Download as PDF, PPTX





![amqplib
var amqp = require('amqplib/callback_api');
amqp.connect('amqp://localhost', function(err, conn) {
conn.createChannel(function(err, ch) {
var q = 'hello';
ch.assertQueue(q, {durable: false});
ch.sendToQueue(q, new Buffer('Hello World!'));
console.log(" [x] Sent 'Hello World!'");
});
});
in RabbitMQ Tutorials](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asynchronousmicroservicesinnodejs-151123102512-lva1-app6891/75/Asynchronous-Microservices-in-nodejs-20-2048.jpg)
![amqplib
var amqp = require('amqplib/callback_api');
amqp.connect('amqp://localhost', function(err, conn) {
conn.createChannel(function(err, ch) {
var q = 'hello';
ch.assertQueue(q, {durable: false});
console.log(" [*] Waiting for messages in %s.", q);
ch.consume(q, function(msg) {
console.log(" [x] Received %s”,
msg.content.toString());
}, {noAck: true});
});
});
in RabbitMQ Tutorials](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asynchronousmicroservicesinnodejs-151123102512-lva1-app6891/75/Asynchronous-Microservices-in-nodejs-21-2048.jpg)


The document discusses asynchronous microservices in Node.js, emphasizing the advantages of a microservices architecture such as decentralization and being organized around business capabilities. It covers both synchronous and asynchronous communication topologies, highlighting the use of the Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP) for