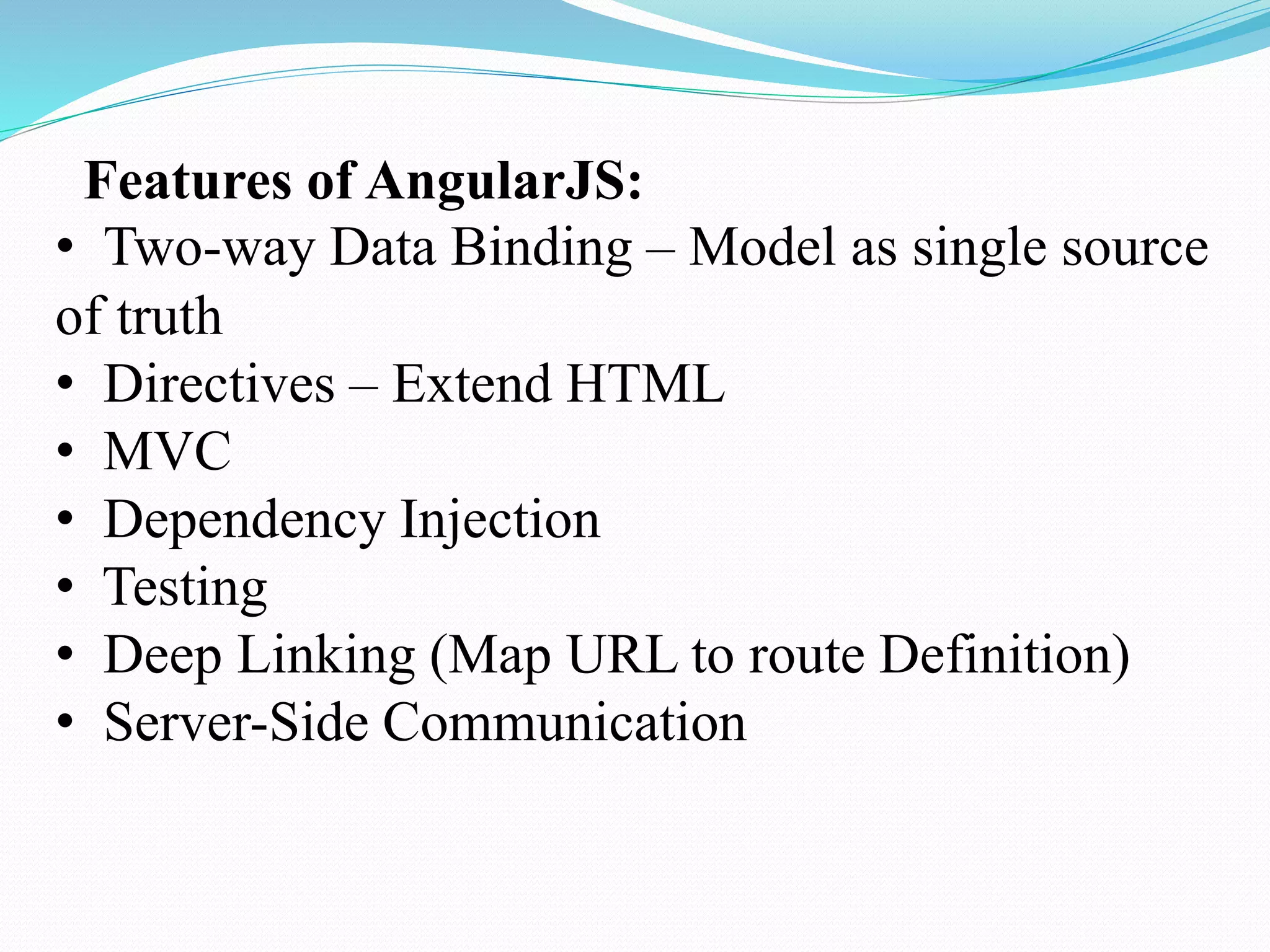
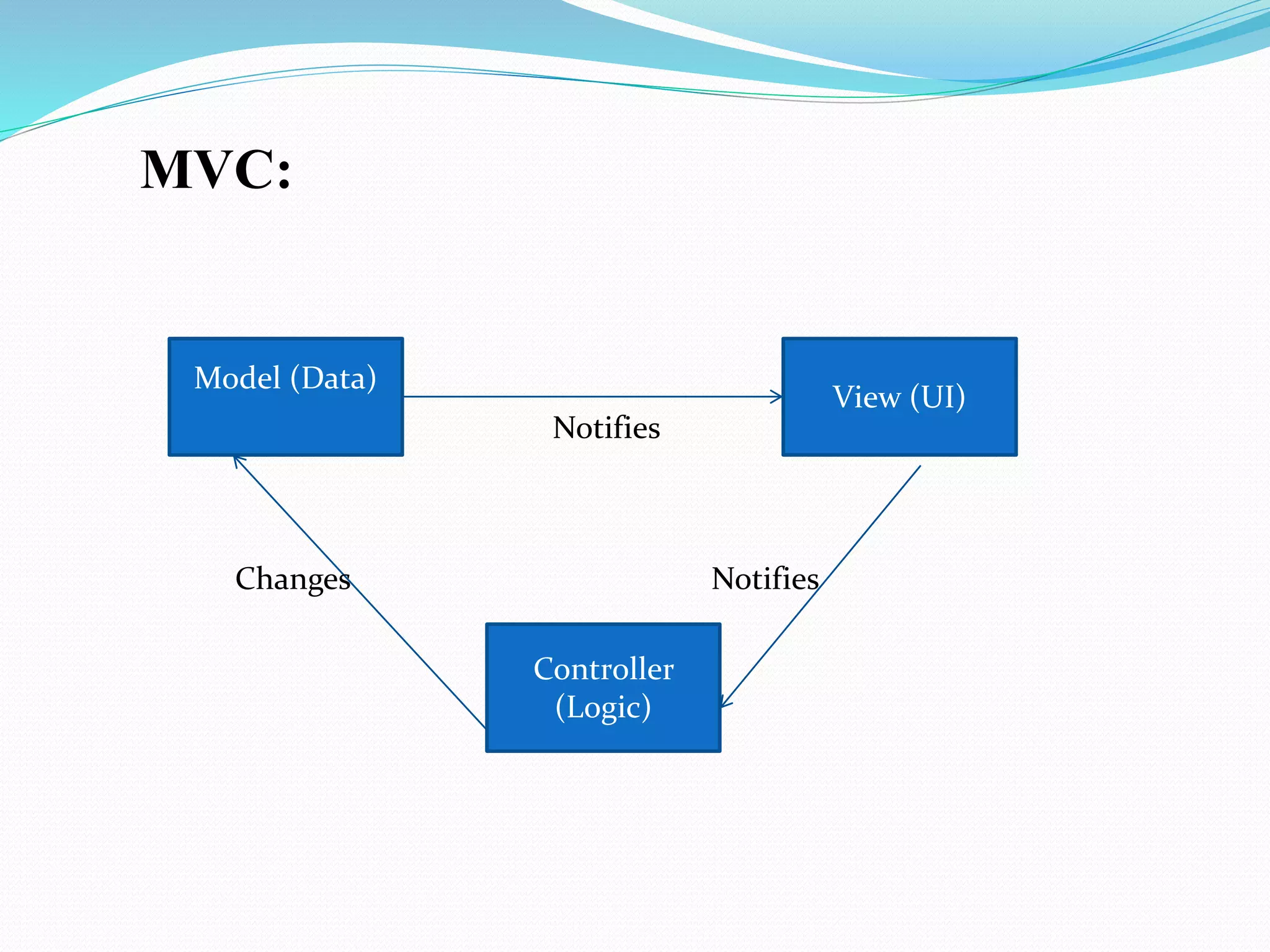
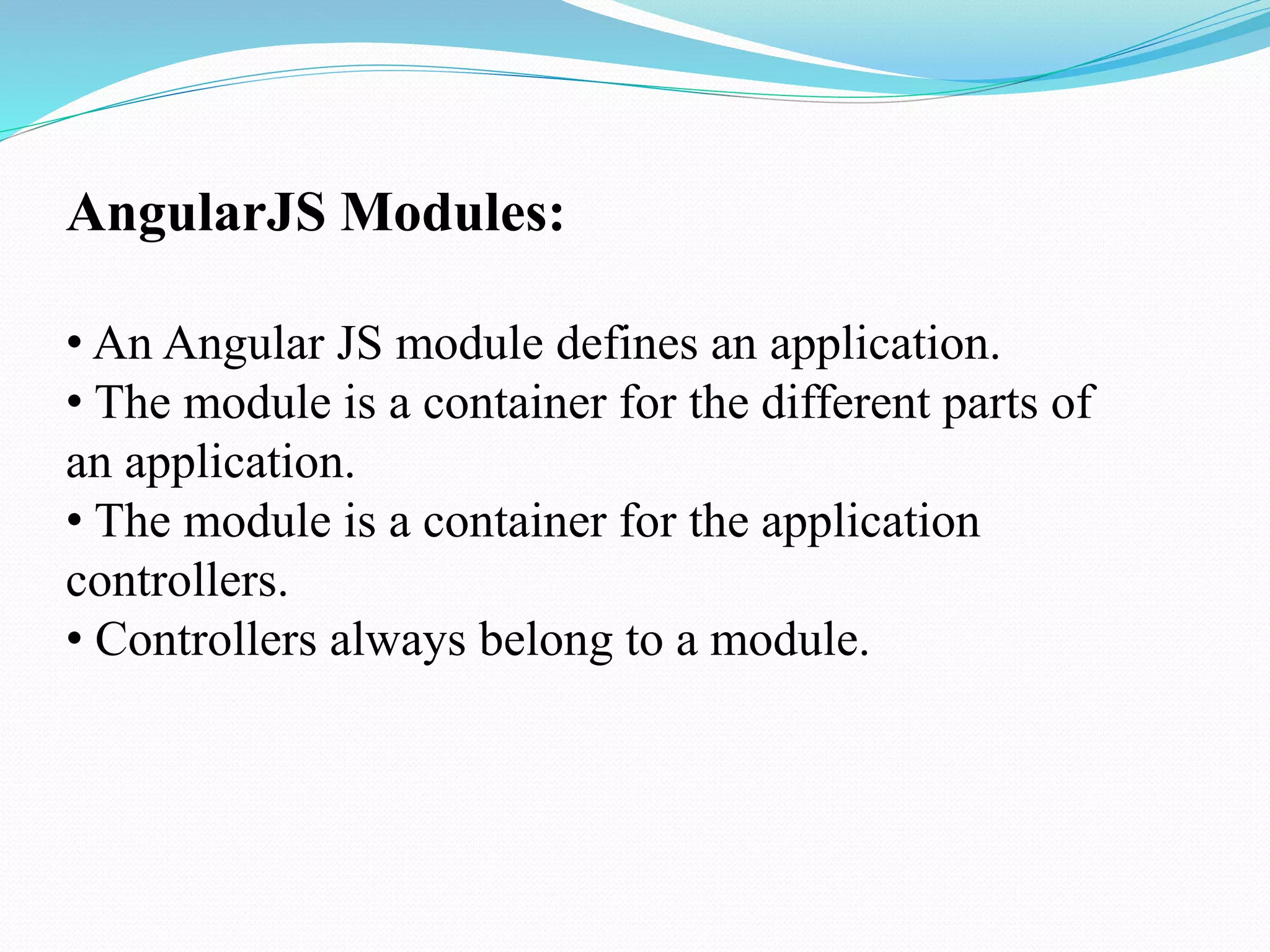
AngularJS is a JavaScript framework that enhances HTML with directives and supports two-way data binding, making it suitable for dynamic views. It offers features such as modules, controllers, and services, and is designed to create structured, maintainable web applications. The document outlines AngularJS fundamentals, including its integration into HTML and capabilities compared to other frameworks like jQuery.