The document provides a comprehensive overview of arrays and collections in C#, including simple, multidimensional, and jagged arrays, as well as the Array and ArrayList classes. It covers array declaration, initialization, accessing elements, and methods provided by the Array class for manipulation. Additionally, it highlights differences between traditional arrays and ArrayLists, emphasizing the dynamic resizing capability of the latter.

![Arrays
• If you need to work with multiple elements/
objects of the same type, you can use arrays
and collections.
• Arrays :
- An array stores a fixed-size sequential collection of
elements of the same type.
- An array is a data structure that contains a number
of elements of the same type.
- Reference data type.
eg: string[] cars = {"Volvo", "BMW", "Ford", "Mazda"};
int[] myNum = {10, 20, 30, 40};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-240422054329-f910e402/75/arrays-in-c-including-Classes-handling-arrays-2-2048.jpg)
![Array Declaration & Array Initialization
• The array cannot be resized after the size is
mentioned
• Syntax
datatype[] arrayName;
where,
● datatype is used to specify the type of elements in the array.
● [ ] specifies the size of the array. The rank specifies the size of the
array.
● arrayName specifies the name of the array.
eg:
int[] myArray; // array of integers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-240422054329-f910e402/75/arrays-in-c-including-Classes-handling-arrays-3-2048.jpg)
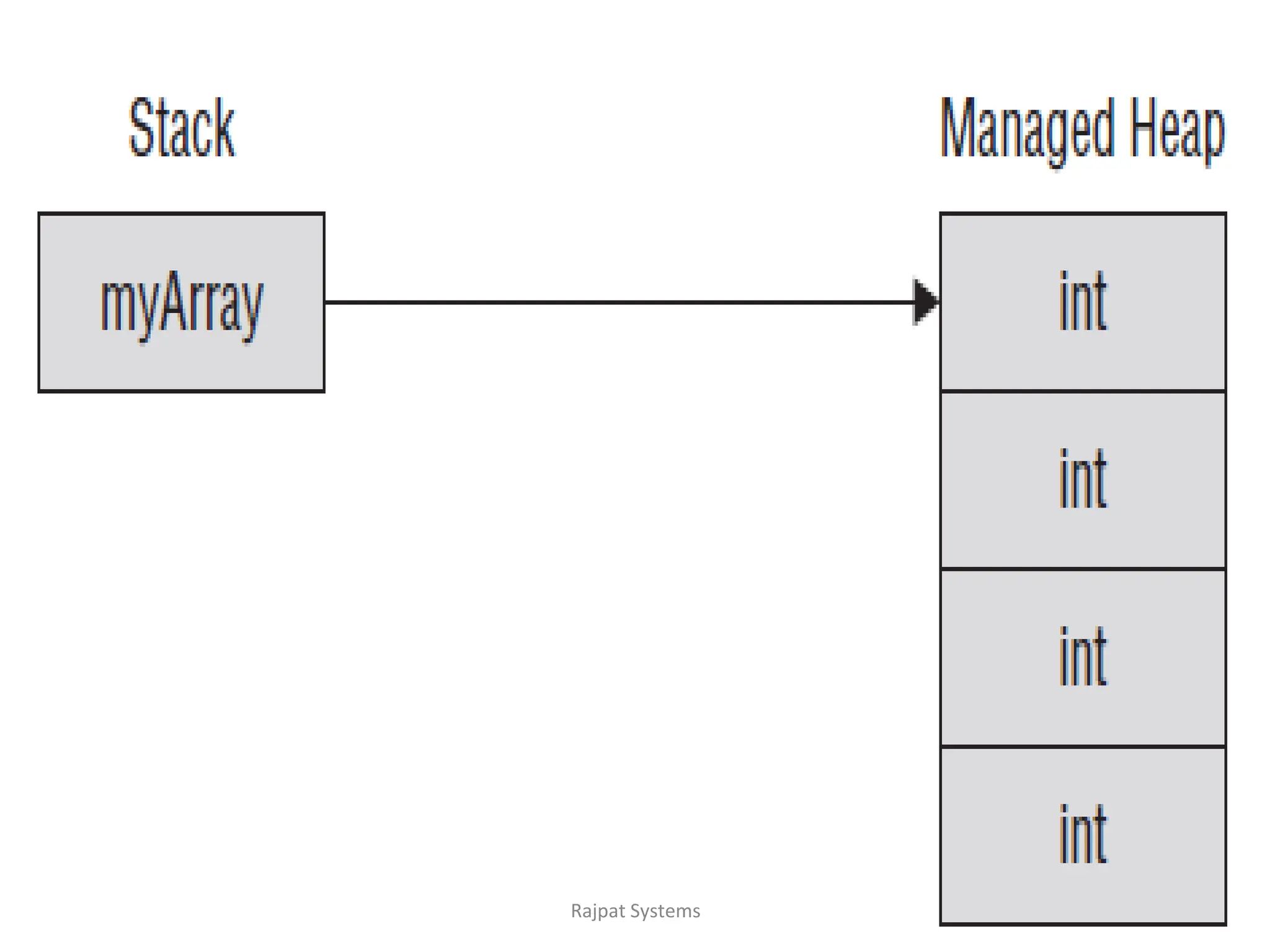
![Memory Allocation & Array Initialization
Initializing an Array
➢ Declaring an array does not initialize the array in the memory.
When the array variable is initialized, you can assign values to
the array.
➢ Array is a reference type, so you need to use the new keyword
to create an instance of the array. For example,
myArray = new int[4];
// Assign values
int[] myArray = new int[4] {4, 7, 11, 2};
int[] myArray = new int[] {4, 7, 11, 2};
int[] myArray = {4, 7, 11, 2};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-240422054329-f910e402/75/arrays-in-c-including-Classes-handling-arrays-4-2048.jpg)