loosely coupled systems. Code examples illustrate how to implement message queues and consuming messages in RabbitMQ, along with patterns like work queues and webhooks.



















![amqplib
var amqp = require('amqplib/callback_api');
amqp.connect('amqp://localhost', function(err, conn) {
conn.createChannel(function(err, ch) {
var q = 'hello';
ch.assertQueue(q, {durable: false});
ch.sendToQueue(q, new Buffer('Hello World!'));
console.log(" [x] Sent 'Hello World!'");
});
});
in RabbitMQ Tutorials](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asynchronousmicroservicesinnodejs-151123102512-lva1-app6891/75/Asynchronous-Microservices-in-nodejs-20-2048.jpg)
![amqplib
var amqp = require('amqplib/callback_api');
amqp.connect('amqp://localhost', function(err, conn) {
conn.createChannel(function(err, ch) {
var q = 'hello';
ch.assertQueue(q, {durable: false});
console.log(" [*] Waiting for messages in %s.", q);
ch.consume(q, function(msg) {
console.log(" [x] Received %s”,
msg.content.toString());
}, {noAck: true});
});
});
in RabbitMQ Tutorials](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asynchronousmicroservicesinnodejs-151123102512-lva1-app6891/75/Asynchronous-Microservices-in-nodejs-21-2048.jpg)





Bruno Pedro introduces the topic of Asynchronous Microservices in Node.js, dated November 2015.
Summary of key topics: reasons for microservices, differences between synchronous and asynchronous topologies, broker approach, code examples, and patterns.
