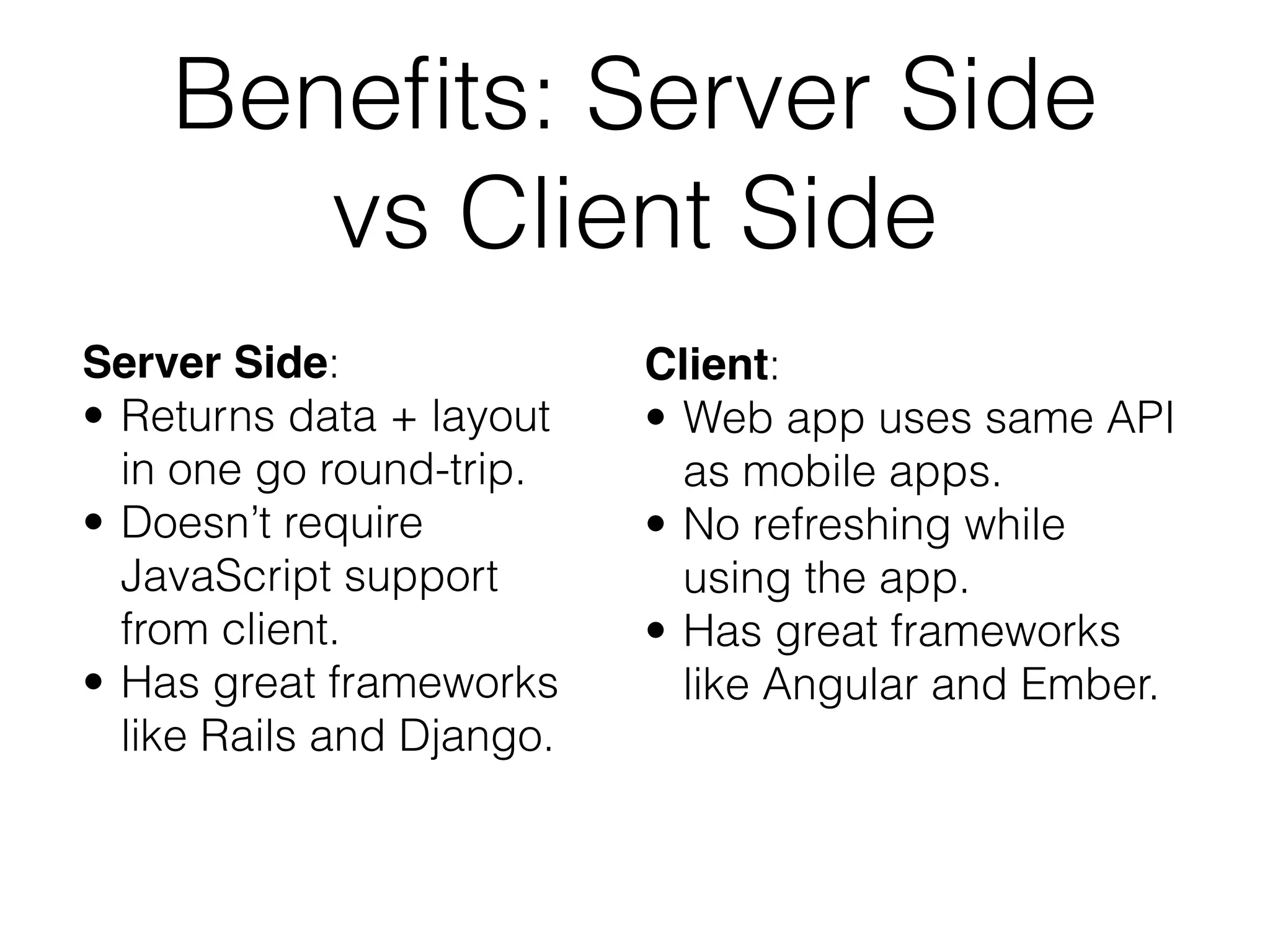
The document discusses the differences between server-side and client-side rendering in web applications, highlighting their respective benefits. It introduces the concept of API pre-fetching to improve performance, demonstrating how it can lead to faster rendering times. Additionally, the document outlines essential back-end requirements for implementing API pre-fetching and mentions relevant libraries and frameworks.





