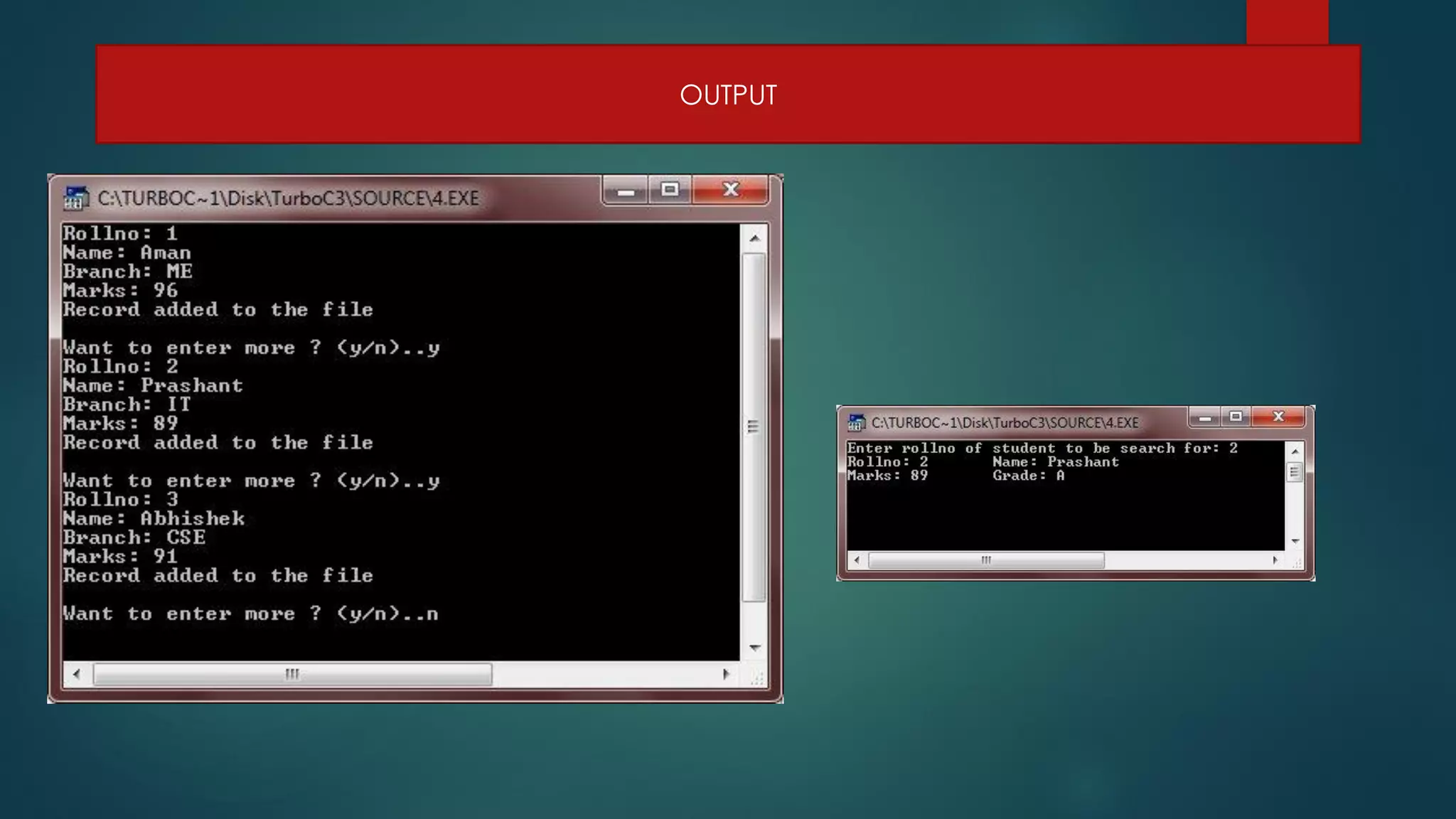
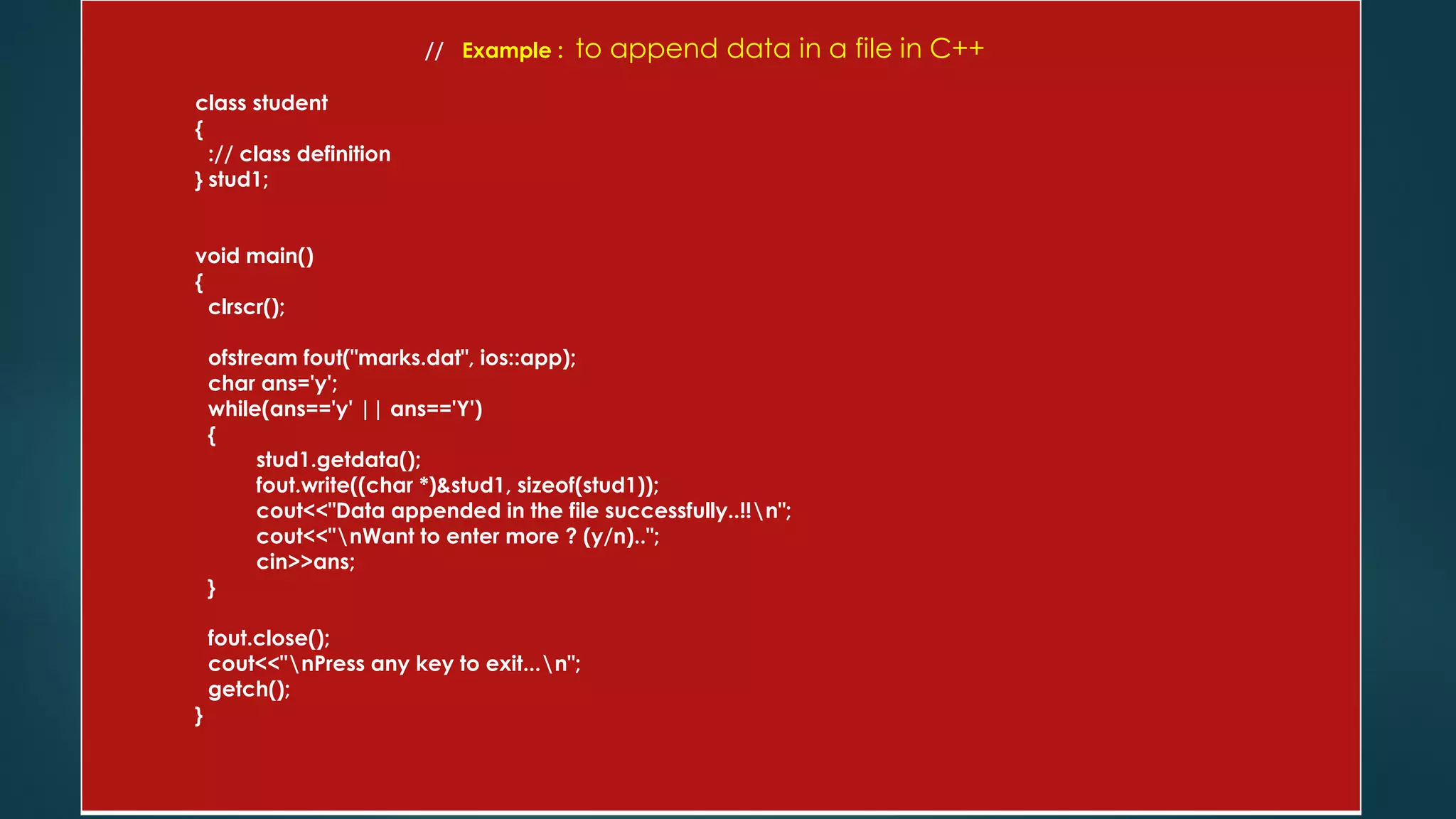
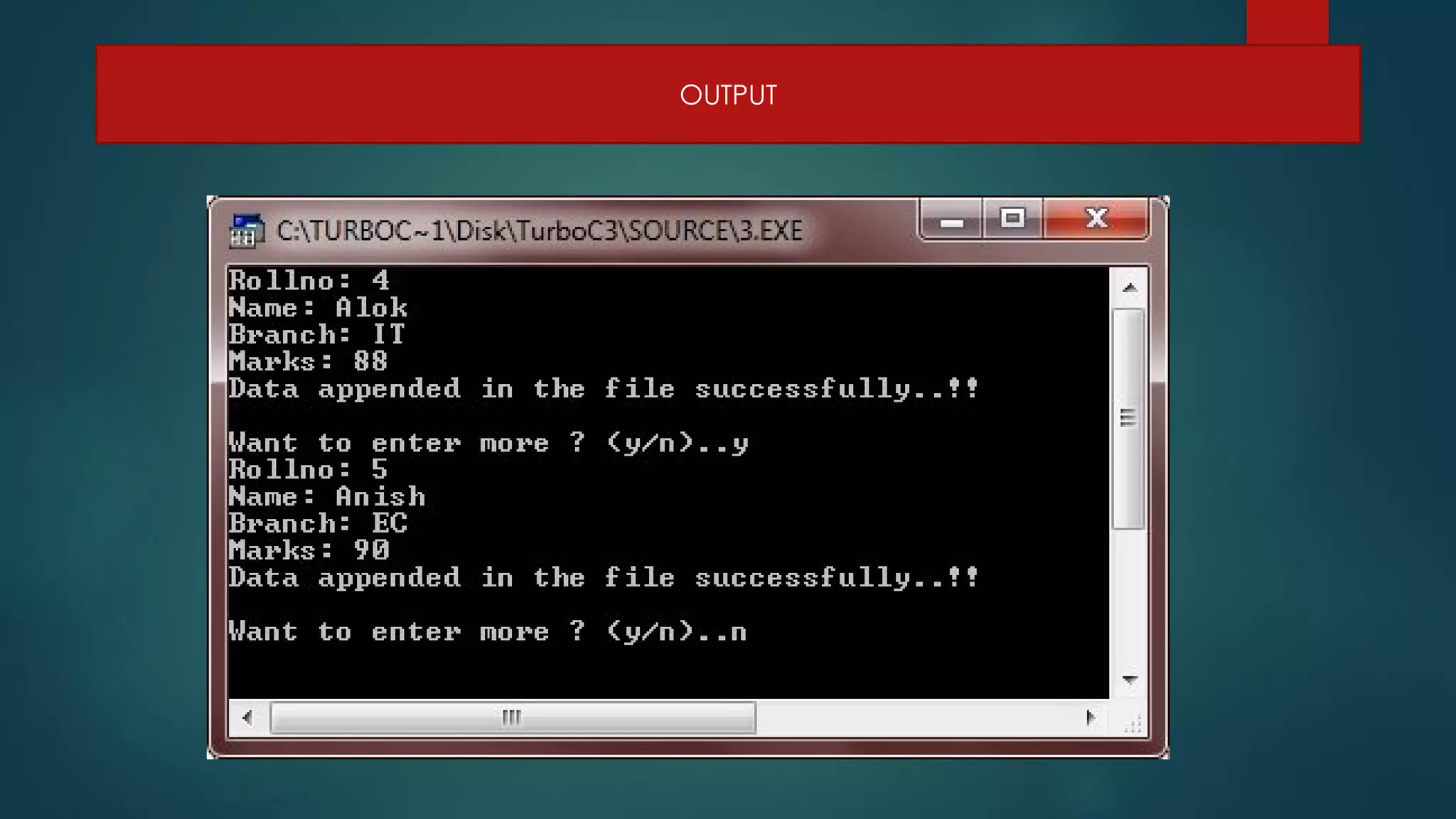
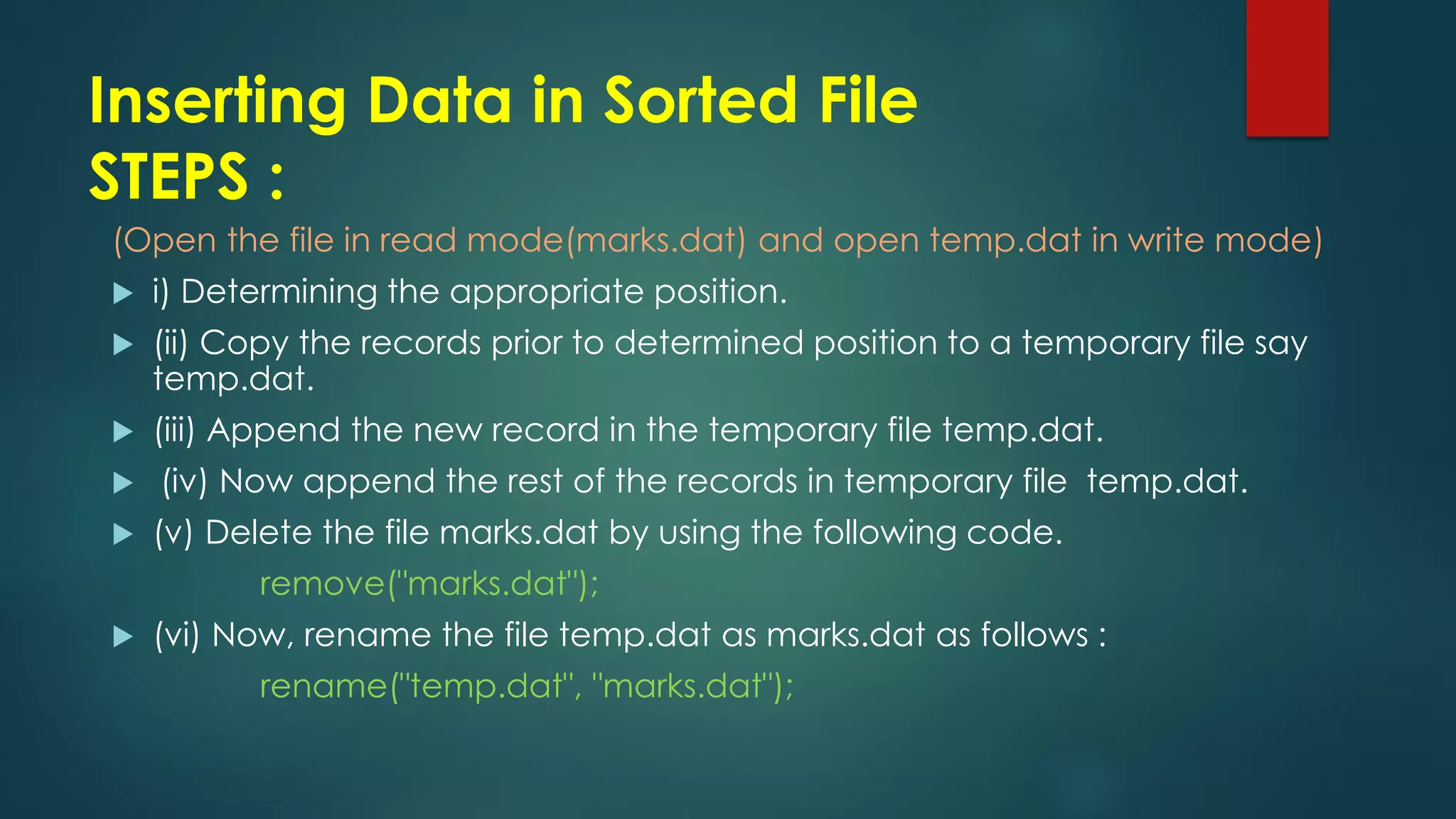
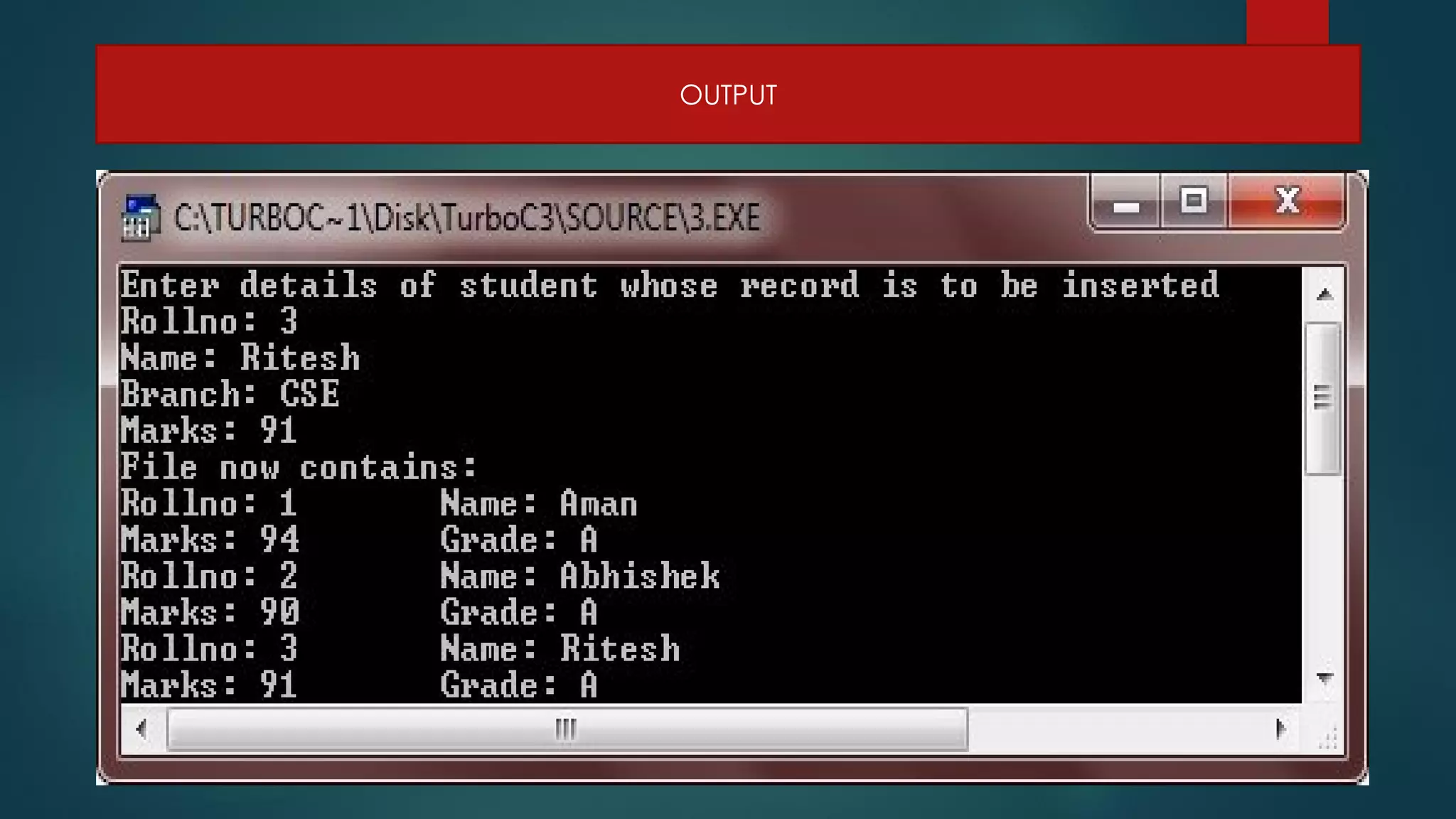
The document discusses basic file operations in binary files in C++, including searching, appending, inserting, modifying, and deleting records.
It provides code examples to search a binary file for a student record by roll number, append new student records, insert a new record in sorted order, modify an existing record, and delete a record by rewriting the file without the deleted record. Functions like read(), write(), seekg(), tellg() are used to perform these operations on binary files opened in modes like ios::in, ios::out, ios::app.




![#include<fstream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
class student
{
int rollno;
char name[20];
char branch[3];
float marks;
char grade;
public:
void getdata()
{
cout<<"Rollno: ";
cin>>rollno;
cout<<"Name: ";
cin>>name;
cout<<"Branch: ";
cin>>branch;
cout<<"Marks: ";
cin>>marks;
if(marks>=75)
grade = 'A';
else if(marks>=60)
grade = 'B';
else if(marks>=50)
grade = 'C';
else if(marks>=40)
grade = 'D';
else
grade = 'F';
}
void putdata()
{
cout<<"Rollno: "<<rollno<<"tName: "<<name<<"n";
cout<<"Marks: "<<marks<<"tGrade: "<<grade<<"n";
}
int getrno()
{
return rollno;
}
} stud1;
// class student created](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicfileoperationsclassxiiln7-180823064010/75/Basic-file-operations-CBSE-class-xii-ln-7-5-2048.jpg)