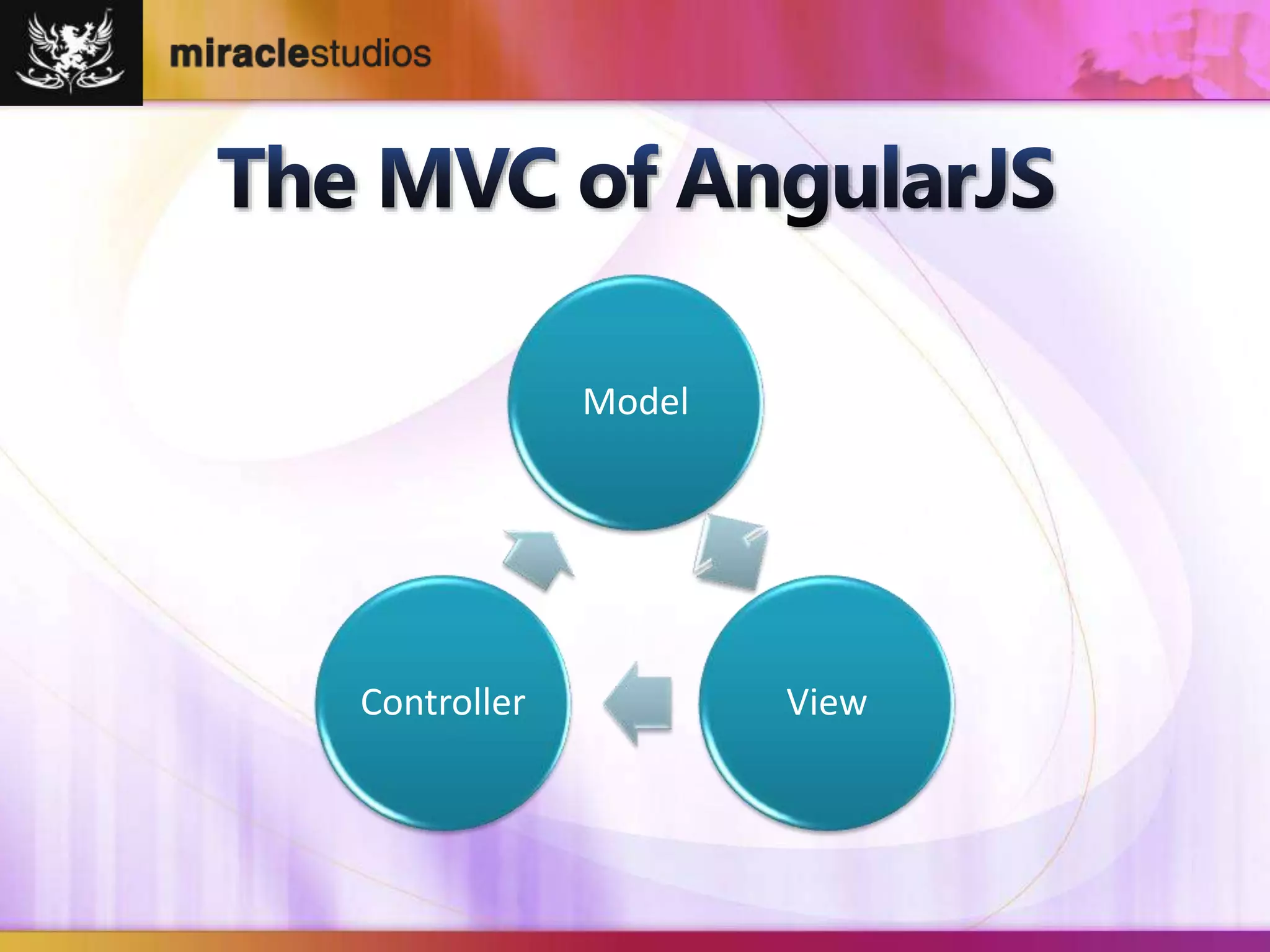
The document discusses AngularJS, a powerful JavaScript framework for building dynamic web applications, emphasizing its model-view-controller architecture, two-way data binding, and dependency injection features. It provides code examples illustrating the usage of directives, controllers, services, and routing in AngularJS applications. Additionally, it touches upon AngularJS's built-in support for internationalization, allowing easy formatting of dates and currencies.




