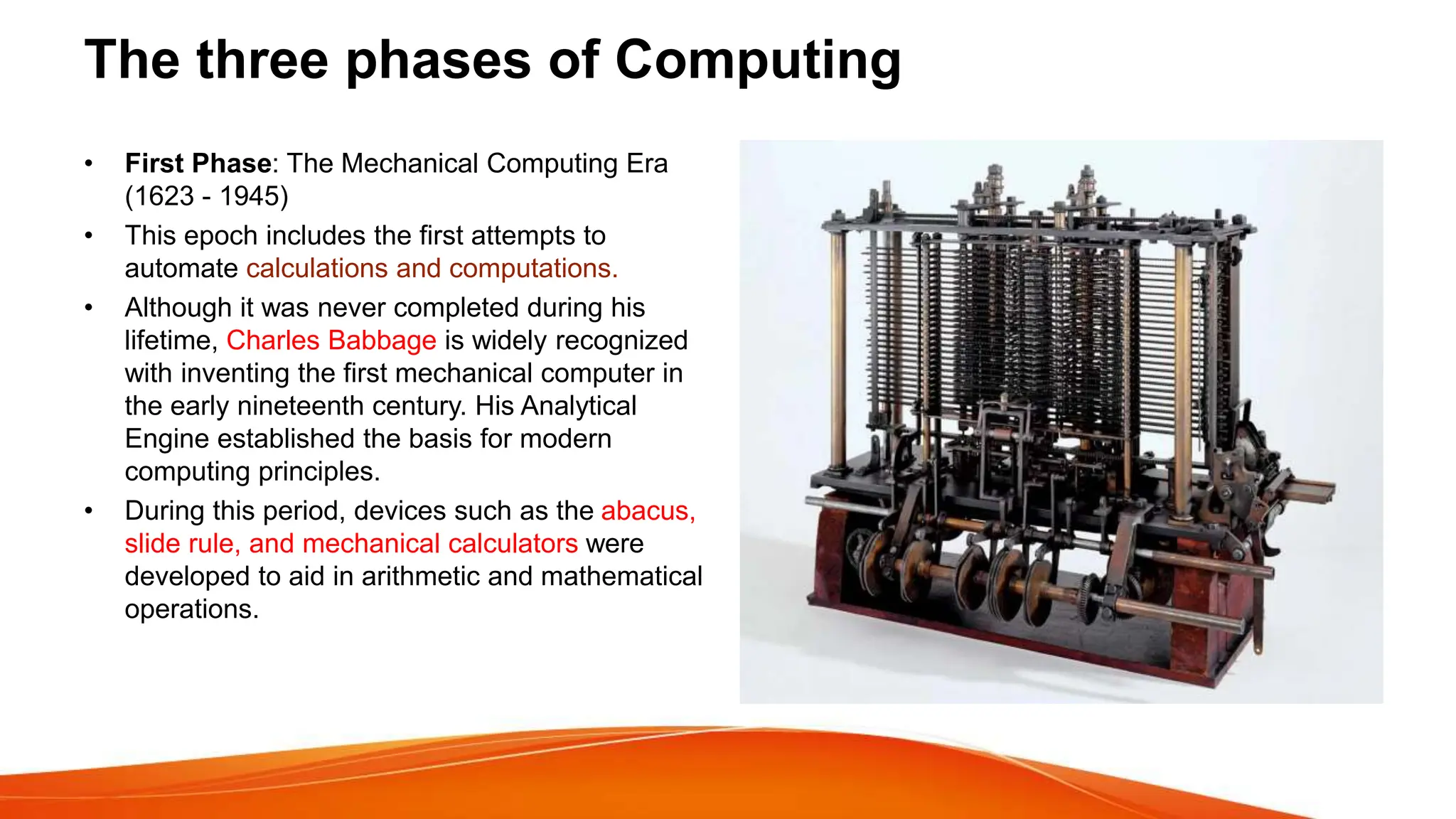
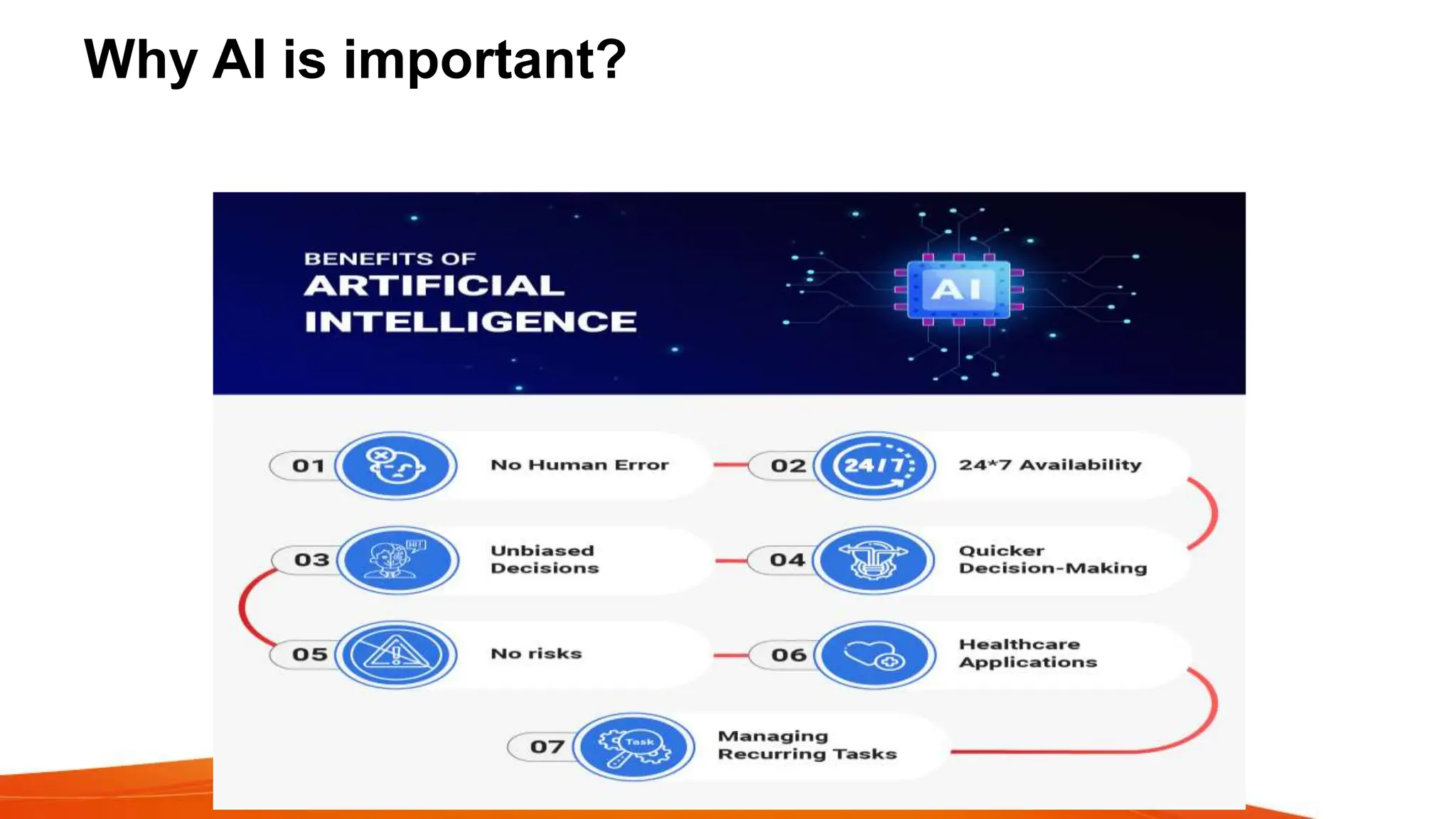
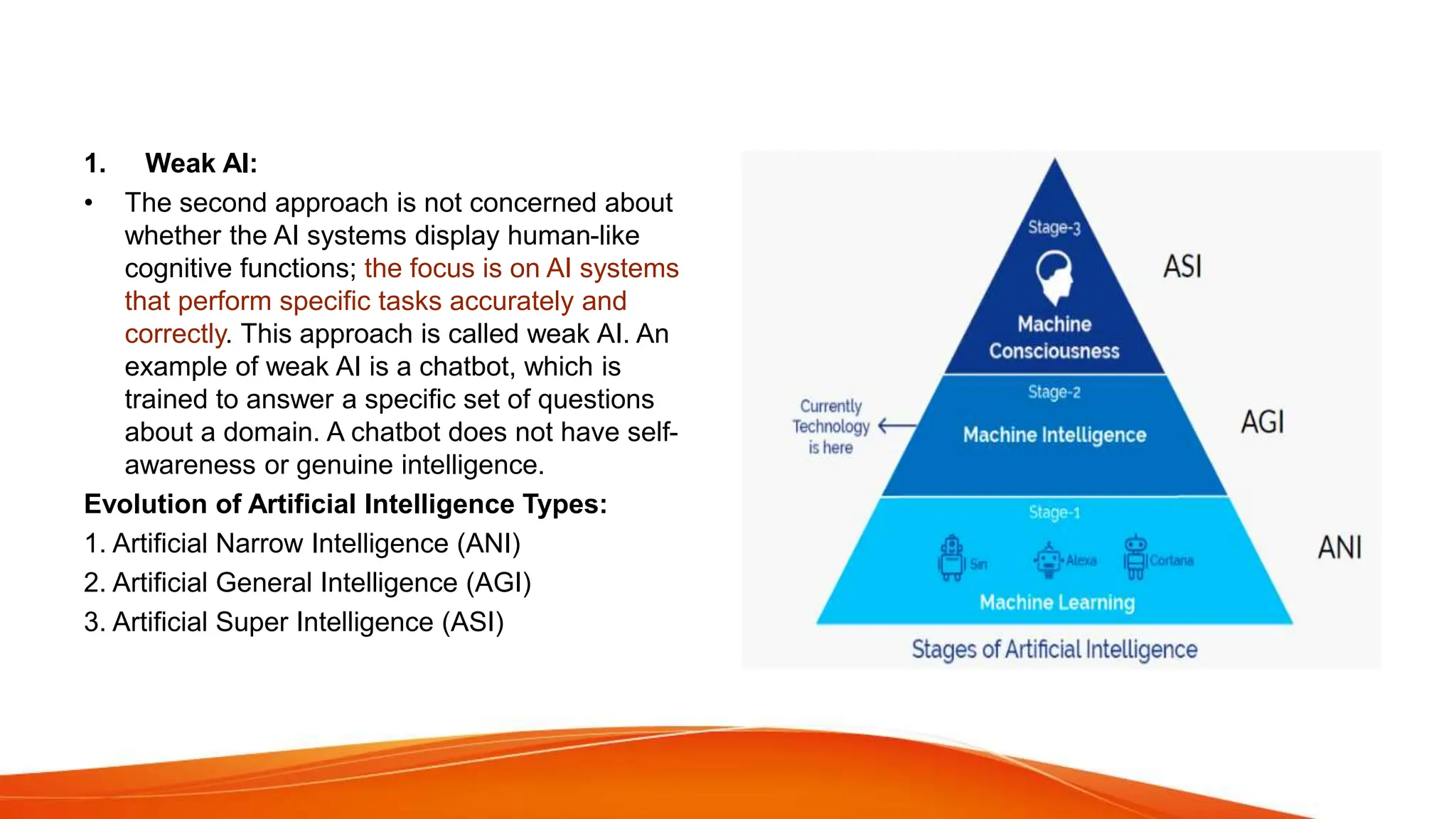
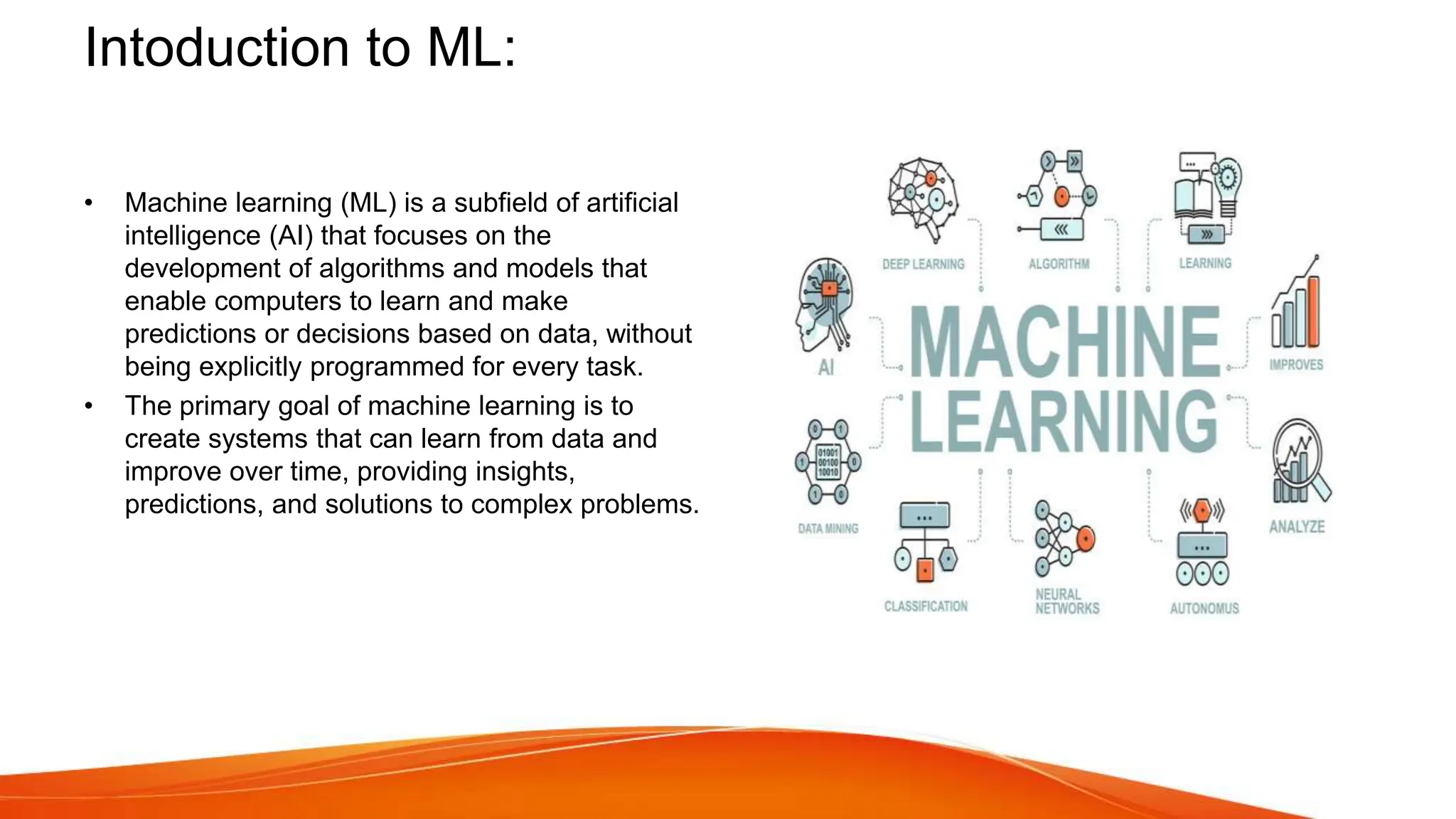
