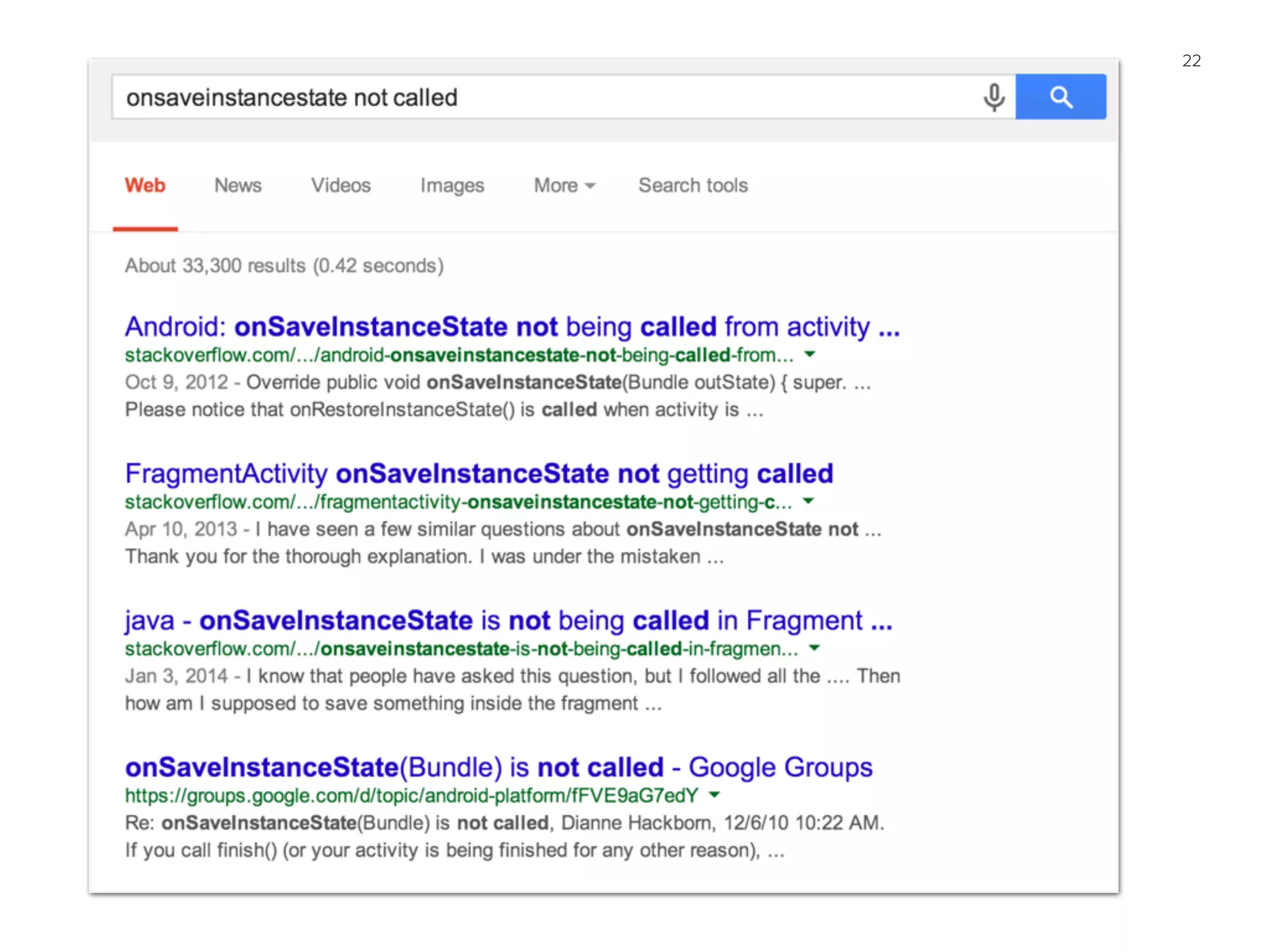
This document discusses techniques for improving Android application performance, including:
