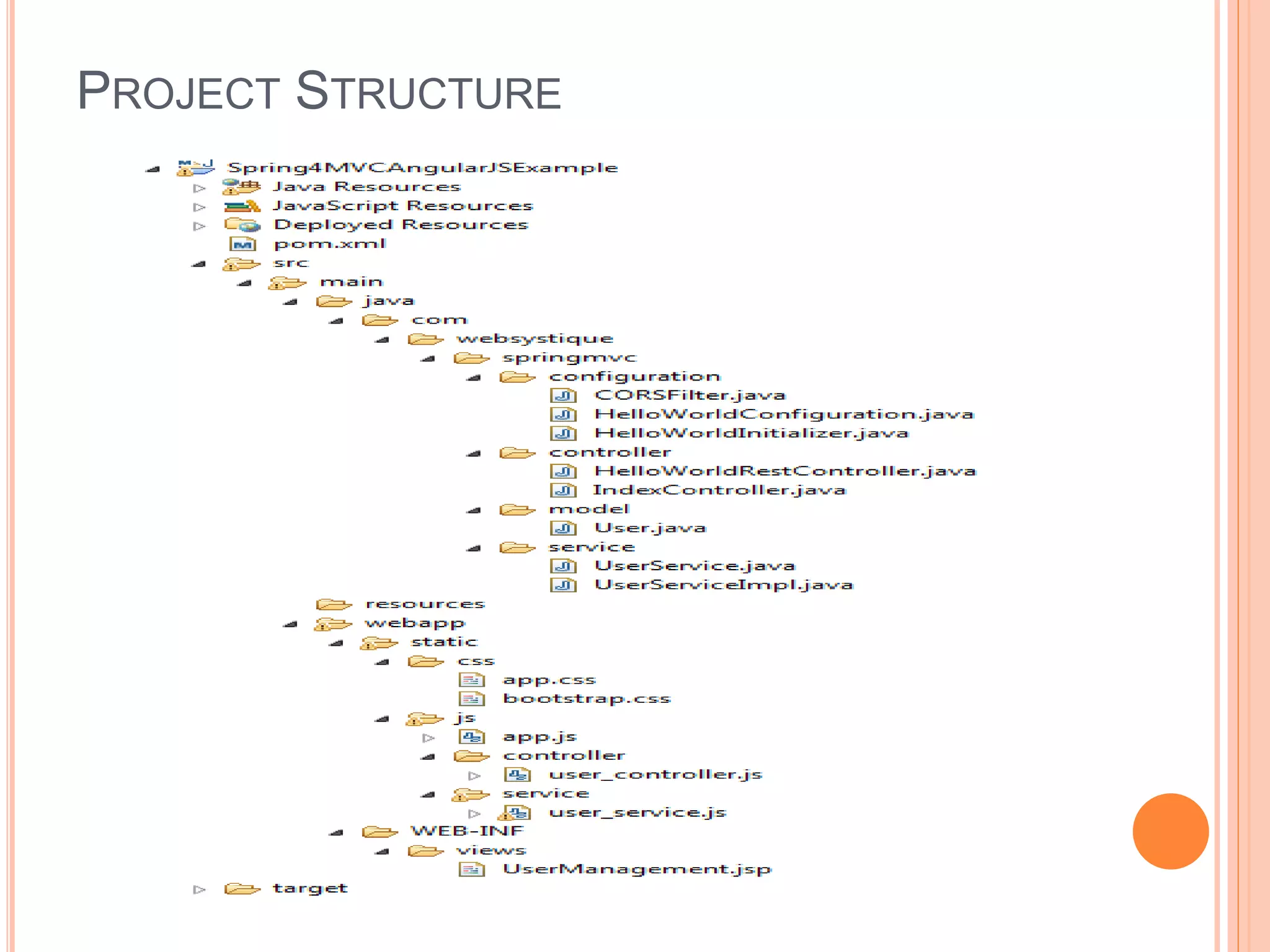
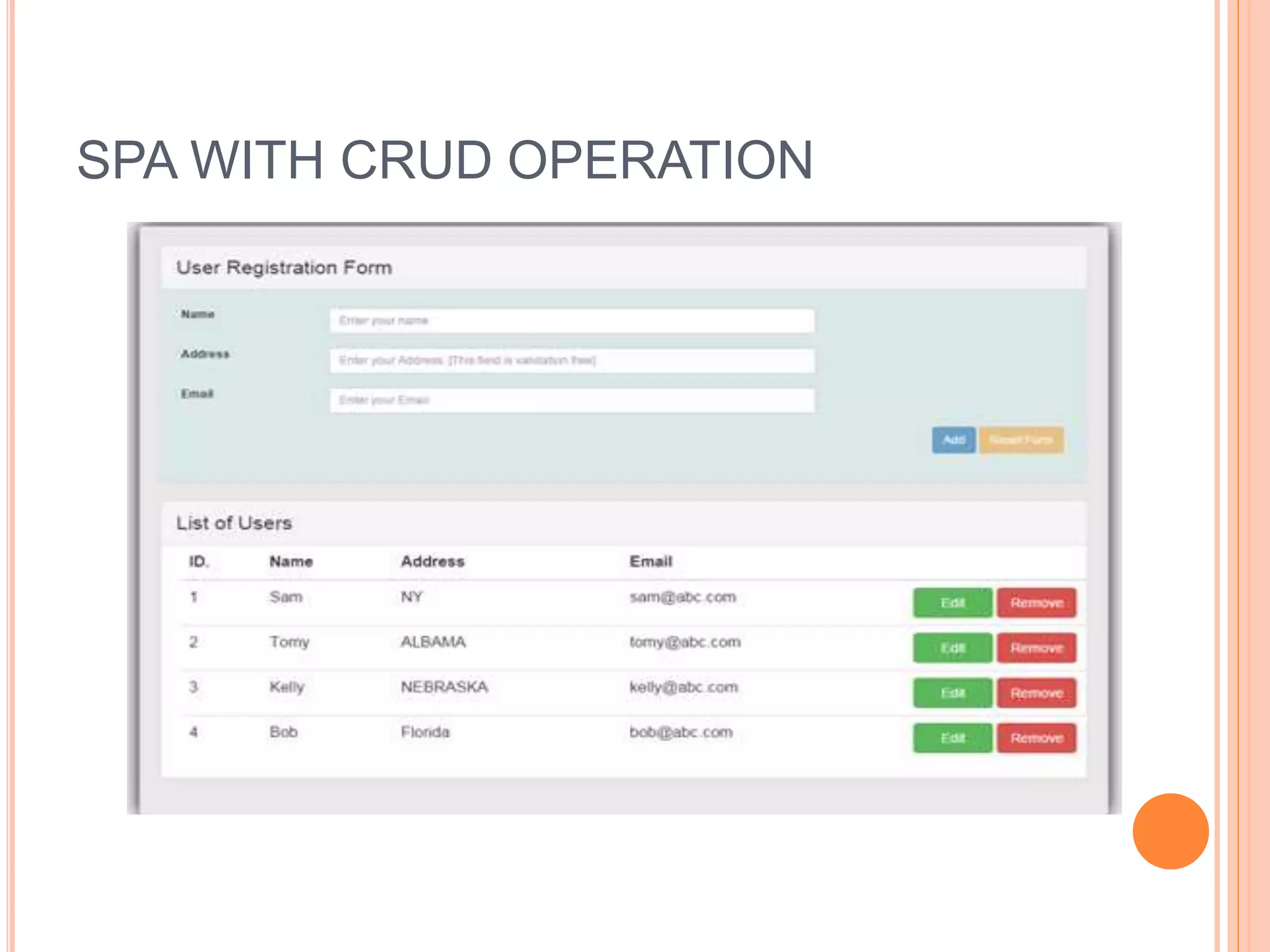
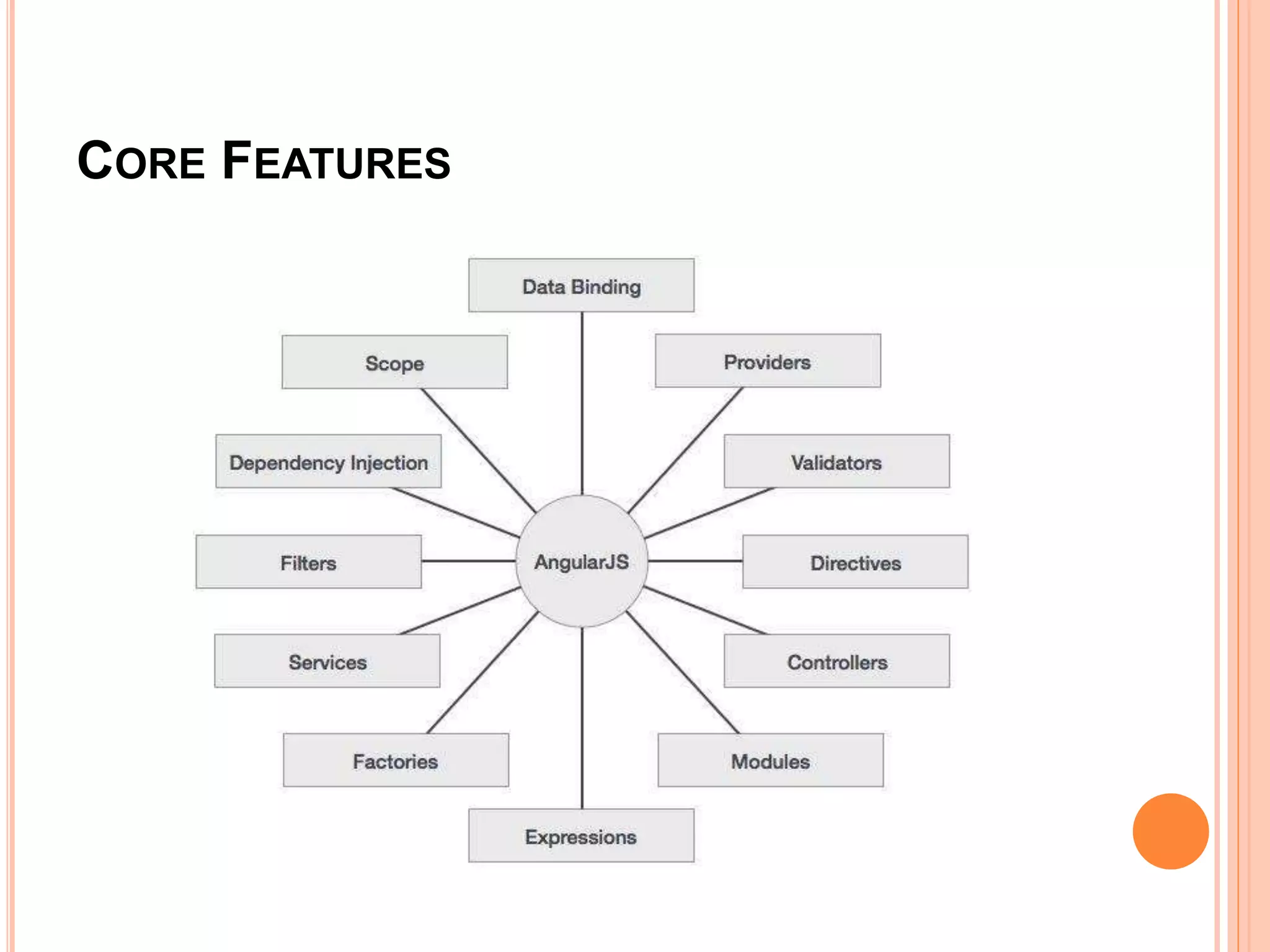
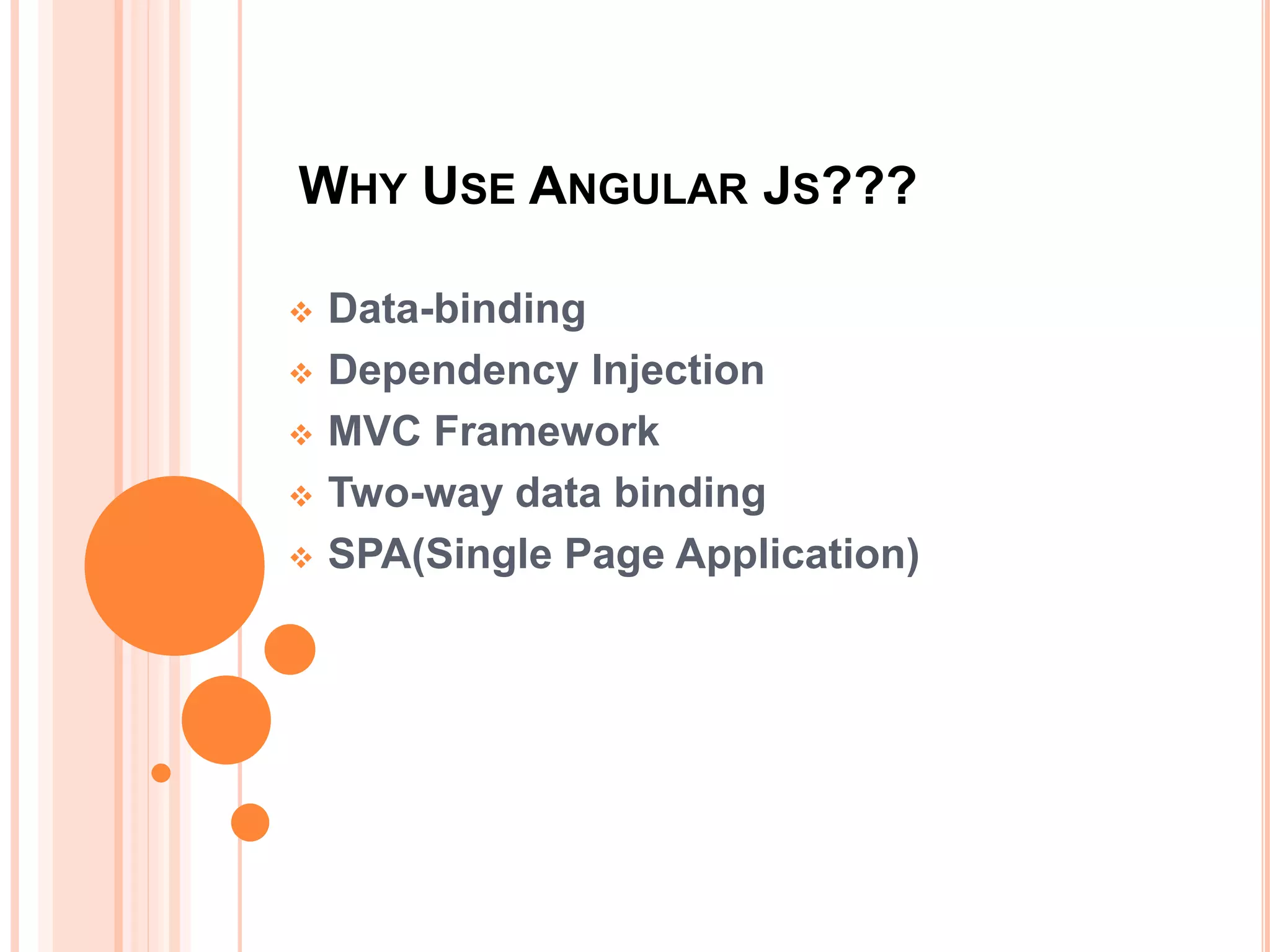