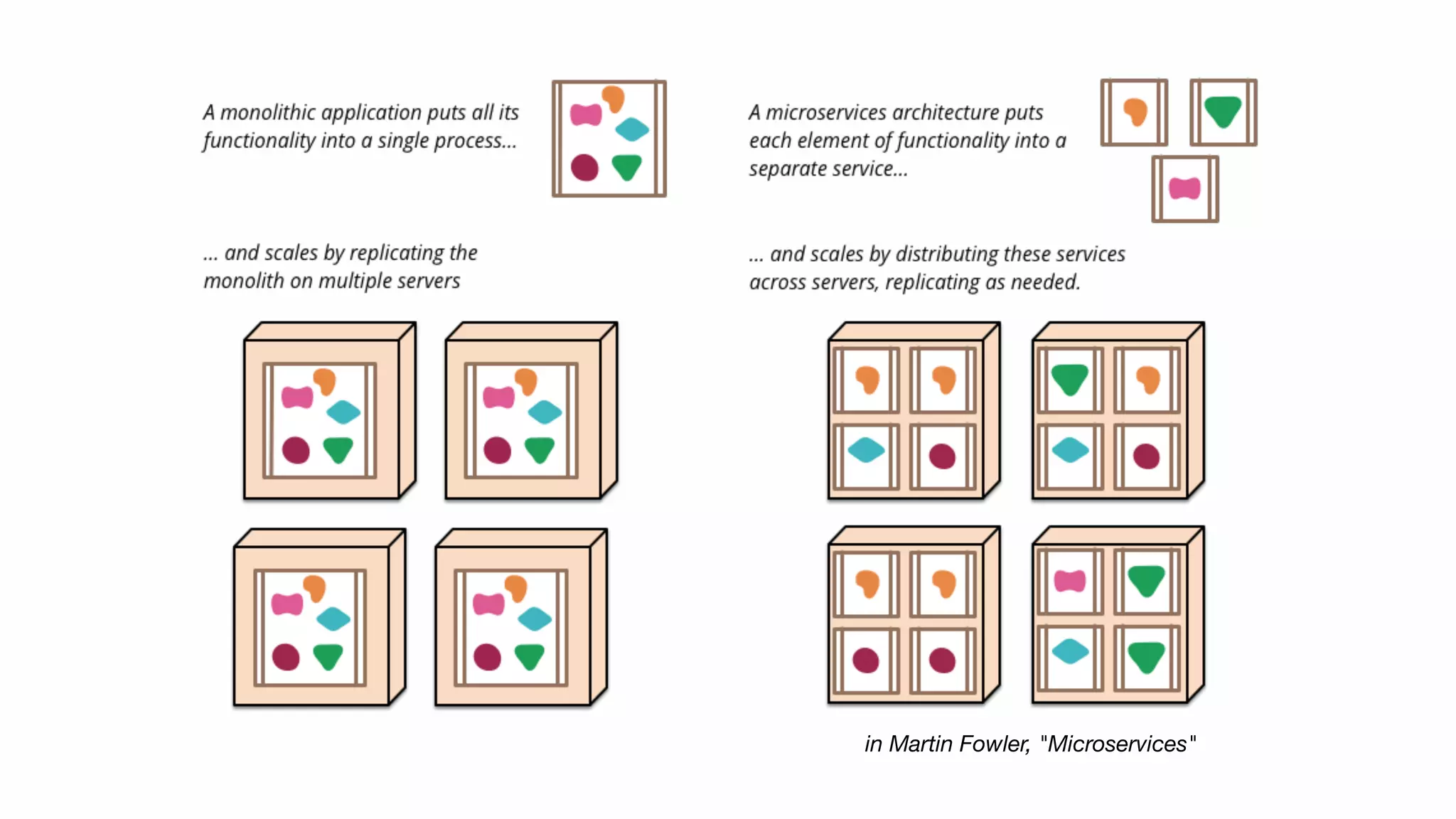
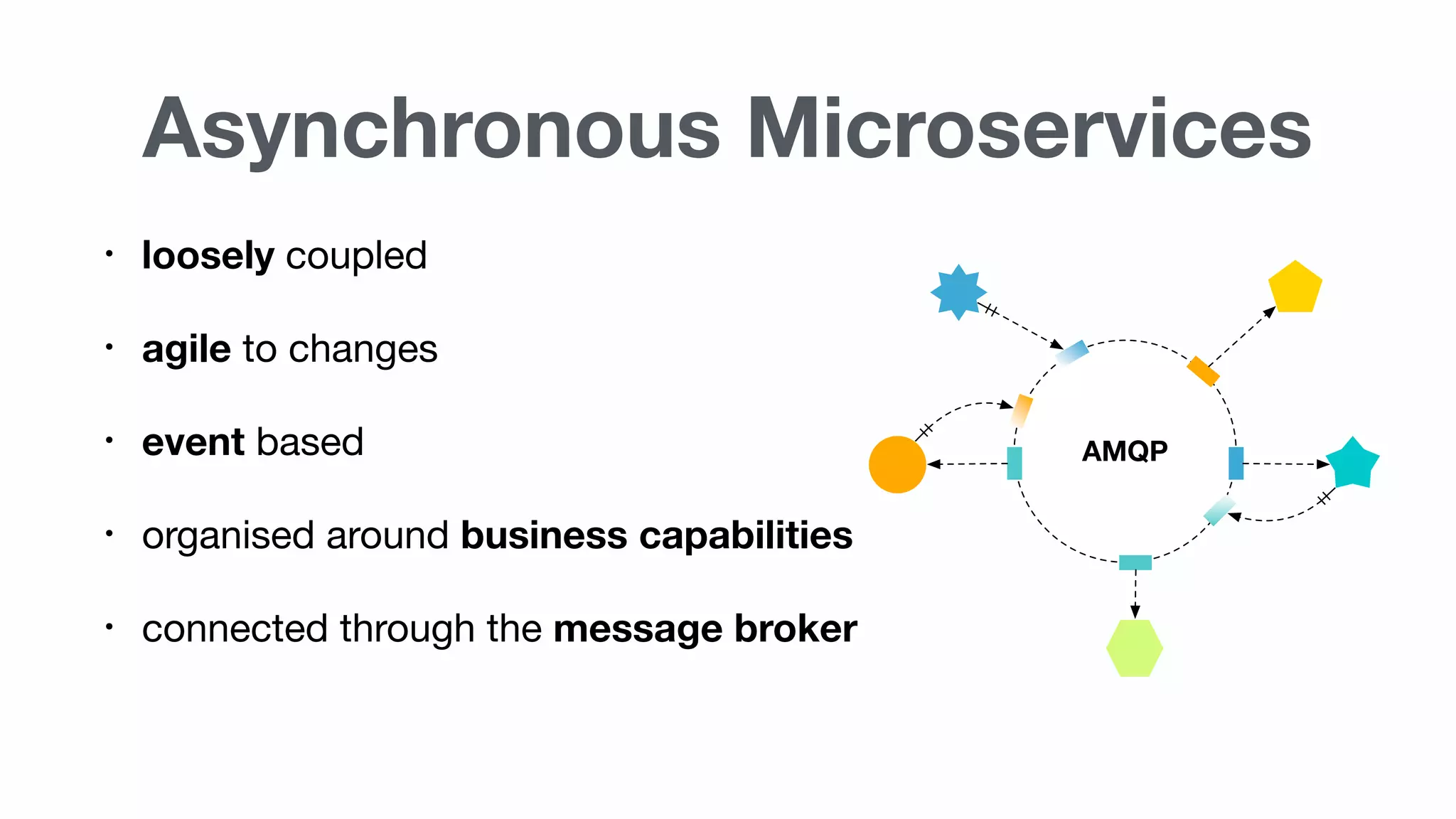
Microservices focus on business capabilities, decentralized governance, automated infrastructure, and are designed for failure, highlighting their responsibility and coupling.
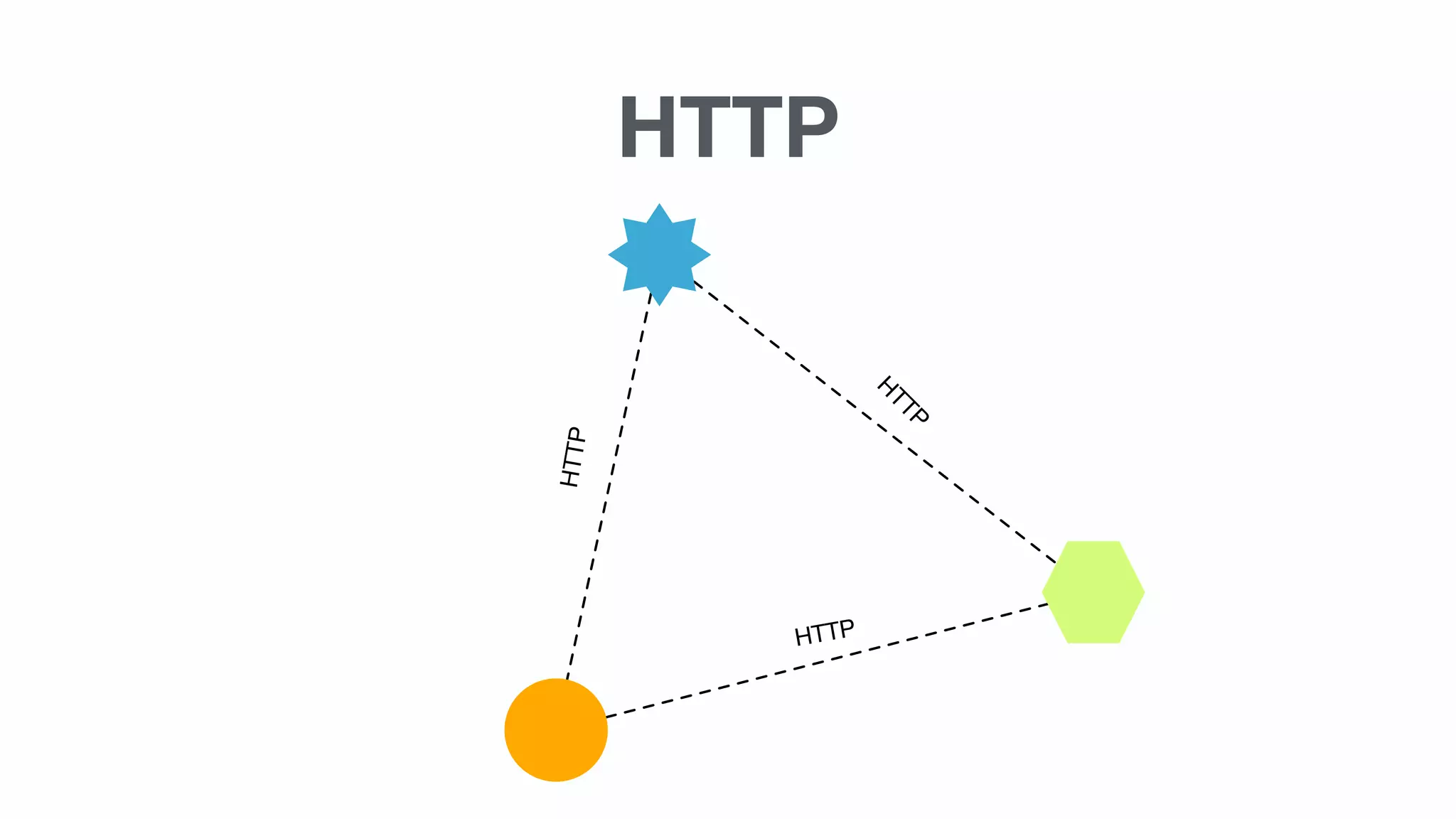
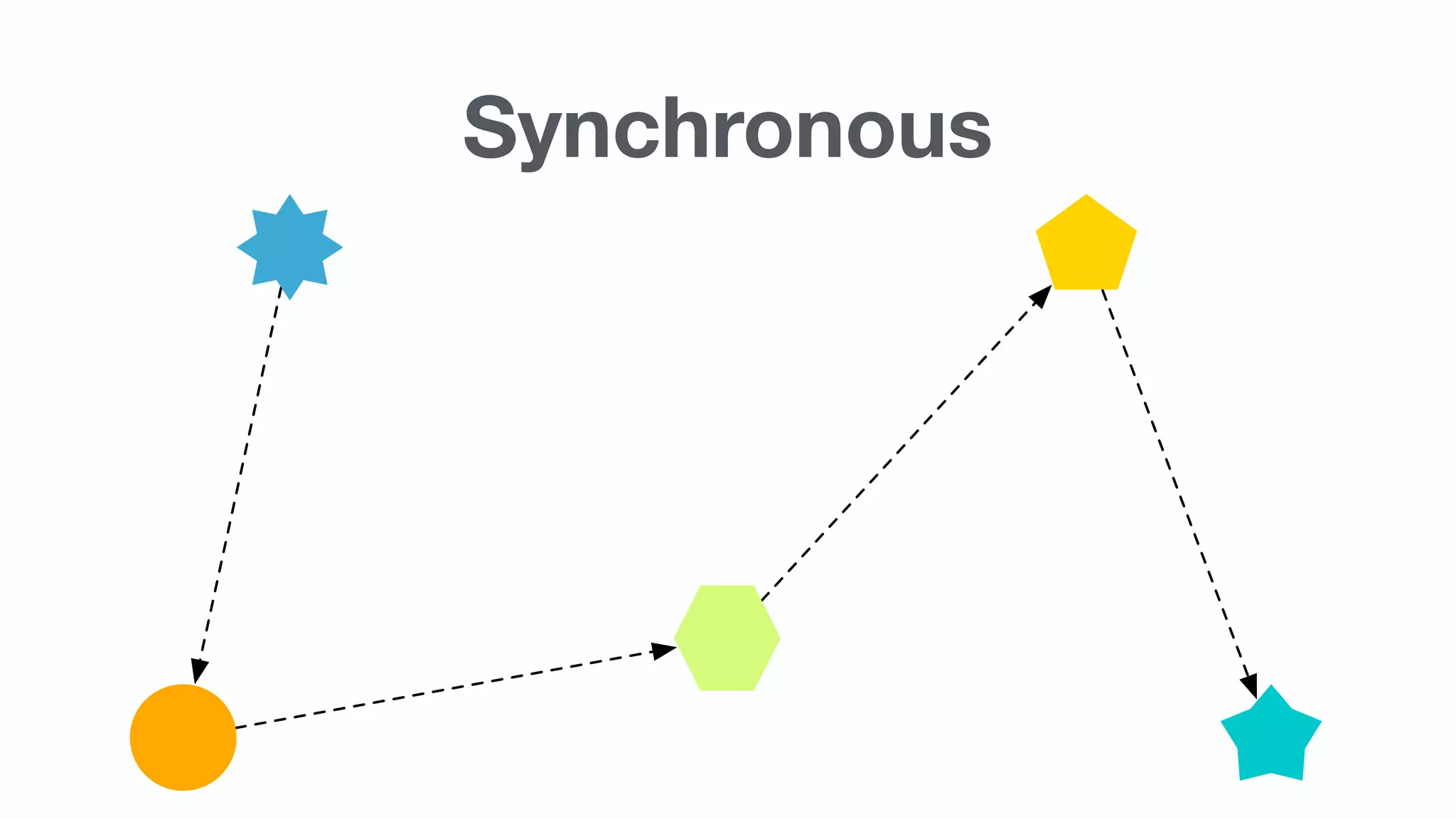
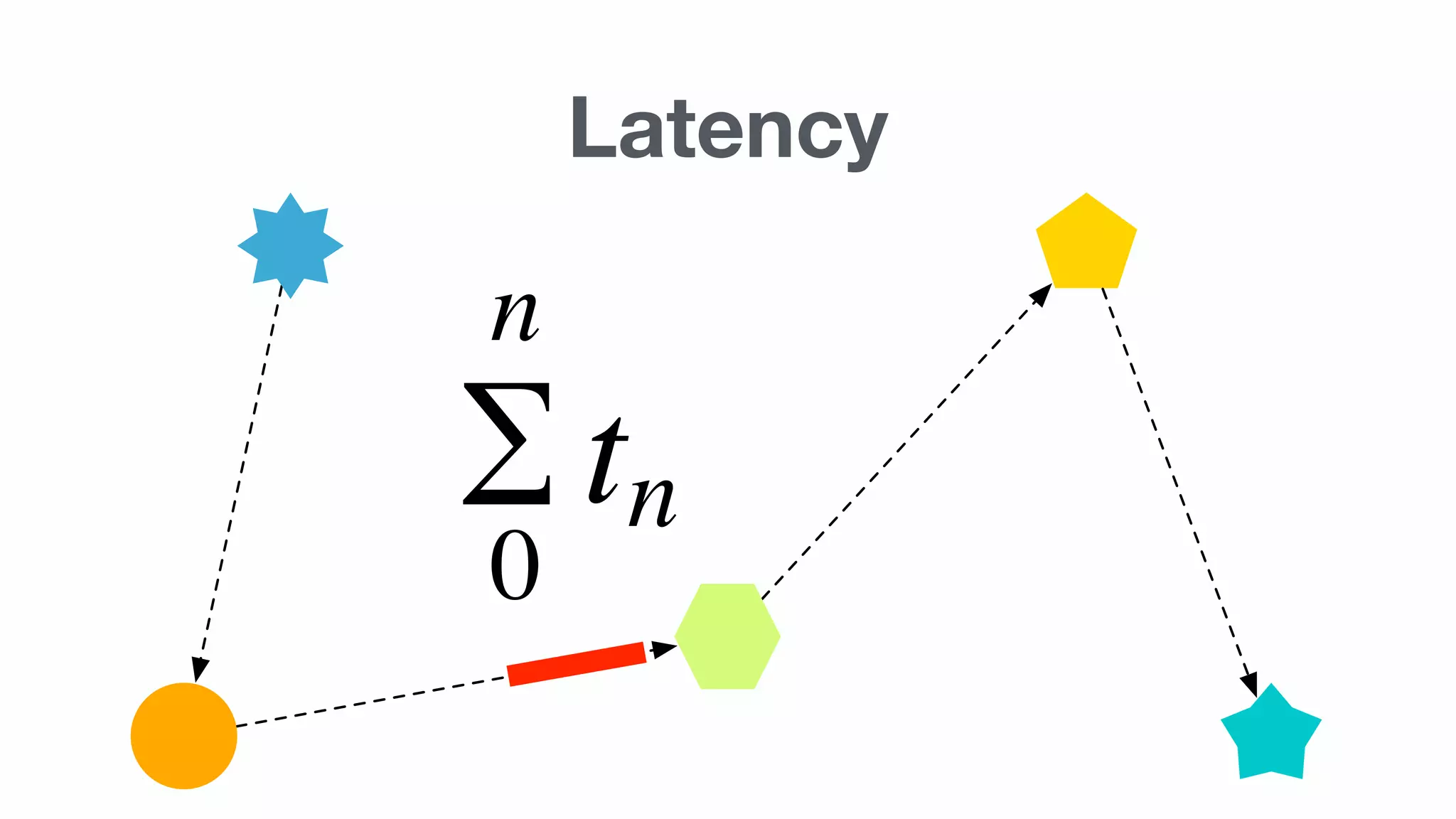
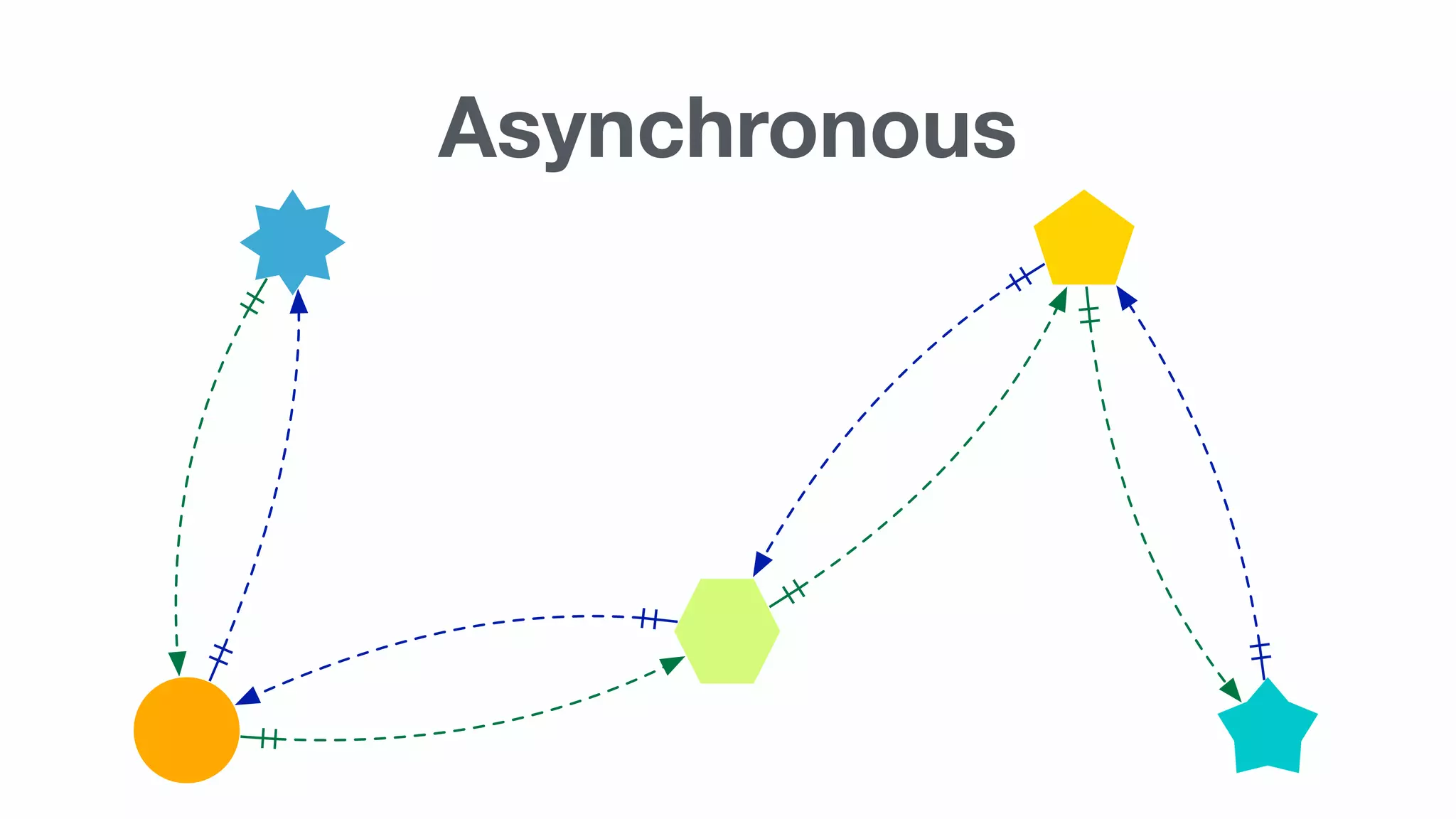
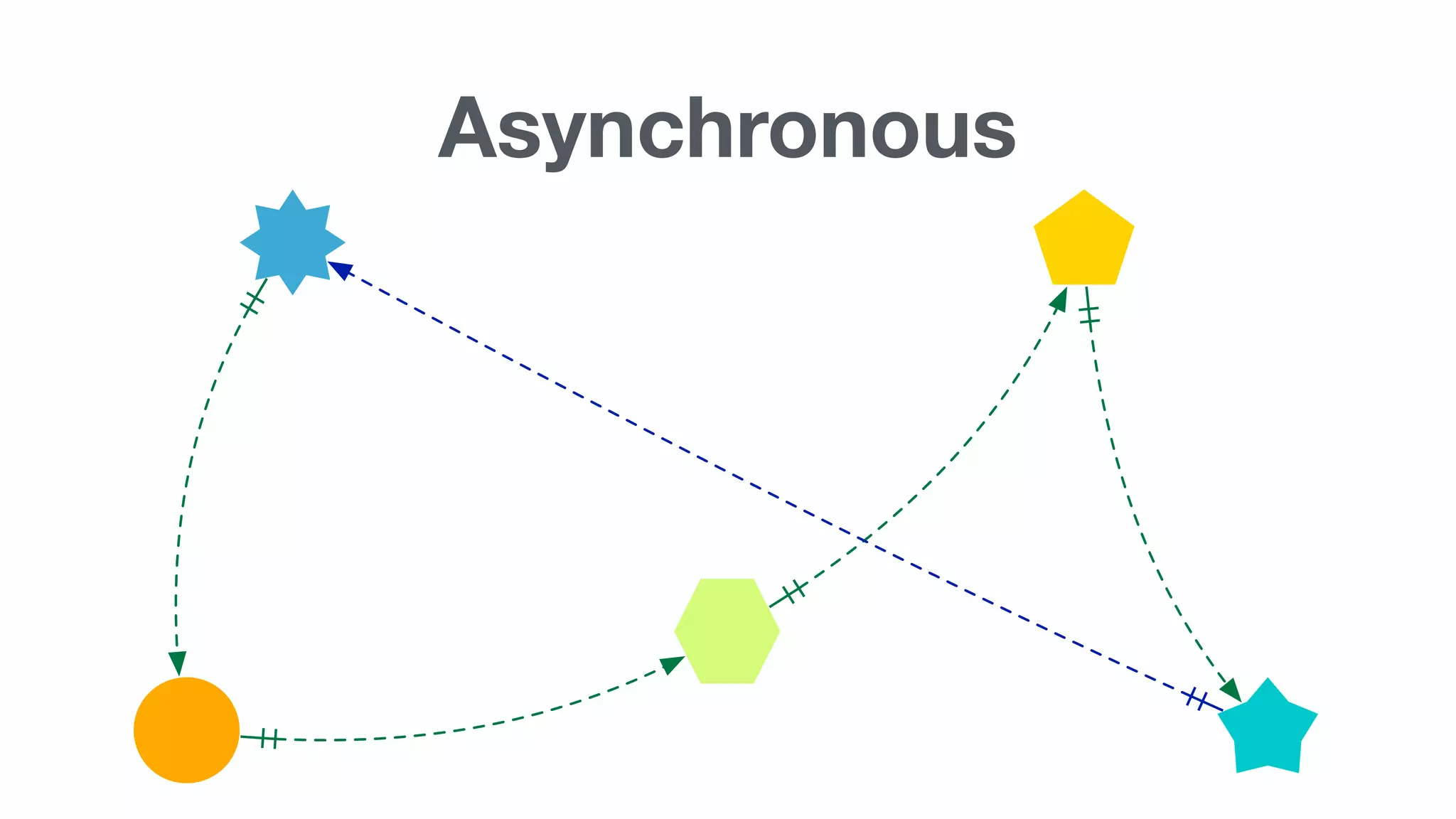
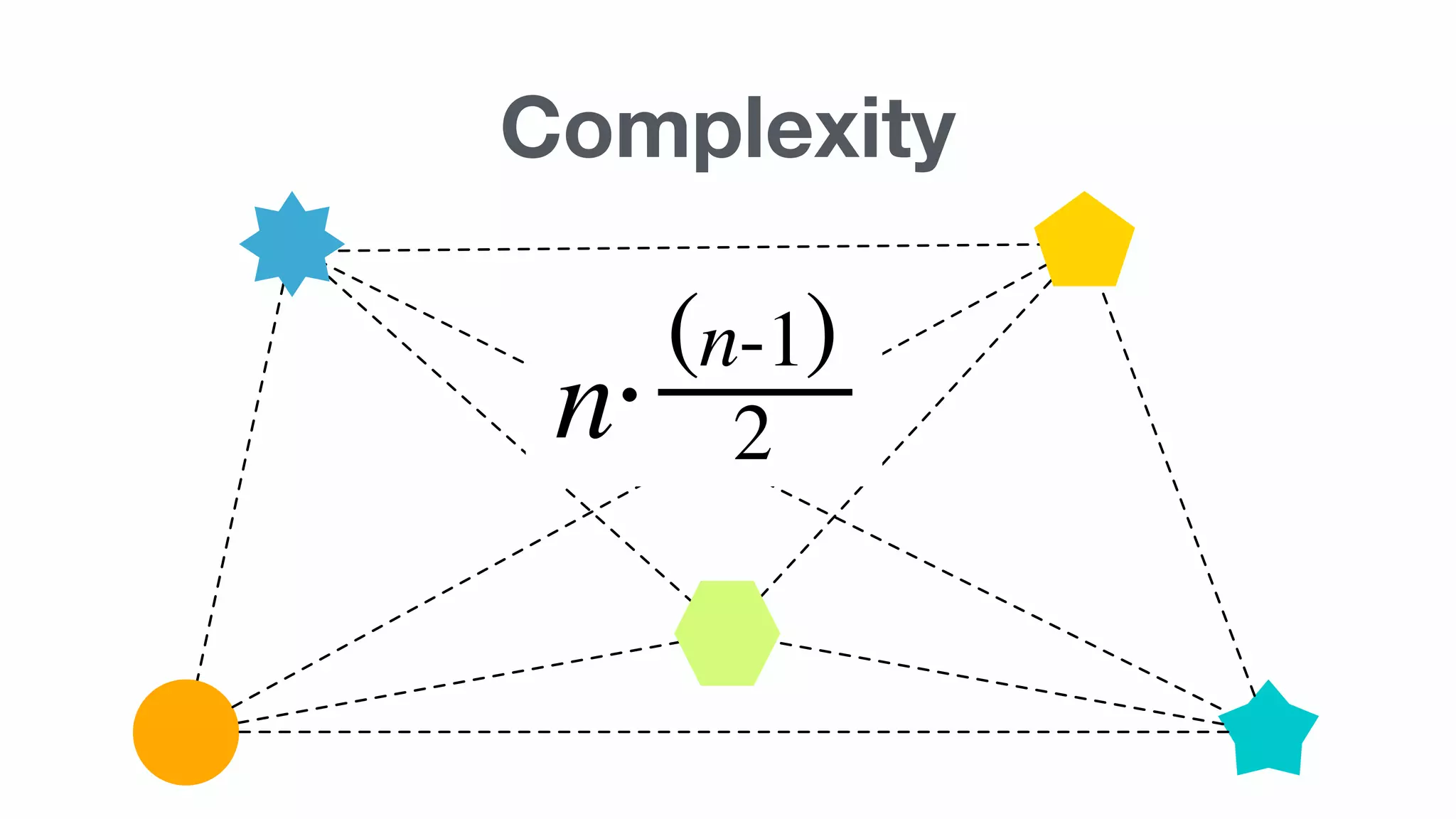
Important concepts including HTTP, synchronous vs asynchronous, latency, and the complexity involved in implementing these methods.