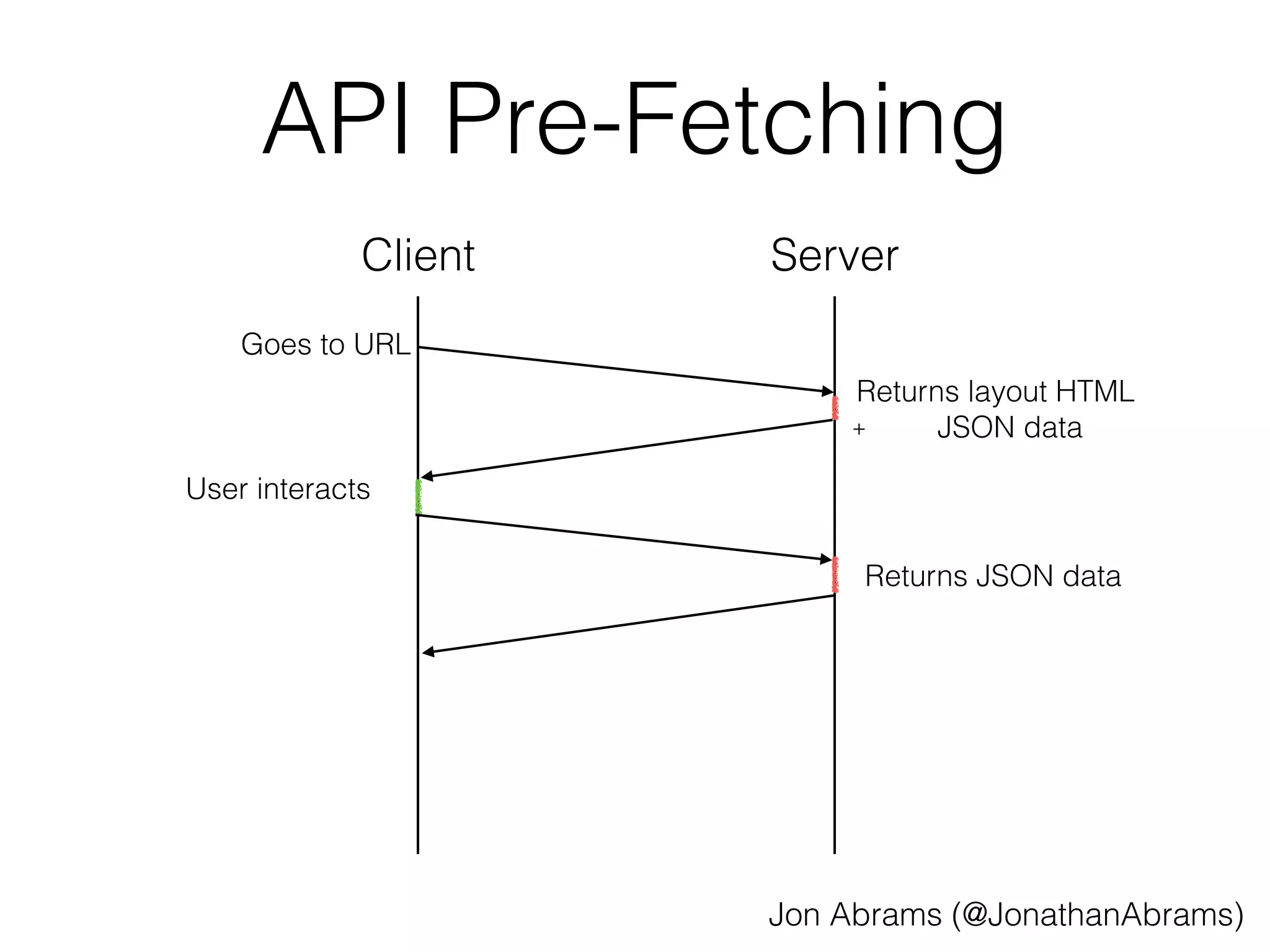
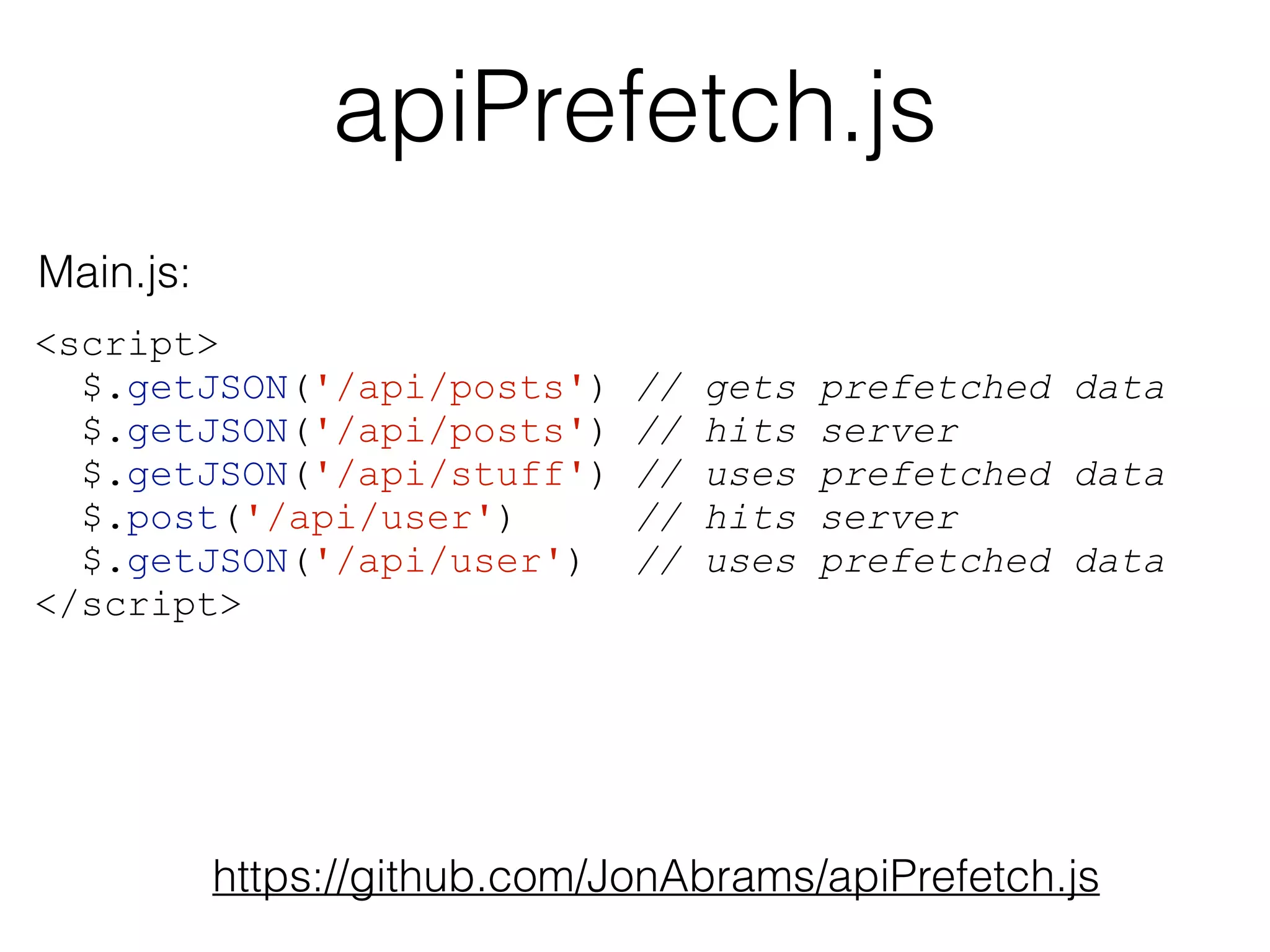
![API Pre-Fetching
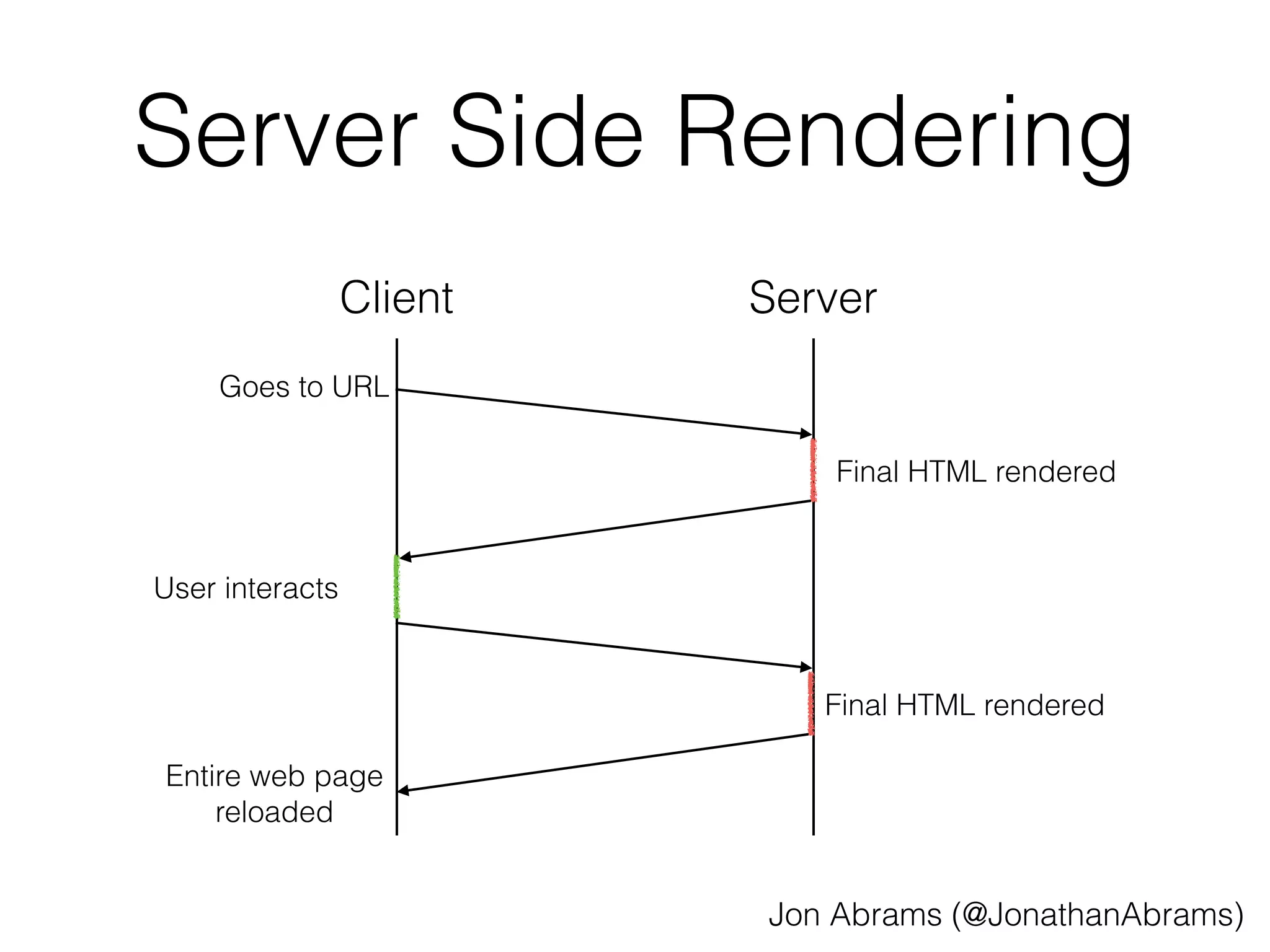
Rendered index.html:
<script src="/jquery.js"></script>
<script>
window.apiPrefetchData = {
"/api/posts": […],
"/api/user": {…}
};
</script>
<script src="/main.js"></script>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2014-10-20-jonabrams-html5devconf-141021193454-conversion-gate02/75/API-Prefetching-HTML5DevConf-Oct-21-2014-11-2048.jpg)
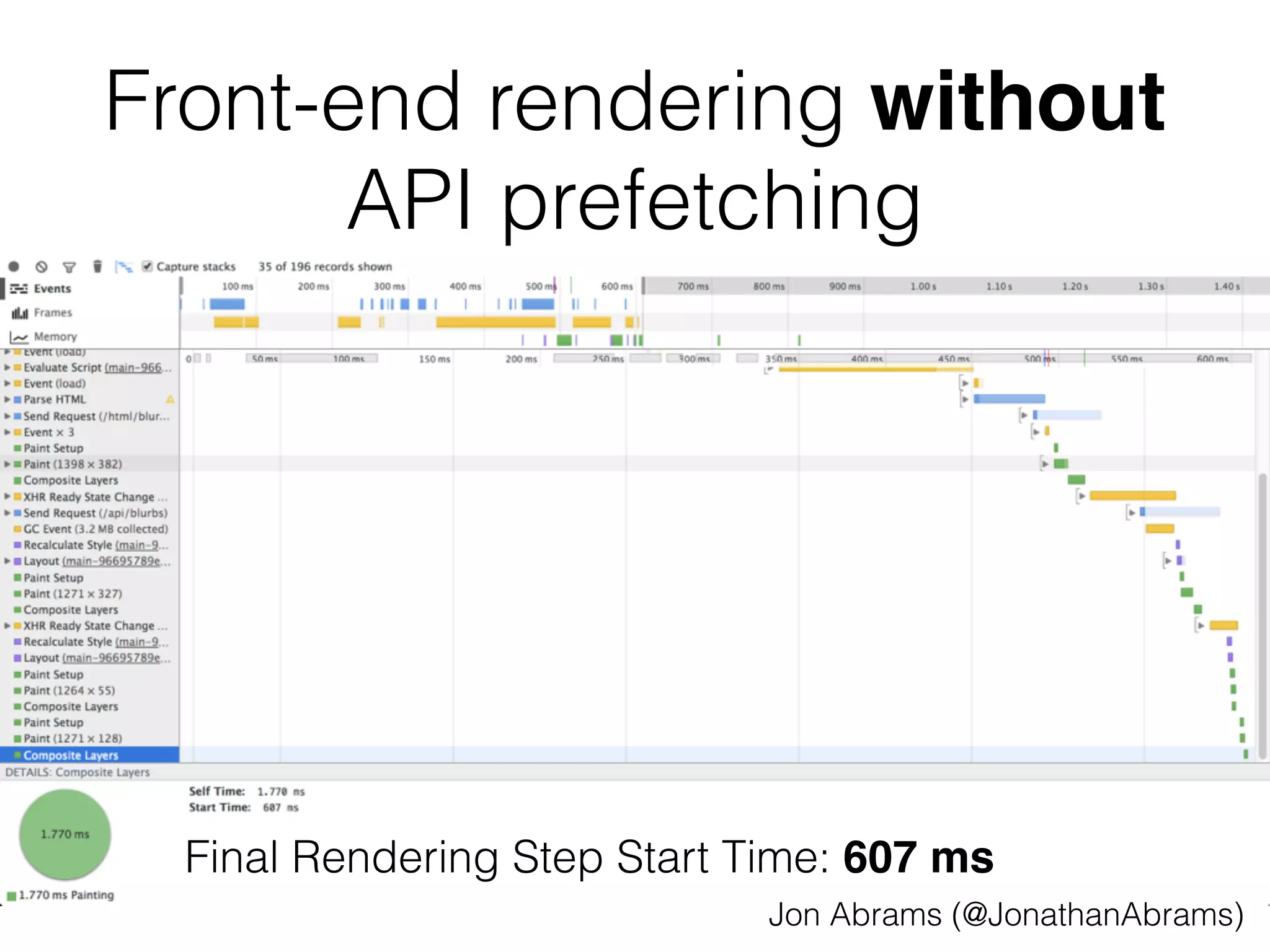