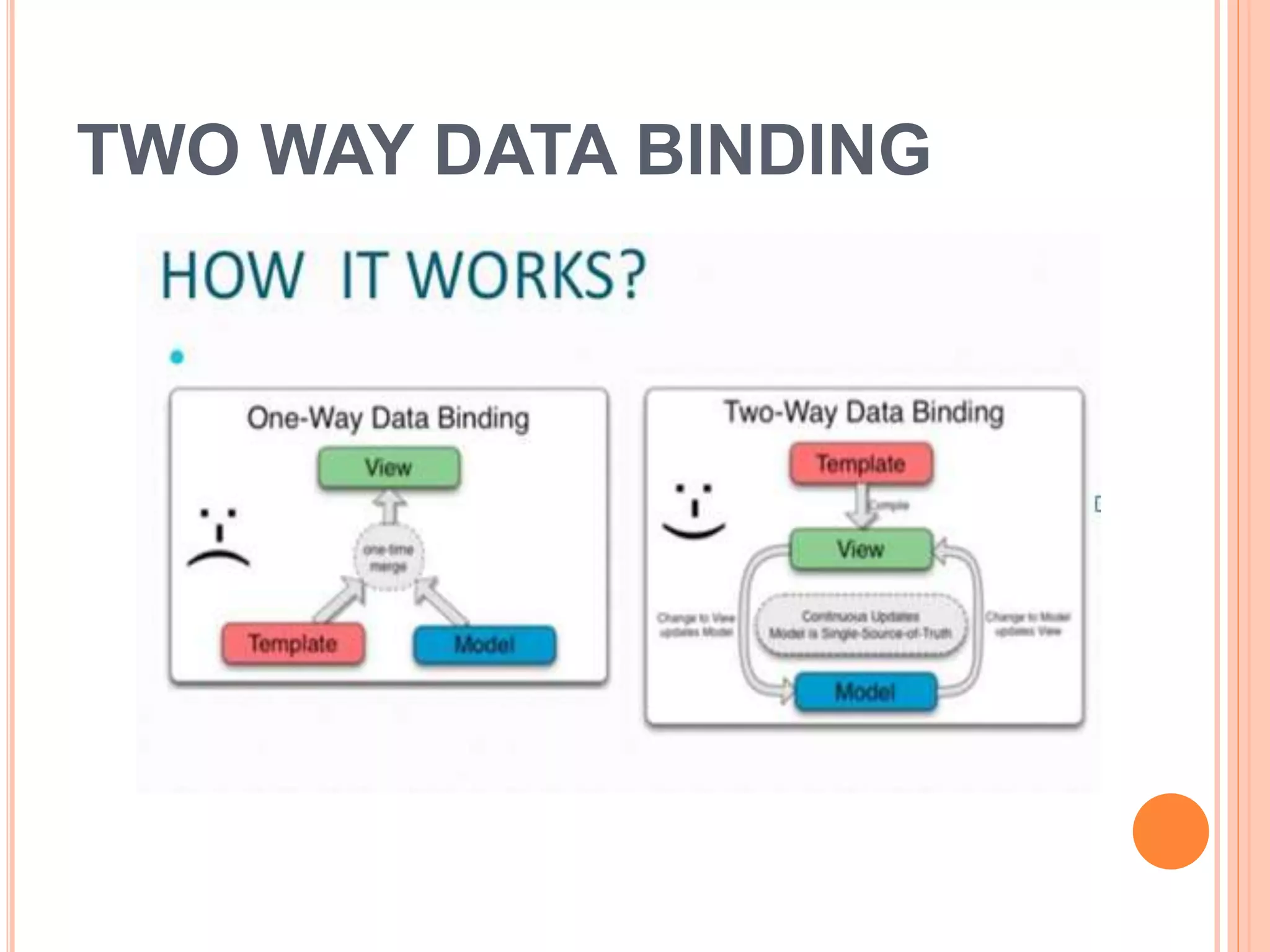
AngularJS is a JavaScript framework that extends HTML attributes with directives to bind data to the page with expressions. It uses MVC architecture with two-way data binding and dependency injection. Core features include directives like ng-app, ng-model, and ng-bind that initialize applications and bind data to HTML. Controllers act as data providers and models define application structure. Services provide reusable utilities, and filters change expression display. AngularJS allows building single page applications with data-driven components.