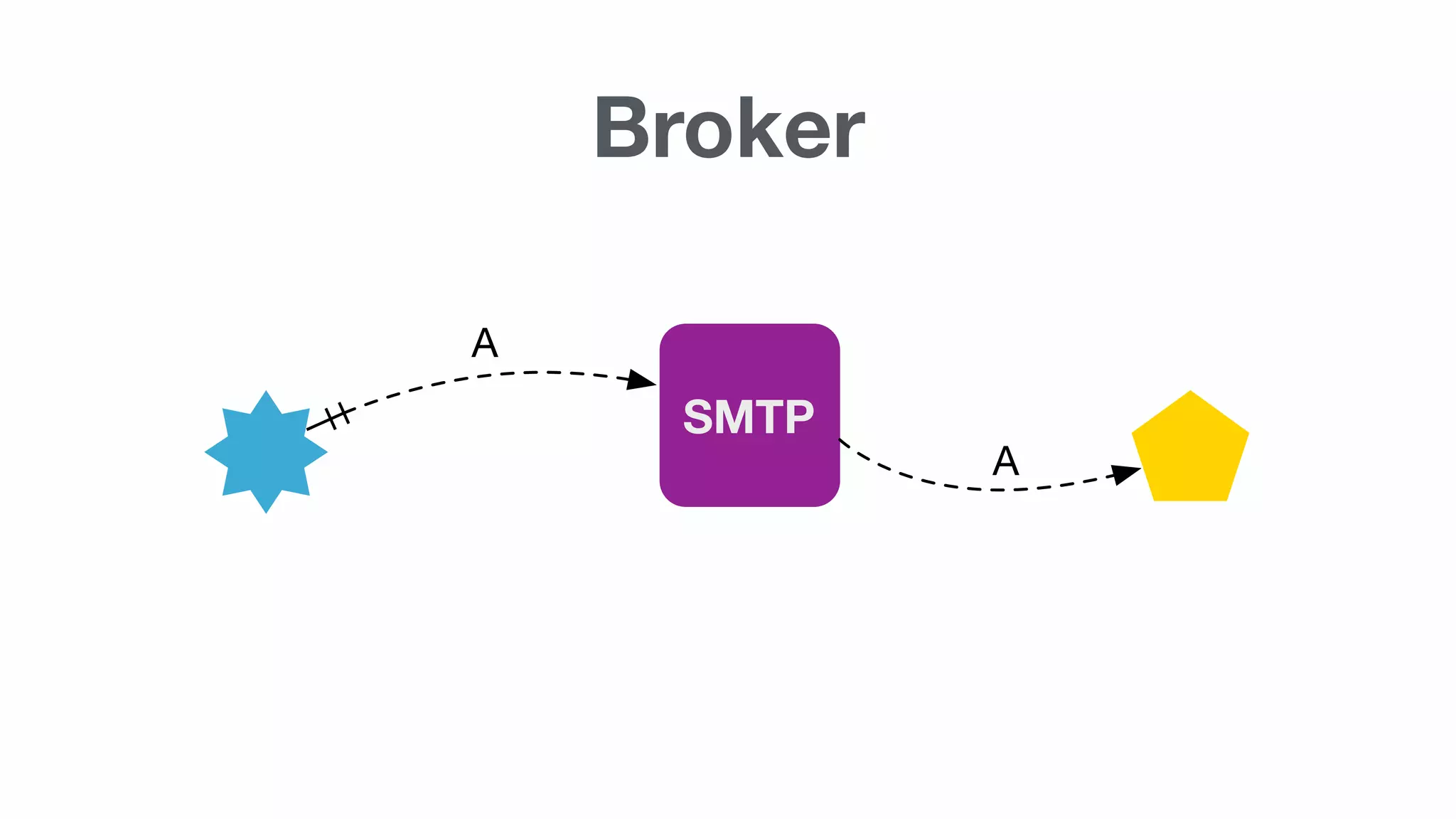
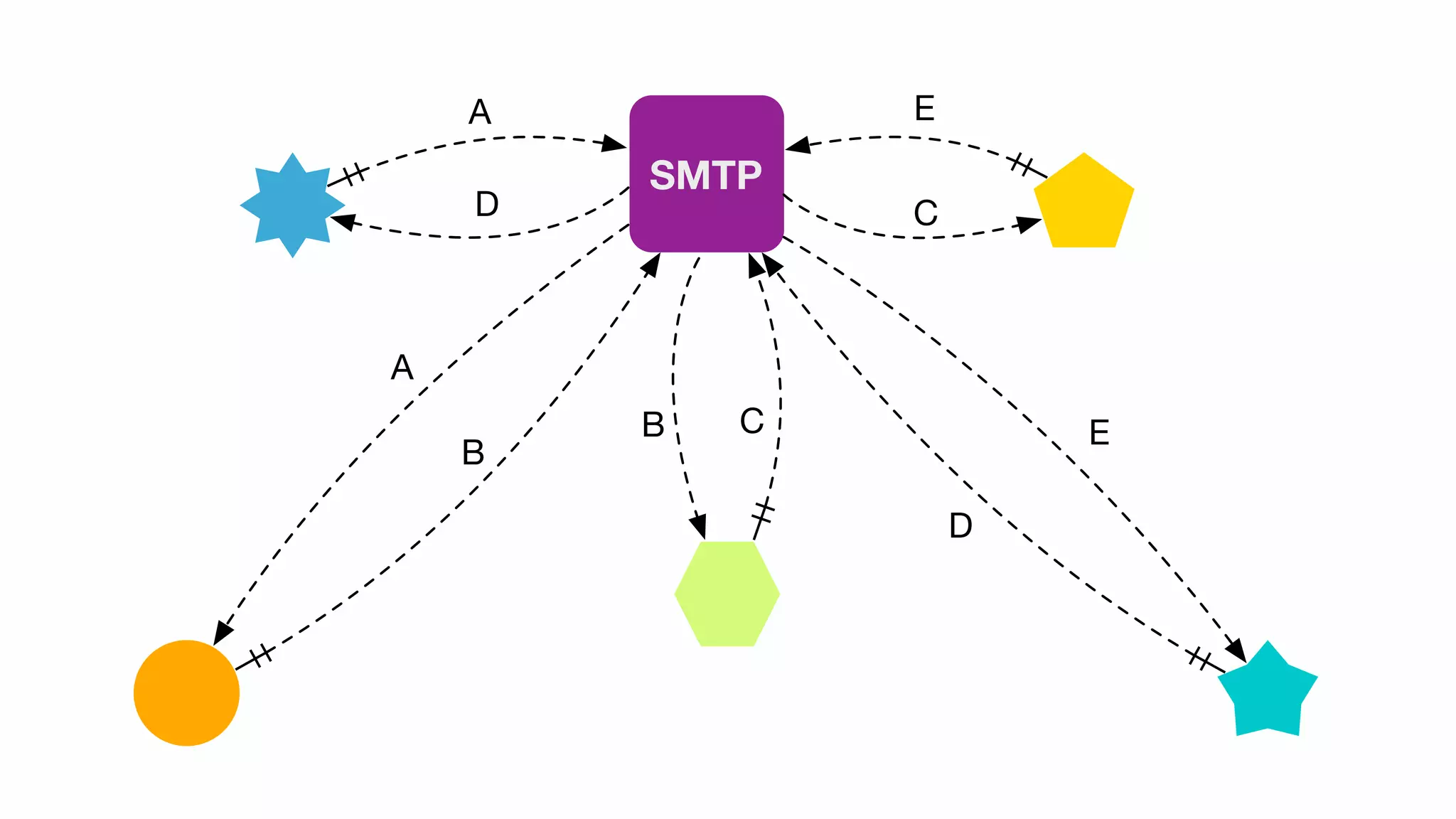
Introduction to SMTP and messaging brokers followed by a conceptual diagram illustrating message flow in a broker-based system.