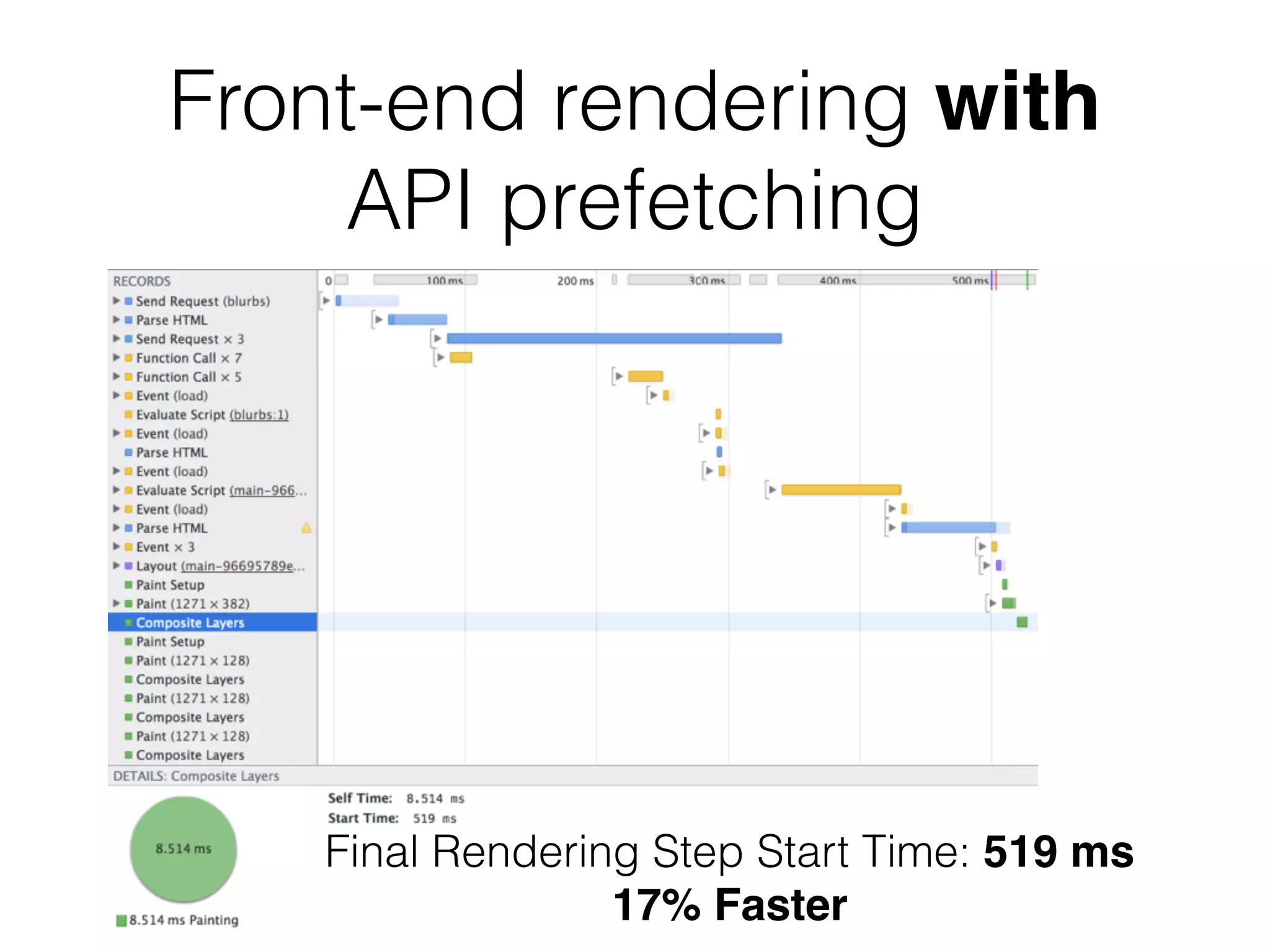

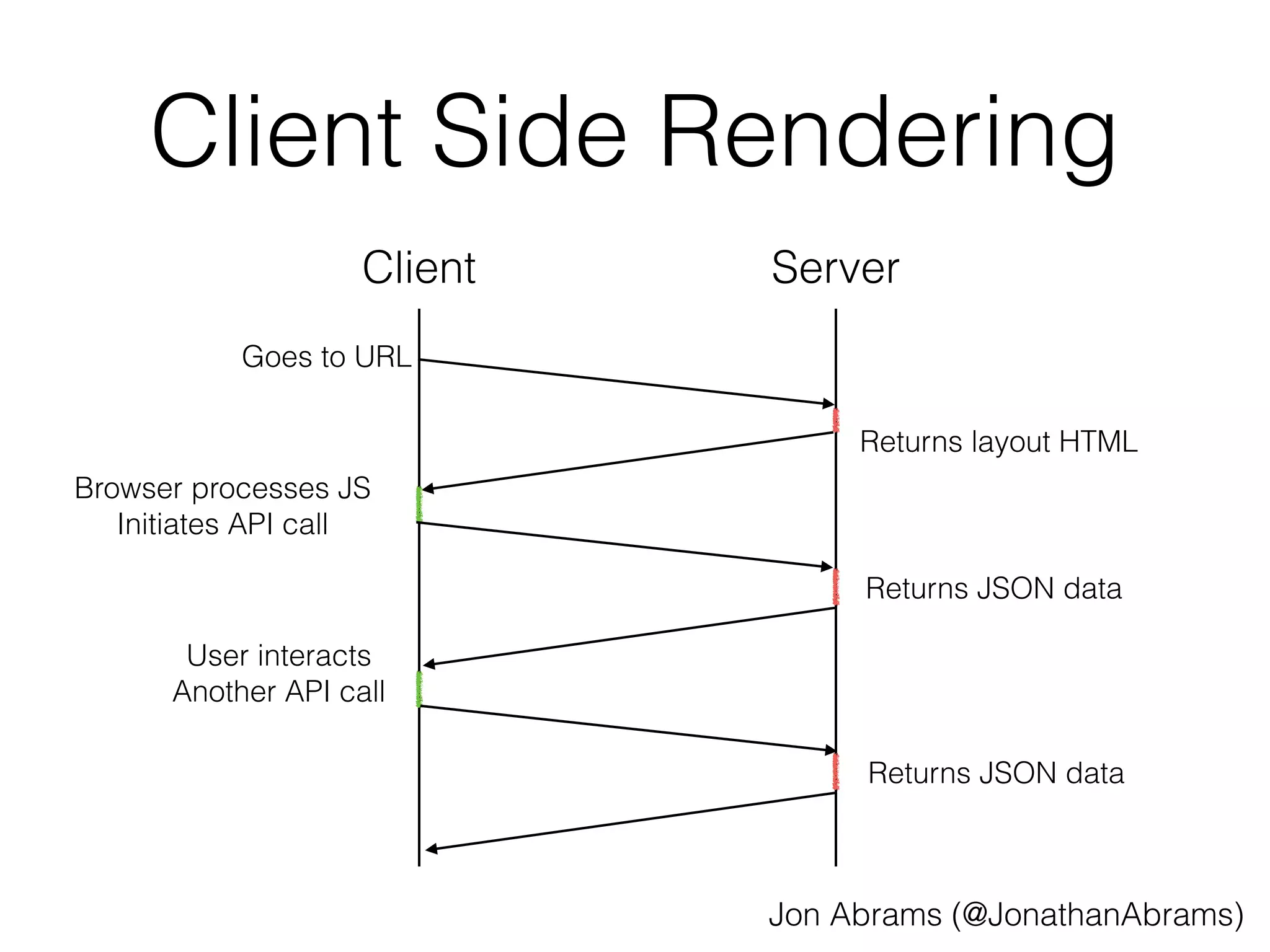
![apiPrefetch.js
<script src="/apiPrefetch.js"></script>
<script src="/jquery.js"></script>
<script>
window.apiPrefetchData = {
"/api/posts": […],
"/api/user": {…}
https://github.com/JonAbrams/apiPrefetch.js
};
</script>
<script src="/main.js"></script>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2014-10-20-jonabrams-html5devconf-141021193454-conversion-gate02/75/API-Prefetching-HTML5DevConf-Oct-21-2014-15-2048.jpg)