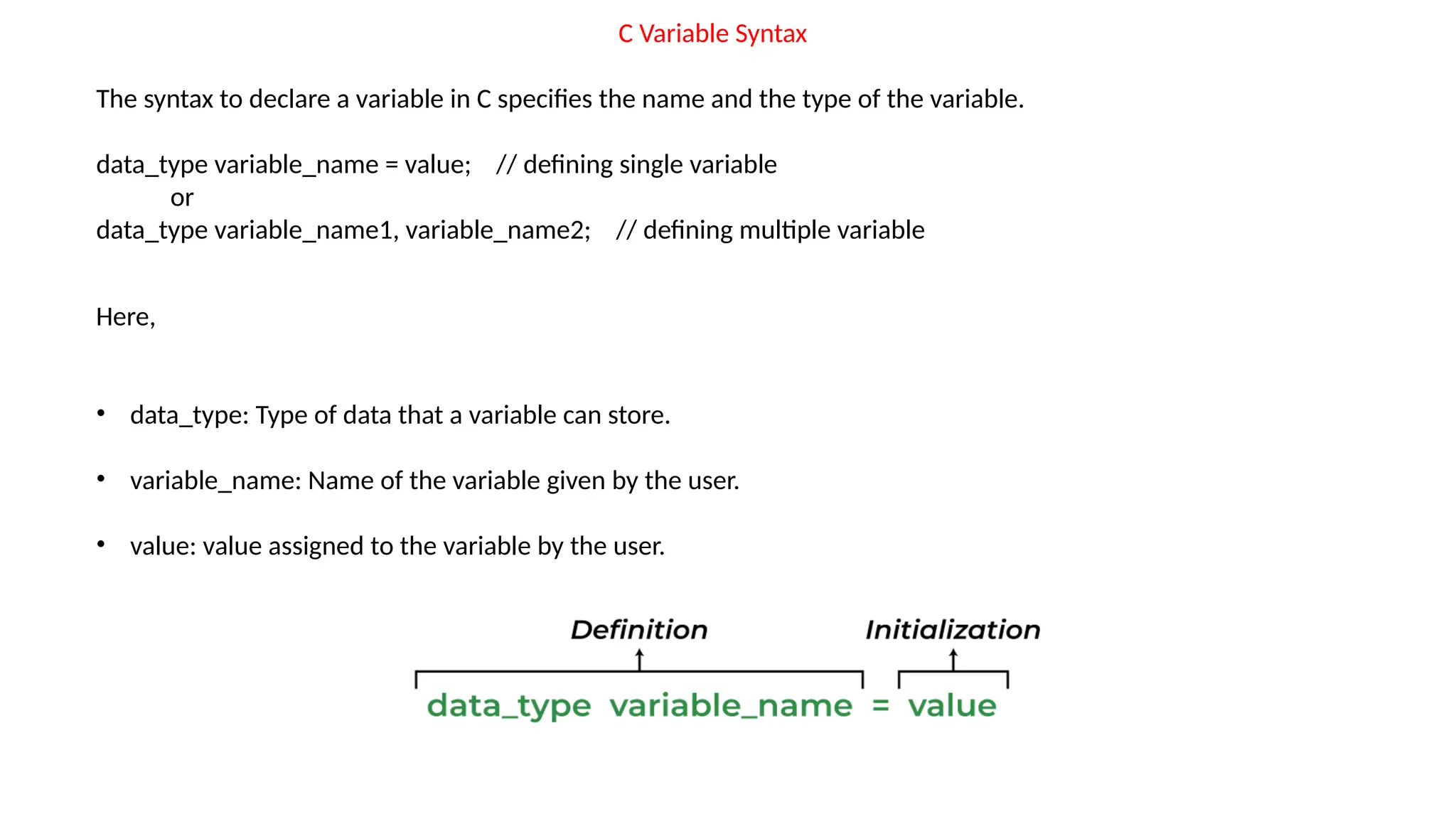
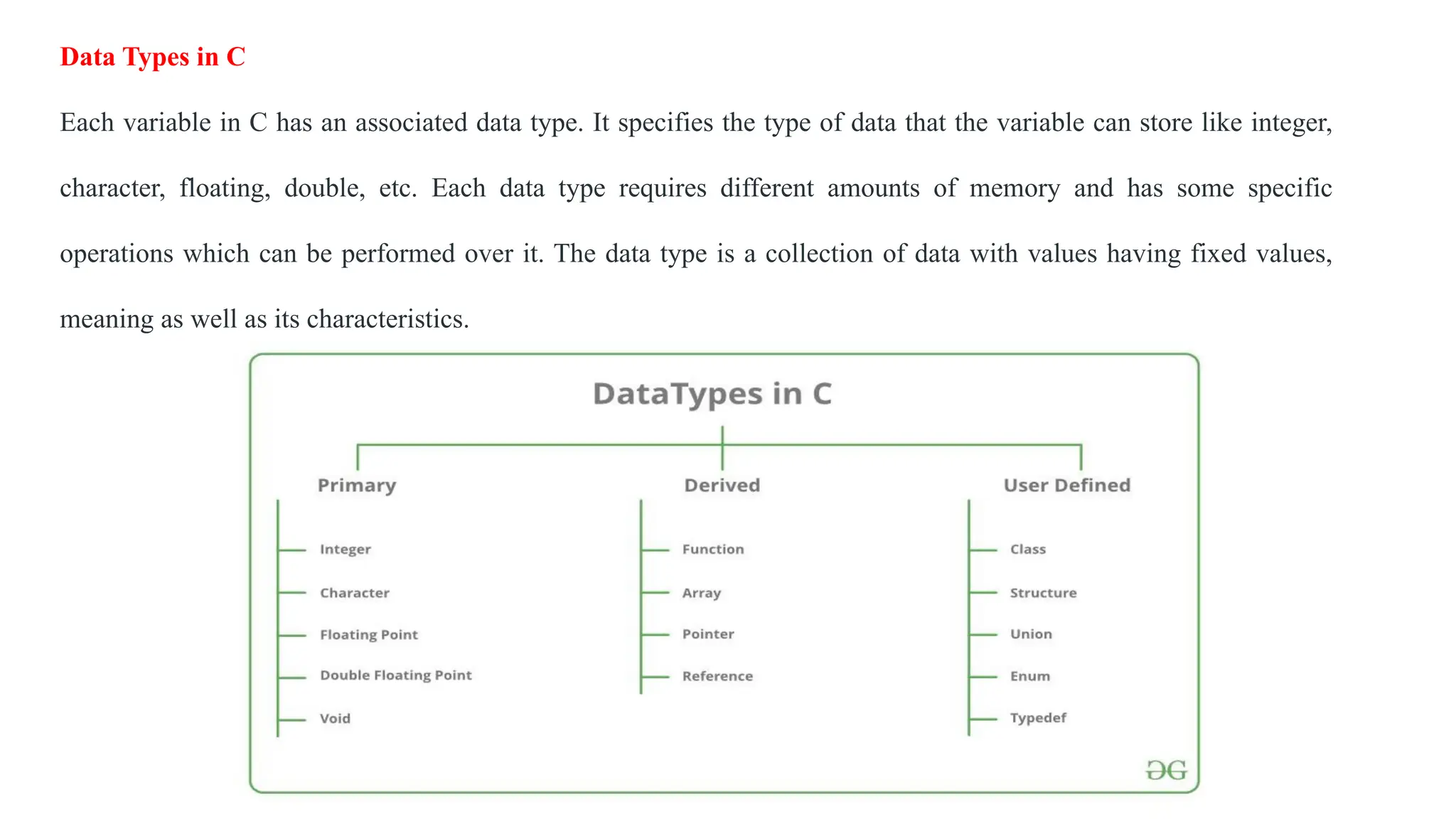
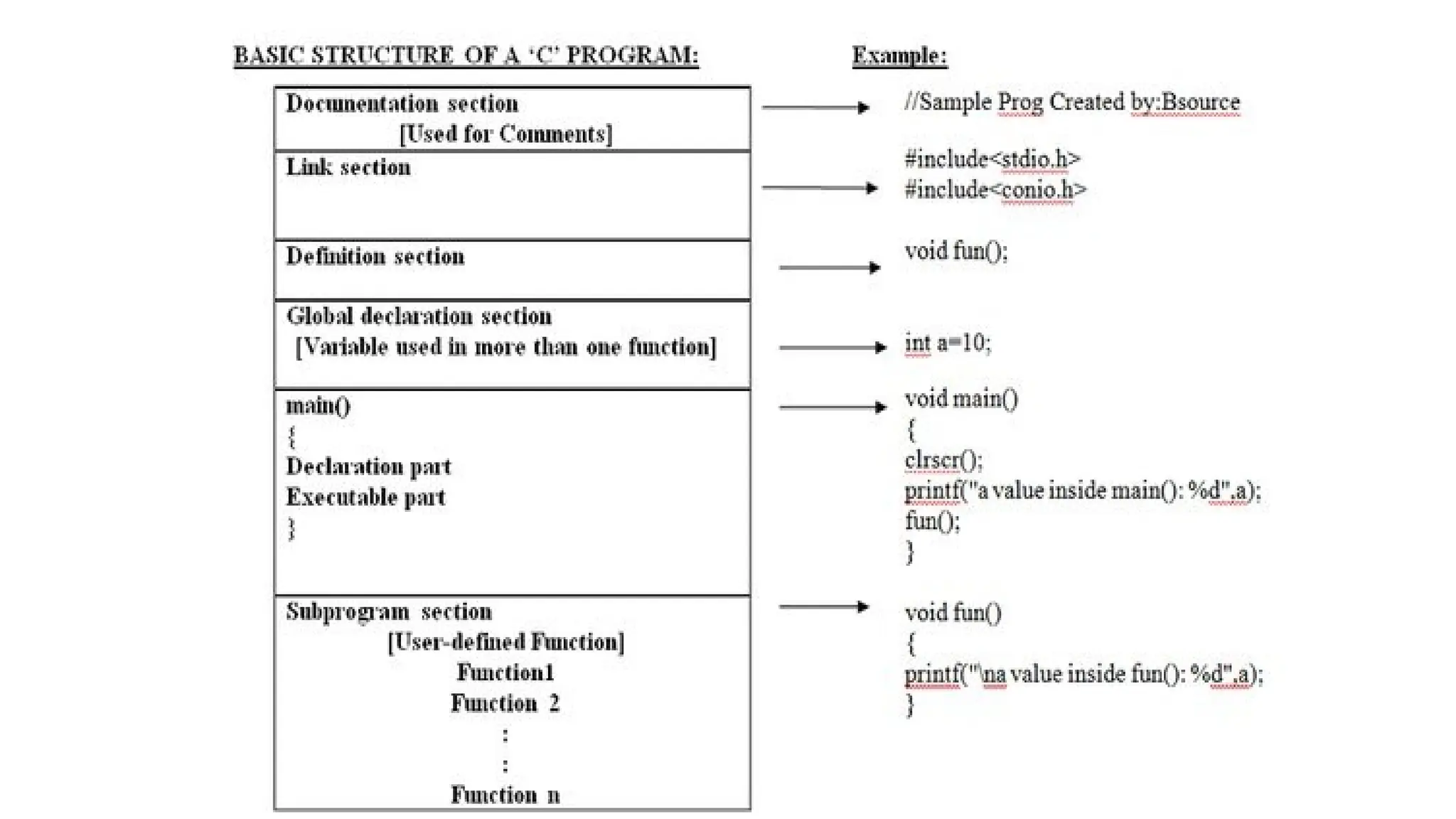
