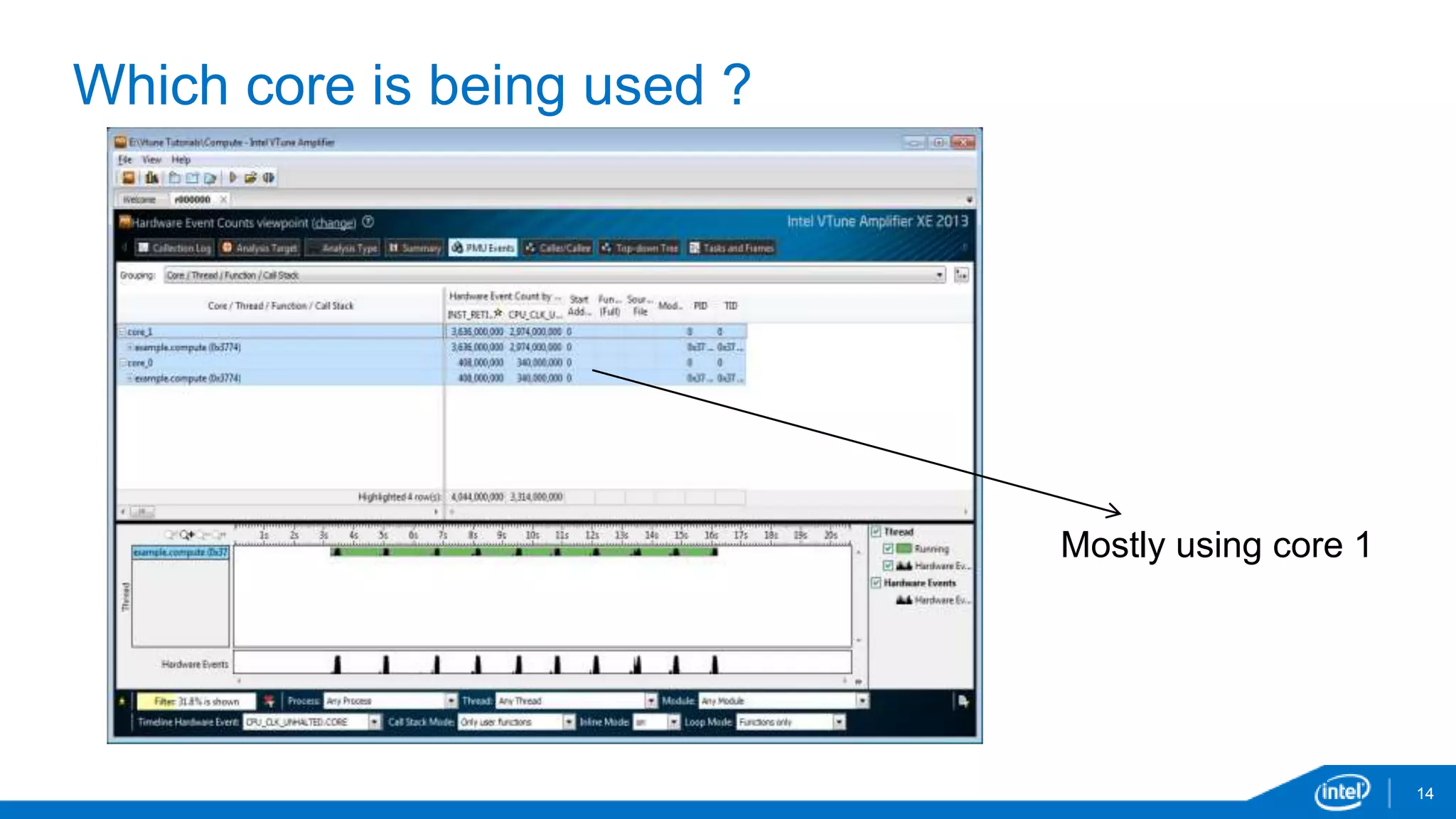
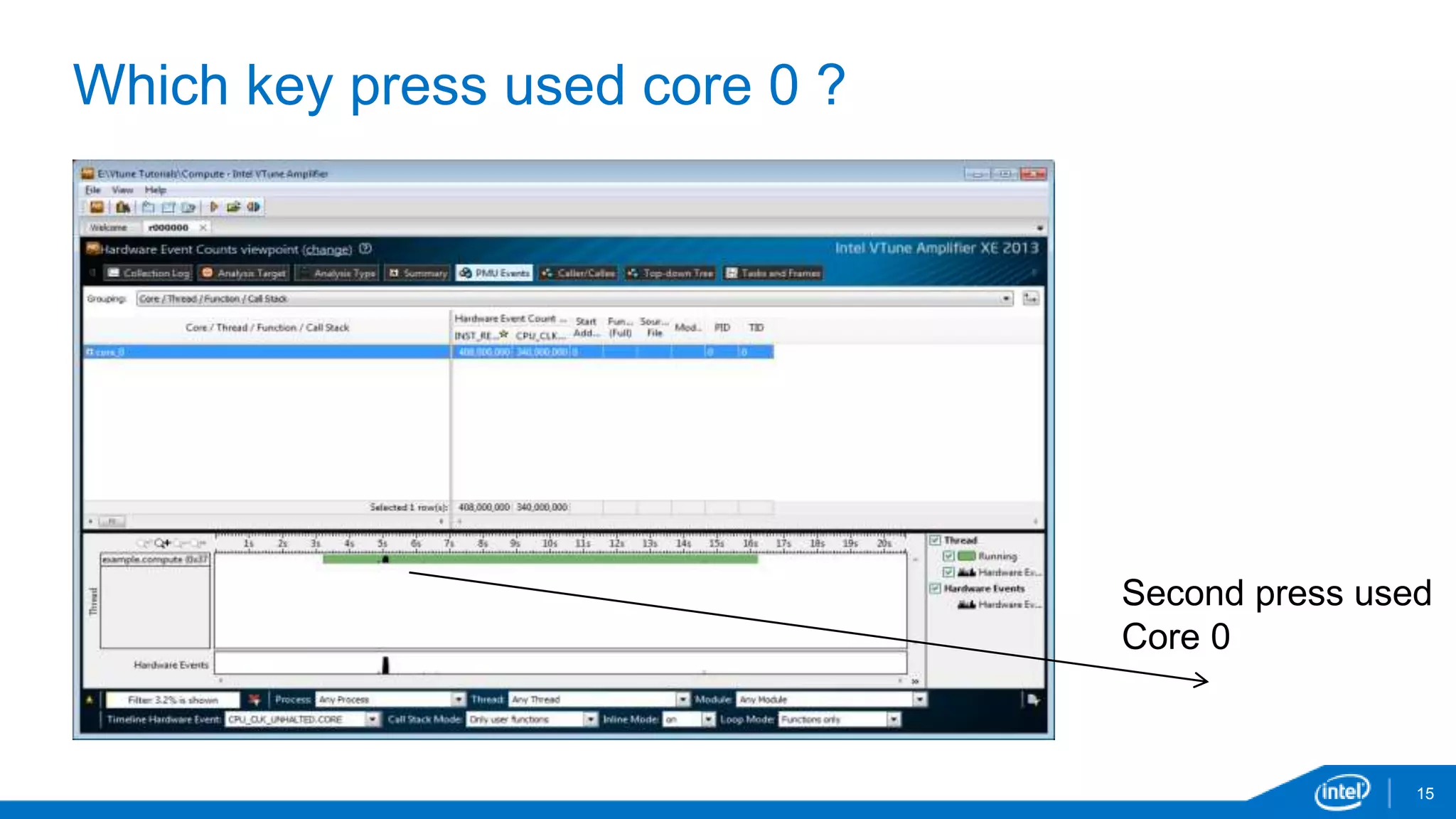
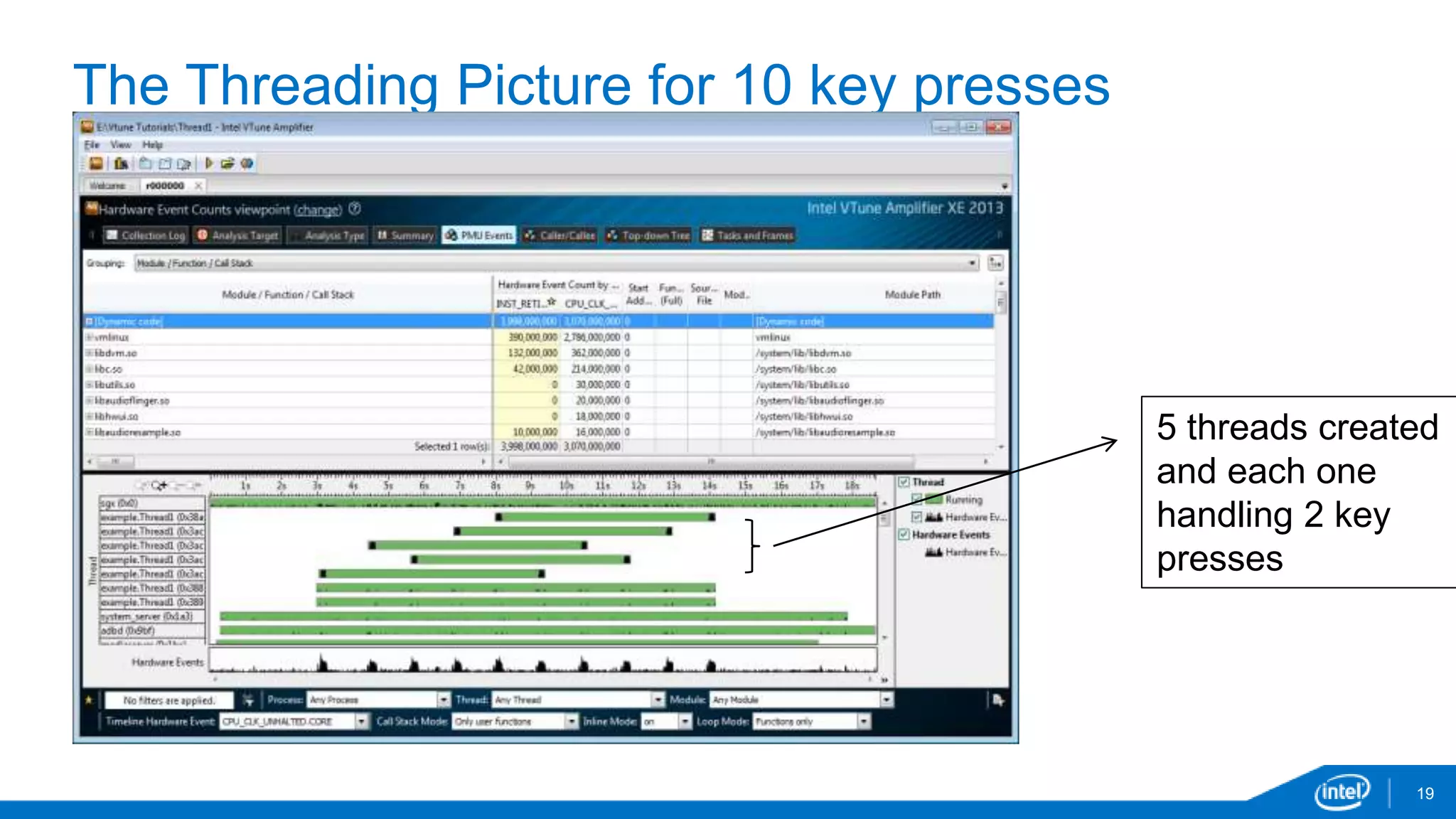
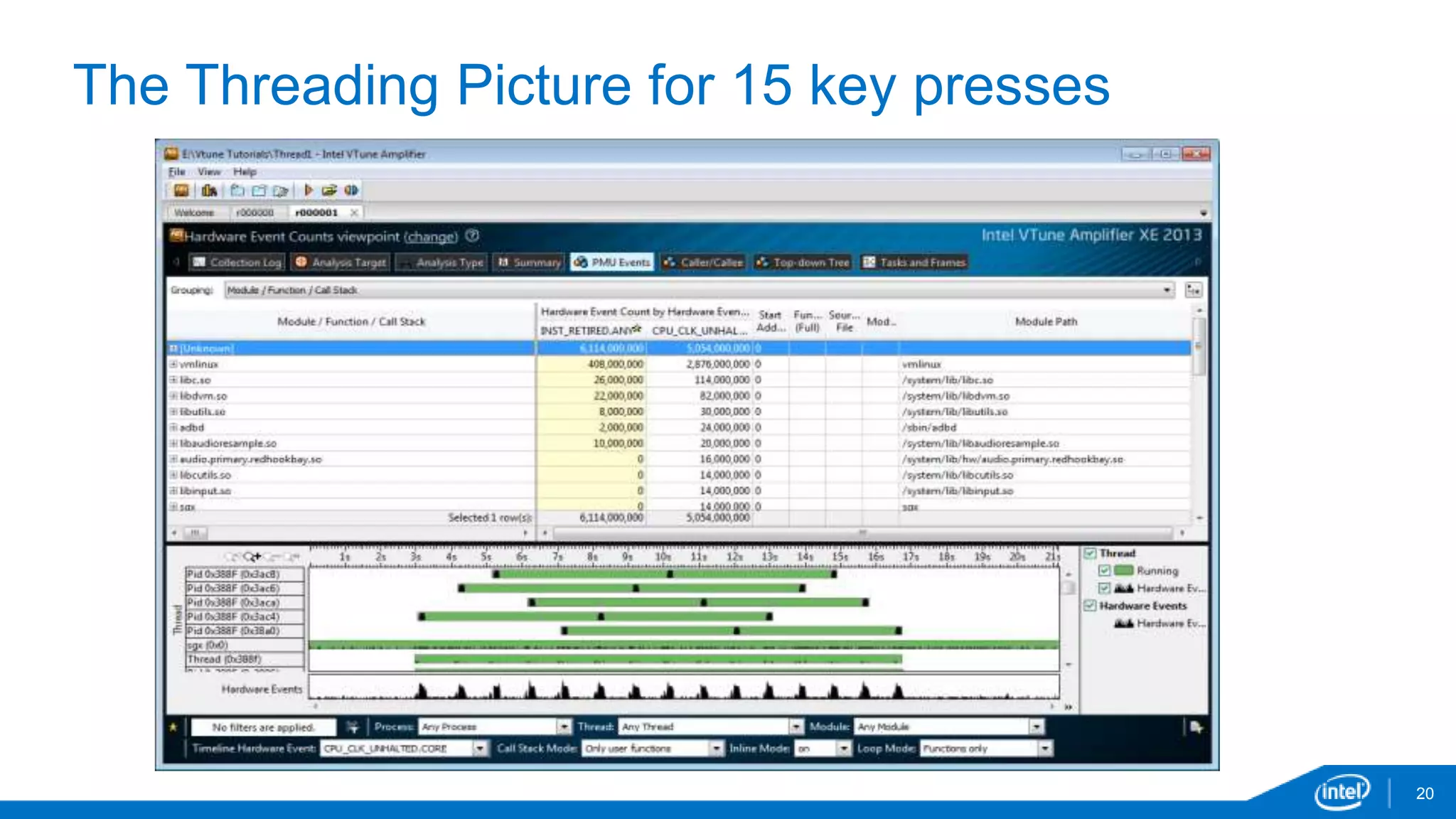
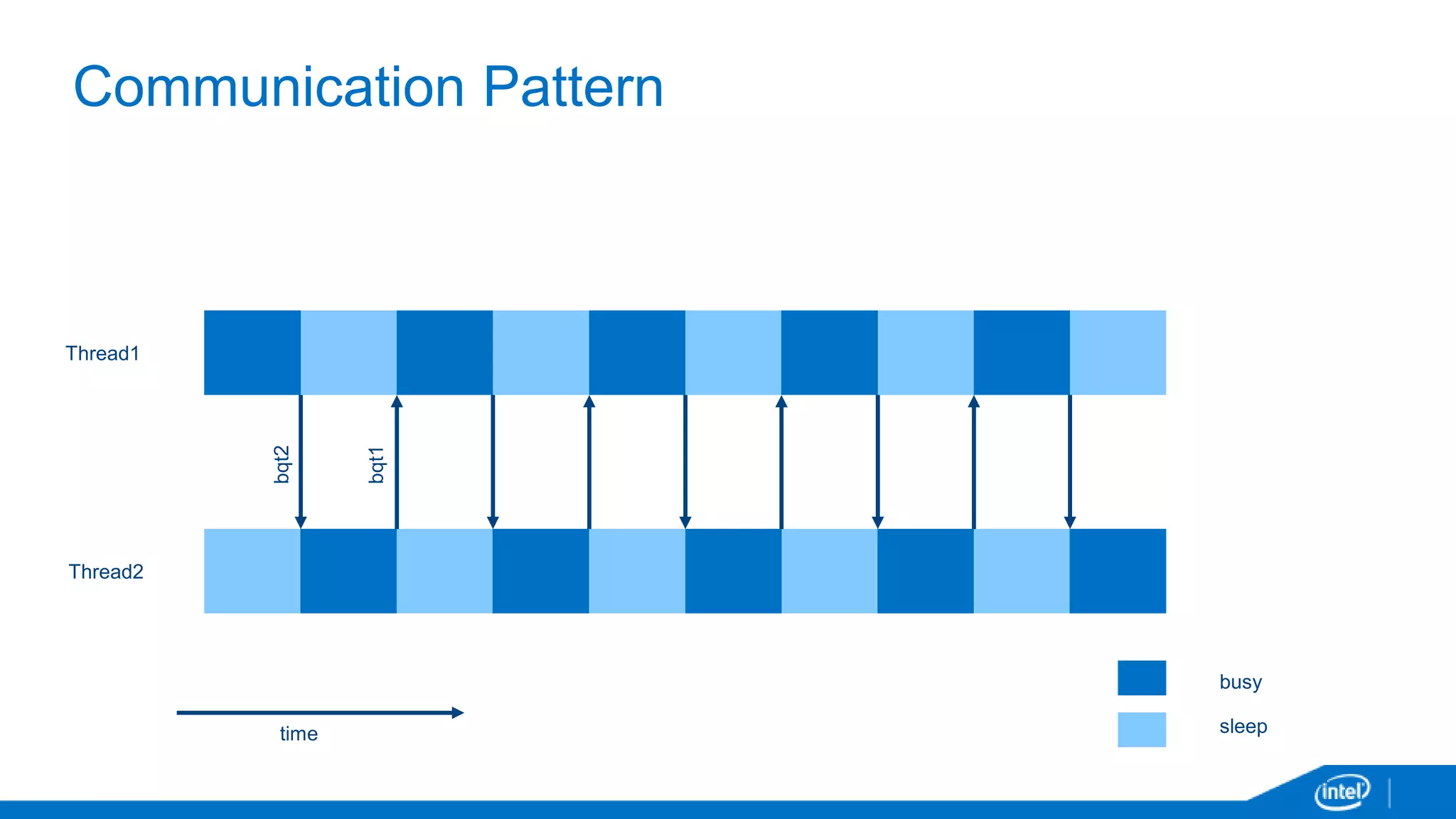
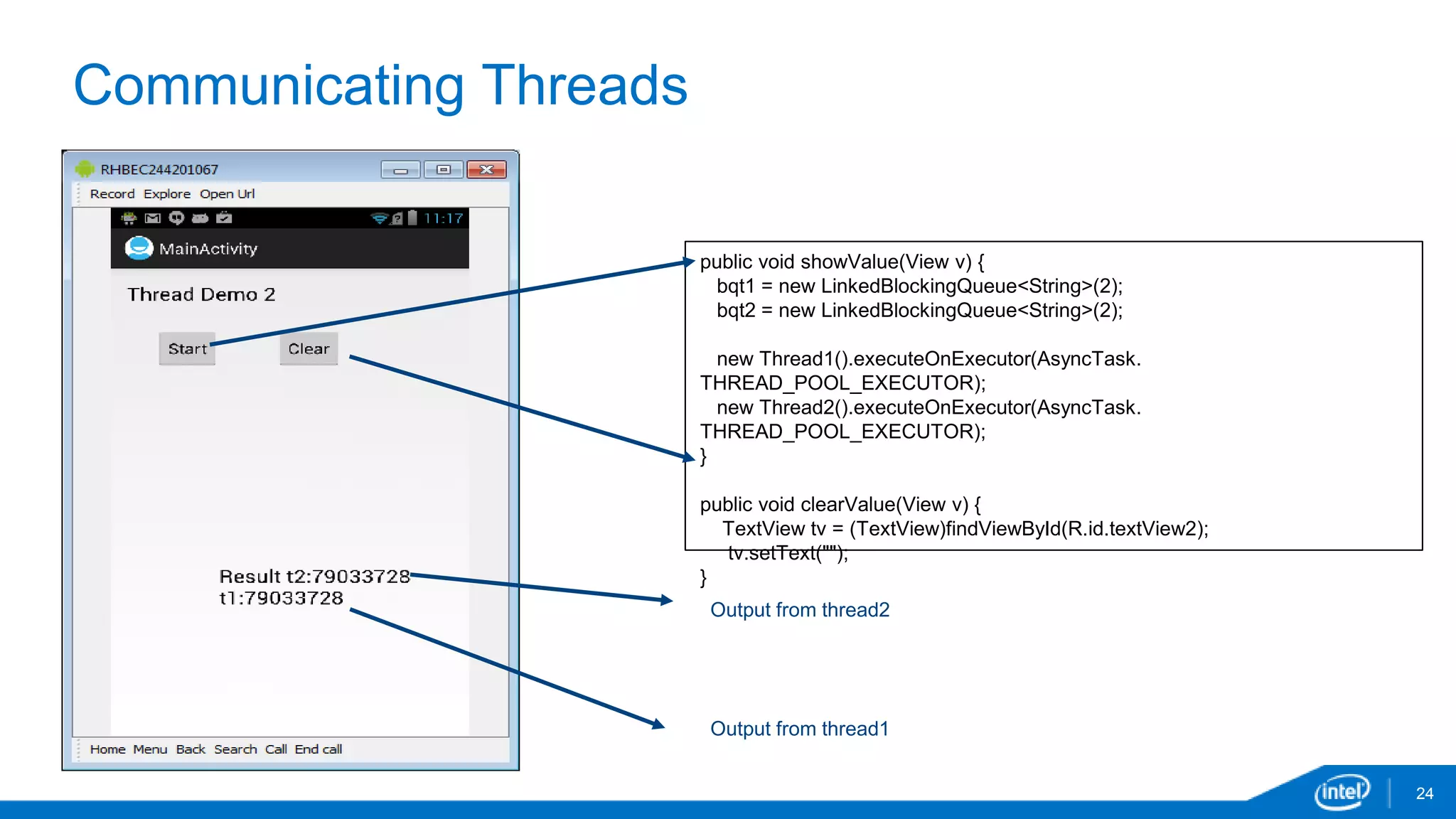
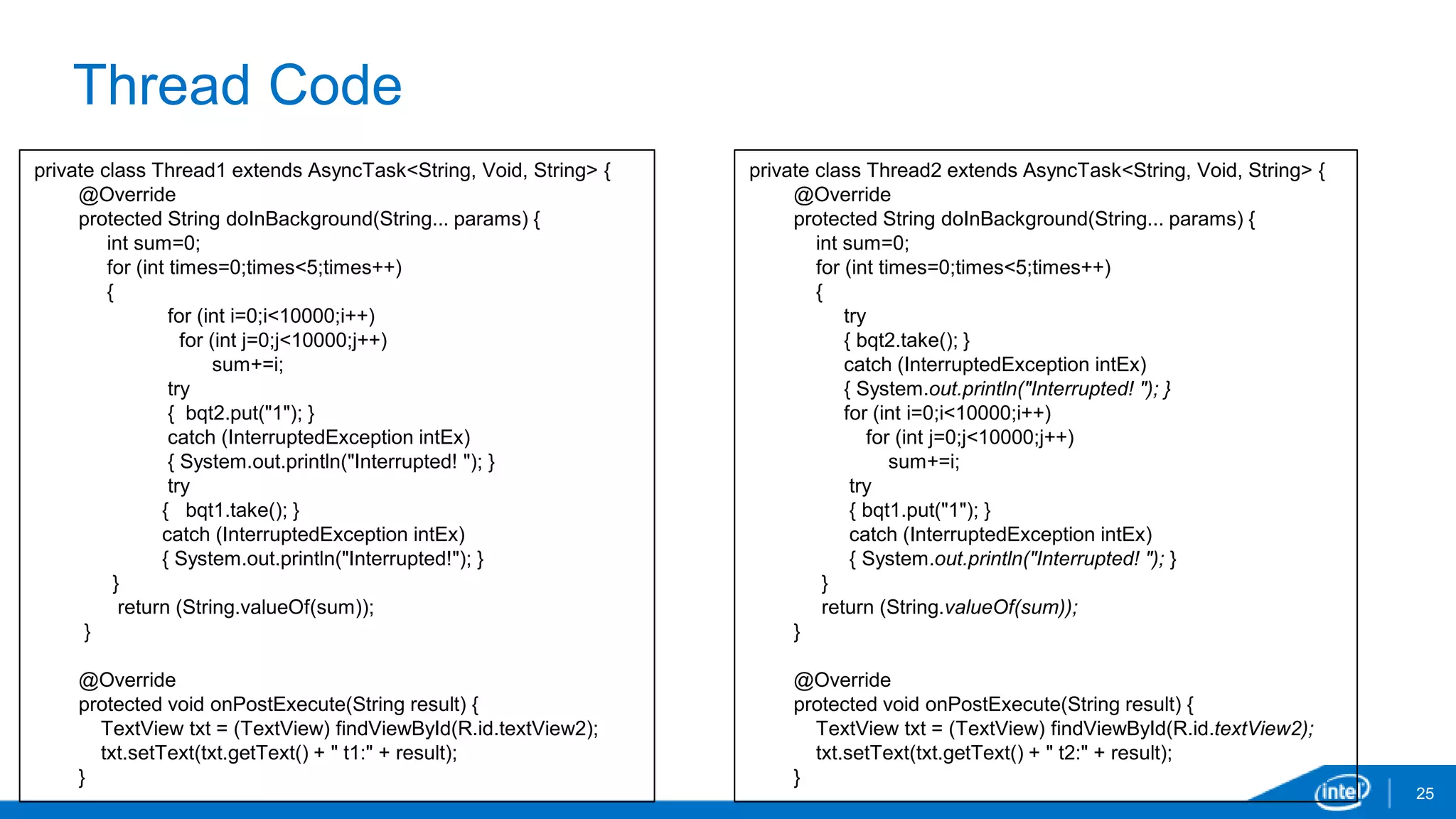
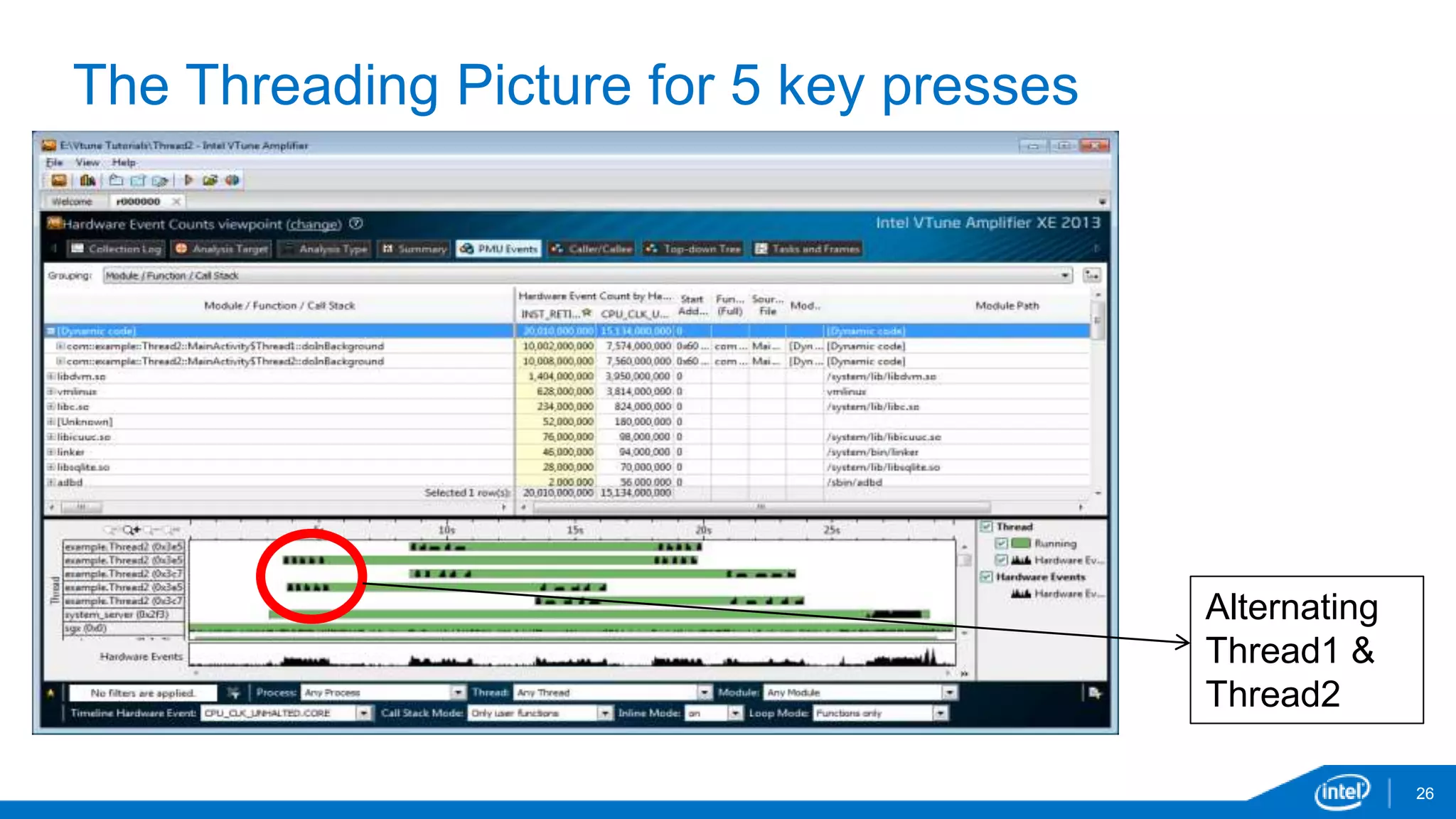
