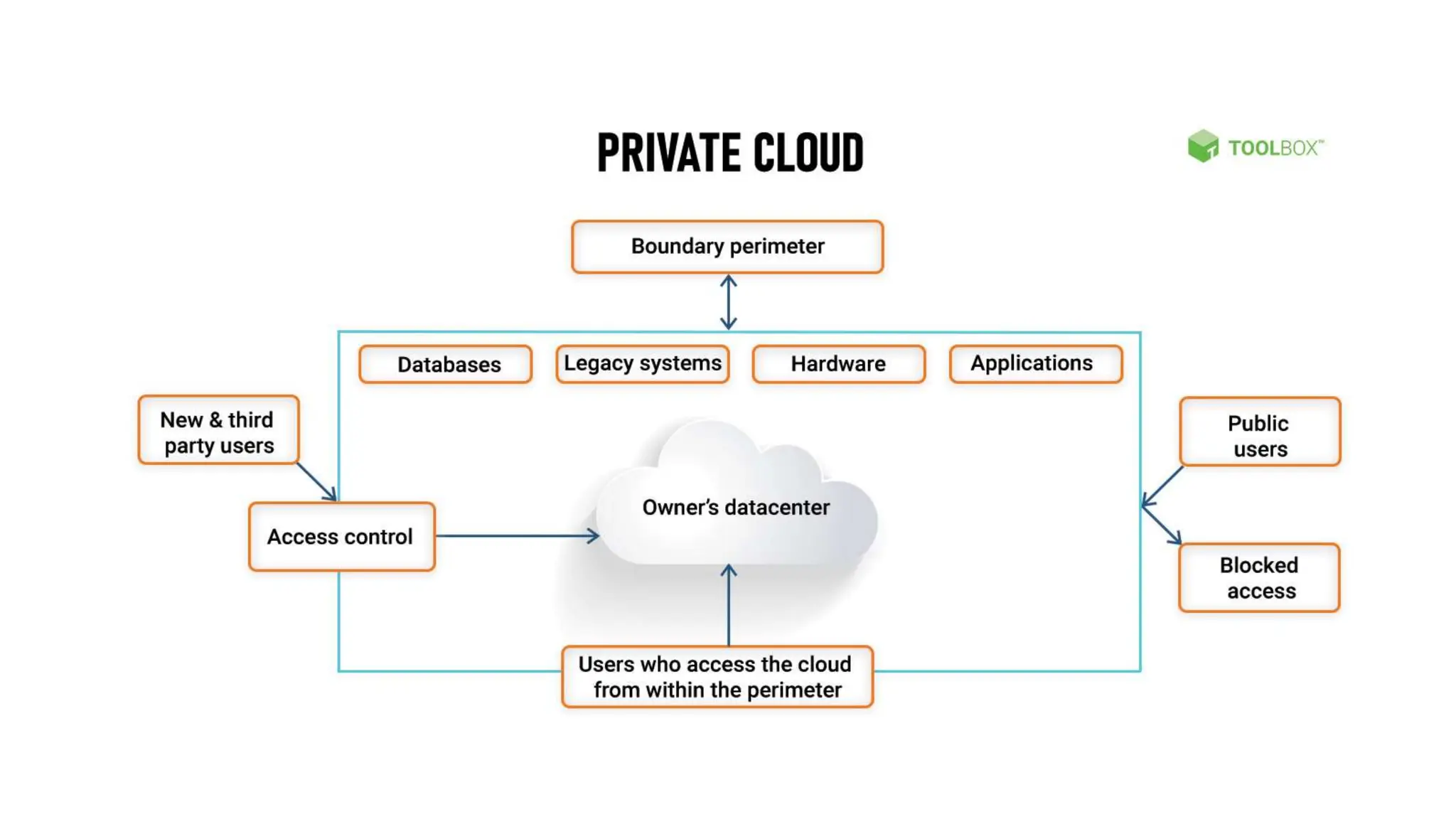
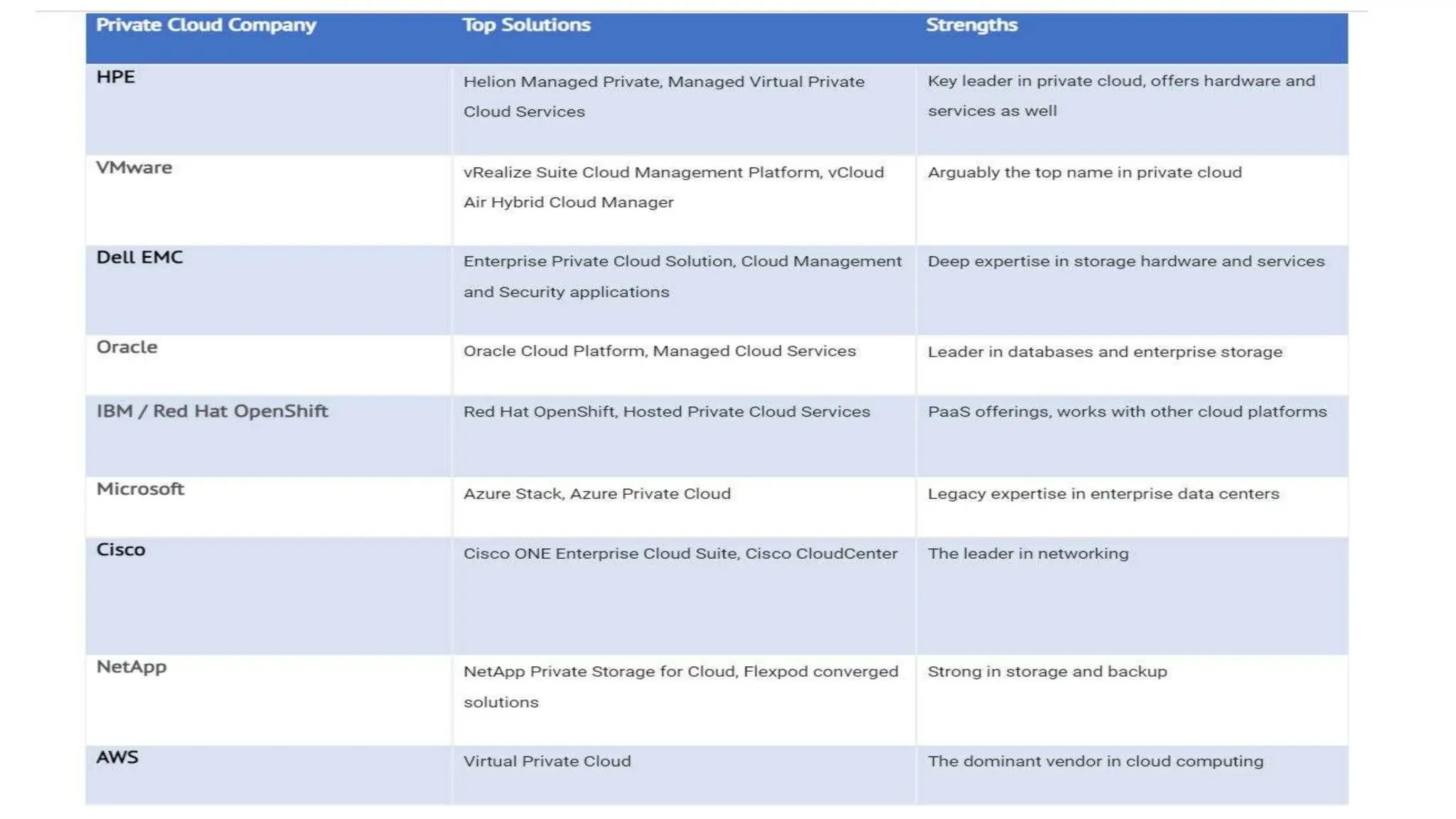
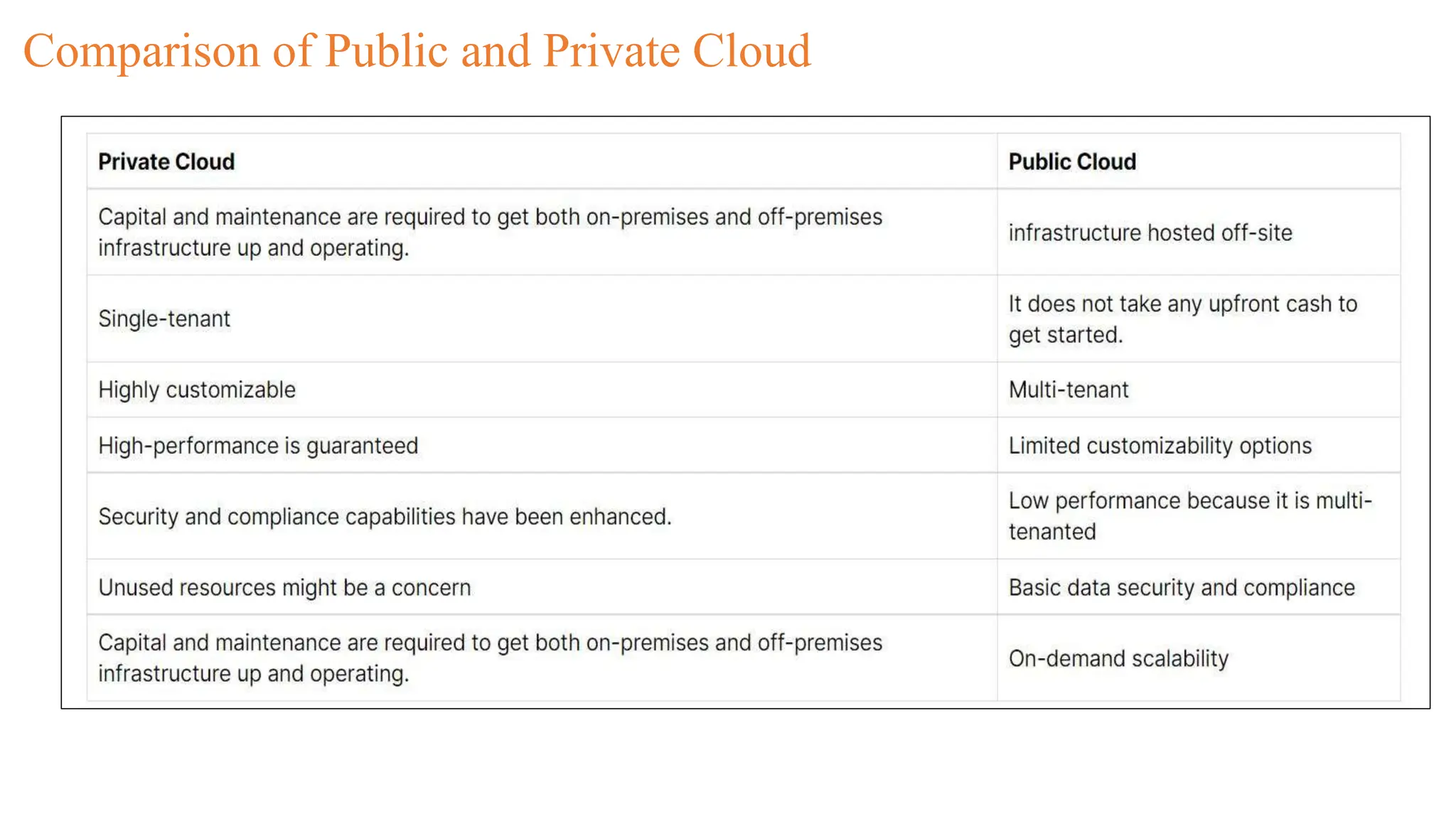
