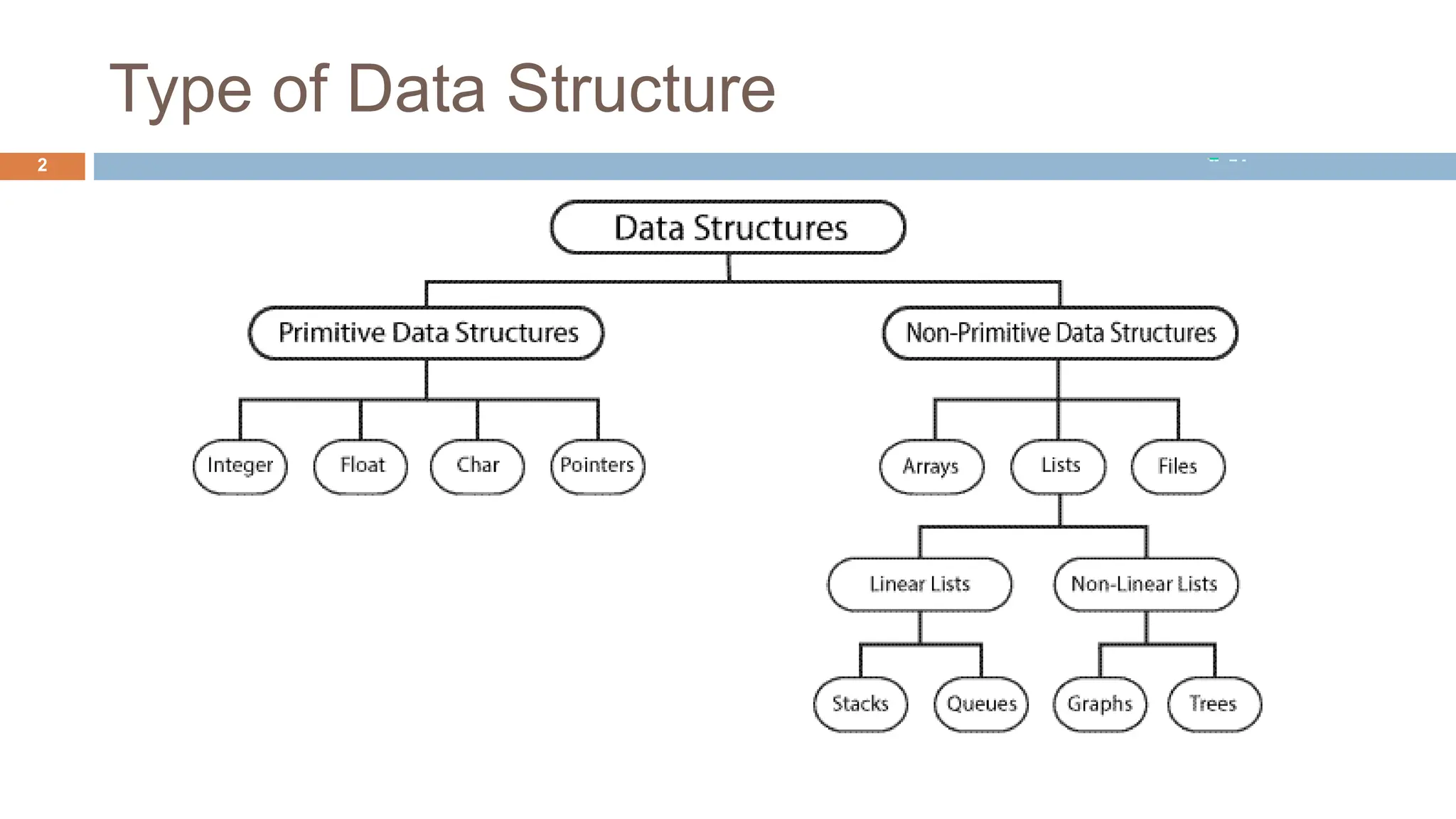
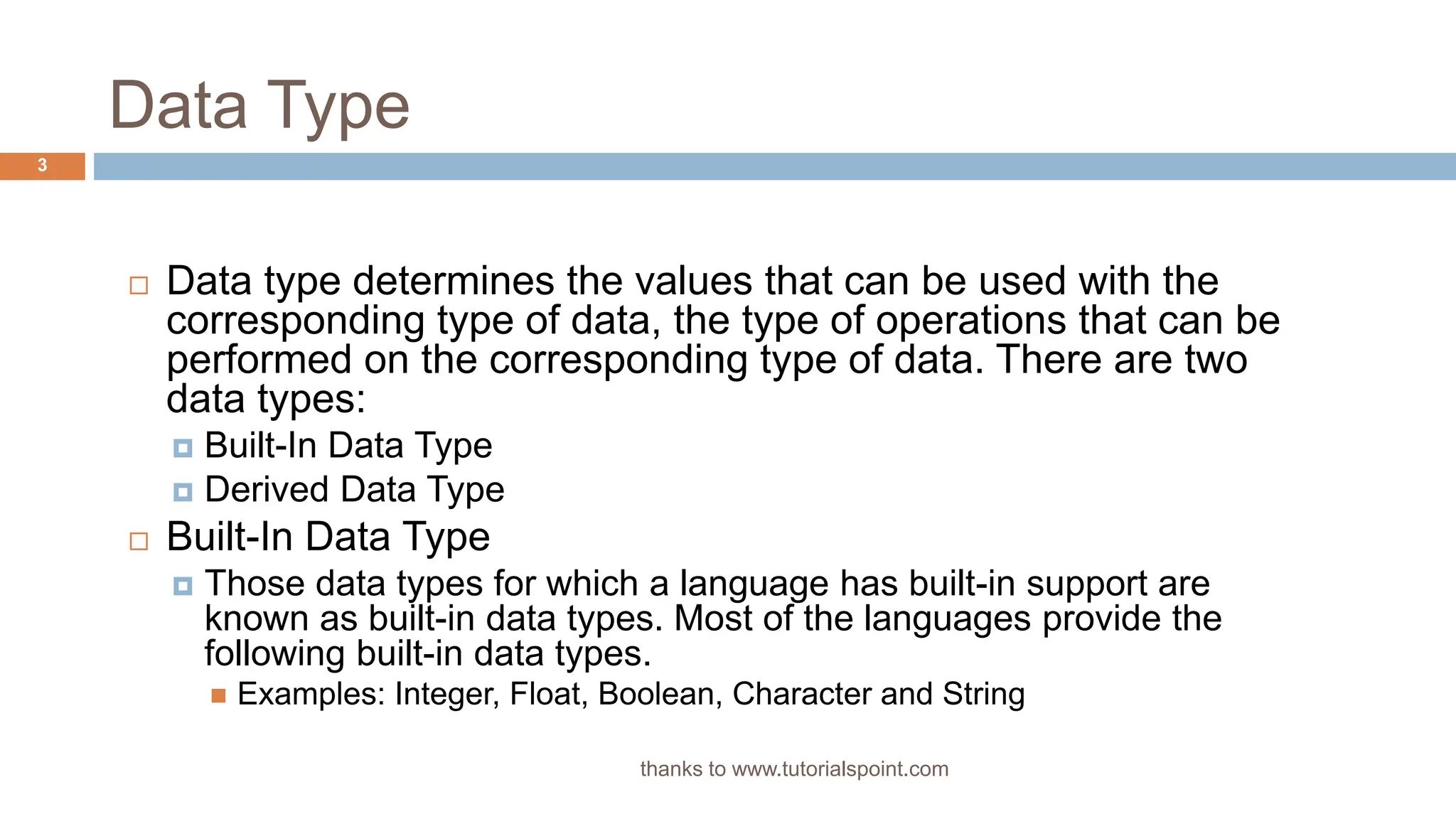
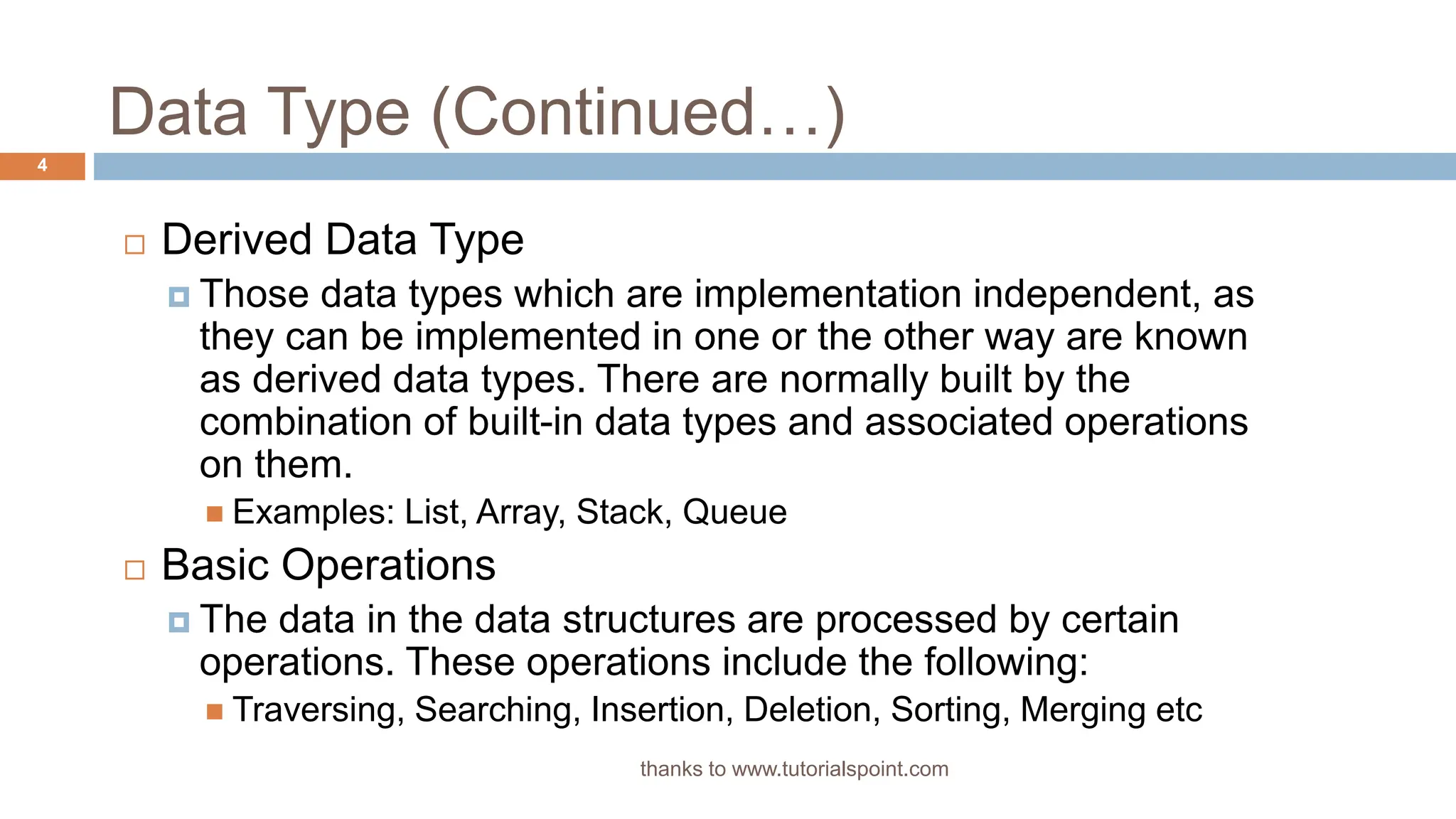
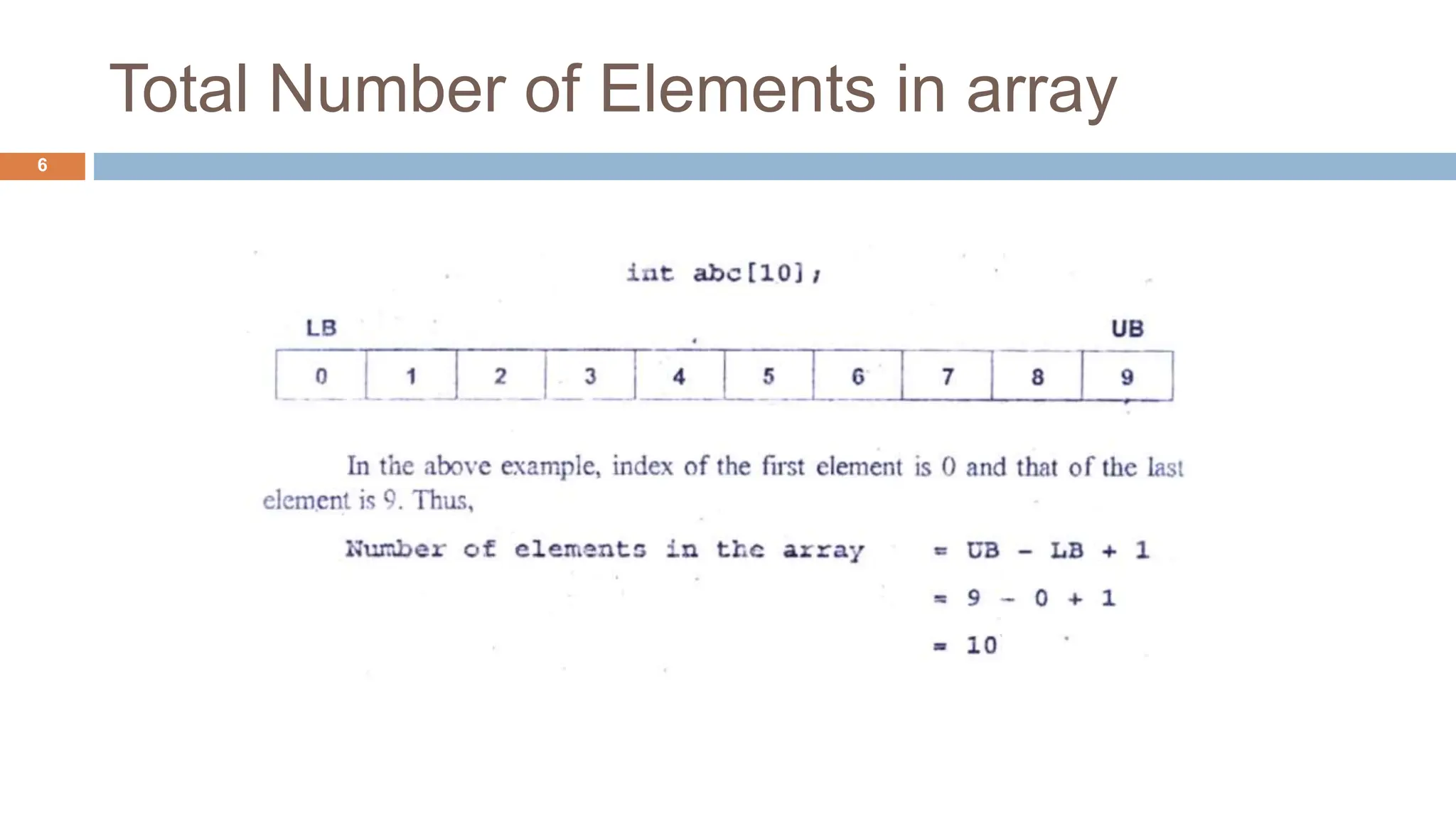
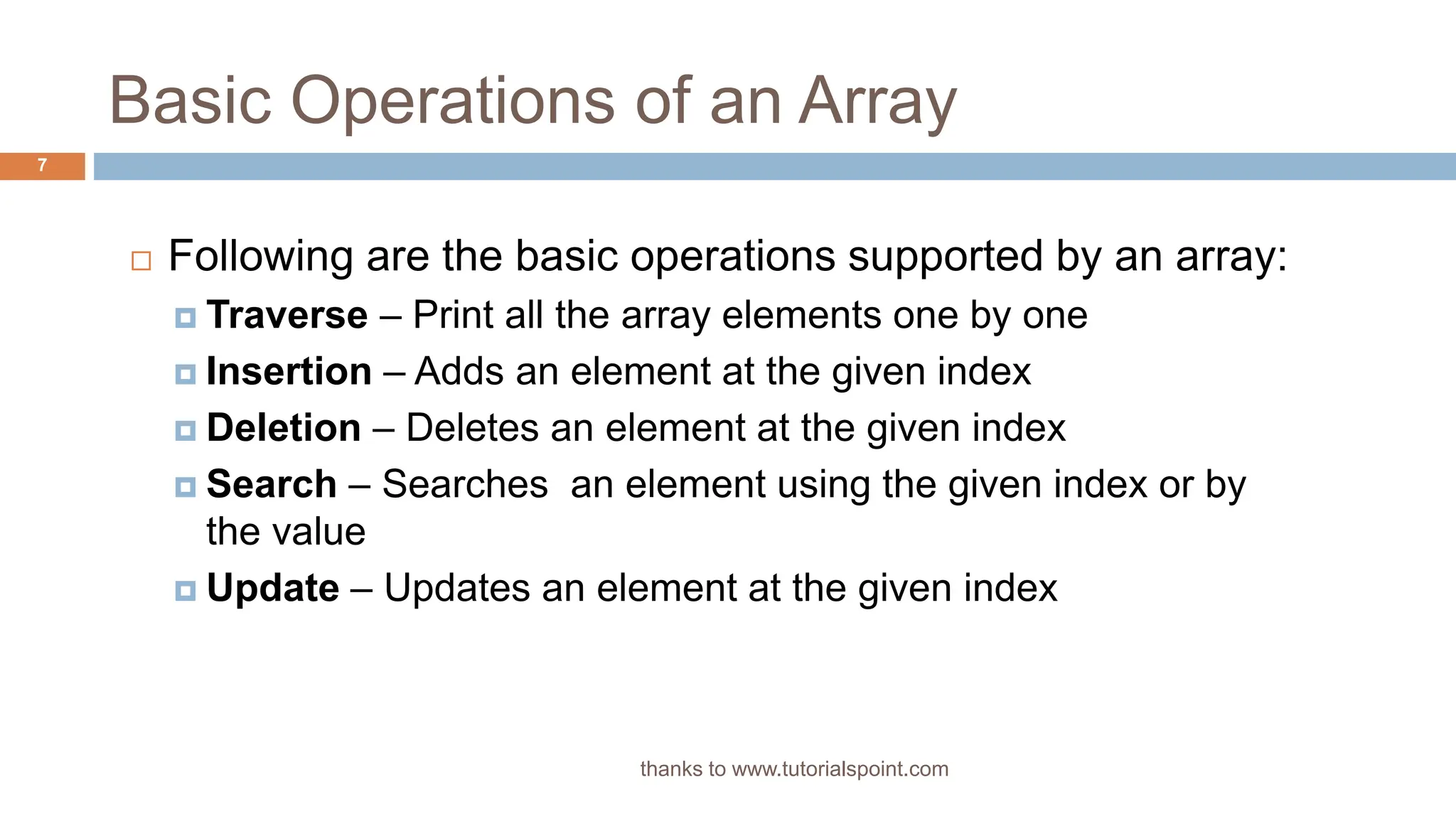
The document outlines data structures, focusing specifically on arrays, data types (built-in and derived), and their associated operations such as insertion, deletion, searching, and updating. It explains how arrays hold a fixed number of items of the same type and provides algorithms for basic array operations. Examples are provided to illustrate the insertion and deletion processes within an array context.