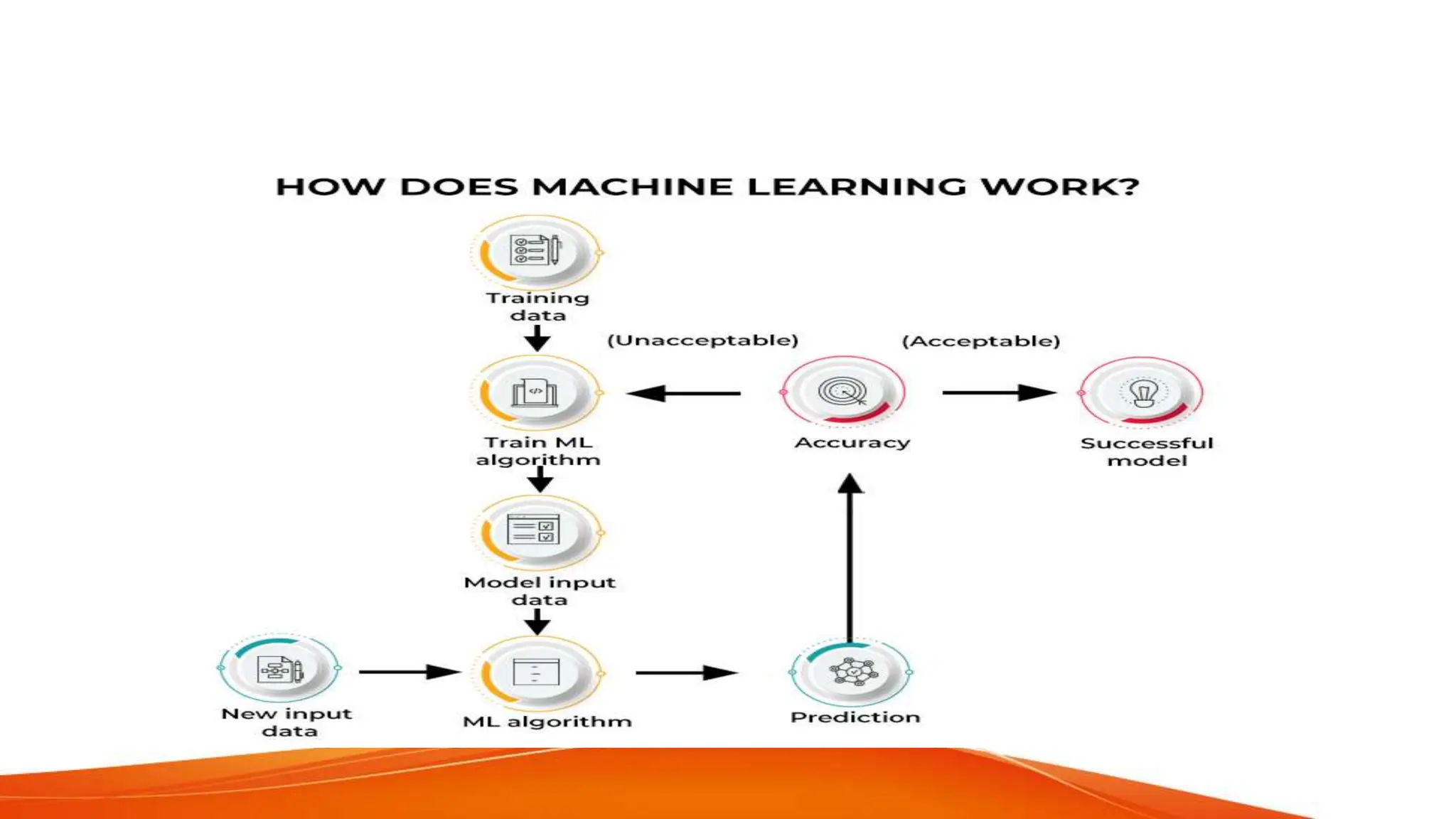
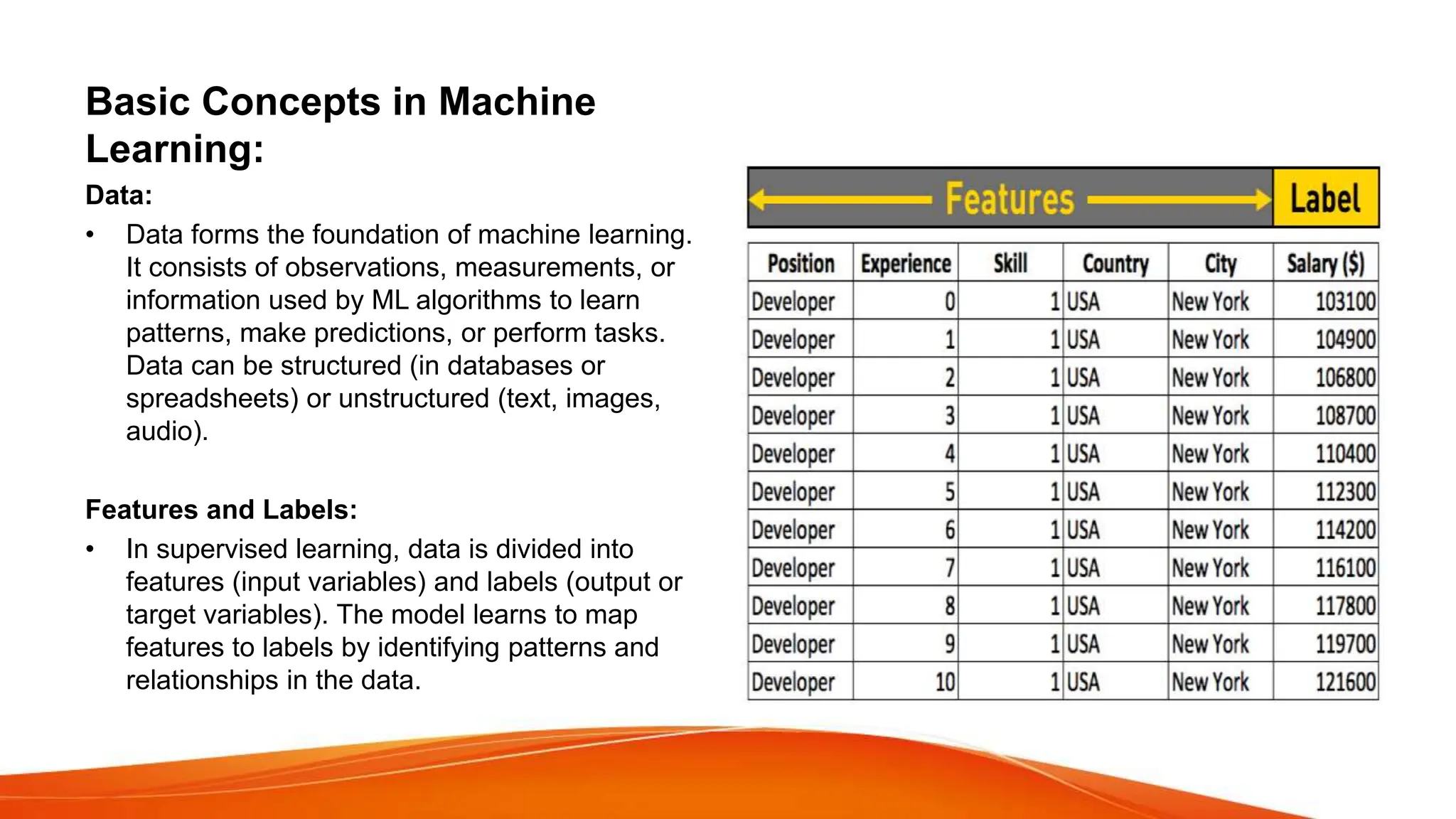
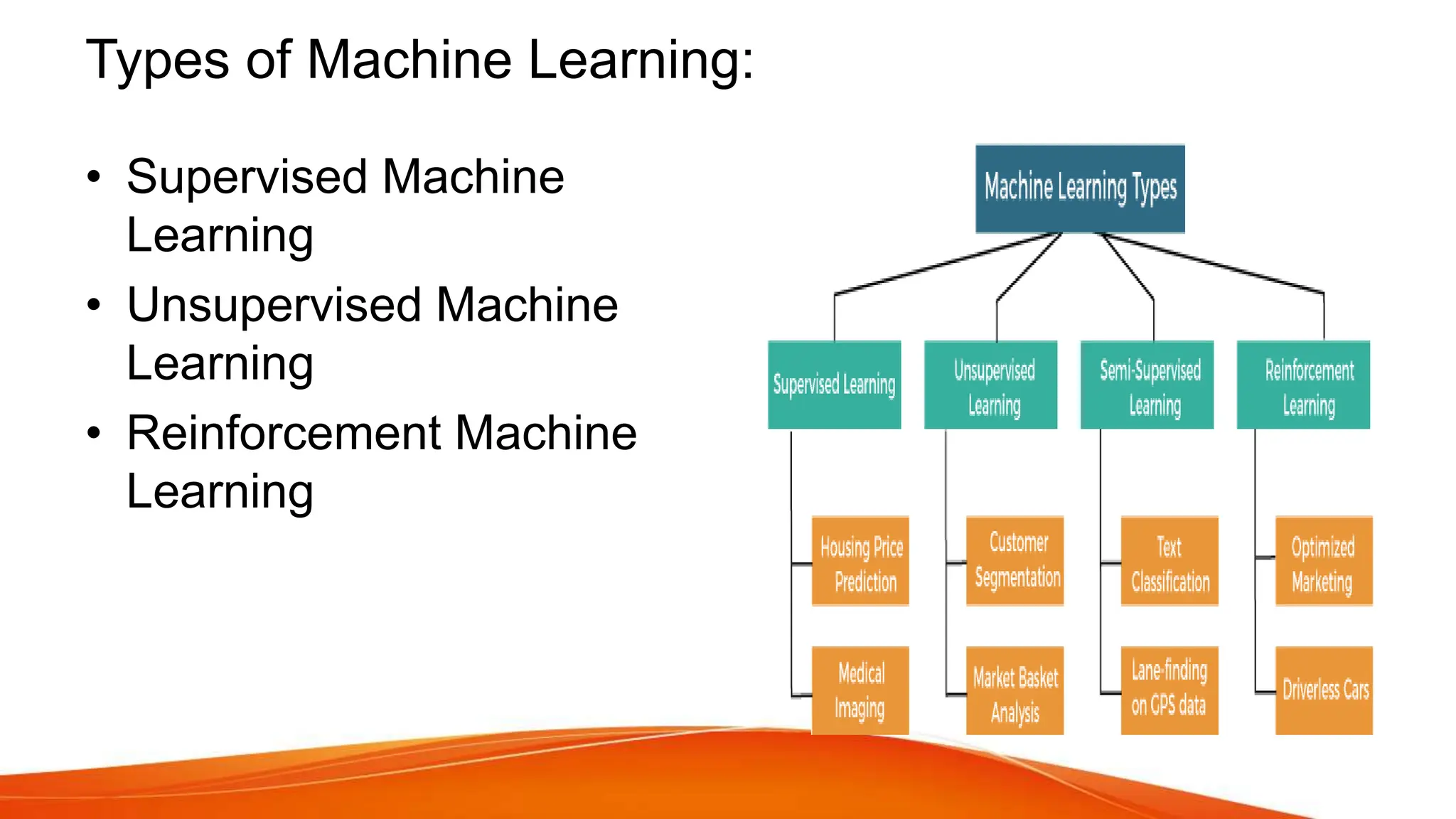
This document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. It begins with definitions of AI and discusses how people commonly interact with AI systems like search engines and virtual assistants. It then describes the three phases of computing and the shift to the current AI computing era. The document outlines why AI is important for automation, decision making, personalization and other applications. It also discusses the main types of AI as strong/narrow AI and weak/general AI. The relationship between AI, machine learning, and deep learning is explained. The document concludes with introductions to machine learning and its key concepts like data, features, labels and common Python libraries. It also covers the main types of machine learning as supervised, unsupervised and