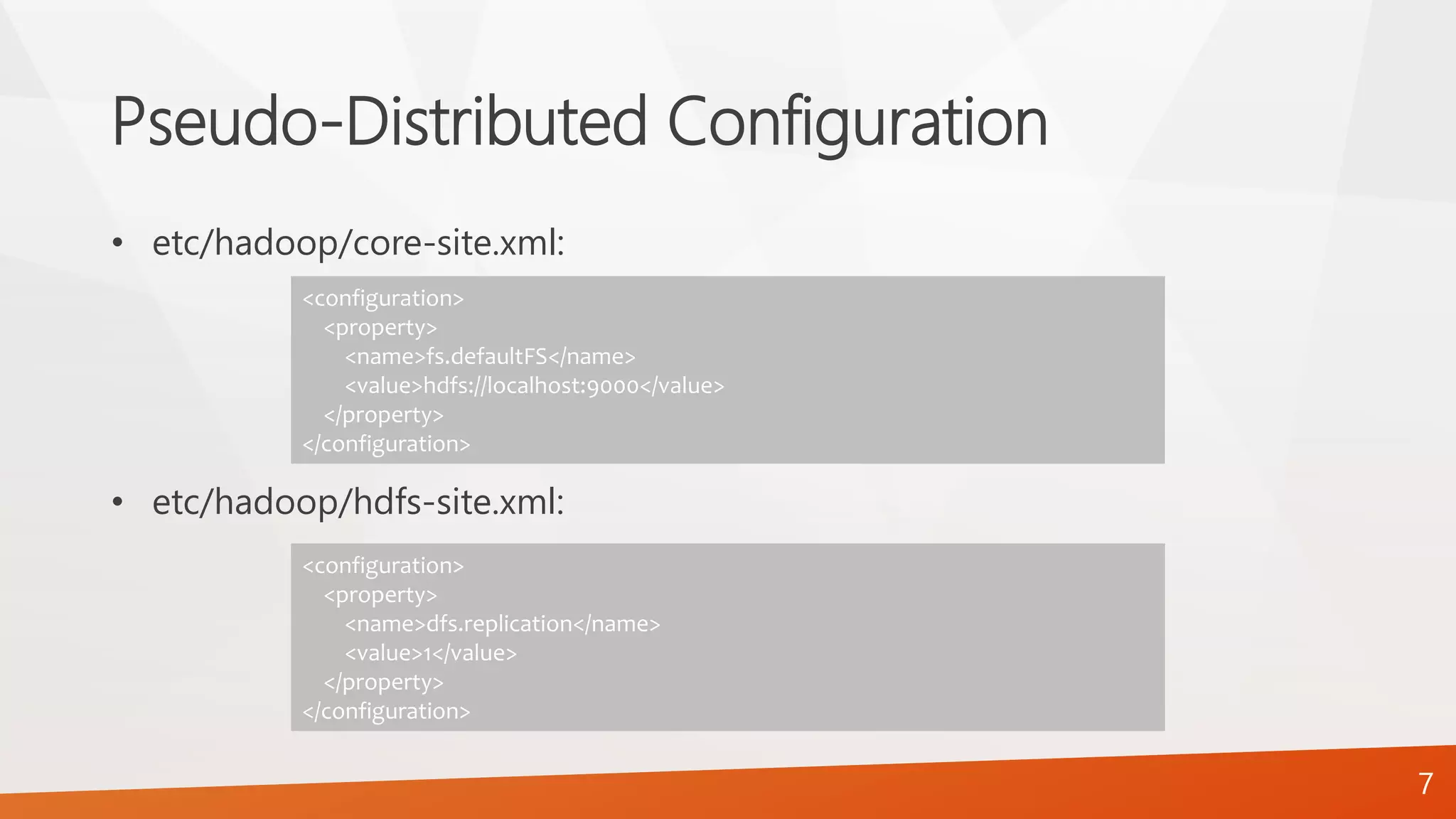
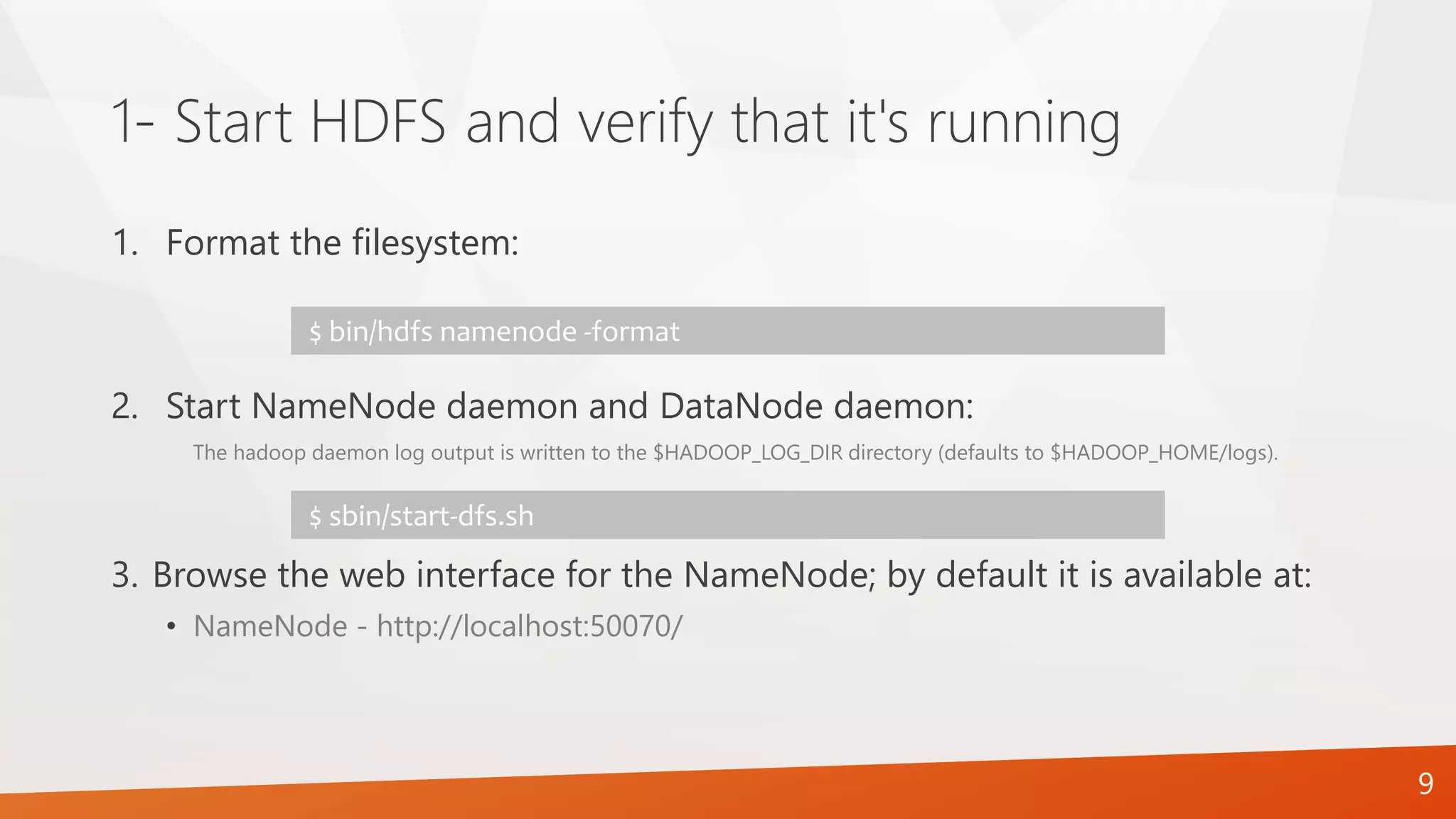
The document provides a comprehensive guide on setting up and configuring a single-node Hadoop installation, specifically focusing on the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS). It outlines the requirements, installation steps, and various operational modes, including local and pseudo-distributed configurations. Additionally, it includes a lab assignment with practical tasks for users to verify and utilize their HDFS setup.