This document discusses arrays in C++. It defines an array as a collection of the same type of data. Arrays can be initialized using a loop or by declaring and initializing in one step. Multidimensional arrays represent 2D data with rows and columns. Examples are provided to demonstrate reading from and printing to arrays, as well as searching, copying, and calculating averages of array elements.

![Introducing Arrays
Array is a data structure that represents a collection of the
same types of data.
arr [0]
arr [1]
arr [2]
arr [3]
arr [4]
arr [5]
arr [6]
arr [7]
arr [8]
arr [9]
int arr[ 10];
arr reference
An array of 10 elements
of type int
Array position starts
from 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160323025924/75/Arrays-in-CPP-2-2048.jpg)
![Declaring Array Variables
Datatype arrayname[arraysize];
Example:
int numbers[10];
datatype arrayname[arraysize]={arrayvalue};
Example:
int numbers[5]={2,3,4,5,6};
Once an array is created, its size is fixed. It cannot
be changed. You can find its size using](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160323025924/75/Arrays-in-CPP-3-2048.jpg)
![Initializing Arrays
Using a loop:
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
myList[i] = i;
Declaring & initializing in one step:
double myList[] = {1.9, 2.9, 3.4, 3.5};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160323025924/75/Arrays-in-CPP-4-2048.jpg)
![Declaring & initializing in one step
double myList[] = {1.9, 2.9, 3.4, 3.5};
This shorthand notation is equivalent to the
following statements:
double myList[4];
myList[0] = 1.9;
myList[1] = 2.9;
myList[2] = 3.4;
myList[3] = 3.5;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160323025924/75/Arrays-in-CPP-5-2048.jpg)
![Example 1
Write a pogram that read and display an array
int main()
{
int a[5], i;
for(i=0;i<5;i++) {
cin>>a[i];
}
for(i=0;i<5;i++) {
cout<<a[i];
}
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160323025924/75/Arrays-in-CPP-6-2048.jpg)
![Example 2
Find the largest of 10 numbers using array.
void main()
{
int i, a[20],max=0;
for (i=1; i< 10; i++)
{
cout<<“enter number n”;
cin>>a[i];
If (a[i] > max) max = a[i];
}
cout<<max;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160323025924/75/Arrays-in-CPP-7-2048.jpg)
![Example 3
Write a pogram that reads some values and display
average
void main()
{
int i, a[20],sum=0,avg;
for (i=1; i< 10; i++)
{
cout<<“enter number n”;
cin>>a[i];
sum=sum+a[i];
}
avg=sum/10;
cout<<“average is”<<avg;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160323025924/75/Arrays-in-CPP-8-2048.jpg)
![Example 4
Write a program that searches any number from an array
int main()
{
int i,n,a[100],num,found;
cout<<“How many numbers: ";
cin>>n;
for(i=0; i<n; i++){
cin>>a[i];
}
cout<<“Enter any number to search: ";
cin>>num;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160323025924/75/Arrays-in-CPP-9-2048.jpg)