![Accessing Array Elements
• After an array is declared and initialized, you can
access the array elements using an index or subscript.
• Arrays only support indexes that have integer
parameters.
eg:
int[] myArray = new int[] {4, 7, 11, 2};
int v1 = myArray[0]; // read first element
int v2 = myArray[1]; // read second element
myArray[3] = 44; // change fourth element
• If you use a wrong index value where no element
exists, an exception of type
IndexOutOfRangeExceptijon iss thrown.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-240422054329-f910e402/75/arrays-in-c-including-Classes-handling-arrays-6-2048.jpg)
![Array Length
• If you don’ t know the number of elements in
the array, you can use the Length property
for (int i = 0; i < myArray.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(myArray[i]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-240422054329-f910e402/75/arrays-in-c-including-Classes-handling-arrays-7-2048.jpg)
![Demo
using System;
namespace geeksforgeeks {
class onedarr {
// Main Method
public static void Main()
{
// declares a 1D Array of string.
string[] weekDays;
// allocating memory for days.
weekDays = new string[] {"Sun", "Mon", "Tue", "Wed",
"Thu", "Fri", "Sat"};
// Displaying Elements of array
foreach(string day in weekDays)
Console.Write(day + " ");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-240422054329-f910e402/75/arrays-in-c-including-Classes-handling-arrays-8-2048.jpg)
![Multidimensional Arrays
• You cannot change the size after declaring an array.
• A 2-dimensional array can be thought of as a table, which
has x number of rows and y number of columns.
Declaration
int[,] a = new int[3, 3];
Thus, every element in the array a is identified by an element
name of the form a[ i , j ], where a is the name of the array, and
i and j are the subscripts that uniquely identify each element in
array a.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-240422054329-f910e402/75/arrays-in-c-including-Classes-handling-arrays-9-2048.jpg)
![Multidimensional Arrays
• A 2-dimensional array can be thought of as a table, which has x
number of rows and y number of columns.