![myapp = angular.module("myapp", []);
myapp.directive('div', function() {
var directive = {};
directive.restrict = 'E'; /* restrict this directive to elements */
directive.template = "My first directive: {{textToInsert}}";
return directive;
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angualarjsdevelopment-140915073405-phpapp02/75/AngularJs-Superheroic-JavaScript-MVW-Framework-Services-by-Miracle-Studios-7-2048.jpg)



![Below are the core objects and component of AngularJS
1. Value :
A value in AngularJS is a simple object. It can be a number,
string or JavaScript object.
Example:
var myModule = angular.module("myModule", []);
myModule.value("numberValue", 999);
myModule.value("stringValue", "abc");
myModule.value("objectValue", { val1 : 123, val2 : "abc"} );](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angualarjsdevelopment-140915073405-phpapp02/75/AngularJs-Superheroic-JavaScript-MVW-Framework-Services-by-Miracle-Studios-11-2048.jpg)
![2. Factory:
Factory is a function that creates values. When a service,
controller etc. needs a value injected from a factory, the factory
creates the value on demand. Once created, the value is reused
for all services, controllers etc. which need it injected.
Example:
var myModule = angular.module("myModule", []);
myModule.factory("myFactory", function()
{ return "a value"; });
myModule.controller("MyController", function($scope, myFactory)
{ console.log(myFactory); });](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angualarjsdevelopment-140915073405-phpapp02/75/AngularJs-Superheroic-JavaScript-MVW-Framework-Services-by-Miracle-Studios-12-2048.jpg)
![3. Service:
A service in AngularJS is a singleton JavaScript object which
contains a set of functions. The functions contain whatever logic
is necessary for the service to carry out its work.
Example:
function MyService()
{ this.doIt = function() { console.log("done"); } }
var myModule = angular.module("myModule", []);
myModule.service("myService", MyService);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angualarjsdevelopment-140915073405-phpapp02/75/AngularJs-Superheroic-JavaScript-MVW-Framework-Services-by-Miracle-Studios-13-2048.jpg)
![4. Providers
Providers in AngularJS is the most flexible form of factory you
can create. You register a provider with a module just like you do
with a service or factory, except you use the provider() function
instead.
Example:
var myModule = angular.module("myModule", []);
myModule.provider("mySecondService", function() { var
provider = {}; provider.$get = function() { var service = {};
service.doService = function() { console.log("mySecondService:
Service Done!"); }
return service; }
return provider; });](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angualarjsdevelopment-140915073405-phpapp02/75/AngularJs-Superheroic-JavaScript-MVW-Framework-Services-by-Miracle-Studios-14-2048.jpg)
![var myModule = angular.module("myModule", []);
myModule.provider("mySecondService", function() {
var provider = {}; var config = { configParam : "default" };
provider.doConfig = function(configParam) { config.configParam = configParam; }
provider.$get = function() { var service = {}; service.doService = function() {
console.log("mySecondService: " + config.configParam);
}
return service;
}
return provider;
});
myModule.config( function( mySecondServiceProvider ) {
mySecondServiceProvider.doConfig("new config param");
}); myModule.controller("MyController", function($scope, mySecondService) {
$scope.whenButtonClicked = function() { mySecondService.doIt();
}
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angualarjsdevelopment-140915073405-phpapp02/75/AngularJs-Superheroic-JavaScript-MVW-Framework-Services-by-Miracle-Studios-15-2048.jpg)

![<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en">
<head> <title>AngularJS Routes example</title>
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.2.5/angular.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.2.5/angular-route.min.js">
</script>
</head>
<body ng-app="sampleApp"> <a href="#/route1">Route 1</a><br/>
<a href="#/route2">Route 2</a><br/>
<div ng-view></div> <script> var module = angular.module("sampleApp", ['ngRoute']);
module.config(['$routeProvider', function($routeProvider)
{ $routeProvider. when('/route1',
{ templateUrl: 'angular-route-template-1.jsp', controller: 'RouteController' }).
when('/route2',
{ templateUrl: 'angular-route-template-2.jsp', controller: 'RouteController' }). otherwise({ redirectTo: '/' });
}]);
module.controller("RouteController", function($scope) { })
</script>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angualarjsdevelopment-140915073405-phpapp02/75/AngularJs-Superheroic-JavaScript-MVW-Framework-Services-by-Miracle-Studios-17-2048.jpg)

![<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>AngularJS Routes example</title>
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.2.5/angular.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://code.angularjs.org/1.2.5/i18n/angular-locale_da-dk.js">
</script>
</head>
<body ng-app="myapp">
AngularJS I18n
<div ng-controller="mycontroller">
{{theDate | date : "fullDate"}} <br/>
{{theValue | currency }}
</div>
<script> var module = angular.module("myapp", []);
module.controller("mycontroller", function($scope) {
$scope.theDate = new Date();
$scope.theValue = 123.45; });
</script>
</body>
</html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angualarjsdevelopment-140915073405-phpapp02/75/AngularJs-Superheroic-JavaScript-MVW-Framework-Services-by-Miracle-Studios-19-2048.jpg)