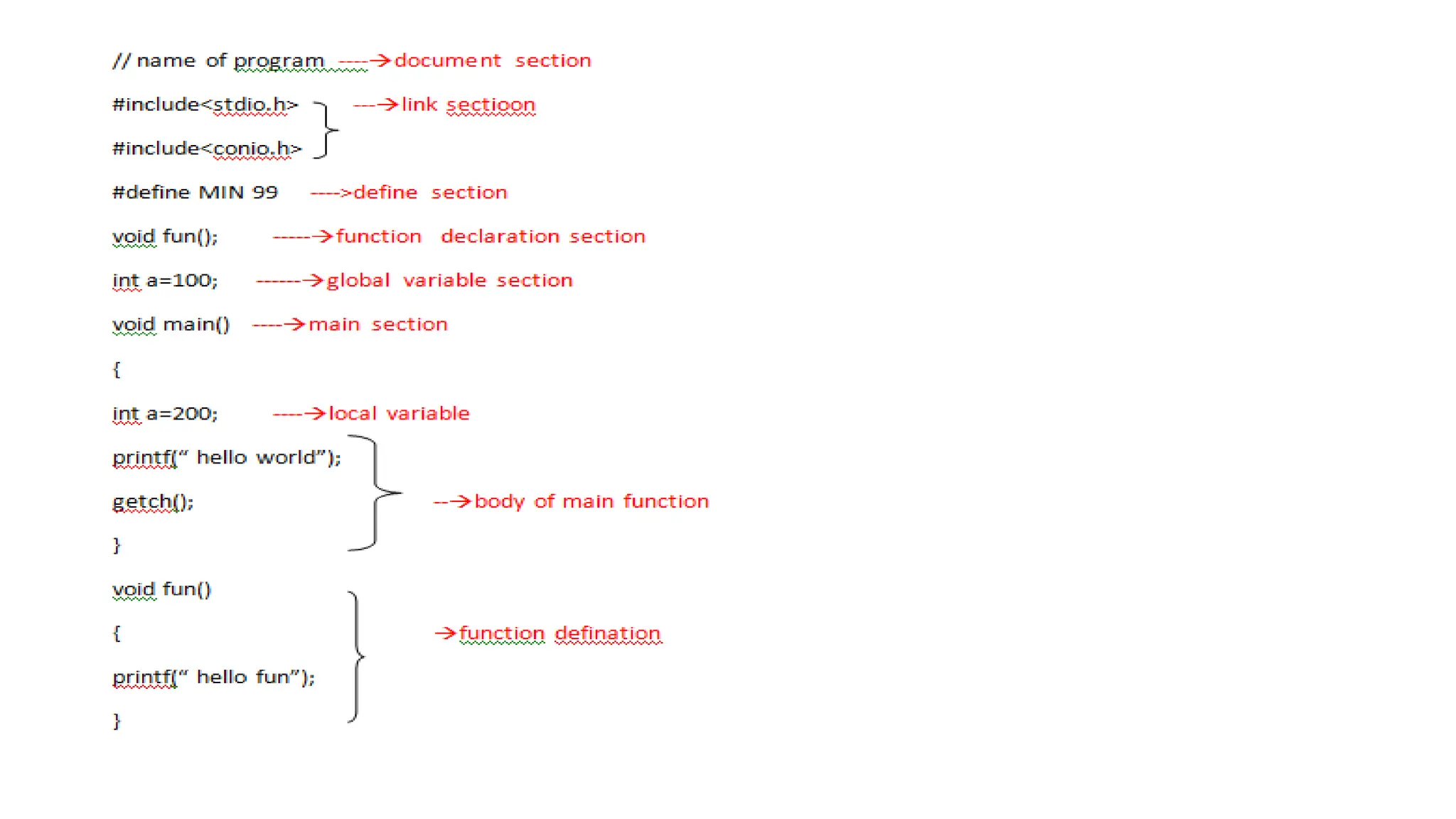
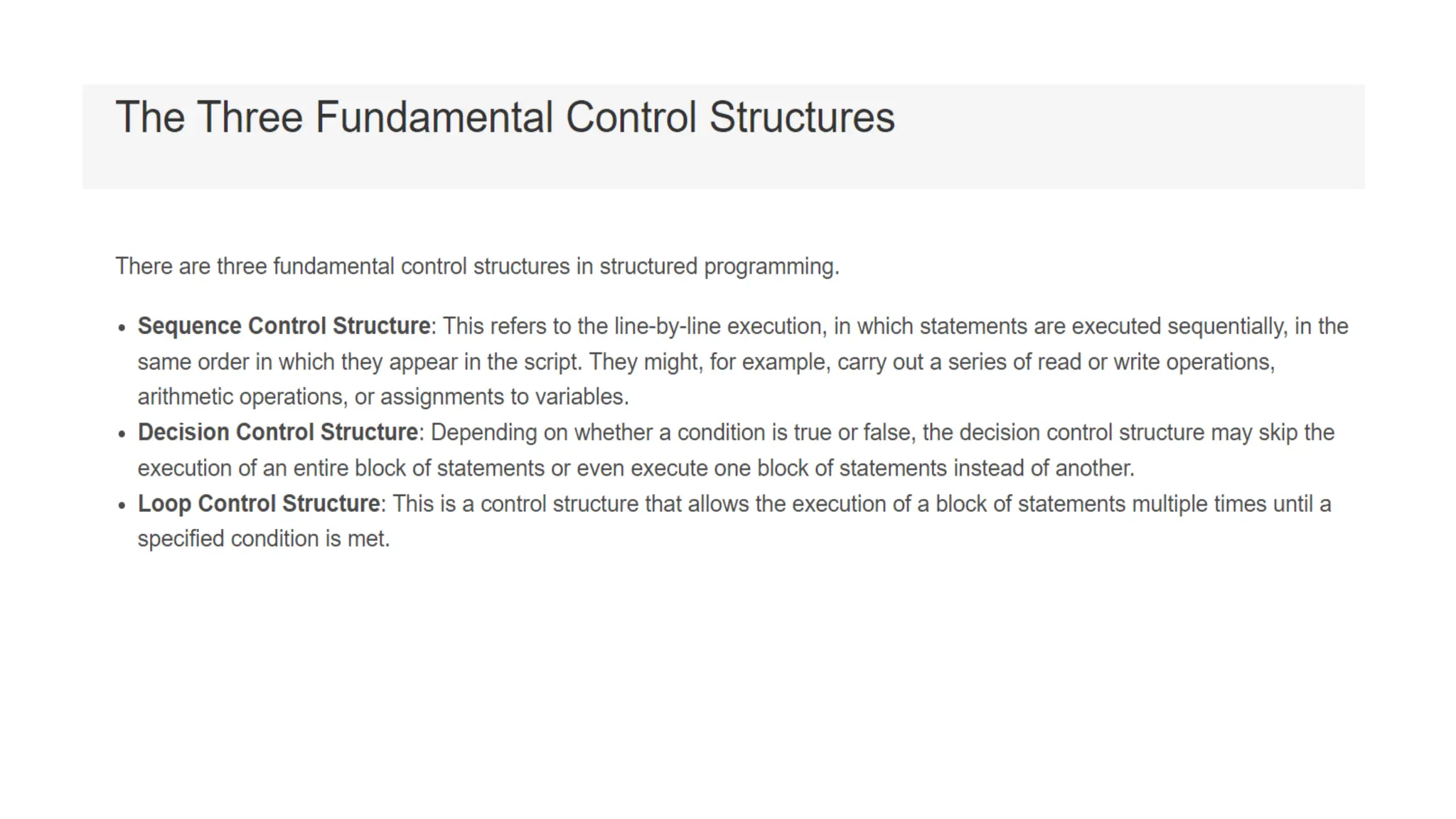