• Also called rectangular arrays
Declaration
int[,] twodim = new int[3, 3];
twodim[0, 0] = 1;
twodim[0, 1] = 2;
twodim[0, 2] = 3;
twodim[1, 0] = 4;
twodim[1, 1] = 5;
twodim[1, 2] = 6;
twodim[2, 0] = 7;
twodim[2, 1] = 8;
twodim[2, 2] = 9;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-240422054329-f910e402/75/arrays-in-c-including-Classes-handling-arrays-10-2048.jpg)

![2D array - Example
using System;
public class twodarr
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[ ,] arr=new int[3,3];//declaration of 2D array
arr[0,1]=10;//initialization
arr[1,2]=20;
arr[2,0]=30;
//traversal
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
Console.Write(arr[i,j]+" ");
}
Console.WriteLine();//new line at each row
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-240422054329-f910e402/75/arrays-in-c-including-Classes-handling-arrays-12-2048.jpg)
![Jagged Arrays - Variable sized arrays
• A jagged array is more flexible in sizing the array.
• With a jagged array every row can have a
different size.
• Array of arrays
int[][] jagged = new int[3][];
jagged[0] = new int[2] { 1, 2 };
jagged[1] = new int[6] { 3, 4, 5, 6,7, 8 };
jagged[2] = new int[3] { 9, 10, 11 };](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-240422054329-f910e402/75/arrays-in-c-including-Classes-handling-arrays-13-2048.jpg)
![Jagged array - Example
public static void Main()
{
// Declare the Jagged Array of four elements:
int[][] jagged_arr = new int[4][];
// Initialize the elements
jagged_arr[0] = new int[] {1, 2, 3, 4};
jagged_arr[1] = new int[] {11, 34, 67};
jagged_arr[2] = new int[] {89, 23};
jagged_arr[3] = new int[] {0, 45, 78, 53, 99};
// Display the array elements:
for (int n = 0; n < jagged_arr.Length; n++)
{ // Print the row number
System.Console.Write("Row : " +n + " :");
for (int k = 0; k < jagged_arr[n].Length; k++)
{
// Print the elements in the row
System.Console.Write( " "+jagged_arr[n][k]);
}
System.Console.WriteLine();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-240422054329-f910e402/75/arrays-in-c-including-Classes-handling-arrays-14-2048.jpg)
![System.Array Class - example
using System;
namespace CSharpProgram
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Creating an array
int[] arr = new int[6] { 5, 8, 9, 25, 0, 7 };
// Creating an empty array
int[] arr2 = new int[6];
// Displaying length of array
Console.WriteLine("length of first array: "+arr.Length);
// Sorting array
Array.Sort(arr);
Console.Write("First array elements: ");
// Displaying sorted array
PrintArray(arr);
// Finding index of an array element
Console.WriteLine("nIndex position of 25 is "+Array.IndexOf(arr,25));
// Coping first array to empty array
Array.Copy(arr, arr2, arr.Length);
Console.Write("Second array elements: ");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-240422054329-f910e402/75/arrays-in-c-including-Classes-handling-arrays-17-2048.jpg)
![System.Array Class - example - contd..
// Displaying second array
PrintArray(arr2);
Array.Reverse(arr);
Console.Write("nFirst Array elements in reverse order: ");
PrintArray(arr);
}
// User defined method for iterating array elements
static void PrintArray(int[] arr)
{
foreach (Object elem in arr)
{
Console.Write(elem+" ");
}
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-240422054329-f910e402/75/arrays-in-c-including-Classes-handling-arrays-18-2048.jpg)
![System.Array Class - example - contd..
