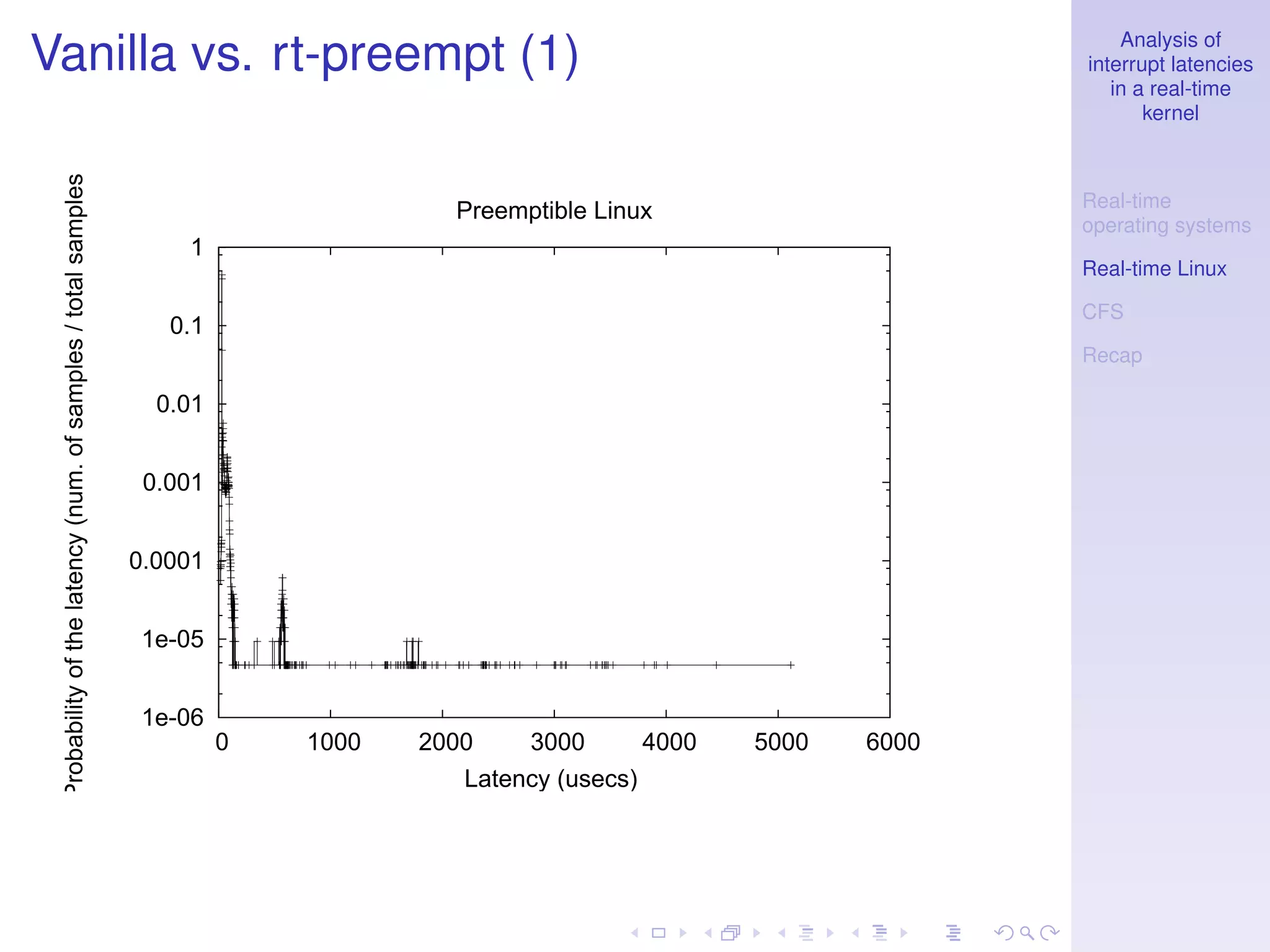
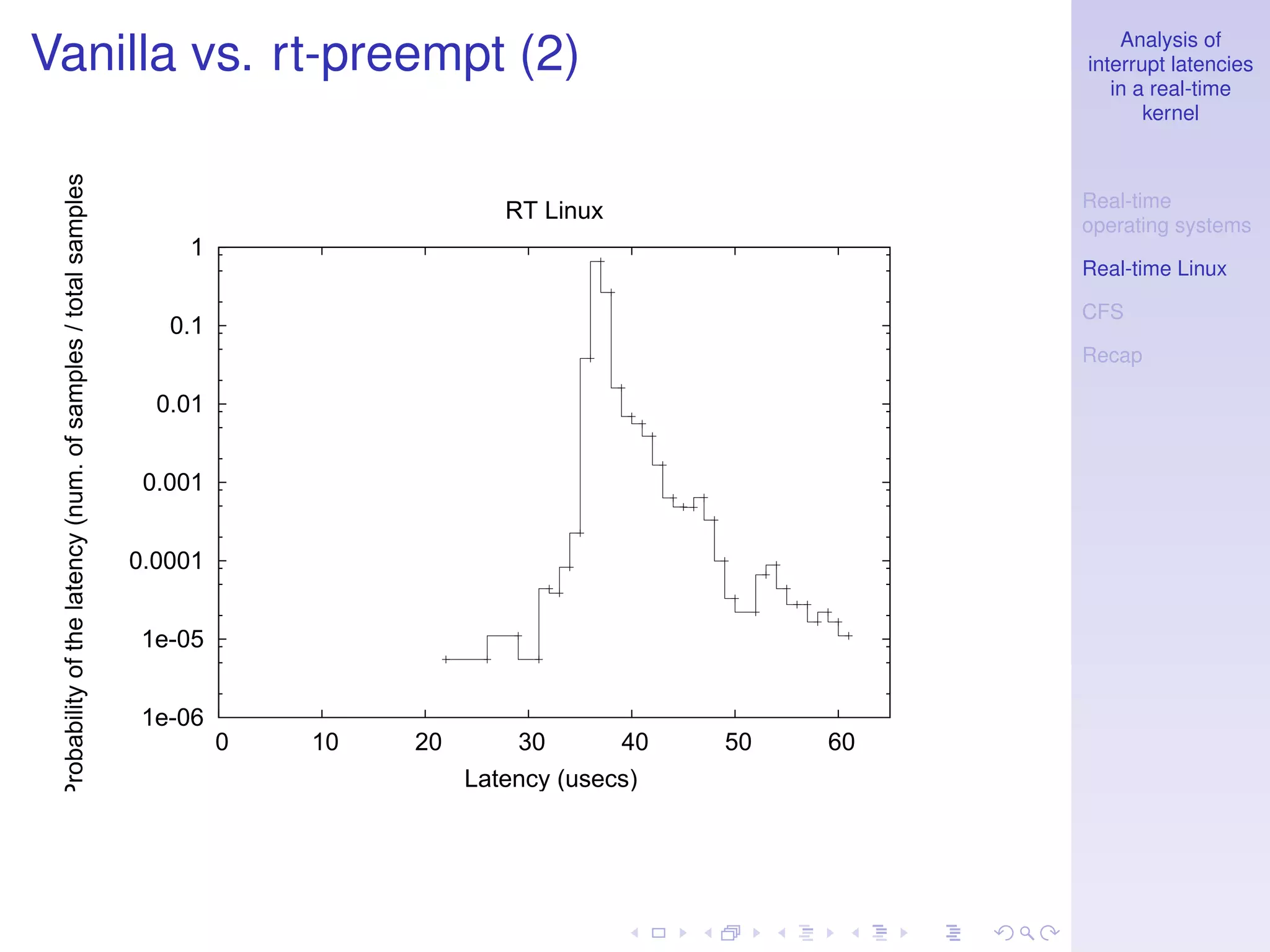
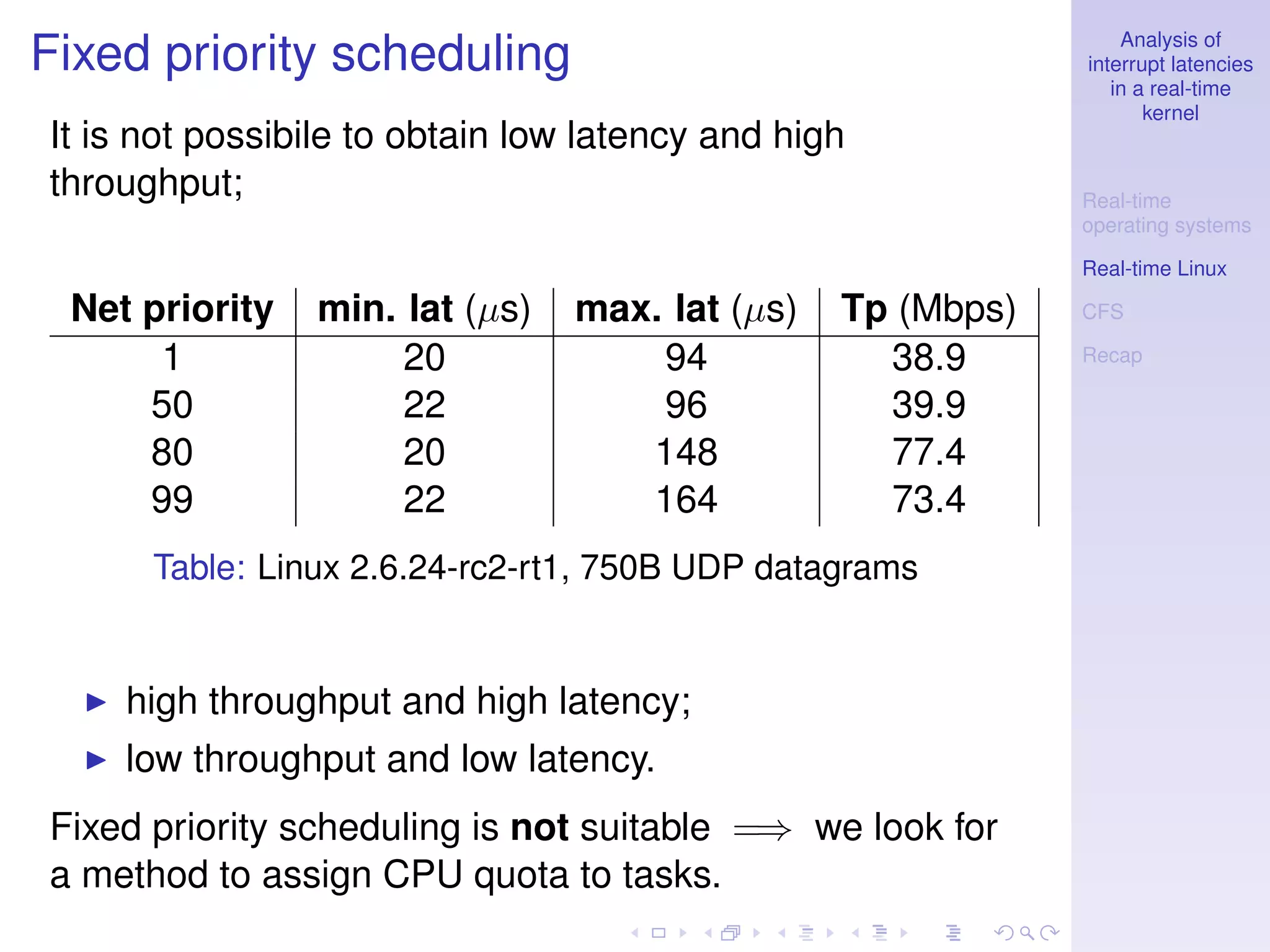
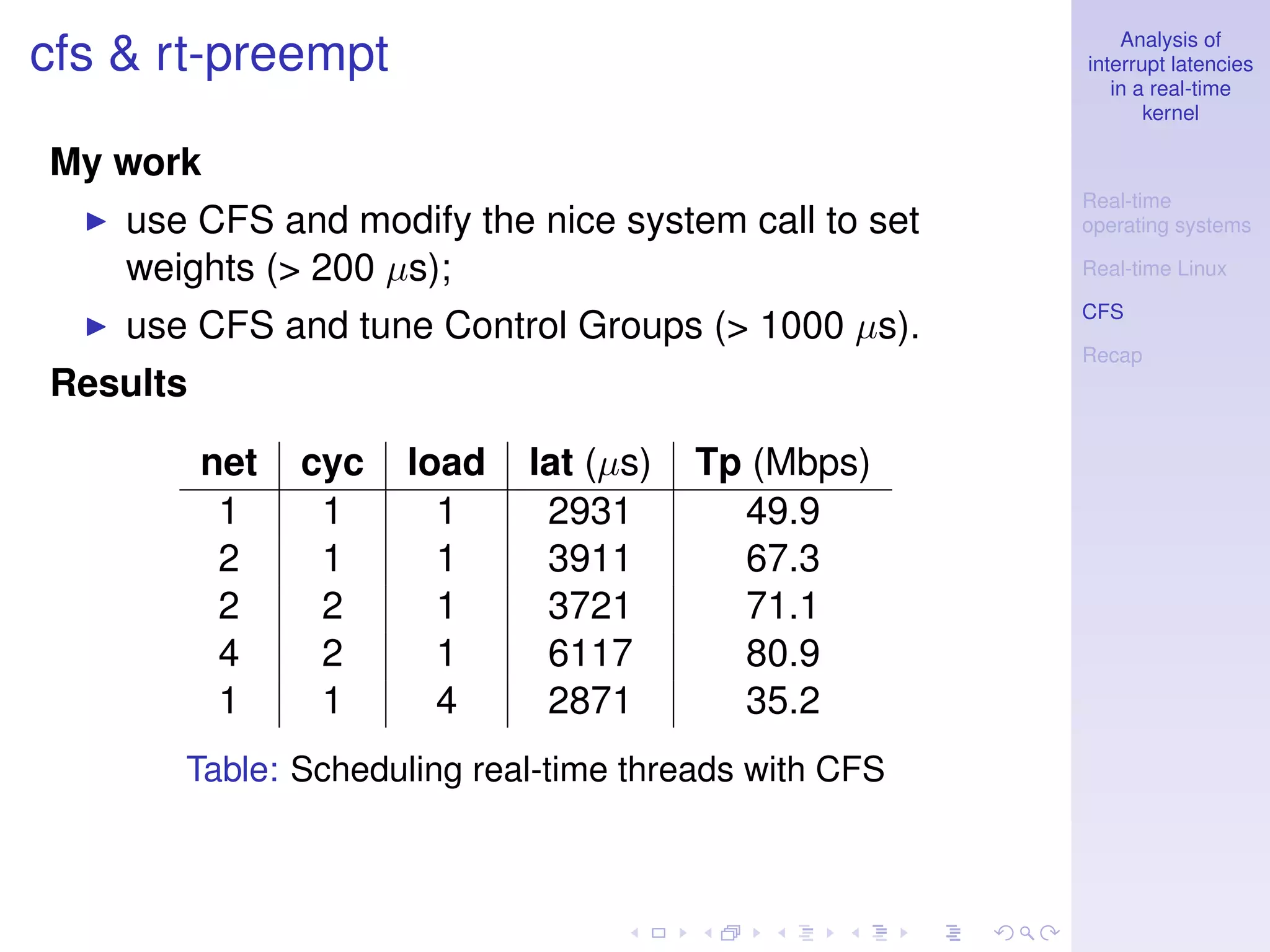
This document analyzes interrupt latencies in a real-time kernel. It discusses how real-time operating systems must ensure operations complete within fixed deadlines to maintain predictability. When dealing with device drivers, this implies managing race conditions and fulfilling temporal constraints. The document evaluates the performance of the Linux real-time preempt patch using cyclictest to measure latency and compares its performance to the standard Linux kernel.