![<TR NG-REPEAT="X IN RECORDS">
<TD>{{X.NAME}}</TD>
<TD>{{X.COUNTRY}}</TD>
</TR>
<SCRIPT>
VAR APP = ANGULAR.MODULE("MYAPP", []);
APP.CONTROLLER("MYCTRL", FUNCTION($SCOPE) {
$SCOPE.RECORDS = [
{
"NAME" : "ALFREDS FUTTERKISTE",
"COUNTRY" : "GERMANY"
}, {
"NAME" : "BERGLUNDS SNABBKÖP",
"COUNTRY" : "SWEDEN"
} ]
});
</SCRIPT>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-160919121922/75/Angular-js-13-2048.jpg)
![<TABLE NG-CONTROLLER="MYCTRL" BORDER="1">
<TR NG-REPEAT="(X, Y) IN MYOBJ">
<TD>{{X}}</TD>
<TD>{{Y}}</TD>
</TR>
</TABLE>
<SCRIPT>
VAR APP = ANGULAR.MODULE("MYAPP", []);
APP.CONTROLLER("MYCTRL", FUNCTION($SCOPE) {
$SCOPE.MYOBJ = {
"NAME" : "ALFREDS FUTTERKISTE",
"COUNTRY" : "GERMANY",
"CITY" : "BERLIN"
}
});
</SCRIPT>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-160919121922/75/Angular-js-14-2048.jpg)
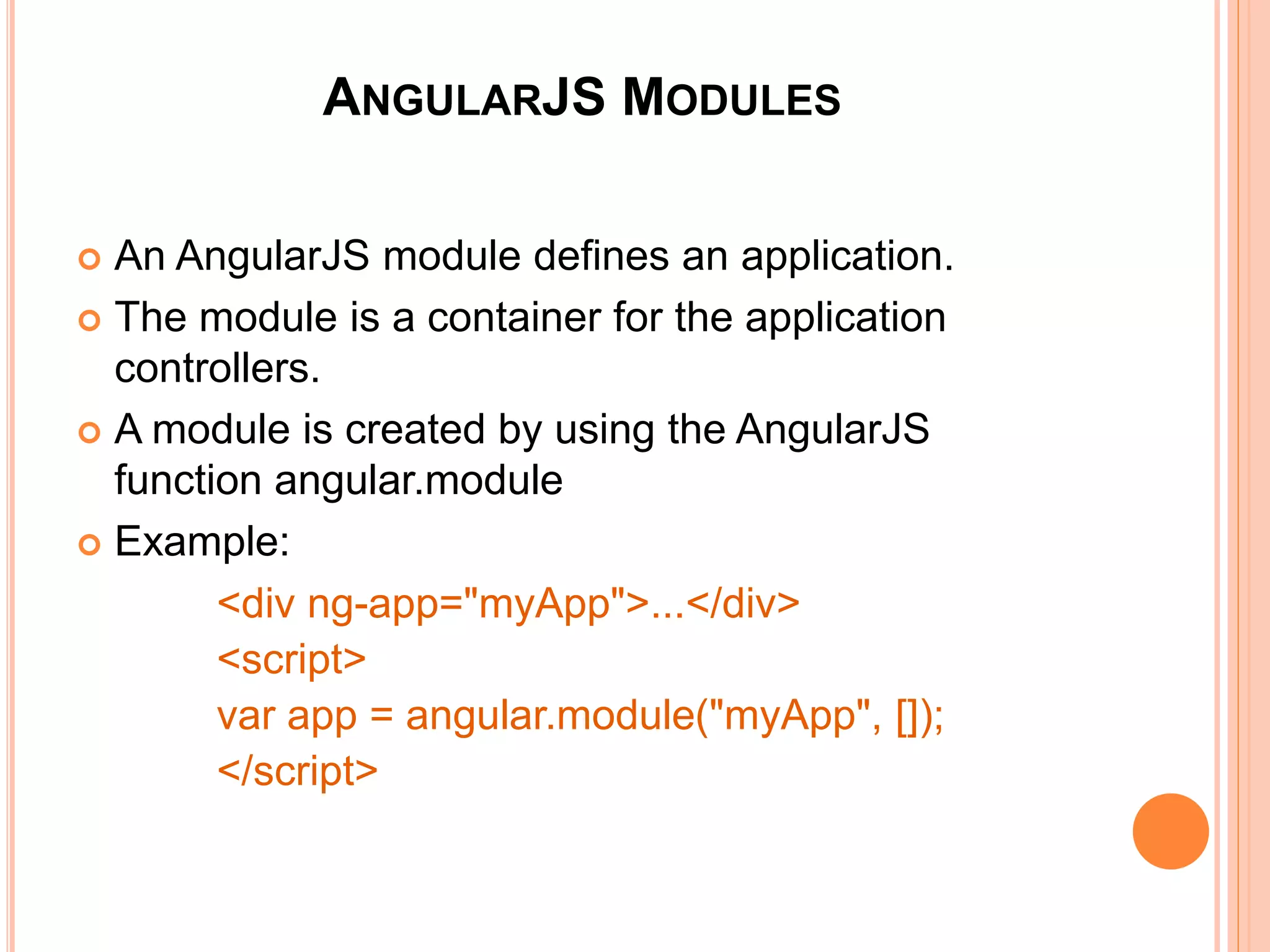

![ANGULARJS MODULES
An AngularJS module defines an application.