// Displaying second array
PrintArray(arr2);
Array.Reverse(arr);
Console.Write("nFirst Array elements in reverse order: ");
PrintArray(arr);
}
// User defined method for iterating array elements
static void PrintArray(int[] arr)
{
foreach (Object elem in arr)
{
Console.Write(elem+" ");
}
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-240422054329-f910e402/75/arrays-in-c-including-Classes-handling-arrays-19-2048.jpg)

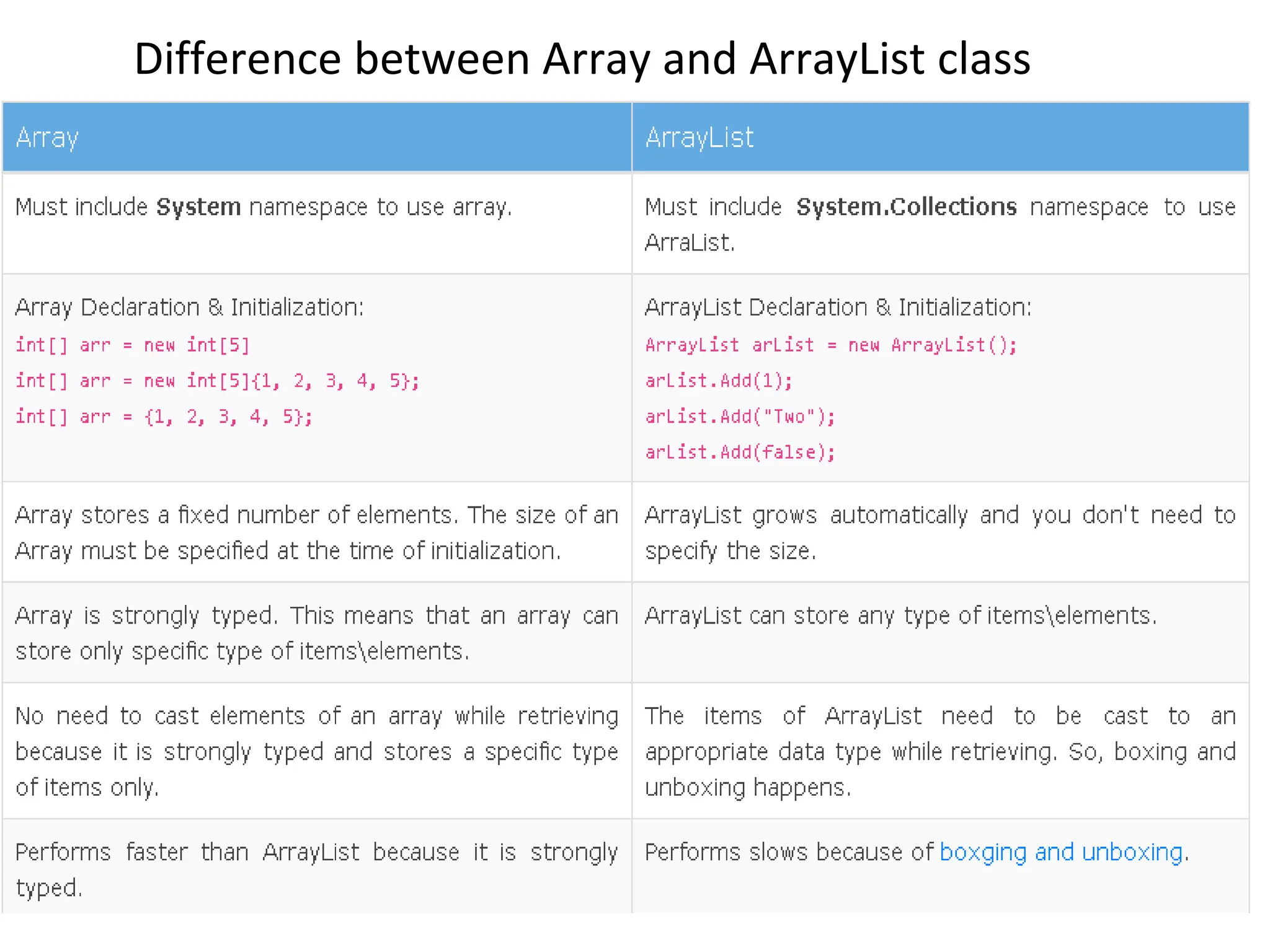
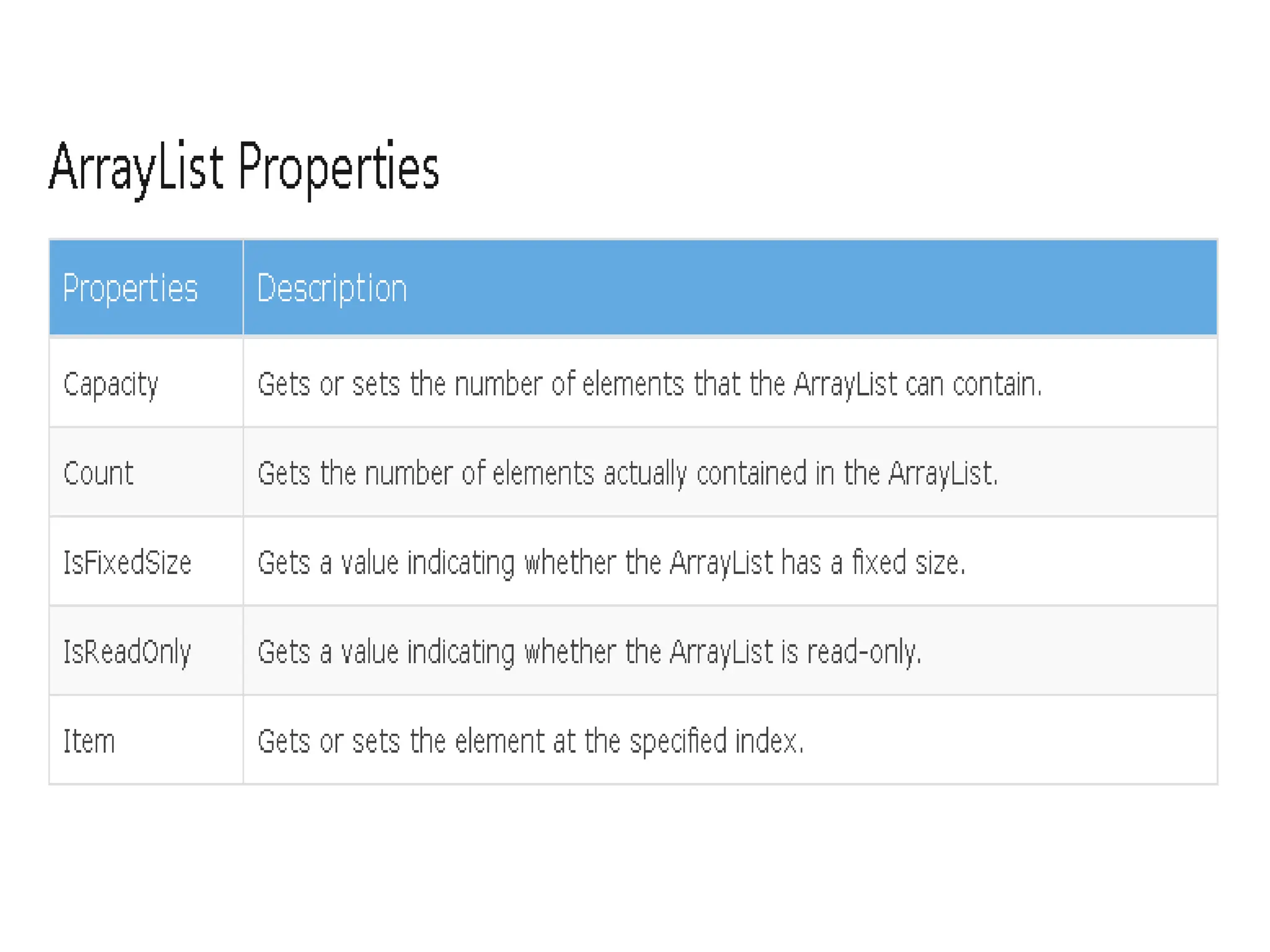

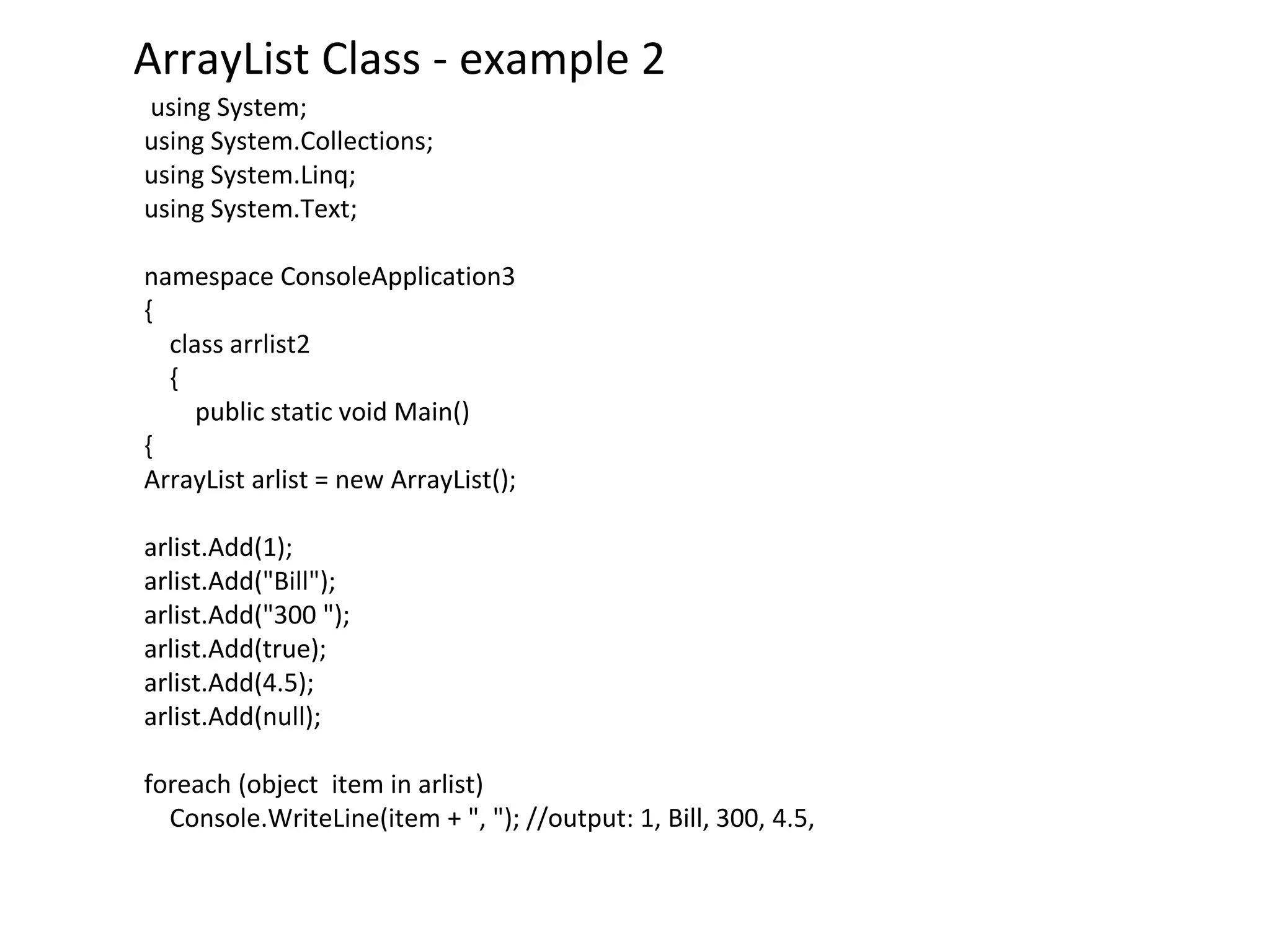
![using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace ConsoleApplication3
{
class arrlistdemo
{ static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Creates and initializes a new ArrayList.
ArrayList myAL = new ArrayList();
myAL.Add("Hello");
myAL.Add("World");
myAL.Add("!");
// Displays the properties and values of the ArrayList.
Console.WriteLine("myAL");
Console.WriteLine(" Count: "+ myAL.Count);
Console.WriteLine(" Capacity: "+ myAL.Capacity);
Console.Write(" Values:");
foreach (Object obj in myAL)
Console.Write(" "+ obj);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
ArrayList Class - example 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-240422054329-f910e402/75/arrays-in-c-including-Classes-handling-arrays-24-2048.jpg)