![Example 4
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
if(a[i]==num)
{
cout<<“Found.";
break;
}
}
if(i==n)
cout<<“Not found.”;
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160323025924/75/Arrays-in-CPP-10-2048.jpg)
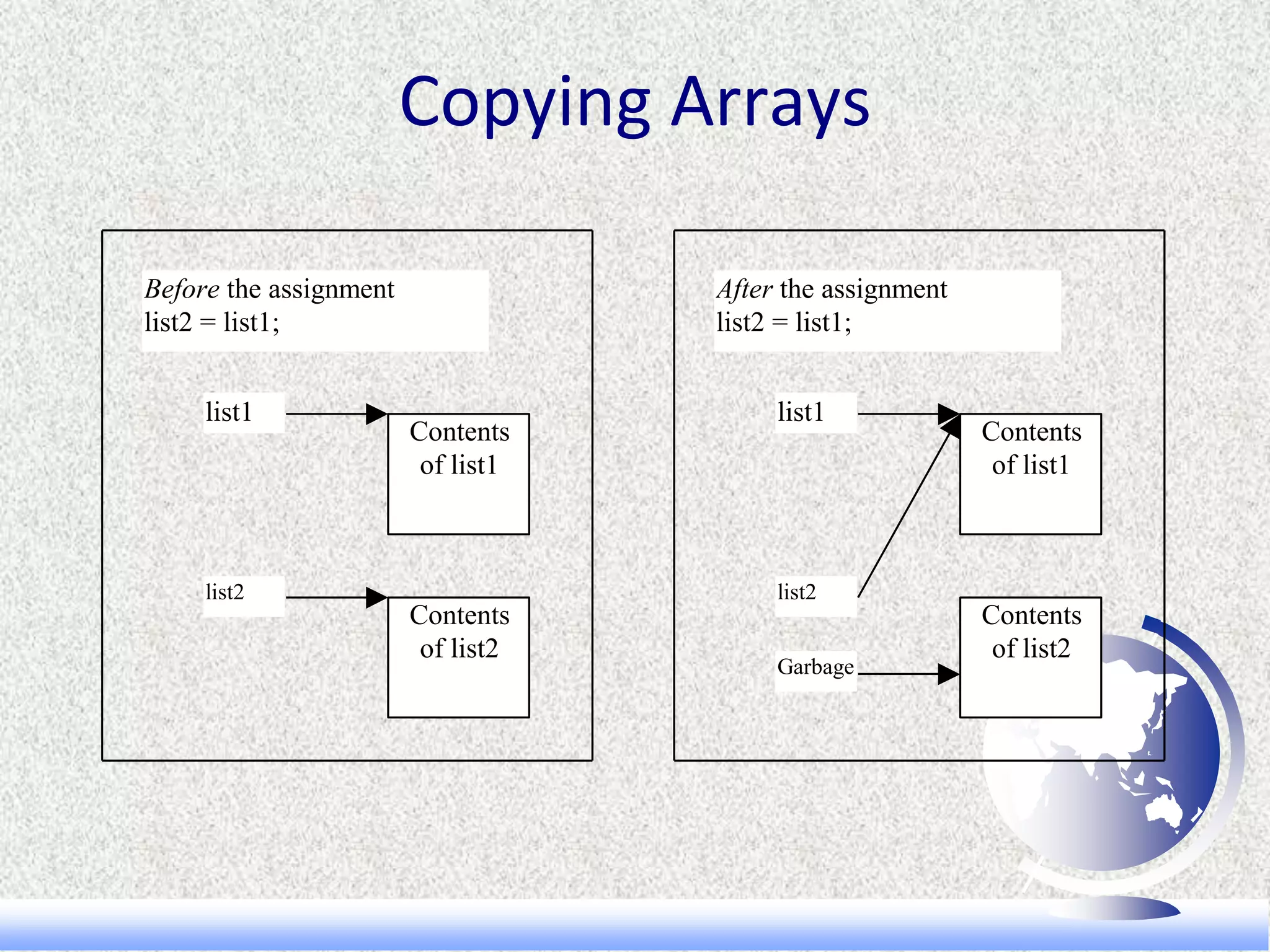
![Copying Arrays
A simple assignment cannot copy arrays. Rather simply
creates two arrays and attempts to copy one to the
other, using an assignment statement.
int list1[] = {2, 3, 1, 5, 10};
int list2[] = {1, 5, 7, 8, 9};
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
list2[i] = list1[i];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160323025924/75/Arrays-in-CPP-11-2048.jpg)
![Multidimensional Arrays
Declaring Variables of Multidimensional Arrays and Creating
Multidimensional Arrays
int array[5][4];
or
int array[][4];
Assigning value at[0][2]position: array[0][2] = 3;
for (i=0; i<5; i++)
for (j=0; j<4; j++)
{
array[i][j] = rand()*1000;
}
double[][] x;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160323025924/75/Arrays-in-CPP-13-2048.jpg)
![Multidimensional Array Illustration
0 1 2 3 4
0
7
0 1 2 3 4
1
2
3
4
0
1
2
3
4
int arr[2][1] = 7;int arr[5][5];
3
7
0 1 2
0
1
2
int arr[][] = {
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6},
{7, 8, 9},
{10, 11, 12}
};
1 2 3
4 5 6
8 9
10 11 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160323025924/75/Arrays-in-CPP-14-2048.jpg)
![Declaring, Creating, and Initializing
You can also use a shorthand notation to declare, create and initialize a
two-dimensional array. For example,
int array[][] = {
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6},
{7, 8, 9},
{10, 11, 12}
};
This is equivalent to the following statements:
int array[4][3];
array[0][0] = 1; array[0][1] = 2; array[0][2] = 3;
array[1][0] = 4; array[1][1] = 5; array[1][2] = 6;
array[2][0] = 7; array[2][1] = 8; array[2][2] = 9;
array[3][0] = 10; array[3][1] = 11; array[3][2] = 12;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160323025924/75/Arrays-in-CPP-15-2048.jpg)
![Ragged Arrays
Each row in a two-dimensional array is itself an array. So, the rows
can have different lengths. Such an array is known as a ragged
array.
For example,
int matrix[][] = {
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5},
{2, 3, 4, 5},
{3, 4, 5},
{4, 5},
{5}
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160323025924/75/Arrays-in-CPP-16-2048.jpg)
![Example 6
Write a program to print a matrix.
int main()
{
int i,j,a[10][10];
for(i=0;i<3;i++){
for(j=0;j<2;j++){
cin>>a[i][j];
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160323025924/75/Arrays-in-CPP-17-2048.jpg)
![Example 6
for(i=0;i<3;i++){
for(j=0;j<2;j++){
cout<<a[i][j];
}
cout<<“n”;
}
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160323025924/75/Arrays-in-CPP-18-2048.jpg)