The module is a container for the application
controllers.
A module is created by using the AngularJS
function angular.module
Example:
<div ng-app="myApp">...</div>
<script>
var app = angular.module("myApp", []);
</script>
<div ng-app="myApp">...</div>
<script>
var app = angular.module("myApp", []);
</script>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-160919121922/75/Angular-js-17-2048.jpg)
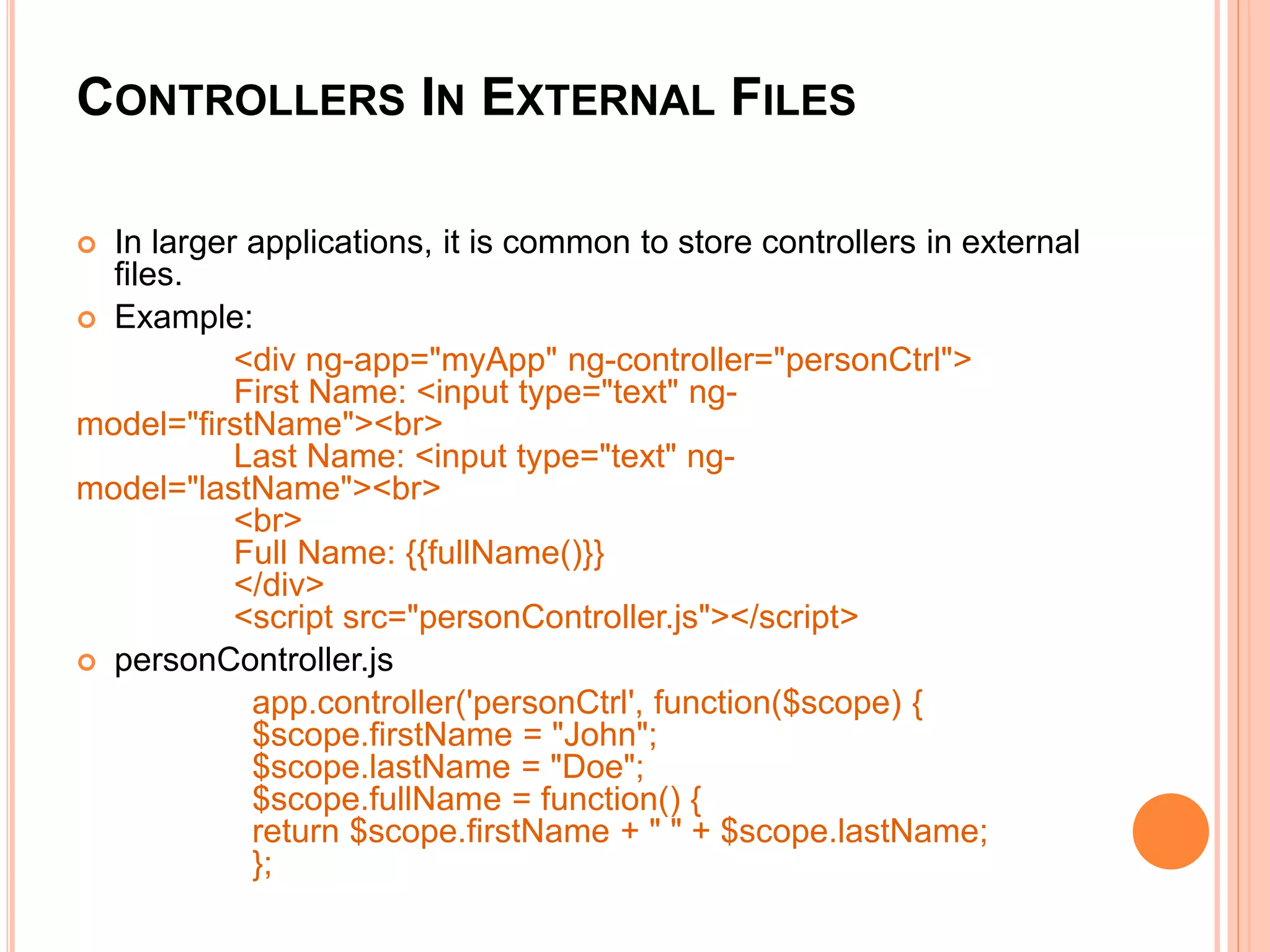
![ANGULARJS CONTROLLERS
AngularJS applications are controlled by controllers. They act as
containers.
The ng-controller directive defines the application controller.
Example:
<div ng-app="myApp" ng-controller="myCtrl">
First Name: <input type="text" ng-model="firstName"><br>
Last Name: <input type="text" ng-model="lastName"><br>
<br>
Full Name: {{firstName + " " + lastName}}
</div>
<script>
var app = angular.module('myApp', []);
app.controller('myCtrl', function($scope) {
$scope.firstName = "John";
$scope.lastName = "Doe"; });
</script>
<div ng-app="myApp" ng-controller="myCtrl">
First Name: <input type="text" ng-
model="firstName"><br>
Last Name: <input type="text" ng-
model="lastName"><br>
<br>
Full Name: {{firstName + " " + lastName}}
</div>
<script>
var app = angular.module('myApp', []);
app.controller('myCtrl', function($scope) {
$scope.firstName = "John";
$scope.lastName = "Doe"; });
</script>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-160919121922/75/Angular-js-19-2048.jpg)


![ANGULARJS SCOPE
The scope is the binding part between the HTML (view)
and the JavaScript (controller).
Example:
<div ng-app="myApp" ng-
controller="myCtrl">