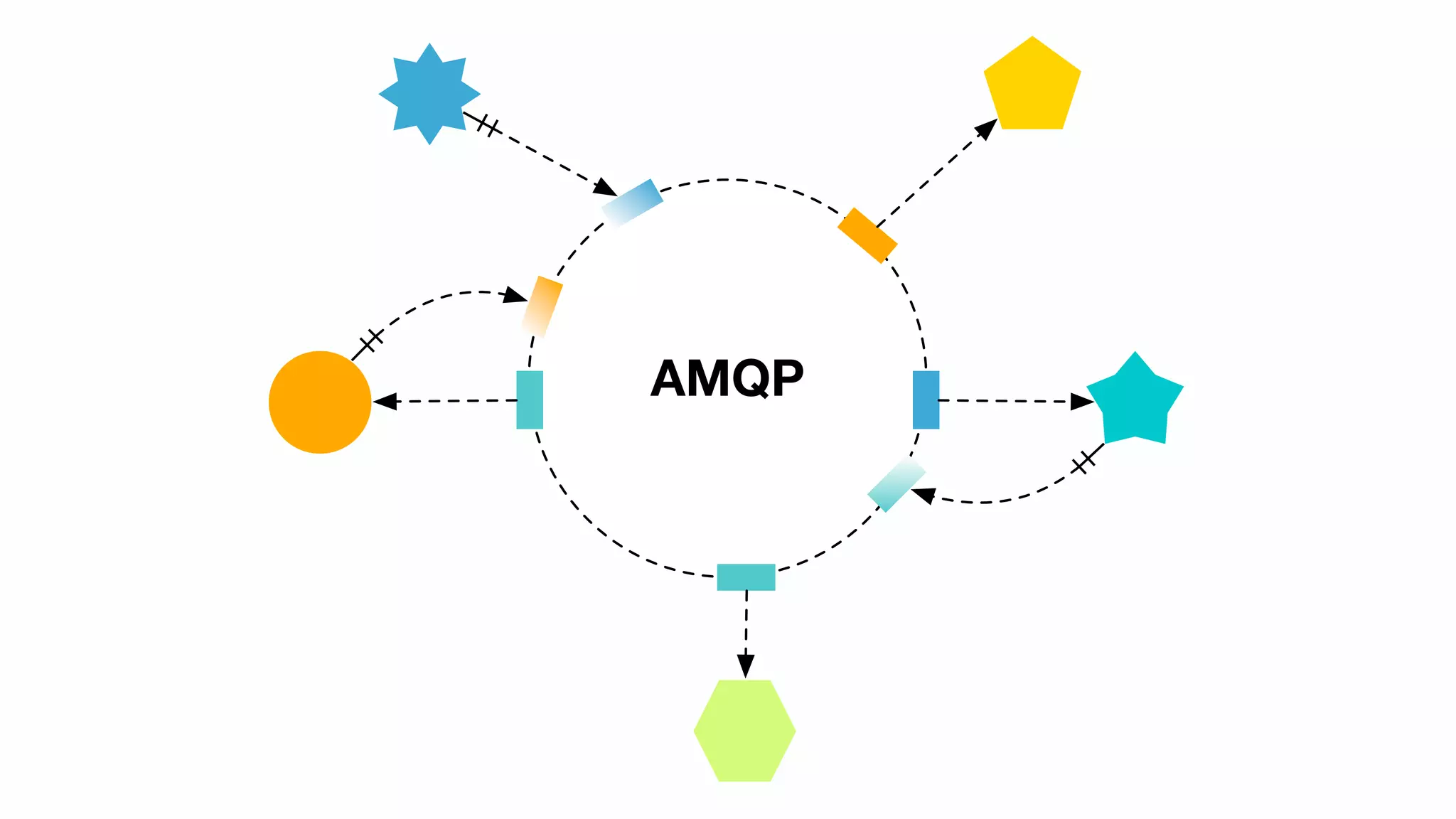
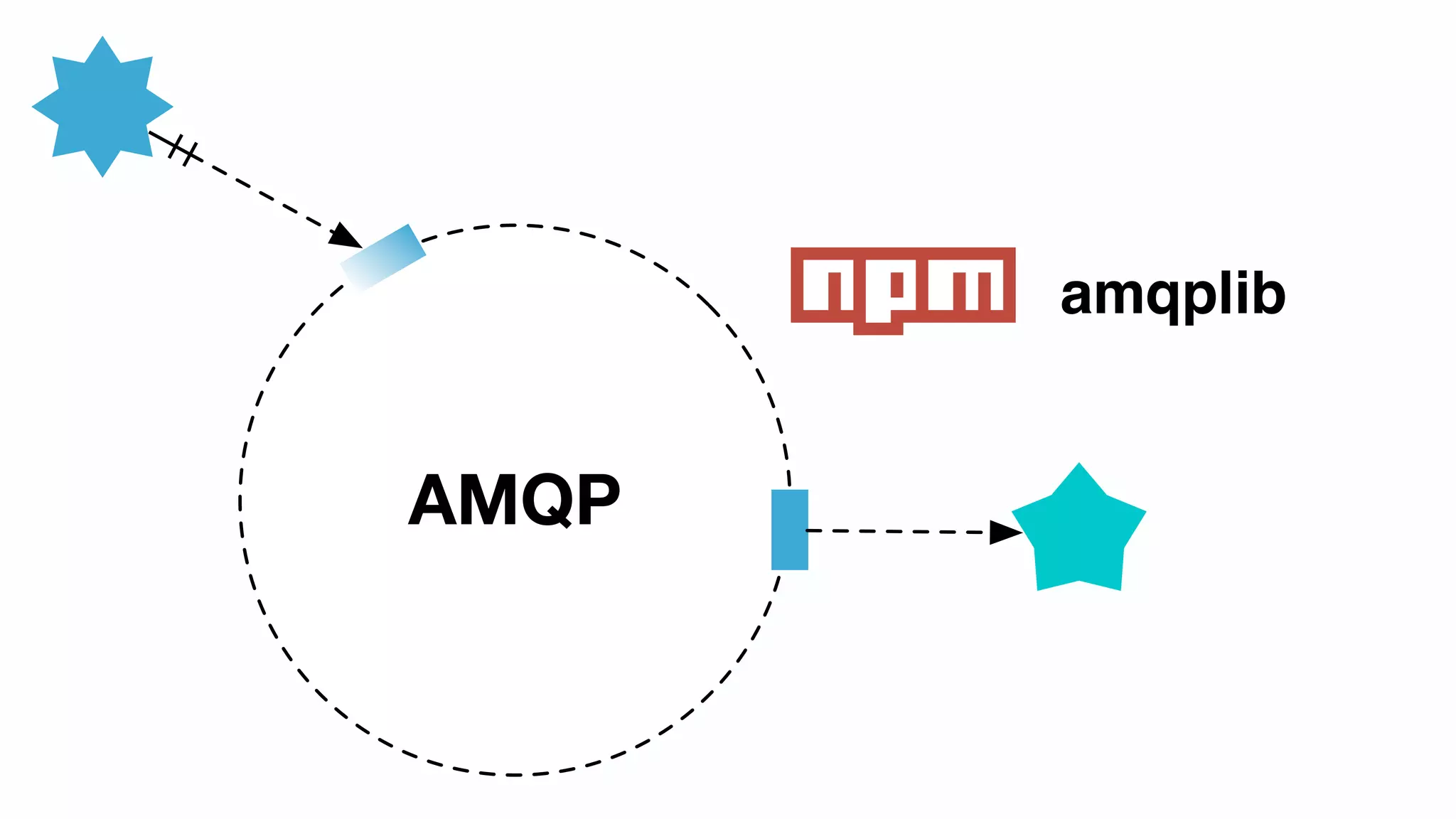
Detailed explanation of AMQP (Advanced Message Queueing Protocol) including its features like interoperability and its support in Node.js.
Code examples demonstrating how to send and receive messages using the amqplib library in RabbitMQ tutorials.