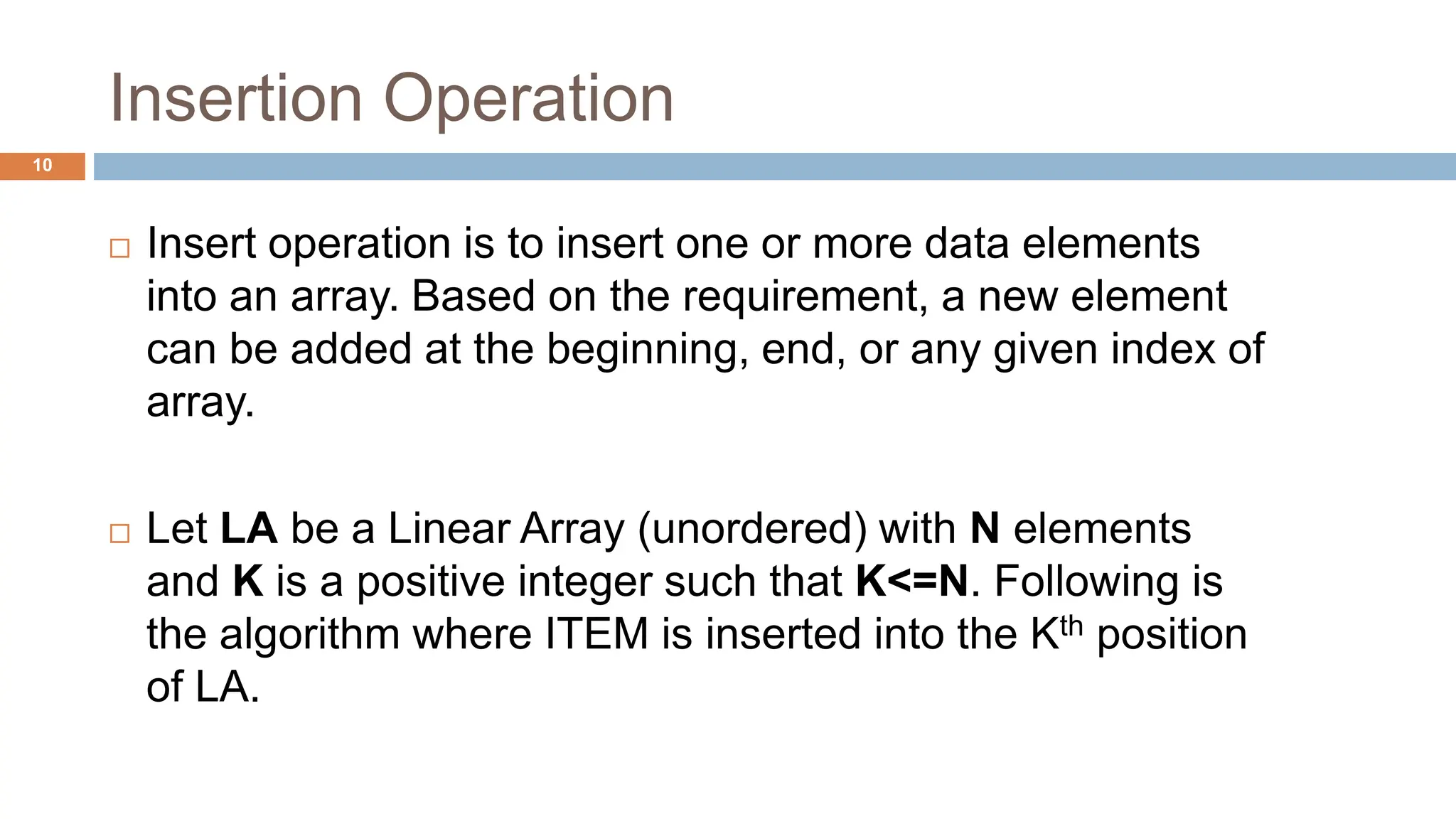
![Insertion Operation (Algorithm)
11
1. Start
2. Set J = N
3. Repeat Step 4 and 5 while J >= K
4. Set LA[ J + 1 ] = LA[ J ]
5. Set J = J – 1
6. Set LA[ K ] = ITEM
7. Stop](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayoperations-240529141941-4841e395/75/Array-Operations-pptxdata-structure-array-indsa-11-2048.jpg)
![Insertion Example
12
int arr[5] = {4, 1, 8, 2};
int val,loc;
cout<<"enter value to insert"<<endl;
cin>>val;