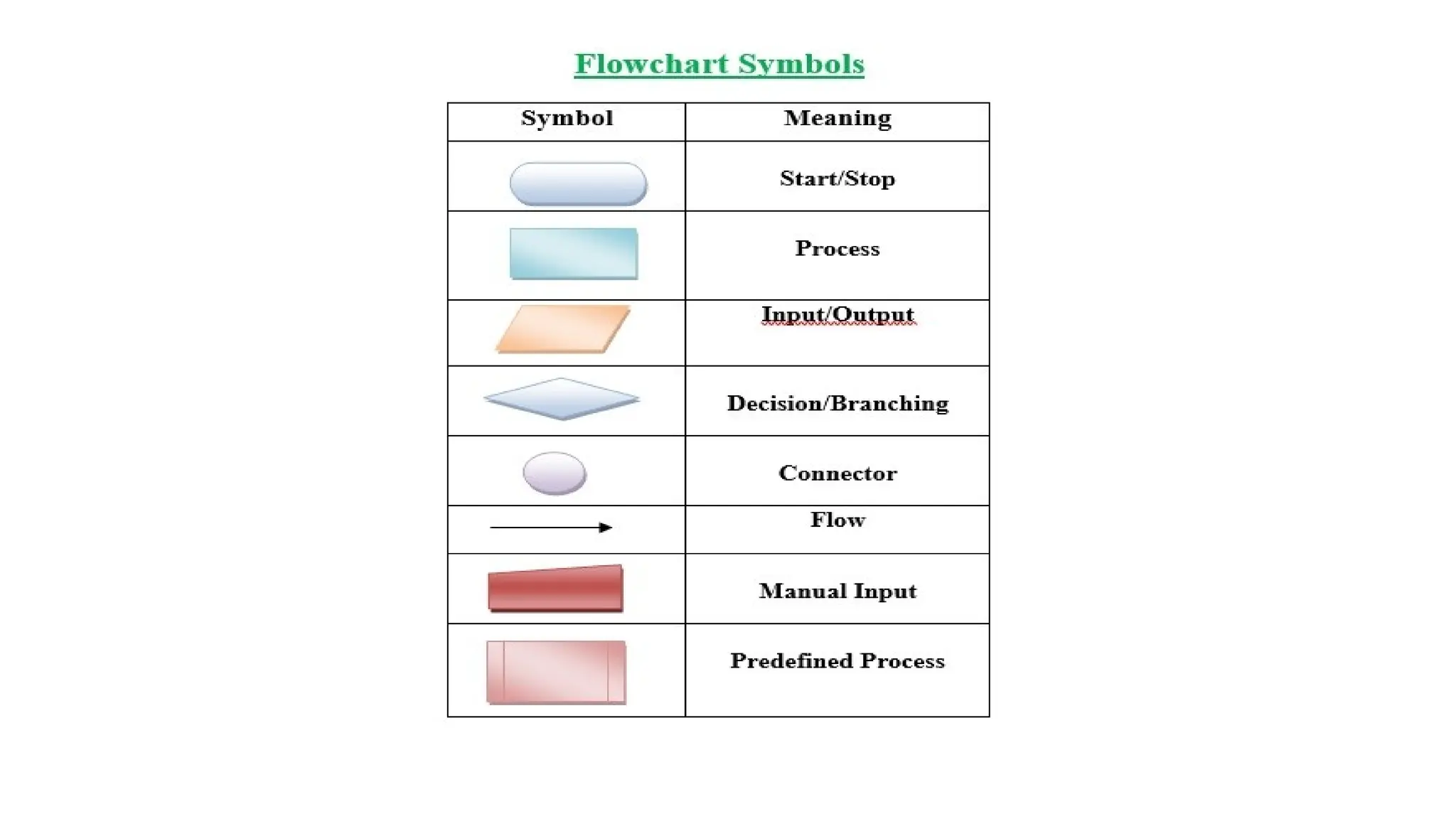
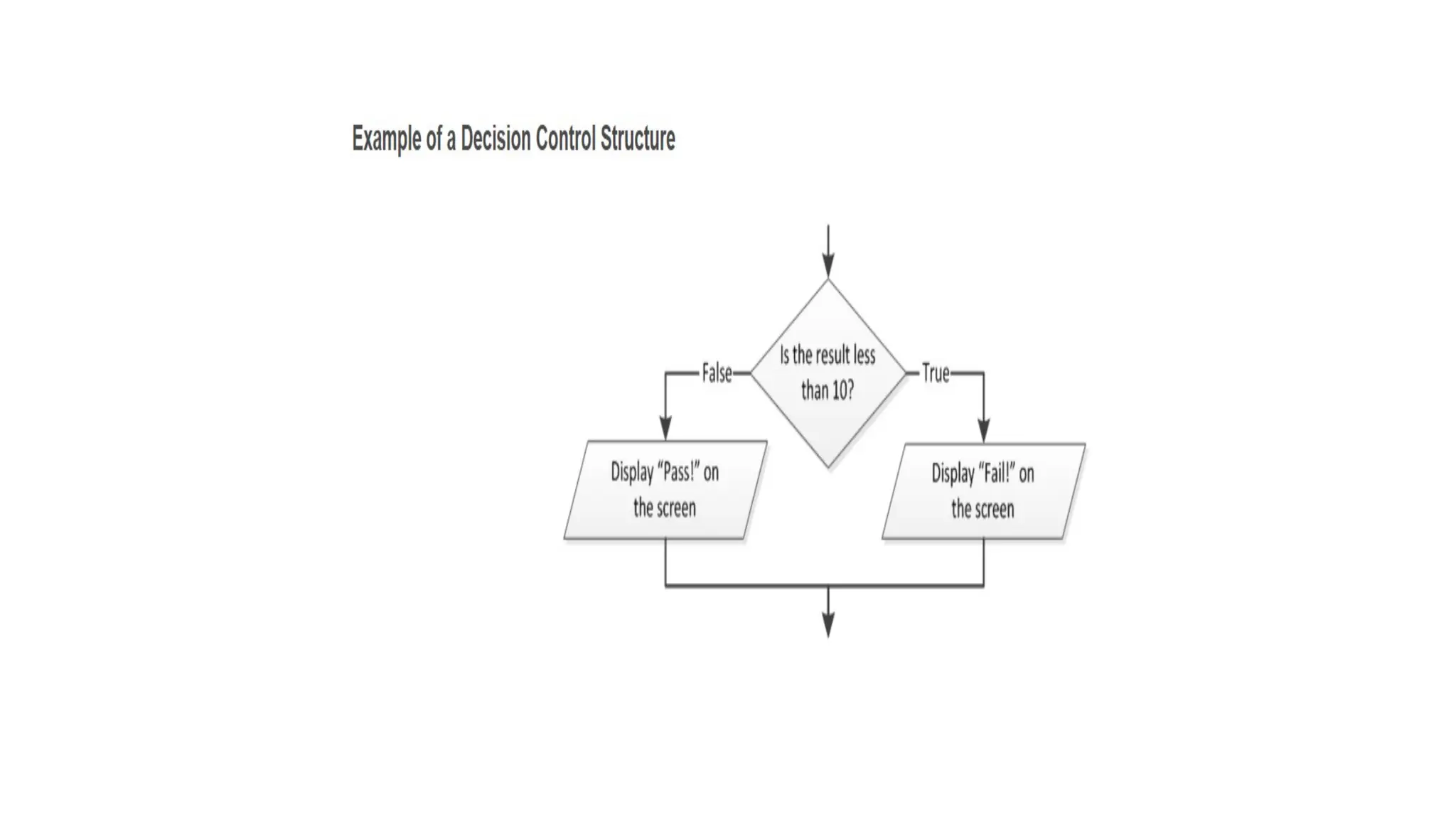
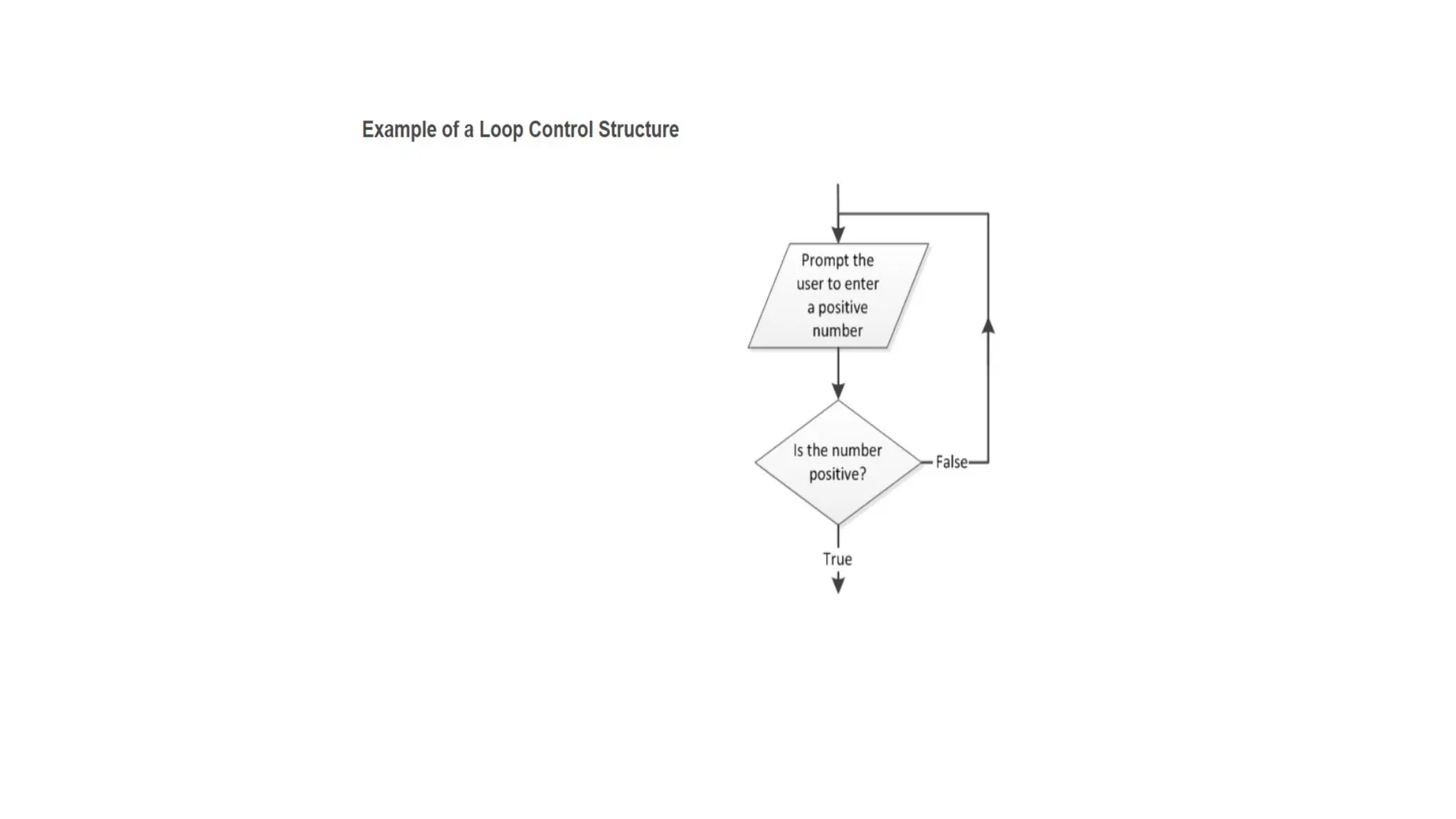
