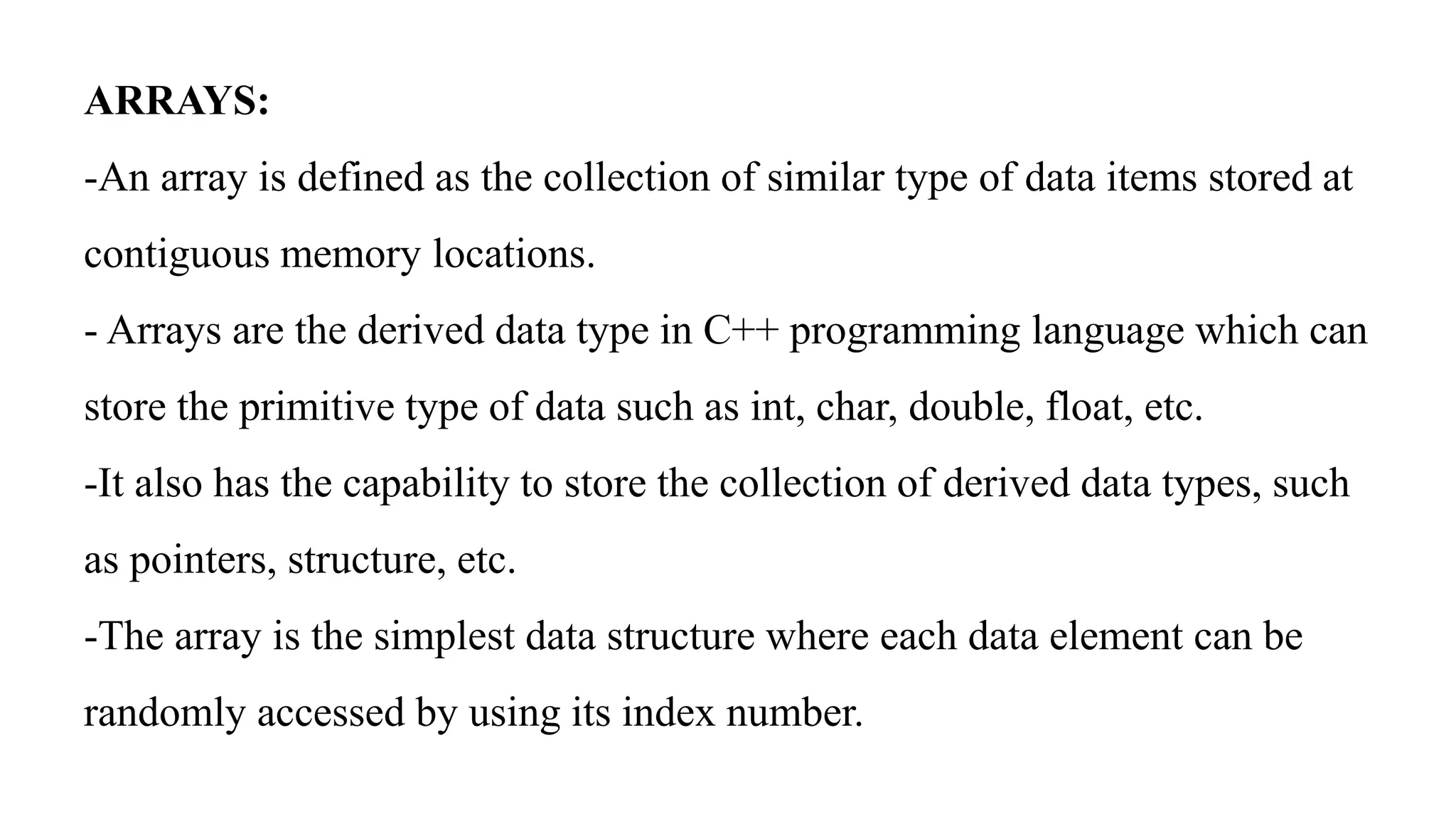
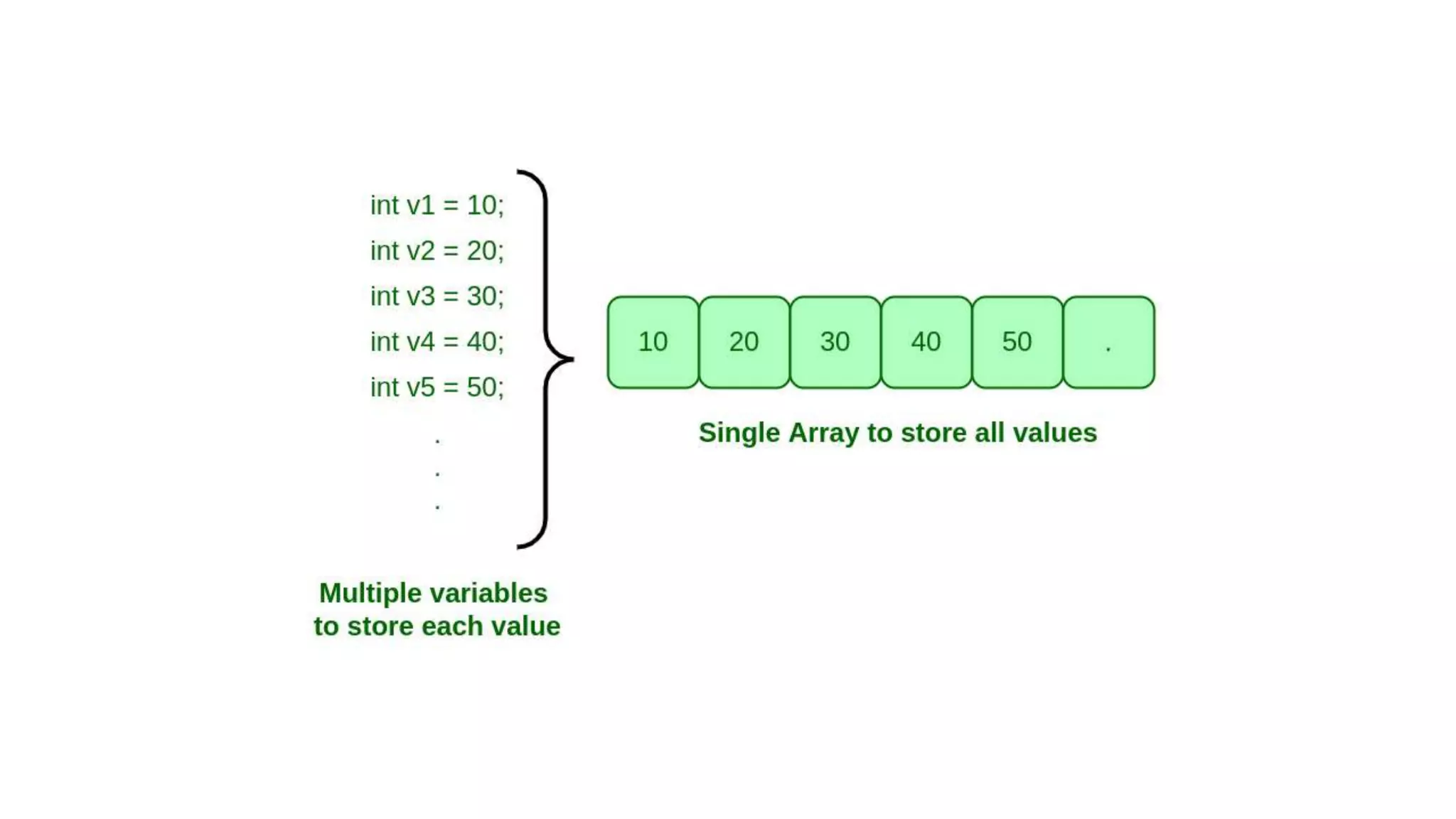
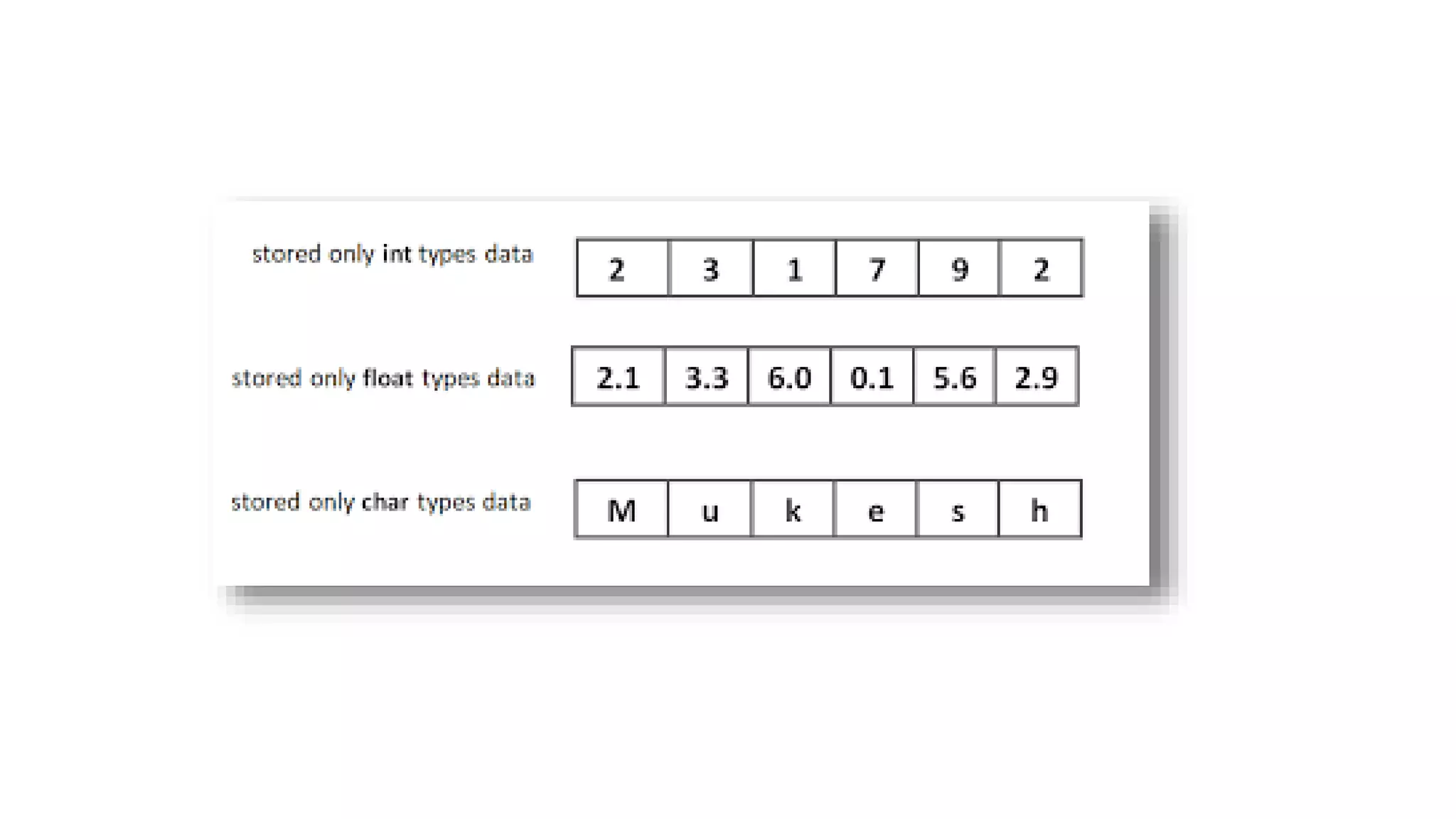
Arrays allow storing multiple values of the same data type in contiguous memory locations. One-dimensional arrays store elements in a single list, accessed by index. Multi-dimensional arrays organize elements into multiple lists, accessed by multiple indices. Arrays can be initialized manually or by user input, and traversed with for loops to access each element sequentially.