<h1>{{carname}}</h1>
</div>
<script>
var app = angular.module('myApp', []);
app.controller('myCtrl', function($scope) {
$scope.carname = "Volvo";
});
</script>
<div ng-app="myApp" ng-controller="myCtrl">
<h1>{{carname}}</h1>
</div>
<script>
var app = angular.module('myApp', []);
app.controller('myCtrl', function($scope) {
$scope.carname = "Volvo";
});
</script>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-160919121922/75/Angular-js-22-2048.jpg)

![ANGULARJS SERVICES
$http Service
The service makes a request to the server, and lets your
application handle the response.
Example:
$http.get("welcome.htm").then(function (resp
onse) {
$scope.myWelcome = response.data;
});
});
var app = angular.module('myApp', []);
app.controller('myCtrl', function($scope, $http)
{
$http.get("welcome.htm").then(function (response) {
$scope.myWelcome = response.data;
});
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-160919121922/75/Angular-js-24-2048.jpg)
![$TIMEOUT SERVICE
$timeout Service
o The $timeout service is AngularJS' version of
the window.setTimeout function.
o Example:
var app = angular.module('myApp', []);
app.controller('myCtrl', function($scope,
$timeout) {
$scope.myHeader = "Hello World!";
$timeout(function () {
$scope.myHeader = "How are you today?";
}, 2000);
});
var app = angular.module('myApp', []);
app.controller('myCtrl', function($scope,
$timeout) {
$scope.myHeader = "Hello World!";
$timeout(function () {
$scope.myHeader = "How are you today?";
}, 2000);
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angularjs-160919121922/75/Angular-js-25-2048.jpg)