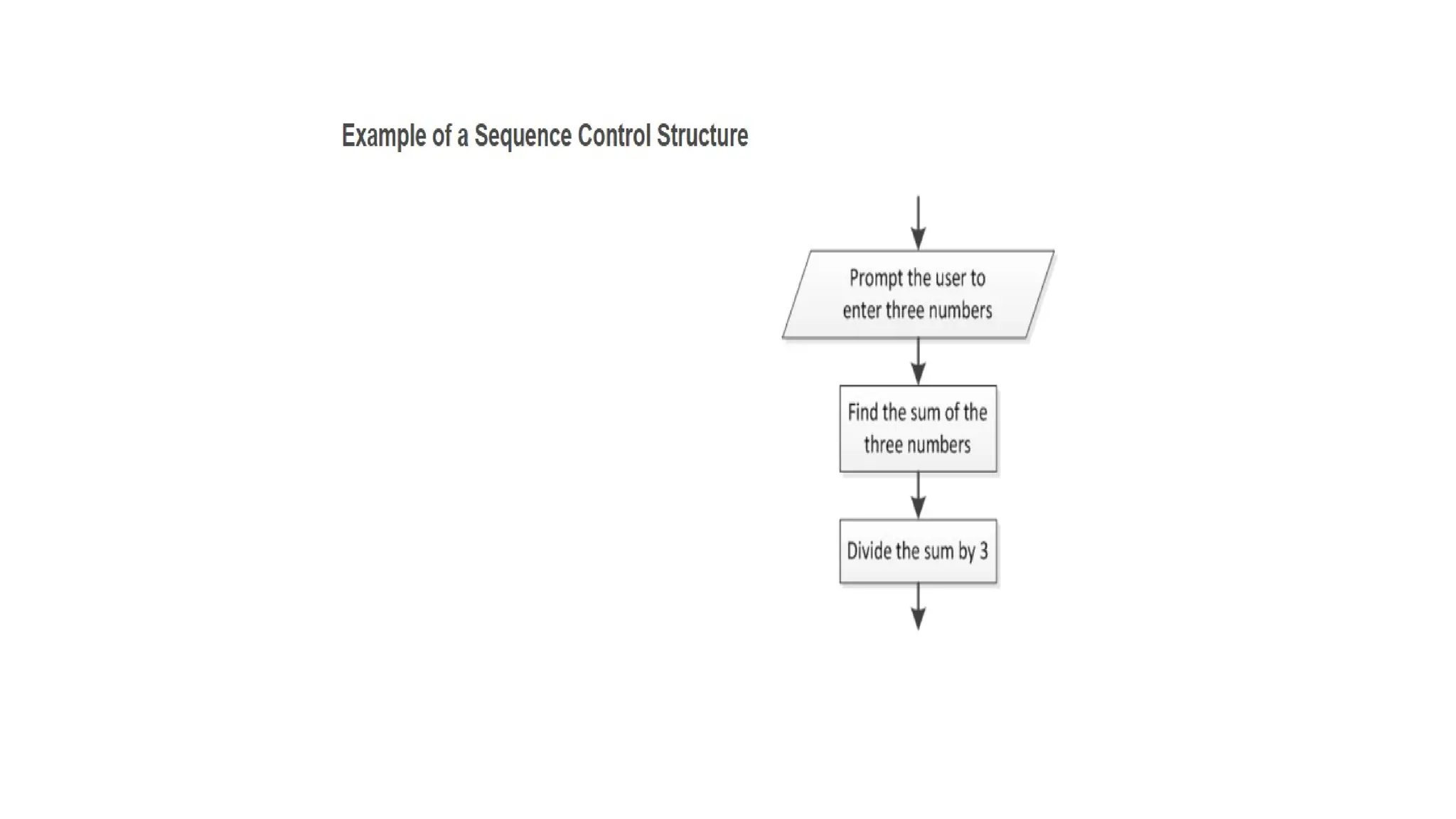
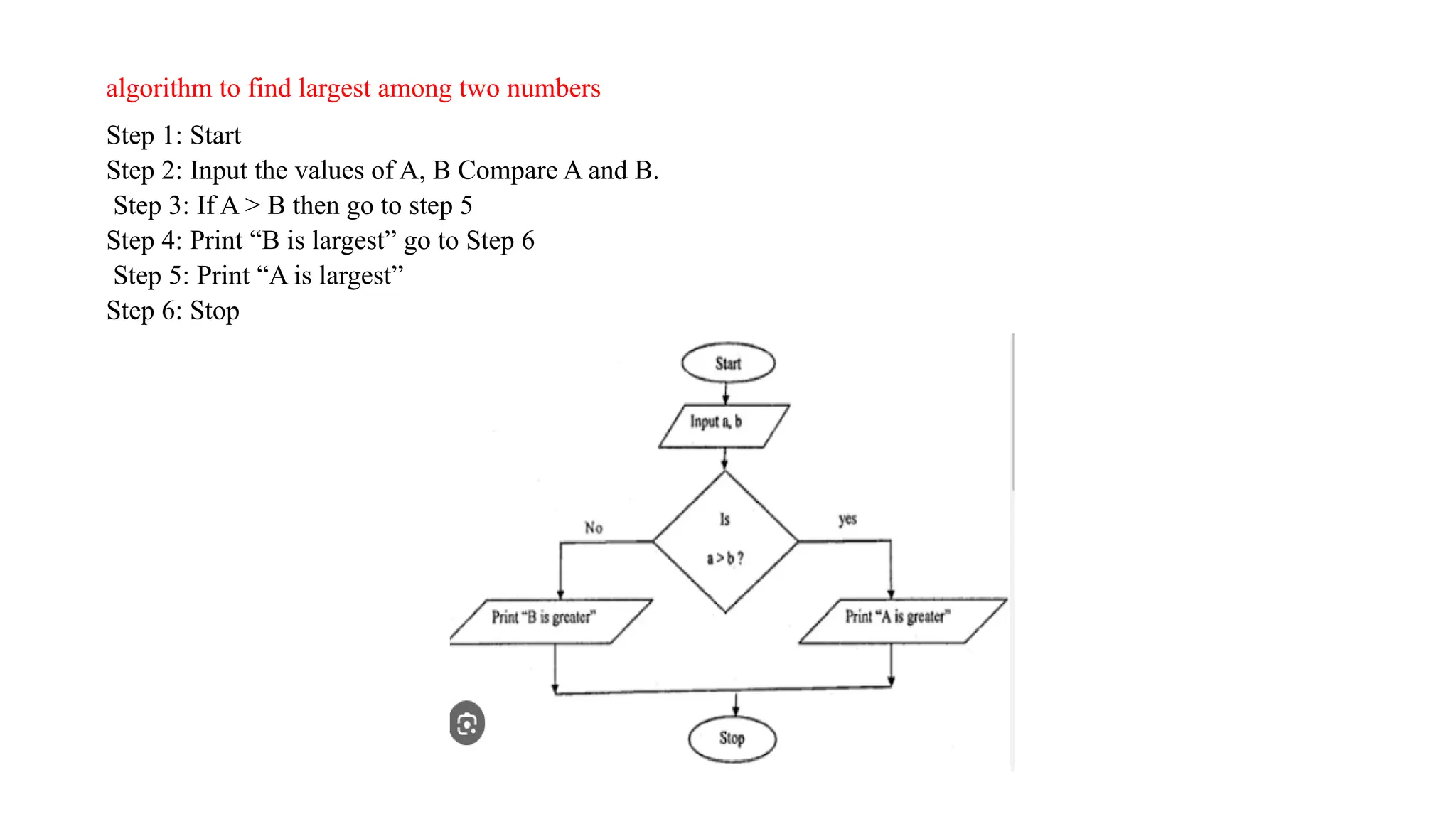
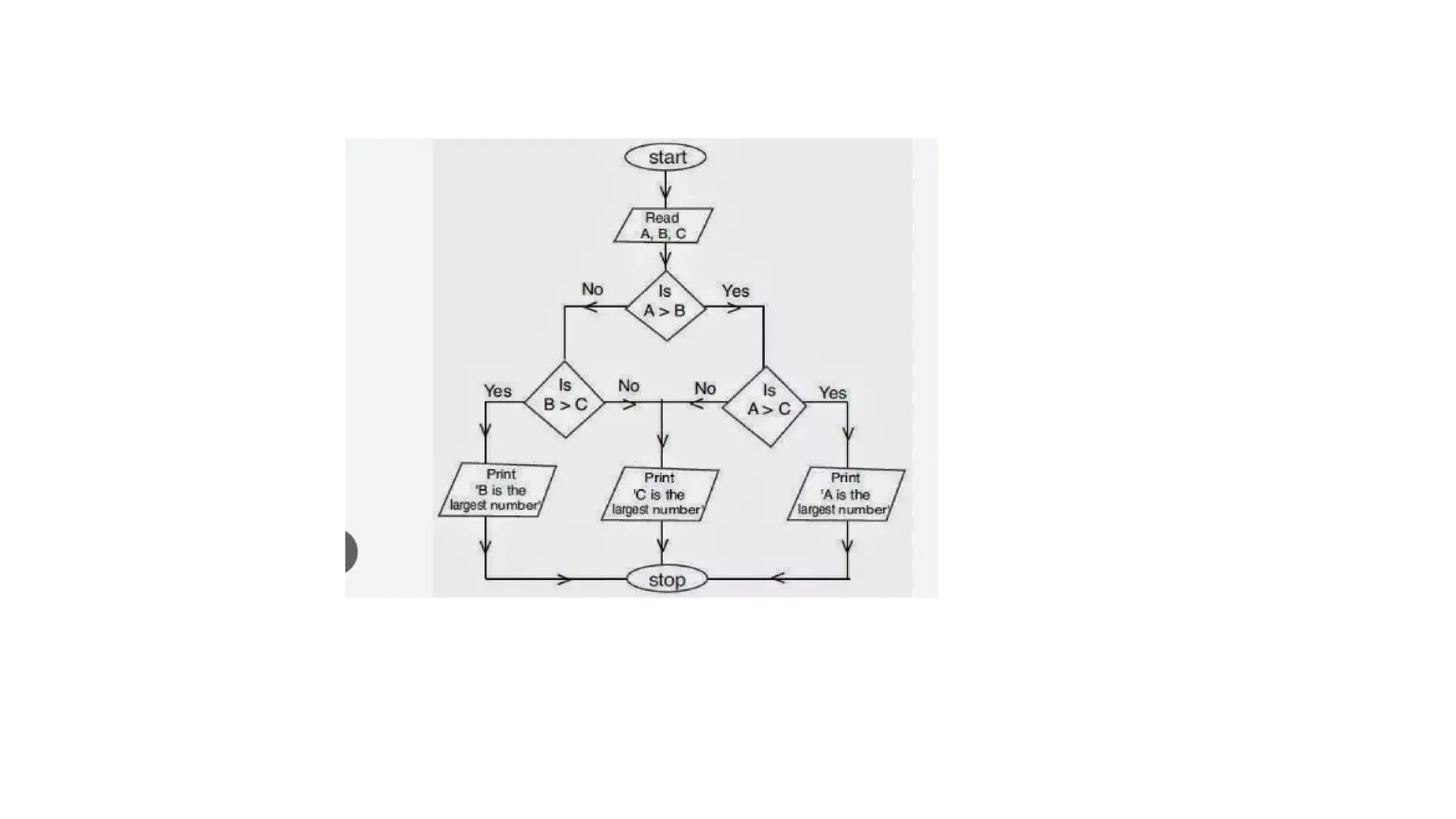
C is a high-level, general-purpose programming language developed by Dennis Ritchie in 1972, primarily for Unix system programming. Variables in C are named memory locations used to store various types of data and can be defined with specific types such as integer, character, and float. C also includes different data types, each with specific memory requirements and operations, with a structured syntax for variable declaration.