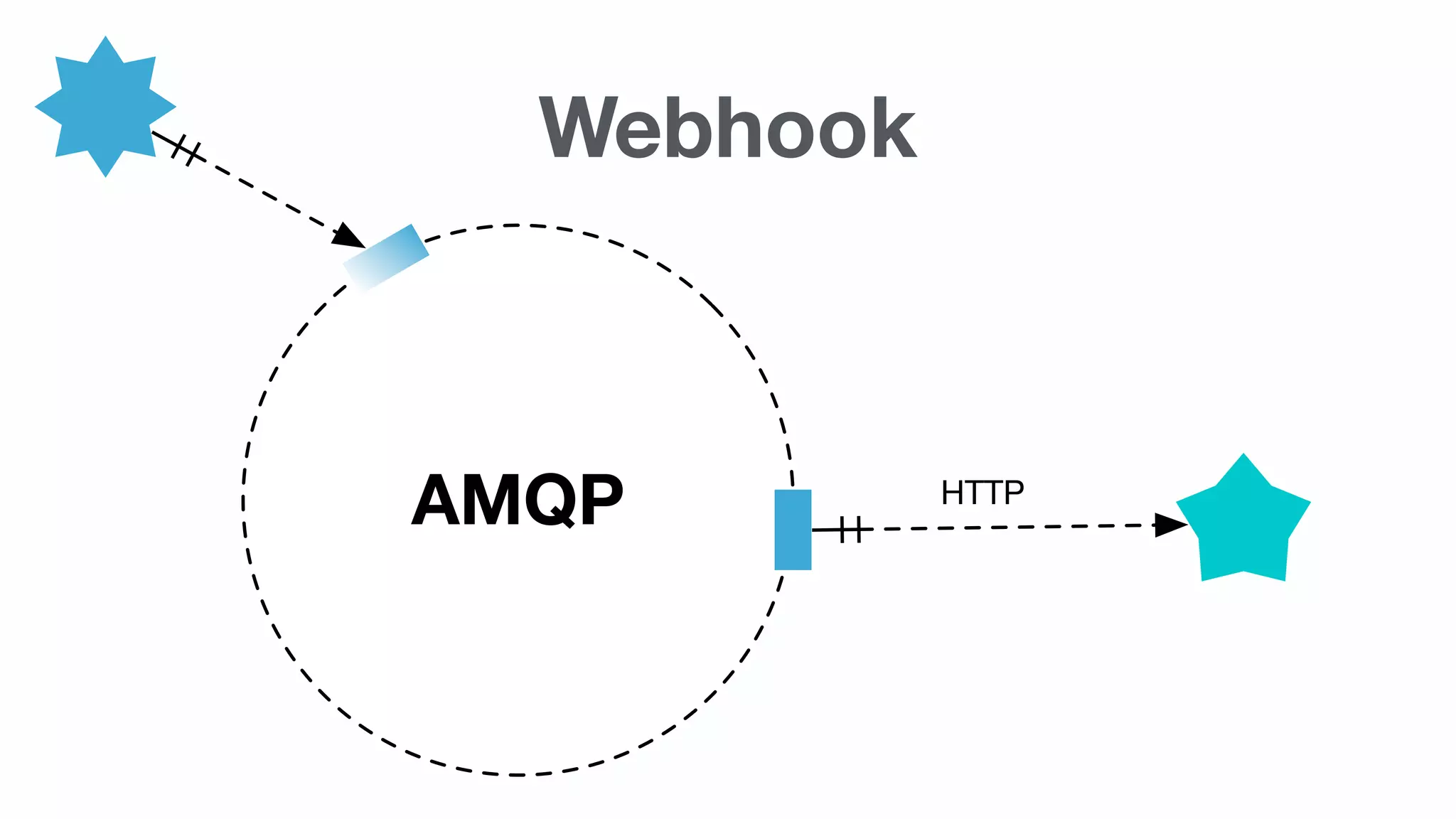
Connection between AMQP and HTTP, specifically referencing the Webhook concept for integrating services.
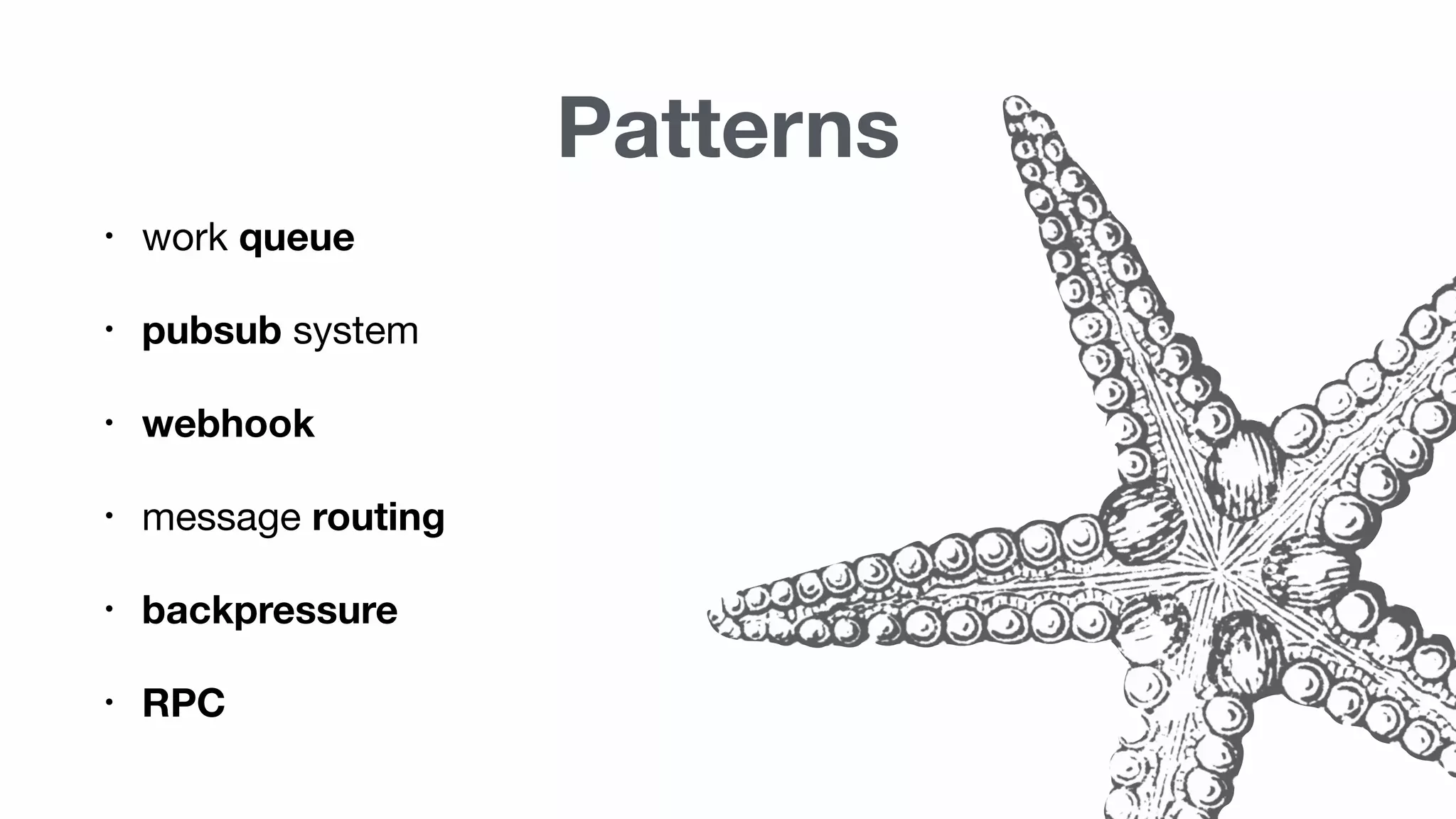
Patterns relevant to microservices including work queues, pub/sub systems, webhooks, message routing, backpressure, and RPC.
Summary of advantages of asynchronous microservices which are loosely coupled, agile, event-based, connected via AMQP.
Wrap-up of microservices advantages, focus on asynchronous approaches, broker implementation, with a thank you note from Bruno Pedro.