cout<<"enter location"<<endl;
cin>>loc;
for(int i=4; i>loc; i--){
// arr[i+1]=arr[i];
arr[i]=arr[i-1];
}
arr[loc]=val;
for(int i=0; i<=4; i++)
cout<<"Values are "<<i<< " = "<<arr[i]<<endl;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayoperations-240529141941-4841e395/75/Array-Operations-pptxdata-structure-array-indsa-12-2048.jpg)

![Deletion Operation (Algorithm)
thanks to www.tutorialspoint.com
14
1. Start
2. Set J = K
3. Repeat Step 4 and 5 while J < N
4. Set LA[ J ] = LA[ J+1 ]
5. Set J = J + 1
6. Set N = N – 1
7. Stop](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayoperations-240529141941-4841e395/75/Array-Operations-pptxdata-structure-array-indsa-14-2048.jpg)

![Search Operation (Algorithm)
thanks to www.tutorialspoint.com
16
1. Start
2. Set J = 0
3. Repeat Step 4 and 5 while J < N
4. IF LA [ J ] is equal ITEM THEN GOTO Step 6
5. Set J = J + 1
6. Print J, ITEM
7. Stop](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayoperations-240529141941-4841e395/75/Array-Operations-pptxdata-structure-array-indsa-16-2048.jpg)
![Update Operation
thanks to www.tutorialspoint.com
17
Update operation refers to updating an existing element from
the array at a given index.
Consider LA is a linear array with N elements and K is a
positive integer such that K<=N. Following is the algorithm to
update an element available at the Kth position of LA.
1. Start
2. Set LA [ K – 1 ] = ITEM
3. Stop
Complexity…?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayoperations-240529141941-4841e395/75/Array-Operations-pptxdata-structure-array-indsa-17-2048.jpg)
![18
int main(){
int input[100], count, i, num;
cout << "Enter Number of Elements in Arrayn";
cin >> count;
cout << "Enter " << count << " numbers n";
// Read array elements
for(i = 0; i < count; i++){
cin >> input[i];
}
cout << "Enter a number to serach in Arrayn";
cin >> num;
// search num in inputArray from index 0 to elementCount-1
for(i = 0; i < count; i++){
if(input[i] == num){
cout << "Element found at index " << i;
break;
}
}
if(i == count){
cout << "Element Not Present in Input Arrayn";
}
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayoperations-240529141941-4841e395/75/Array-Operations-pptxdata-structure-array-indsa-18-2048.jpg)