![ONE DIMENSIONALARRAY:
SYNTAX:
Data_Type array_name[array_size];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayscpp-230419053000-d360678e/75/ARRAYSCPP-pptx-4-2048.jpg)
![EXAMPLE
int marks[9]={40,55,63,17,22,68,89,97,89};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayscpp-230419053000-d360678e/75/ARRAYSCPP-pptx-6-2048.jpg)

![// Array declaration by specifying size
int arr1[10];
// declare an array of user specified size
int n = 10;
int arr2[n];
// Array declaration by initializing elements
int arr[] = { 10, 20, 30, 40};
// Array declaration by specifying size and initializing elements
int arr[6] = { 10, 20, 30, 40 };](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayscpp-230419053000-d360678e/75/ARRAYSCPP-pptx-8-2048.jpg)
![int marks[5];//declaration of array
INITIALIZATION OF ARRAY
FIRST METHOD:
marks[0]=80;
marks[1]=60;
marks[2]=70;
marks[3]=85;
marks[4]=75;
SECOND METHOD:
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
cin>>marks[i];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayscpp-230419053000-d360678e/75/ARRAYSCPP-pptx-9-2048.jpg)
![EXAMPLE OF 1 D ARRAY
int main()
{
int values[5];
// taking input and storing it in an array
for(int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
cin>>values[i];
}
// printing elements of an array
for(int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
cout<<values[i];
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayscpp-230419053000-d360678e/75/ARRAYSCPP-pptx-10-2048.jpg)
![MULTI DIMENSIONALARRAYS
• Arrays of arrays.(ie) an array containing one or more arrays.
SYNTAX:
Data_Type array_name[1st dimension][2nd dimension][]..[Nth
dimension] ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayscpp-230419053000-d360678e/75/ARRAYSCPP-pptx-11-2048.jpg)
![TWO DIMENSIONAL ARRAYS:
Data_Type array_name [][];
int a[n][n];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayscpp-230419053000-d360678e/75/ARRAYSCPP-pptx-12-2048.jpg)
![TWO DIMENSIONAL ARRAY
int x[3][3];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayscpp-230419053000-d360678e/75/ARRAYSCPP-pptx-13-2048.jpg)
![Initializing Two – Dimensional Arrays:
First Method:
int x[3][4] = {0, 1 ,2 ,3 ,4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11}
Second Method:
int x[3][4] = {{0,1,2,3}, {4,5,6,7}, {8,9,10,11}};
Third Method:
int x[3][4];
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j++){
cin>>x[i][j];
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayscpp-230419053000-d360678e/75/ARRAYSCPP-pptx-14-2048.jpg)
![EXAMPLE OF 2D ARRAY
int main()
{
int disp[2][3];
int i, j;
for(i=0; i<2; i++) {
for(j=0;j<3;j++) {
cout<<"Enter values for array”;
cin>>disp[i][j];
}}
cout<<"Two Dimensional array elements:n";
for(i=0; i<2; i++) {
for(j=0;j<3;j++) {
cout<< disp[i][j];
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayscpp-230419053000-d360678e/75/ARRAYSCPP-pptx-15-2048.jpg)
![3D Arrays
Example:
int arr[3][3][3];
3 tables each with 3 rows and 3 columns](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayscpp-230419053000-d360678e/75/ARRAYSCPP-pptx-16-2048.jpg)
![JAGGED ARRAYS
- Ragged arrays
- Array of arrays such that member arrays can be of different sizes.
- 2-D arrays with variable number of columns in each row.
int s[4][];
s[0]={1};
s[1]={2,3};
s[2]={4,5,6};
s[3]={7,8,9,10};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayscpp-230419053000-d360678e/75/ARRAYSCPP-pptx-17-2048.jpg)
![arr[][] = { {0, 1, 2},
{6, 4},
{1, 7, 6, 8, 9},
{5} };](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrayscpp-230419053000-d360678e/75/ARRAYSCPP-pptx-18-2048.jpg)