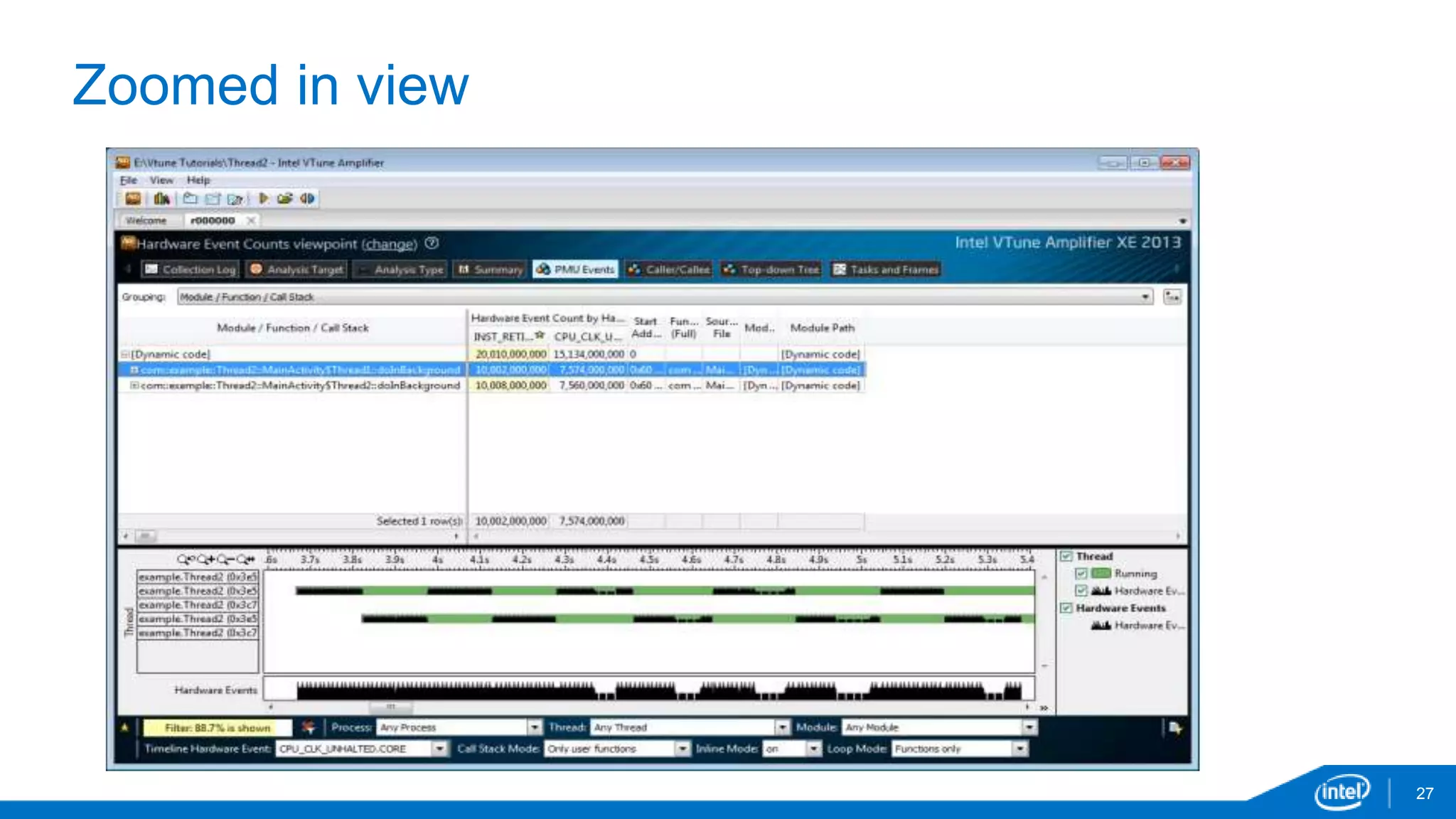
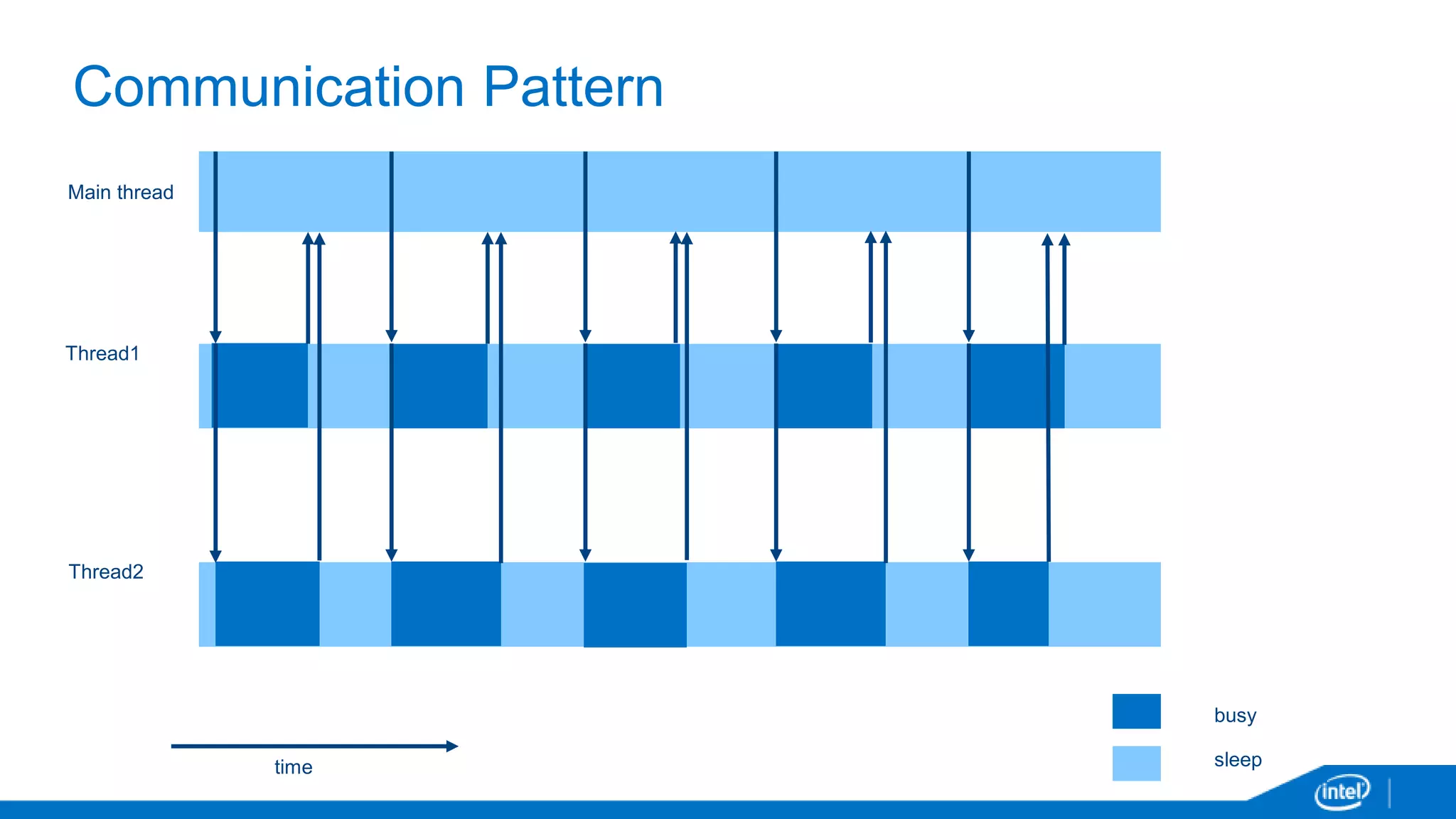
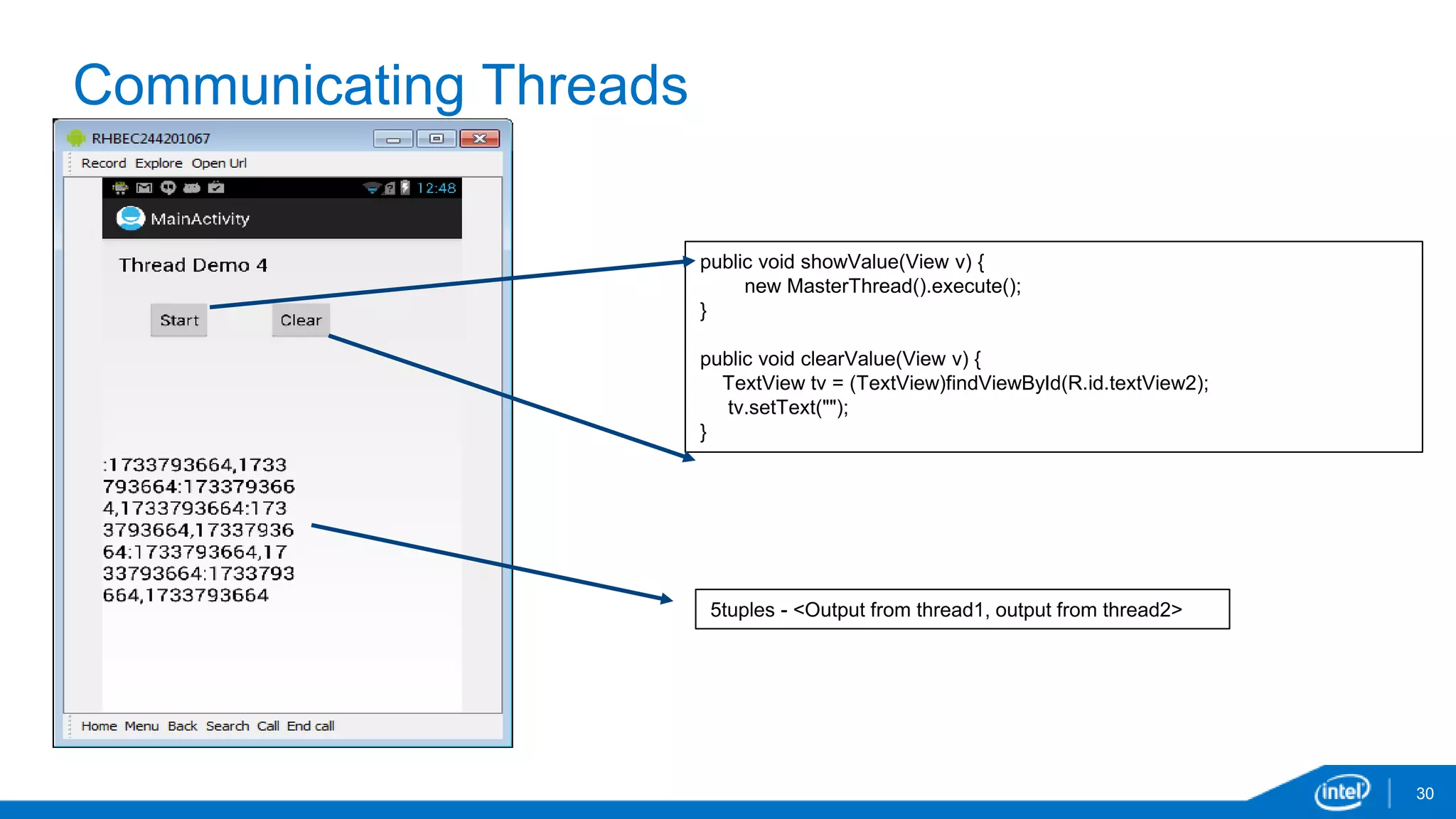
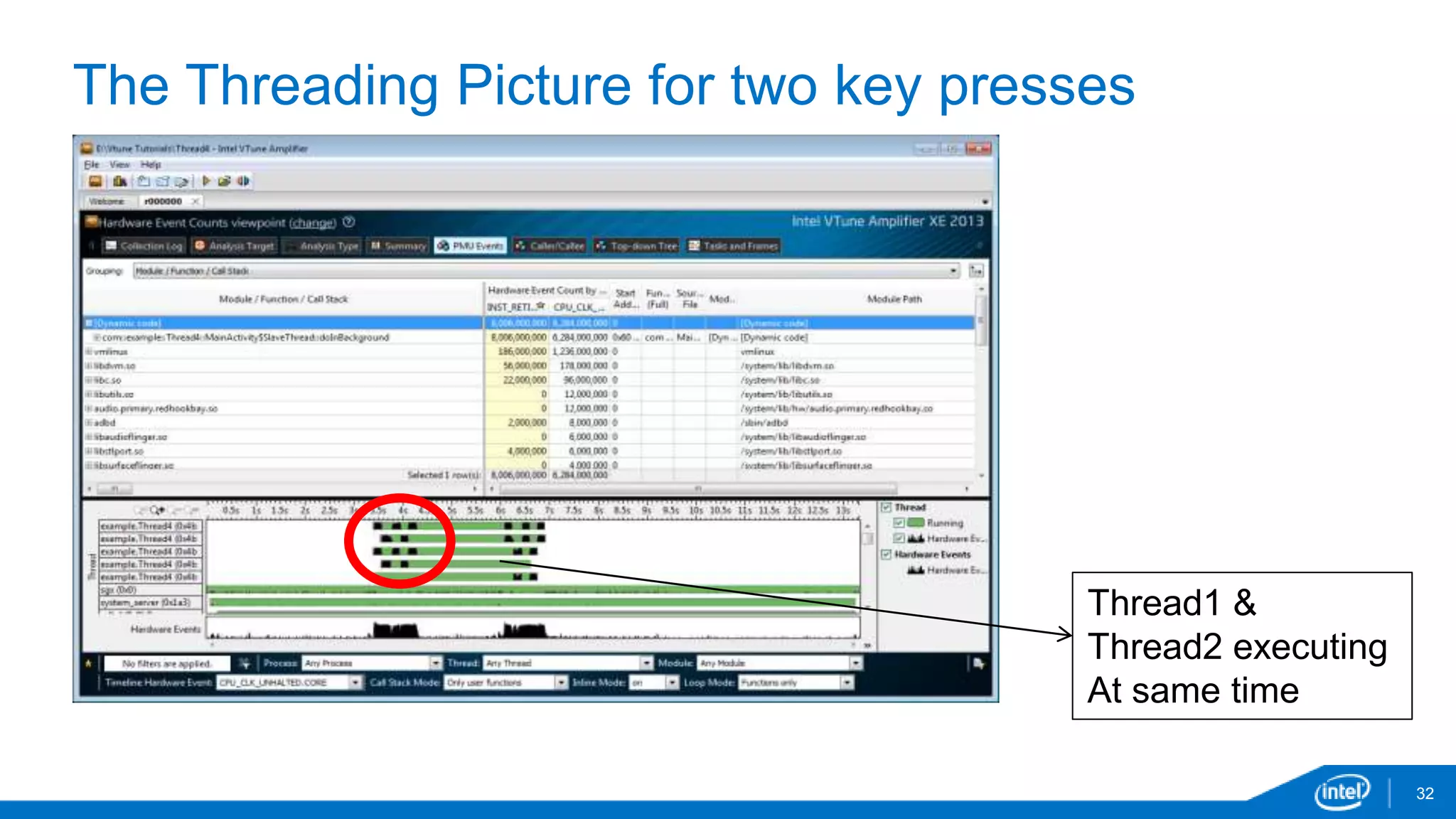
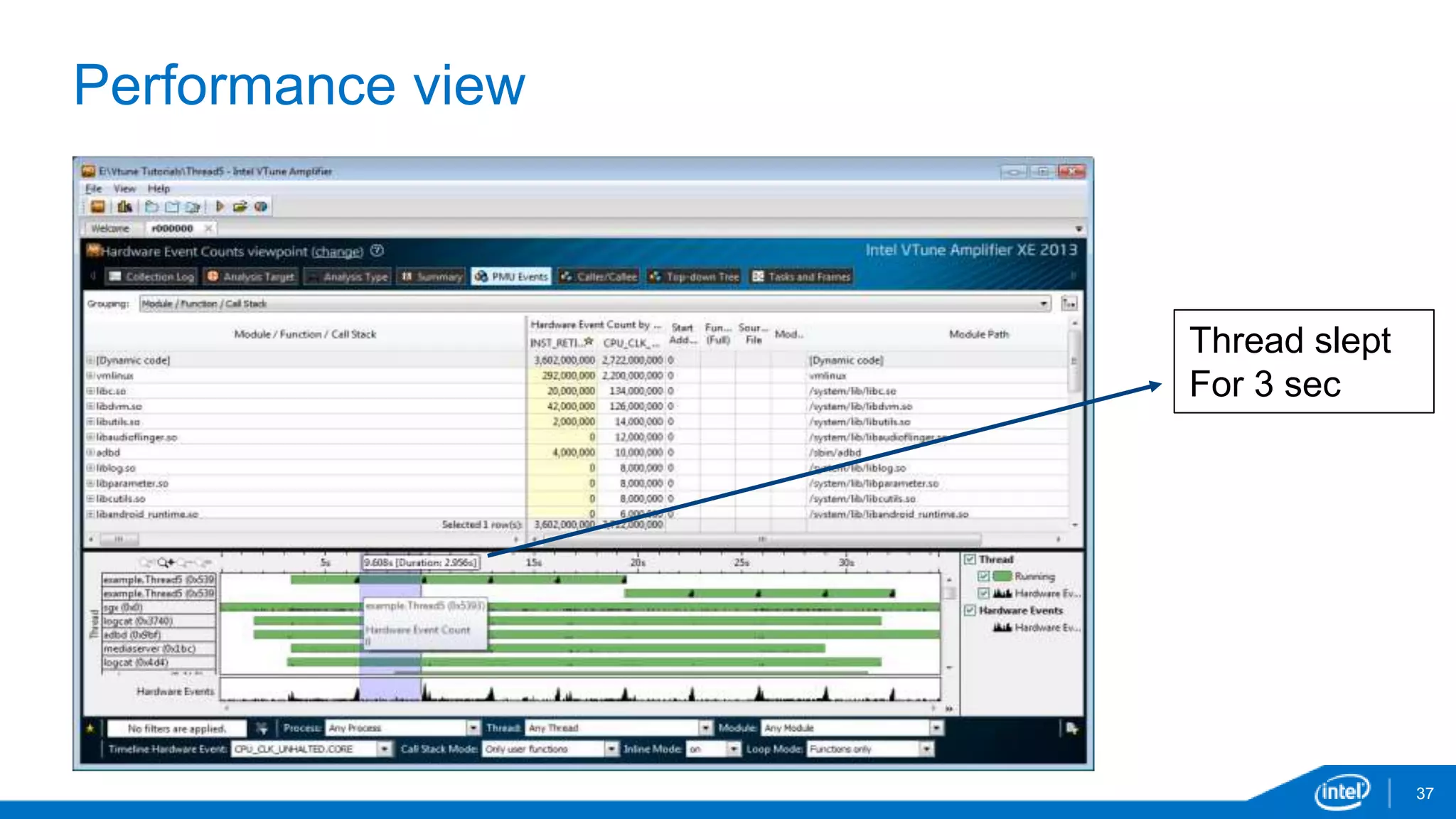
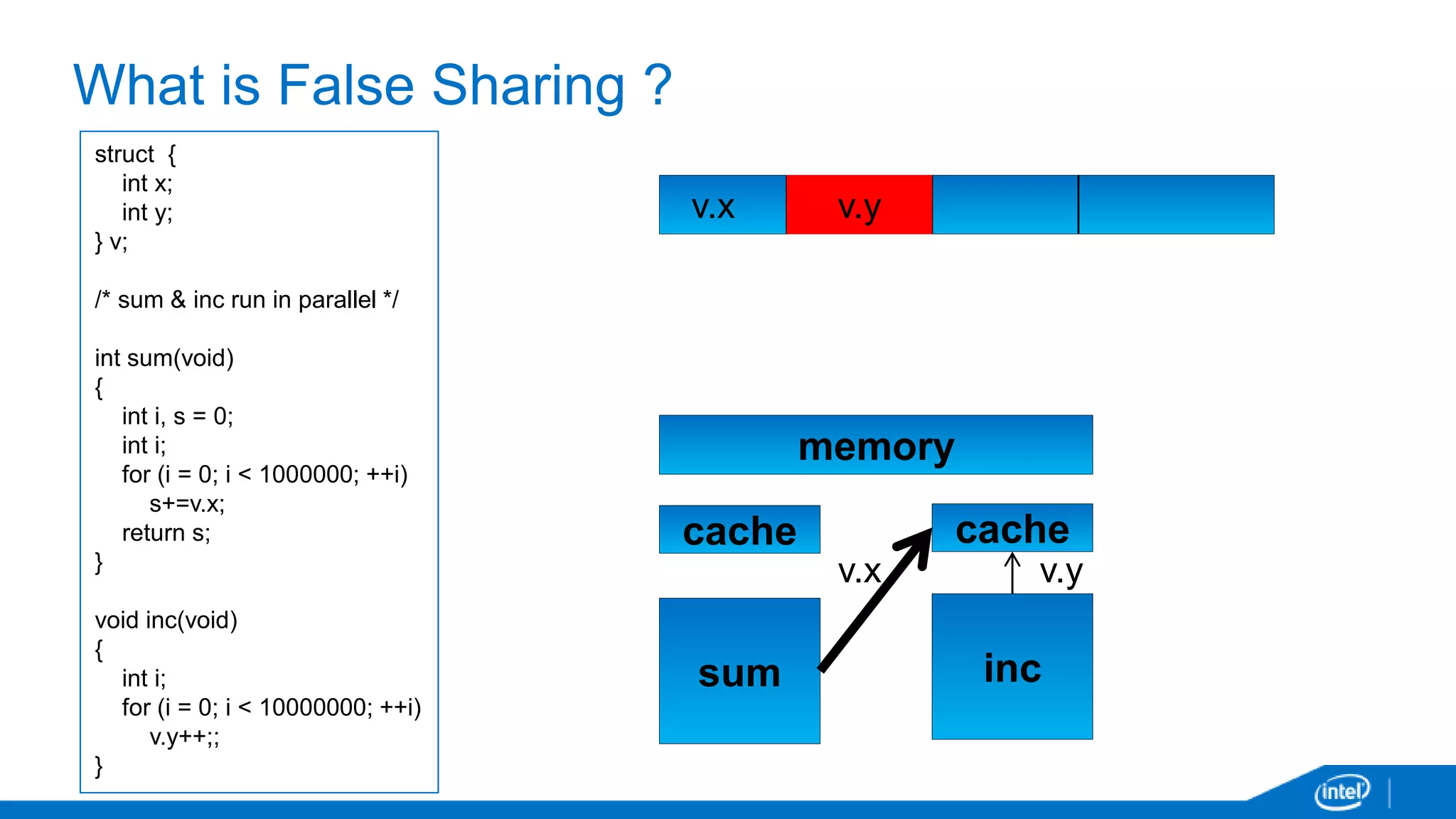
The document discusses tools and techniques for analyzing threading