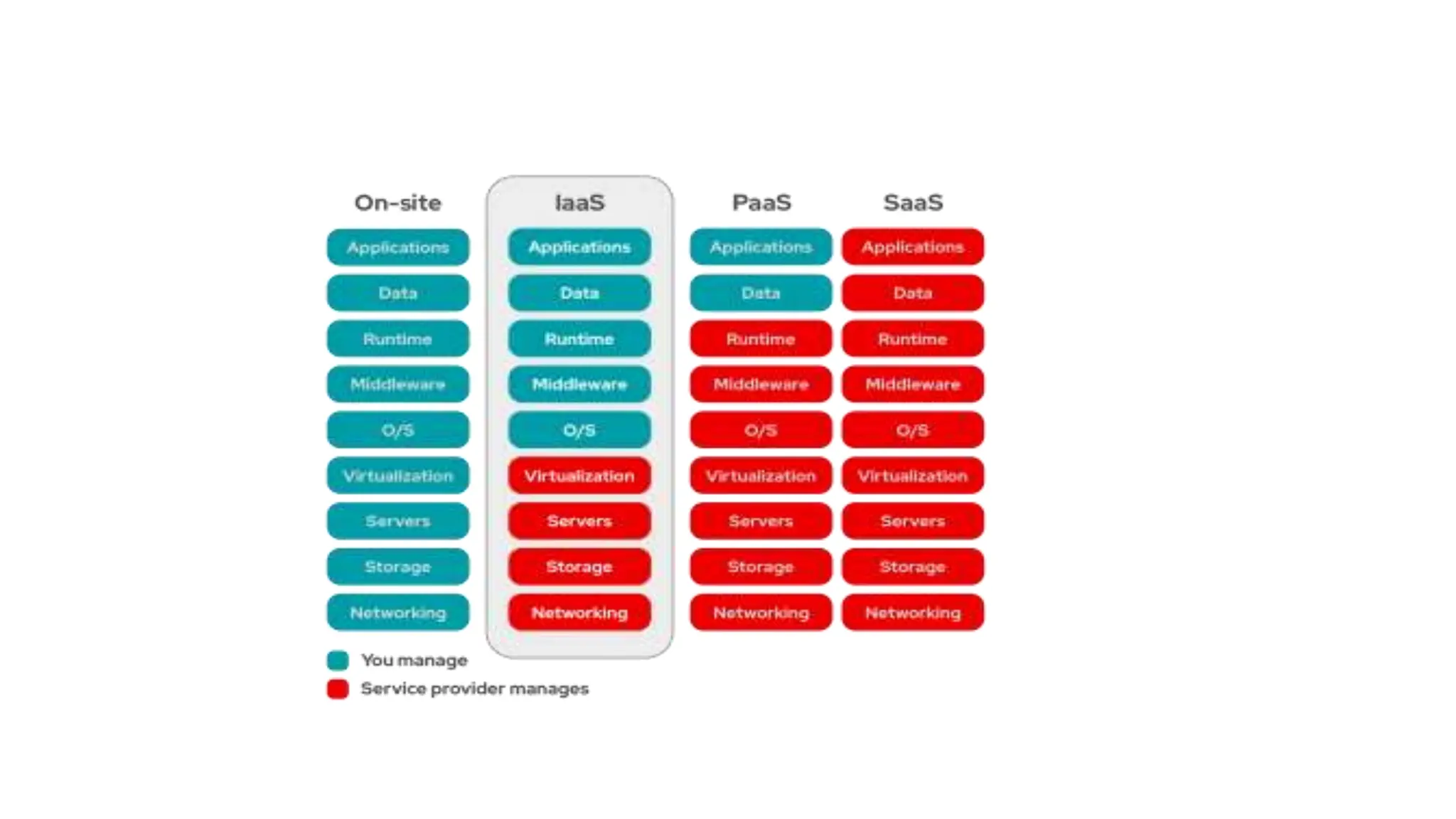
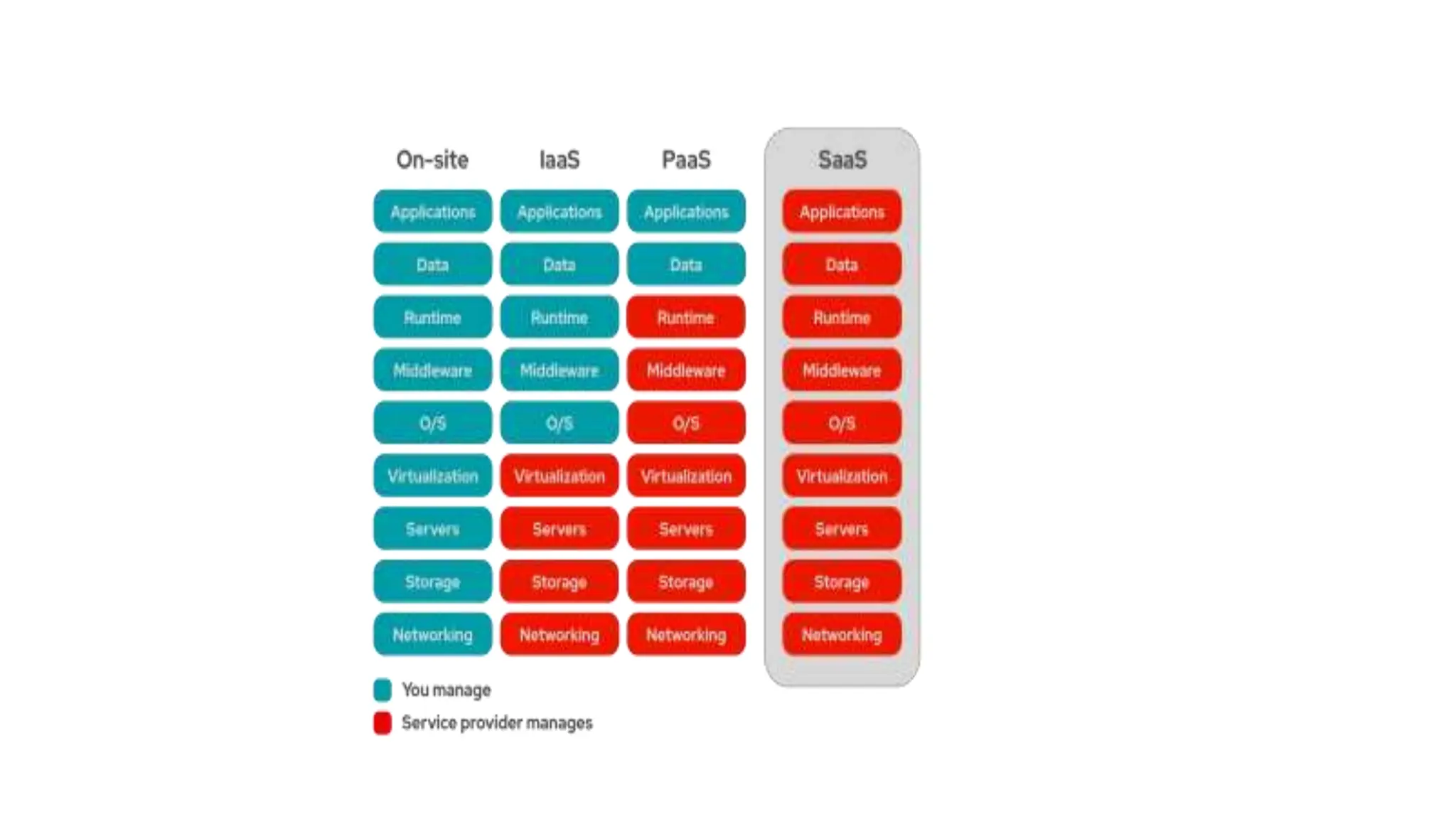
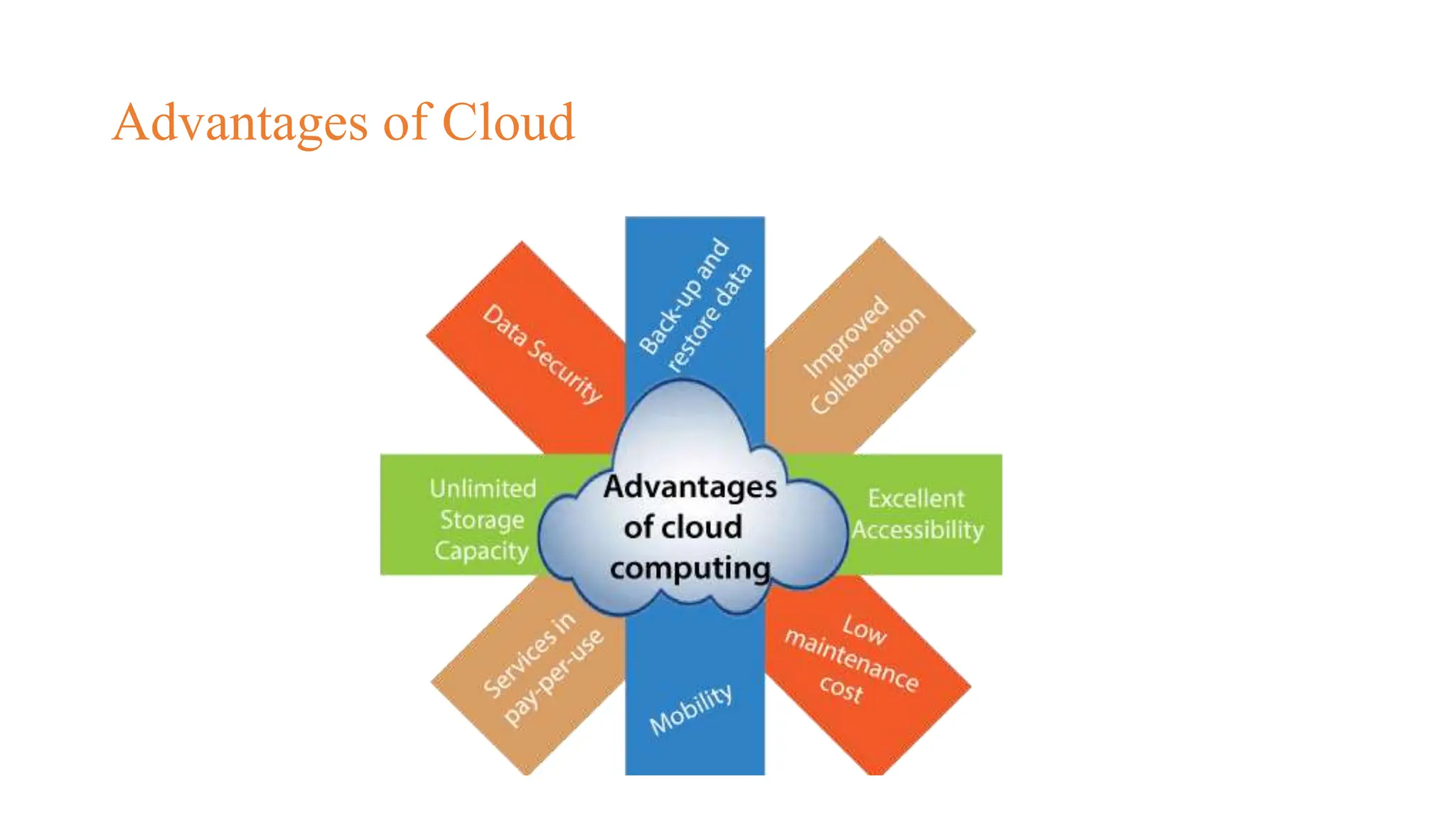
The document discusses cloud computing concepts, focusing on types like public, private, and hybrid clouds. It details the characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of private clouds, including models like virtual, managed, hosted, and on-premise private clouds, as well as the features of public clouds offered by various providers. Additionally, it outlines migration methods to cloud environments and various cloud service types such as IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.