1. Using static factory methods and object pooling to improve memory management.
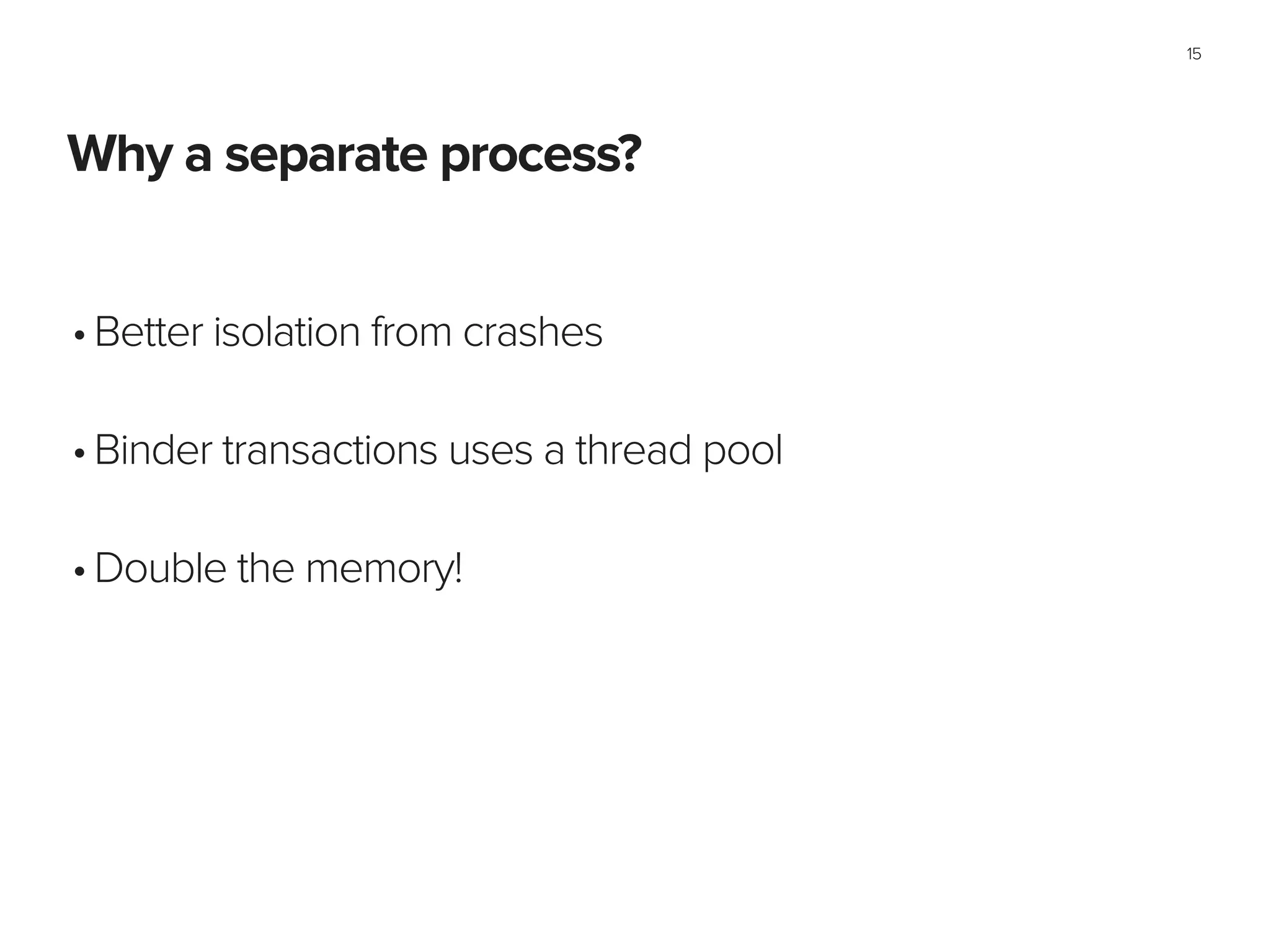
2. Configuring applications and services to run in separate processes to improve isolation and increase available memory.
3. Implementing multi-threading correctly using Handlers to schedule work off the UI thread and reduce garbage collection calls.
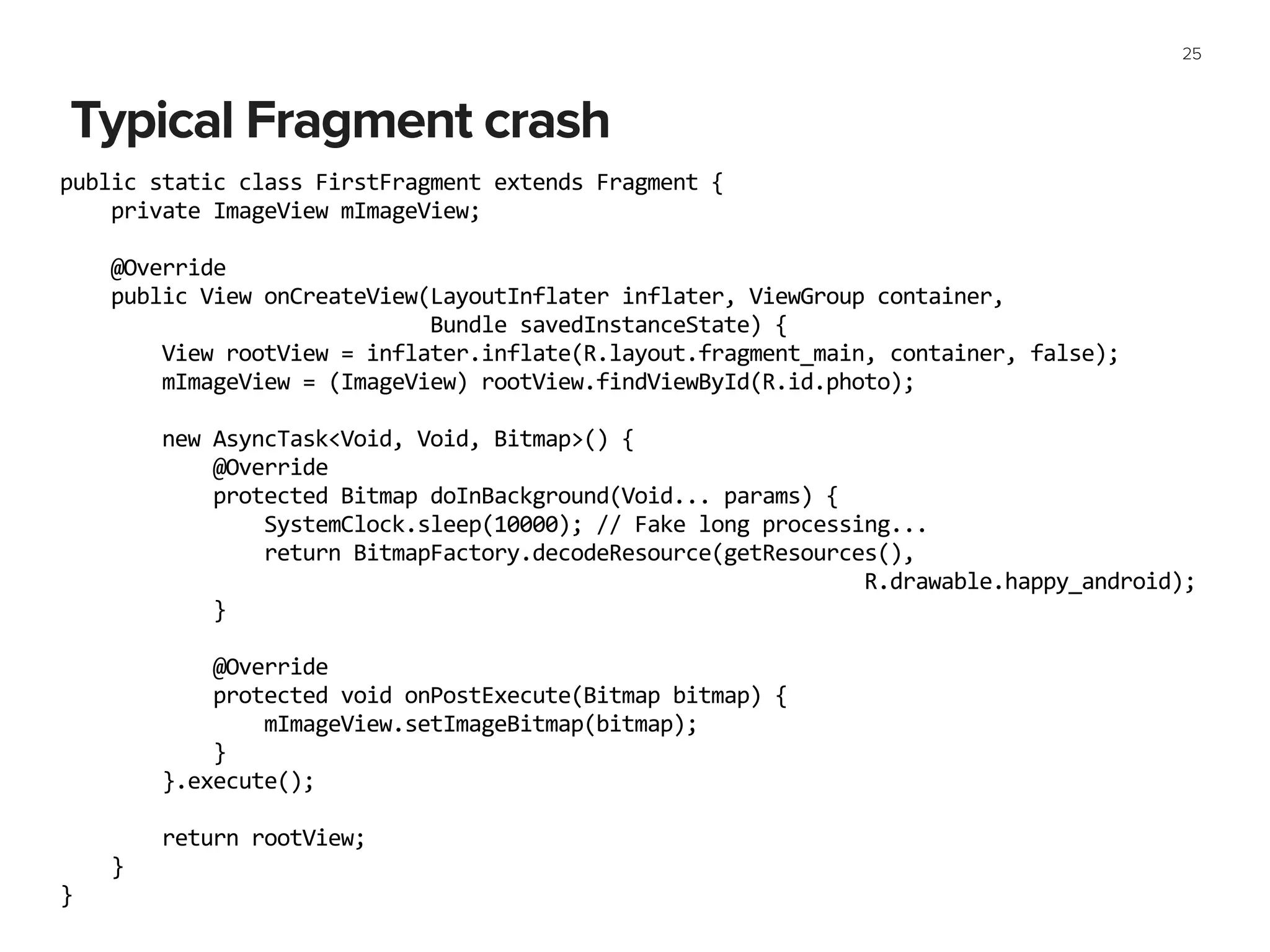
4. Understanding how to use Android application and activity components like Services and Fragments appropriately.

















![Support library can be upgraded!
24
dependencies
{
compile
'com.android.support:appcompat-‐v7:+'
compile
'com.android.support:support-‐v4:19.1.+'
compile
fileTree(dir:
'libs',
include:
['*.jar'])
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidprogramming-pushingthelimits-droidconde2014-clean-140609162610-phpapp01/75/Android-programming-_pushing_the_limits-24-2048.jpg)






![Most common ContentProvider mistake :)
32
@Override
public
Cursor
query(Uri
uri,
String[]
projection,
String
selection,
String[]
selectionArgs,
String
sortOrder)
{
SQLiteDatabase
db
=
mDatabaseHelper.getReadableDatabase();
int
match
=
sUriMatcher.match(uri);
Cursor
cursor
=
null;
switch
(match)
{
case
ALL_ROWS:
cursor
=
db.query(Contract.TABLE_NAME,