behavior in Android applications, focusing on performance analysis tools like Intel VTune and Google Systrace. It includes practical examples of threading models and how to implement simple micro-benchmarks to interpret performance data. Additionally, it addresses concepts such as lazy threads and false sharing, highlighting their impact on application responsiveness and efficiency.









![False Sharing App
40
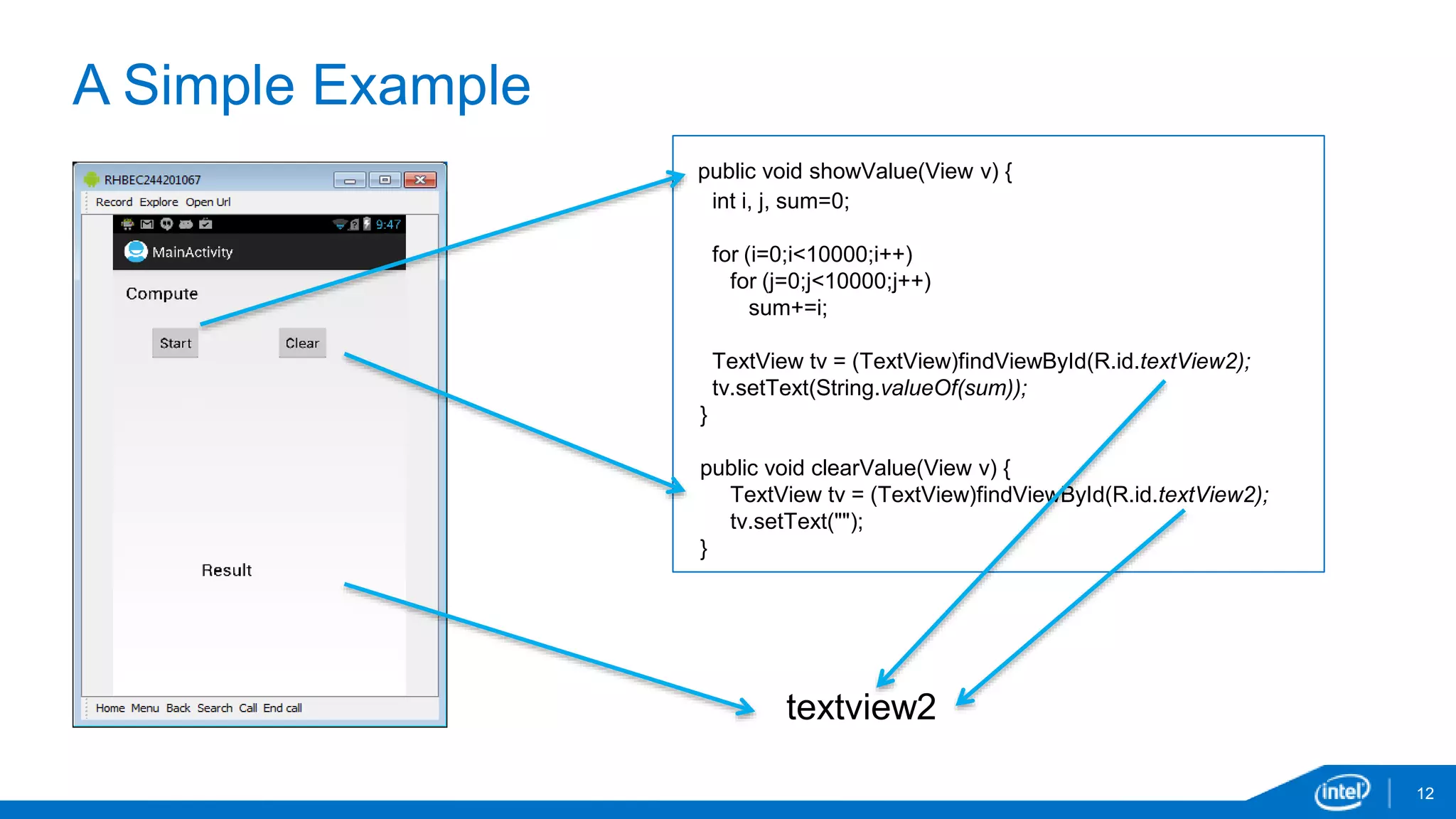
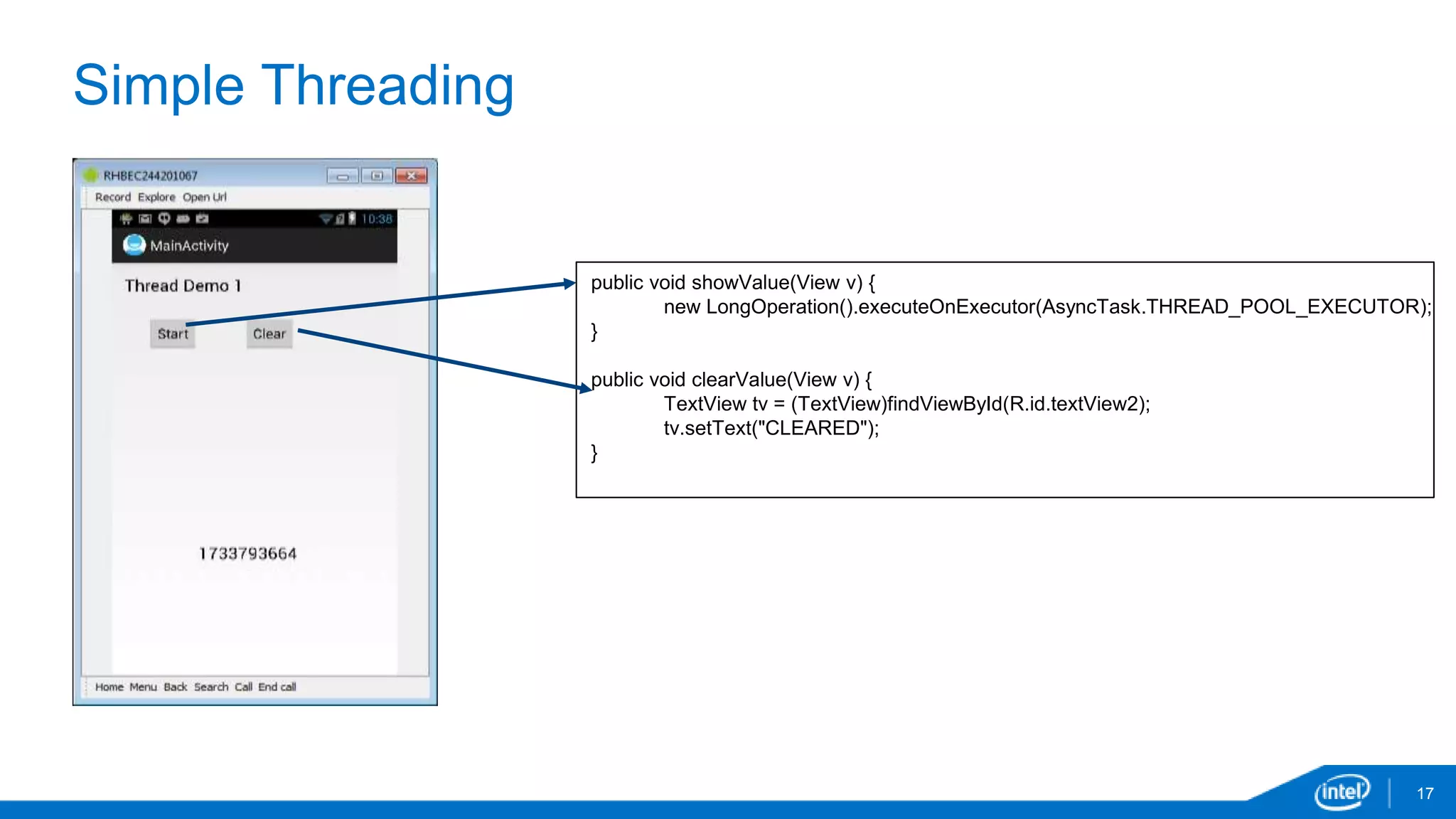
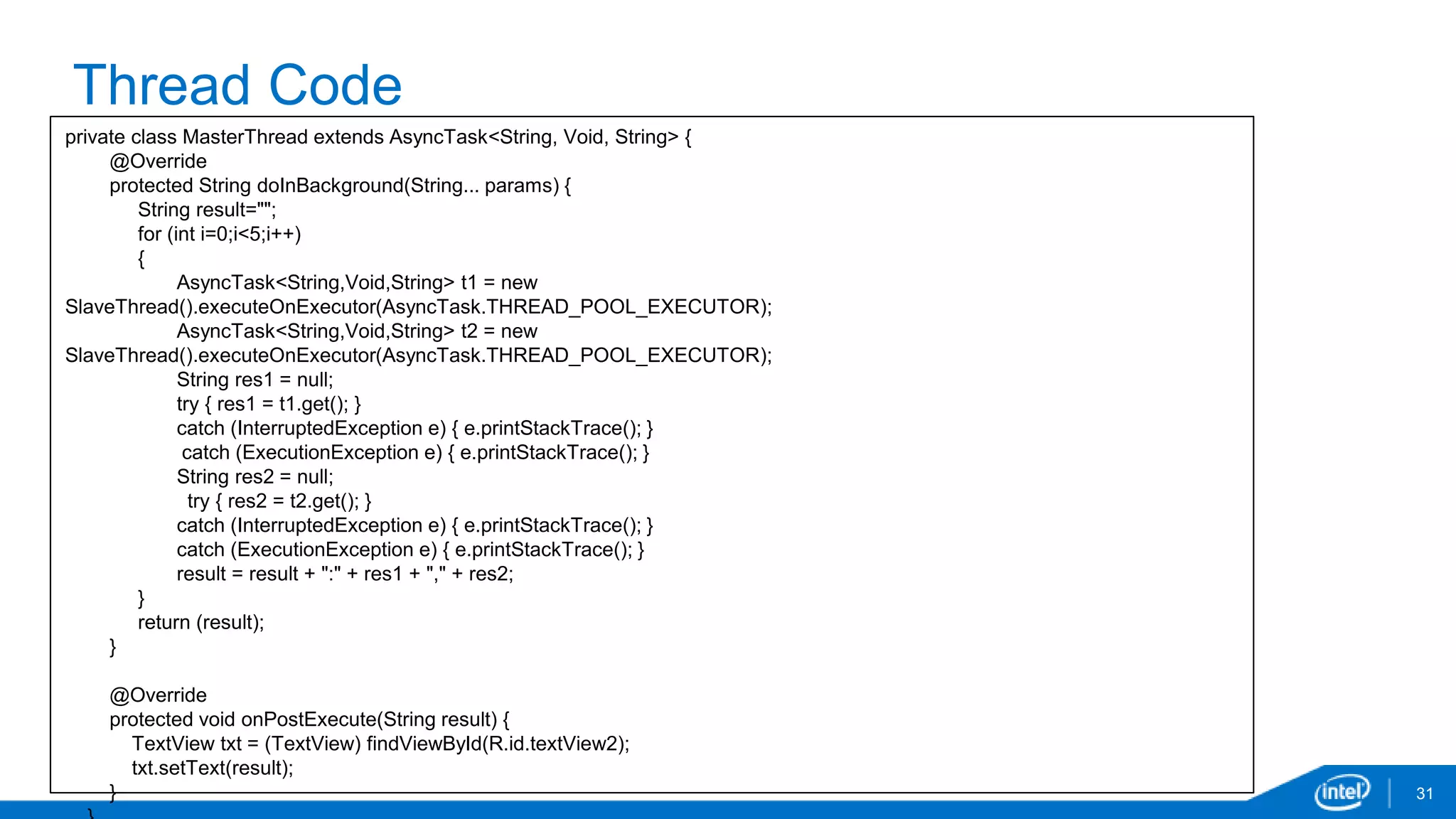
public void showValue1(View v) {
for (int i=0;i<256;i++)
a[i]=0;
for (int i=0;i<4;i++)
new Thread().executeOnExecutor(AsyncTask.THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR, String.valueOf(i));
}
// No False Sharing
public void showValue2(View v) {
for (int i=0;i<256;i++)
a[i]=0;
for (int i=0;i<4;i++)
new Thread().executeOnExecutor(AsyncTask.THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR,
String.valueOf(i*64));
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/andevcon-threadingbehaviorandroid-141125203546-conversion-gate02/75/Tools-and-Techniques-for-Understanding-Threading-Behavior-in-Android-40-2048.jpg)
![Thread Body
41
private class Thread extends AsyncTask<String, Void, String> {
@Override
protected String doInBackground(String... params) {
int tid=Integer.parseInt(params[0]);
int lim = tid+32;
for (int j=0;j<1000;j++)
for (int k=0;k<10000;k++)
for (int i=tid;i<lim;i+=4)
a[i]=a[i]+1;
return (params[0]);
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(String result) {
TextView txt = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView2);
txt.setText(txt.getText() + " " + result + ":" + a[Integer.parseInt(result)]);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/andevcon-threadingbehaviorandroid-141125203546-conversion-gate02/75/Tools-and-Techniques-for-Understanding-Threading-Behavior-in-Android-41-2048.jpg)