projection,
selection,
selectionArgs,
"",
"",
sortOrder);
break;
case
SINGLE_ROW:
String
id
=
uri.getLastPathSegment();
cursor
=
db.query(Contract.TABLE_NAME,
projection,
"_id
=
?",
new
String[]{id},
"",
"",
sortOrder);
break;
}
if(cursor
!=
null)
{
cursor.setNotificationUri(getContext().getContentResolver(),
uri);
}
return
cursor;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidprogramming-pushingthelimits-droidconde2014-clean-140609162610-phpapp01/75/Android-programming-_pushing_the_limits-32-2048.jpg)

![Don’t forget bulkInsert() !!!
34
@Override
public
int
bulkInsert(Uri
uri,
ContentValues[]
values)
{
SQLiteDatabase
db
=
mDatabaseHelper.getWritableDatabase();
int
match
=
sUriMatcher.match(uri);
int
inserted
=
0;
switch
(match)
{
case
TASKS_CODE:
try
{
db.beginTransaction();
for
(ContentValues
value
:
values)
{
long
id
=
db.insert(Contract.TABLE_NAME,
"",
value);
if
(id
<=
0)
throw
new
SQLException("Failed
with
inserting.");
inserted++;
}
db.setTransactionSuccessful();
getContext().getContentResolver().notifyChange(uri,
null);
}
finally
{
db.endTransaction();
}
}
return
inserted;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidprogramming-pushingthelimits-droidconde2014-clean-140609162610-phpapp01/75/Android-programming-_pushing_the_limits-34-2048.jpg)


